- Shell Script: Execute a python program from within a shell script
- 12 Answers 12
- Method 1 — Create a shell script:
- Method 2 (BETTER) — Make the python itself run from shell:
- Как запустить небольшой код Python в Bash
- Как выполнить код Python в Bash
- Как в скрипте Bash запустить программу на Python
- Как в скрипте Bash запустить программу на Python и присвоить её вывод переменной
- Как в скрипт Bash встроить код Python
Shell Script: Execute a python program from within a shell script
I’ve tried googling the answer but with no luck. I need to use my works supercomputer server, but for my python script to run, it must be executed via a shell script. For example I want job.sh to execute python_script.py How can this be accomplished?
what exactly have you tried and what is the problem? Either you did not do that good of a google search, or there is a lot that you are not telling us.
This is a rather old question but the best/most complete answer is the one by João Víctor. Be sure to read down to it.
12 Answers 12
Just make sure the python executable is in your PATH environment variable then add in your script
python path/to/the/python_script.py #!/bin/sh python python_script.py - Execute this command to make the script runnable for you : chmod u+x job.sh
- Run it : ./job.sh
It depends on your system. Python 3 may be the default python runtime, or may not be. You can check by running python —version , and you can enforce the version with python3 hello.py .
It means you launched the wrong python binary or the environment is not right. In that case, you should populate a virtualenv, then run source PATH/TO/VENV/bin/activate then call python python_script.py
I’m trying to do this in automator, and I’m getting an error; /path/to/Python: can’t open file ‘/path/to/script’: [Errno 1] Operation not permitted is there a way to include my python code in-line within the bash script?
Method 1 — Create a shell script:
Suppose you have a python file hello.py Create a file called job.sh that contains
Method 2 (BETTER) — Make the python itself run from shell:
Modify your script hello.py and add this as the first line
Please edit your answer to make it more readable. You can use the 101010 button in the answer editor to mark the script contents as code.
I always forget #!/usr/bin/env python . Remember to make sure you’re referencing the right python version + path for your system!
Also make sure the python script works with the system python and doesn’t need a virtual environment.
You should be able to invoke it as python scriptname.py e.g.
# !/bin/bash python /home/user/scriptname.py Also make sure the script has permissions to run.
You can make it executable by using chmod u+x scriptname.py .
Save the following program as print.py :
#!/usr/bin/python3 print('Hello World') Then in the terminal type:
Is quite wrong, especially in these days. Which python? python2.6? 2.7? 3.0? 3.1? Most of times you need to specify the python version in shebang tag of python file. I encourage to use
#!/usr/bin/env python2 #or python2.6 or python3 or even python3.1
In such case, is much better to have the script executable and invoke it directly:
This way the version of python you need is only written in one file. Most of system these days are having python2 and python3 in the meantime, and it happens that the symlink python points to python3, while most people expect it pointing to python2.
This works for me:
- Create a new shell file job. So let’s say: touch job.sh and add command to run python script (you can even add command line arguments to that python, I usually predefine my command line arguments). chmod +x job.sh
- Inside job.sh add the following py files, let’s say: python_file.py argument1 argument2 argument3 >> testpy-output.txt && echo «Done with python_file.py» python_file1.py argument1 argument2 argument3 >> testpy-output.txt && echo «Done with python_file1.py»
I use this usually when I have to run multiple python files with different arguments, pre defined.
Note: Just a quick heads up on what’s going on here:
python_file.py argument1 argument2 argument3 >> testpy-output.txt && echo "completed with python_file.py" . - Here shell script will run the file python_file.py and add multiple command-line arguments at run time to the python file.
- This does not necessarily means, you have to pass command line arguments as well.
- You can just use it like: python python_file.py , plain and simple. Next up, the >> will print and store the output of this .py file in the testpy-output.txt file.
- && is a logical operator that will run only after the above is executed successfully and as an optional echo «completed with python_file.py» will be echoed on to your cli/terminal at run time.
This works best for me: Add this at the top of the script:
(C:\Python27\python.exe is the path to the python.exe on my machine) Then run the script via:
chmod +x script-name.py && script-name.py Just to clarify, this is Windows-specific. And the prompt that I use is the Git bash. I find it super useful. Especially in the Windows environment
I use this and it works fine
#/bin/bash /usr/bin/python python python_script.py Since the other posts say everything (and I stumbled upon this post while looking for the following).
Here is a way how to execute a python script from another python script:
execfile("somefile.py", global_vars, local_vars) with open("somefile.py") as f: code = compile(f.read(), "somefile.py", 'exec') exec(code, global_vars, local_vars) and you can supply args by providing some other sys.argv
If you have a bash script and you need to run inside of it a python3 script (with external modules), I recommend that you point in your bash script to your python path like this.
#!/usr/bin/env bash -- bash code -- /usr/bin/python3 your_python.py -- bash code -- Here I have demonstrated an example to run python script within a shell script. For different purposes you may need to read the output from a shell command , execute both python script and shell command within the same file.
To execute a shell command from python use os.system() method. To read output from a shell command use os.popen() .
Following is an example which will grep all processes having the text sample_program.py inside of it. Then after collecting the process IDs (using python) it will kill them all.
#!/usr/bin/python3 import os # listing all matched processes and taking the output into a variable s s = os.popen("ps aux | grep 'sample_program.py'").read() s = '\n'.join([l for l in s.split('\n') if "grep" not in l]) # avoiding killing the grep itself print("To be killed:") print(s) # now manipulating this string s and finding the process IDs and killing them os.system("kill -9 " + ' '.join([x.split()[1] for x in s.split('\n') if x])) Как запустить небольшой код Python в Bash
Bash — это не только и даже не столько встроенные функции оболочки сколько программы (утилиты) командной строки. Запуская эти команды и передавая полученные данные конвейеру (по трубе) можно автоматизировать самые различные вещи, на программирование которых в других языках программирования может понадобиться очень много усилий.
Эта заметка расскажет, как запустить код Python в Bash, а также как в скрипте Bash запустить выполнение программы на Python
Как выполнить код Python в Bash
В командной строке Bash для выполнения кода используйте конструкцию вида:
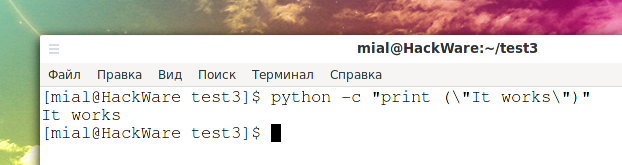
Ещё один вариант, который может пригодиться в более экзотических обстоятельствах:
bash -c 'python -c "print (\"КОД\")"'
bash -c 'python -c "print (\"It works\")"'
Как в скрипте Bash запустить программу на Python
Для выполнения программы Python в скрипте Bash используйте команду вида:
python СКРИПТ.py АРГУМЕНТ1 АРГУМЕНТ2 АРГУМЕНТ3
Пример запуска скрипта extractor.py с передачей ему двух аргументов: значение переменной $line и 8080:
python extractor.py $line 8080
Как в скрипте Bash запустить программу на Python и присвоить её вывод переменной
Если вам нужно запустить скрипт Python, а затем вывод программы присвоить переменной Bash, то используйте конструкцию вида:
ПЕРЕМЕННАЯ=`python СКРИПТ.py АРГУМЕНТ1 АРГУМЕНТ2 АРГУМЕНТ3`
response=`python extractor.py $line 8080 2>/dev/null | sed -E "s/\/\/.+:/\/\/$line:/"`
Как в скрипт Bash встроить код Python
Если код Python невозможно использовать в одной строке и вы не хотите использовать для вызова внешний скрипт, тогда вам подойдёт следующая конструкция:
Там где КОД вставьте код Python.
Данный пример является рабочим:
#!/bin/bash value="I will be in the script!" script=`cat

Ещё один вариант этой конструкции:
И ещё один вариант, в котором вывод присваивается в качестве значения переменной ABC:
