- How to Encode and Decode a base64 String From the Command Line?
- How to Encode a String in base64?
- Syntax:
- How to Decode a base64 String?
- Decode base64 Through .bashrc
- Verify the Result
- How to Encode Text Files in base64?
- How to Decode a base64 Text File?
- How to Encode the User Input in Base64?
- How to Decode the User Base64 Input?
- Conclusion
- Bash base64 encode and decode
- Syntax:
- base64 [OPTION] [INFILE] [OUTFILE]
- Options:
- Example#1: Encoding text data
- Example#2: Decoding text data
- Example#3: Encoding text file
- Example#4: Decoding text file
- Example#5: Encoding any user-defined text
- Example#6: Checking user validity by decoding text
- Conclusion:
- References:
- About the author
- Fahmida Yesmin
How to Encode and Decode a base64 String From the Command Line?
Encode and decode are the processes to encrypt and decrypt the data. In Linux, the encoding and decoding processes of Binary to ASCII (and ASCII to Binary) are performed through the base64 command. It converts the binary data into base64 string comprised of ASCII characters and also decodes it into its original format.
This article will briefly demonstrate how to encode and decode base64 string from the command line:
- How to Encode a String in base64?
- How to Decode a base64 String?
- How to Encode text Files in base64?
- How to Decode a base64 Text File?
- Decode base64 Through .bashrc
- How to Encode the User Input in Base64?
- How to Decode the User Base64 Input?
How to Encode a String in base64?
To encode a base64 string, the following syntax is used:
Syntax:
Example 1: Encode a base64 String
To encode any string into base64 format is obtained as follows:
$ echo "Welcome to itslinuxfoss" | base64
The above command has encoded the given text.
You can also store the encoded text in the file using the redirection operator as follows:
$ echo "Welcome to itslinuxfoss" | base64 > encode.txt
Let’s check the encoded text in the file (encoede.txt):
The encoded text has been stored in the file.
How to Decode a base64 String?
To decode the base64 string in Linux, the following command syntax is examined:
- Type the string in the echo command.
- Add base64 command with “–decode” flag through pipe (|).
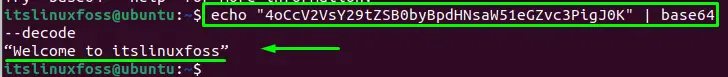
To decode the base6464 string, put it in the echo statement
$ echo "4oCcV2VsY29tZSB0byBpdHNsaW51eGZvc3PigJ0K" | base64 --decode
The encoded data has been converted into its original format.
Decode base64 Through .bashrc
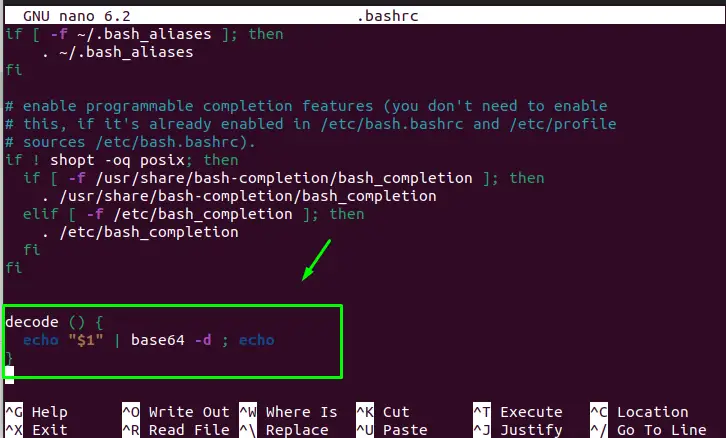
You can also make a script function of decode and paste it into the “.bashrc” file and just call the function name to decode the encoded data. Copy and paste the following decode function into your “.bashrc” file. Go through the following steps to implement this method:
Step 1: Define the Decode Function
Open the .basrch file, copy and paste the following function into the file:
Step 2: Execute the .bashrc
Examine the source command to execute the file to apply the new changes:
The file has been executed.
Verify the Result
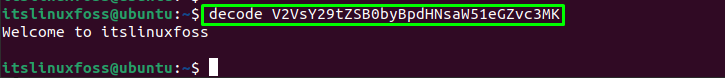
Now, simply type the “decode” (function name) and give the encoded string:
$ decode V2VsY29tZSB0byBpdHNsaW51eGZvc3MK
The data has been decoded.
How to Encode Text Files in base64?
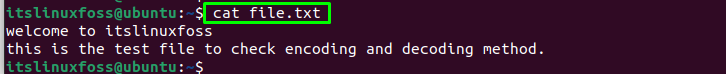
You can also encode any text file in Linux using the base64 command, Consider the following file output for the below implementation:
To encode the text files in Linux, simply type the base64 command along with the file name and redirection operator to save the encoded file output:
$ base64 file.txt > encoded.txt
The file “file.txt” has been encoded to the “encoded.txt” files.
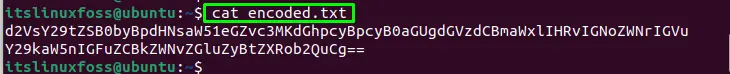
Let’s check the output of the “encoded.txt” file:
The file “encoded.txt” has the encoded data.
How to Decode a base64 Text File?
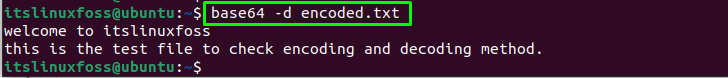
To decode the base64 text file, use the “d” flag in the base64 command and give the file name to decode it:
The file “encoded.txt” has been decoded to its original format.
How to Encode the User Input in Base64?
Another way to encode the data is from the user input, you can use the bash script for that purpose. Use the following script in the bash script file and run it, it will ask you for the input to encode that text:
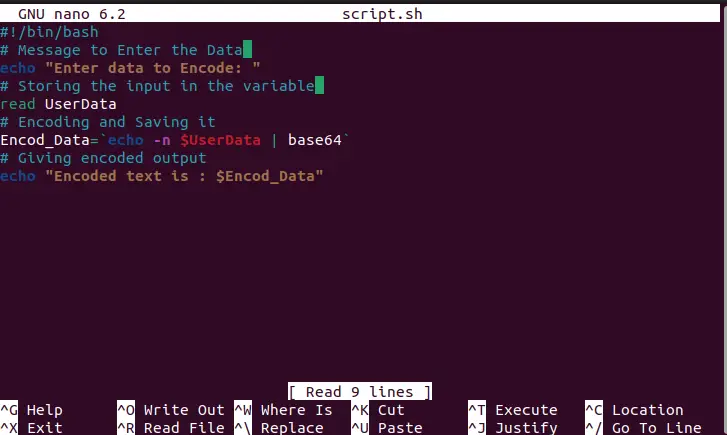
#!/bin/bash # Message to Enter the Data echo "Enter data to Encode: " # Storing the input in the variable read UserData # Encoding and Saving it Encod_Data=`echo -n $UserData | base64` # Giving encoded output echo "Encoded text is : $Encod_Data"
The script is described as:
- “echo” statement for printing the message to the user, and storing the input in “UserData” variable using the “read” property.
- Encoding the user data into base64 string.
- Displaying the encoded string to the user.
Save the file and make it executable using the chmod command:
The script file is executable now.
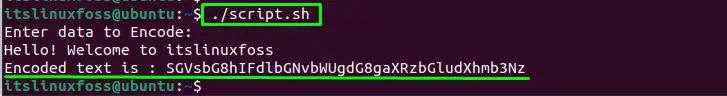
Now, run the script file in the terminal and you will see the message to enter the data to encode it. Once you enter your data, hit the enter button:
The data has been encoded.
How to Decode the User Base64 Input?
To decode data from the user input, use the following script in the bash script file, the script will receive and automatically decode it:
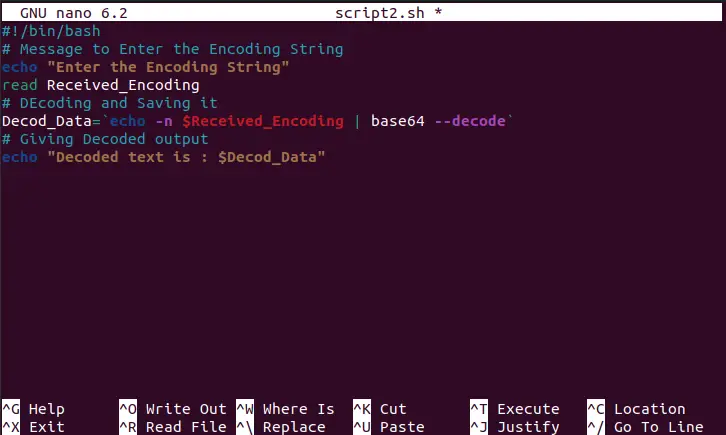
#!/bin/bash # Message to Enter the Encoding String echo "Enter the Encoding String" read Received_Encoding # DEcoding and Saving it Decod_Data=`echo -n $Received_Encoding | base64 --decode` # Giving Decoded output echo "Decoded text is : $Decod_Data"
The script is described as
- “echo” statement for printing the message to the user, and storing the input in “Received_Encoding” variable using the “read” property.
- Decoding the user data into base64 string
- Displaying the decoded string to the user.
Save the file and make it executable as we did in the above section:
The file script file is executable now.
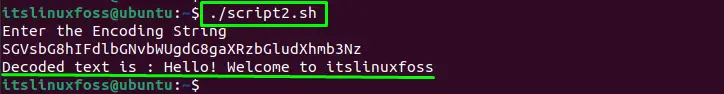
Now, run the script file in the terminal, it will ask you to enter the bae64 encoded data, paste it, and hit the enter button:
The encoded string has been decoded.
Conclusion
To encode or decode the data into base64 string, examine the syntax “echo | base64” for encoding or “echo | base64 –decode” for decoding. Apart from this, the file method or bash method for encoding or decoding can also be considered.
This write-up has illustrated the encoding and decoding process through the base64 command.
Bash base64 encode and decode
To encode or decode standard input/output or any file content, Linux uses base64 encoding and decoding system. Data are encoded and decoded to make the data transmission and storing process easier. Encoding and decoding are not similar to encryption and decryption. Encoded data can be easily revealed by decoding. So, this command line utility tool can’t be used for data security. Alphabet, number and ‘=’ symbol are used to encode any data.
Syntax:
base64 [OPTION] [INFILE] [OUTFILE]
You can use different types of options with base64 command. Data can be taken from any file or standard input while encoding or decoding. After encode or decode, you can send the output in a file or print the output in the terminal.
Options:
-e or –encode
This option is used to encode any data from standard input or from any file. It is the default option.
-d or –decode
This option is used to decode any encoded data from standard input or from any file.
-n or –noerrcheck
By default, base64 checks error while decoding any data. You can use –n or –noerrcheck option to ignore checking at the time of decoding.
-u or –help
This option is used to get information about the usage of this command.
-i, –ignore-garbage
This option is used to ignore non-alphabet character while decoding.
–copyright
It is used to get copyright information.
–version
It is used to get the version information.
How you use the base64 command in Linux is shown in this tutorial by using some examples.
Example#1: Encoding text data
You can encode any text data by using base64 in the command line. When you want to encode any data using base64 then using -e or –encode option is optional. So, if you don’t mention any option with base64 then it will work for encoding. The following command will encode the data, ‘linuxhint.com’ and print the encoded data as output.
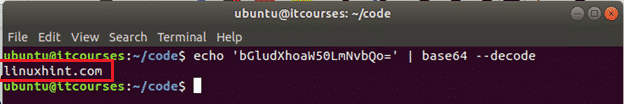
Example#2: Decoding text data
The following command will decode the encoded text, ‘bGludXhoaW50LmNvbQ==‘ and print the original text as output.
Example#3: Encoding text file
Create a text file named, ‘sample.txt’ with the following text that will be encoded by using base64.
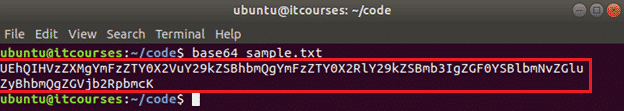
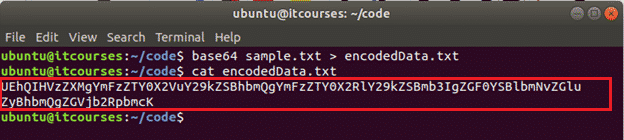
You can print the encoded text in the command line or store the encoded text into another file. The following command will encode the content of the sample.txt file and print the encoded text in the terminal.
The following commands will encode the content of the sample.txt file and save the encoded text into the encodedData.txt file.
Example#4: Decoding text file
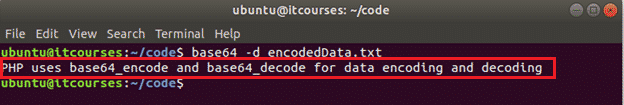
The following command will decode the content of the encodedData.txt file and print the output in the terminal
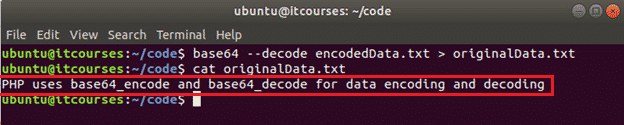
The following commands will decode the content of the encodedData.txt file and store the decoded content into the file, originalData.txt.
Example#5: Encoding any user-defined text
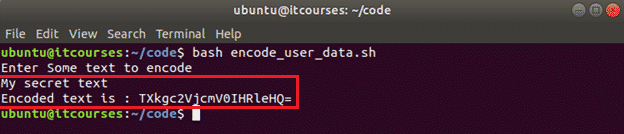
Create a bash file named encode_user_data.sh with the following code. The following script will take any text data as input, encode the text by using base64 and print the encoded text as output.
#!/bin/bash
echo «Enter Some text to encode»
read text
etext = ` echo -n $text | base64 `
echo «Encoded text is : $etext «
Validate the text is encoded correctly by piping the encoded text returned from your execution of the script to base64 –decode to confirm the original text is returned. Below you can see how to validate assuming My secret textwas the string encoded.
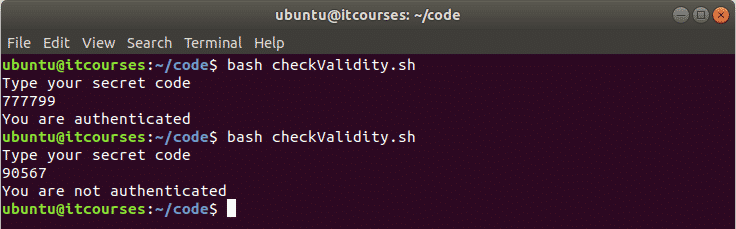
Example#6: Checking user validity by decoding text
Create a bash file named checkValidity.sh and add the following code. In this example, a secret text is taken from the user. A predefined encoded text is decoded by base64 and compared with the user input. If both values are equal then the output will be ‘You are authenticated’ otherwise the output will be ‘You are not authenticated’. Using this simple decoding code, normal validation can be done very easily. In this example the secret text that will result in success is 777799. This would likely not be hard coded in the script but more dynamic in a real world application.
#!/bin/bash
echo «Type your secret code»
read secret
otext = ` echo ‘Nzc3Nzk5Cg==’ | base64 —decode `
if [ $secret == $otext ] ; then
echo «You are authenticated»
else
echo «You are not authenticated»
fi
Conclusion:
For any sensitive data like password or any confidential data, encoding and decoding system is not suitable at all. You must use encryption and decryption system for securing these type of data.
References:
About the author
Fahmida Yesmin
I am a trainer of web programming courses. I like to write article or tutorial on various IT topics. I have a YouTube channel where many types of tutorials based on Ubuntu, Windows, Word, Excel, WordPress, Magento, Laravel etc. are published: Tutorials4u Help.