- Linux vs Android
- Linux
- Android
- Dalvik Virtual Machine
- Head To Head Comparison Between Linux vs Android (Infographics)
- Key Difference Between Linux vs Android
- Linux vs Android Comparison Table
- Conclusion
- Recommended Articles
- Android vs Linux – Detailed Comparison Table
- Linux:
- Android:
- Android vs Linux:
- Conclusion:
- Detailed Comparison table of Android vs Linux:
- Linux software versus Android op de box
- Linux
- Android
- Delen:
Linux vs Android
Linux runs across numerous systems in the market, and it is the majority of a community-based setup. It is a monolithic OS where the operating system executes completely from the kernel. Android is an open-source operating system primarily built for mobiles and tablets. Android plays a vital role on mobile devices, yet it’s a framework that stands on top of this Linux kernel.
Web development, programming languages, Software testing & others
Linux
Linux was built by Linus Torvalds, a Finnish student who aims to provide open-source OS in the market. Linux was a derived version of Unix.
Often compared with Commercial UNIX systems but much more reliable than desktop-oriented systems ideally built for power users and programmers.properties of Linux systems,
- Open source and can be easily downloaded.
- Installation can also be performed with ease.
- Quiet, stable OS.
- A group of Internet developers developed it.
Joining the desktop market. Linux developers resolute networking service as the prior stuff, with office applications being the bottom of the priority. Linux also provides trade services and database support for organizations like Amazon, the German army, US Post Office, etc. Especially internet providers and internet service providers have grown fond of Linux as a firewall, proxy- and web server. You will find a Linux box within reach of every UNIX system administrator who appreciates a comfortable management station. As a Linux user today, all means of getting to know your system inside out, but it is no longer essential to hold the knowledge to make the system comply with your requests.
Android
Android primarily satisfies low-powered devices and uses Java, which executes on virtual machines. Android Inc initially created the platform, which Google later acquired.
Android OS systems are frequently updated, and a new name is associated with each release. The frequent release of versions simultaneously makes several pieces of information on the system obsolete.
Standard features of Android OS:
- Mobile development open platform.
- Hardware reference well suitable primarily for mobile devices.
- Linux 2.6 is used for powering the system.
- An application and UI framework are involved.
Here the application layer acts as the top layer holding its libraries in action. All these libraries are built using C/C++ languages.
Dalvik Virtual Machine
Android-based systems utilize the Dalvik VM, which executes a special bytecode instead of directly managing the resident Java bytecode. To enable this, Android-based systems use an inbuilt tool for converting Java classes to DEX.
The DVM functioning is optimized to carry out as efficiently and effectively as possible on mobile devices usually equipped with a slow CPU. The DVMs are implemented to execute multiple VMs in an optimized manner.
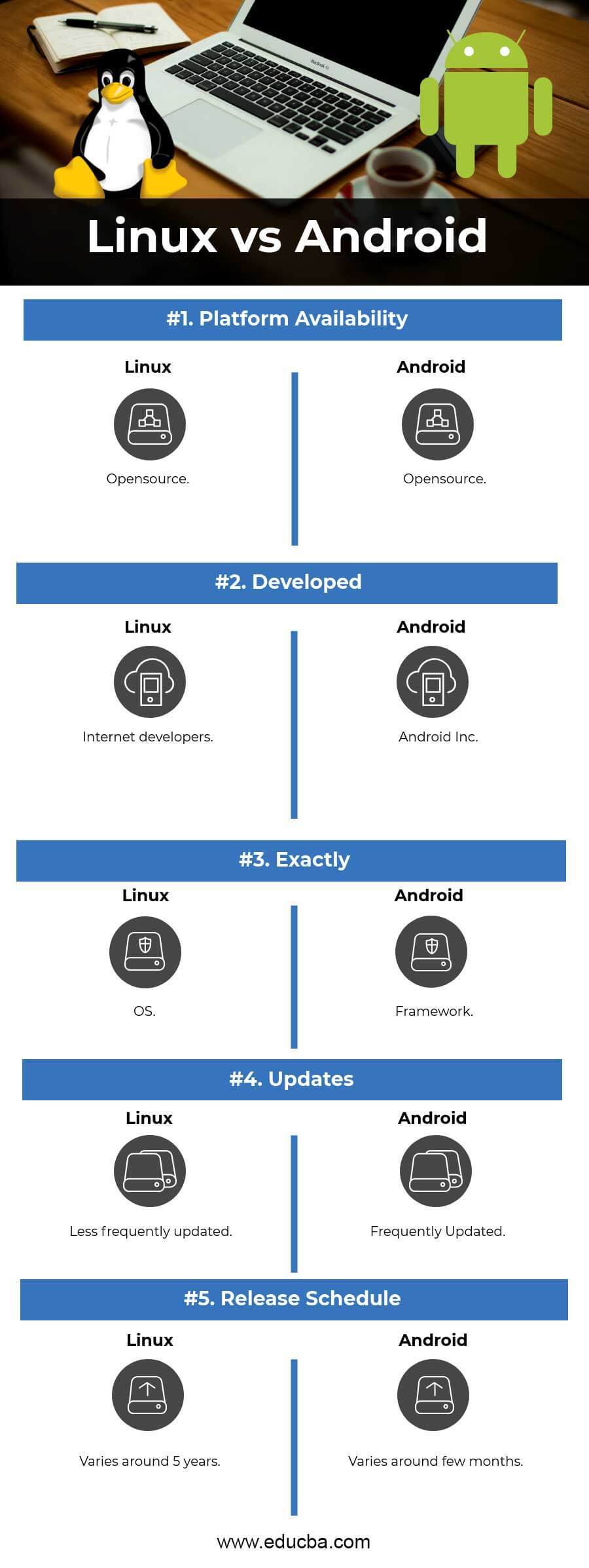
Head To Head Comparison Between Linux vs Android (Infographics)
Below are the top 5 comparisons between Linux vs Android:
Key Difference Between Linux vs Android
Let us discuss some of the major differences between Linux and Android:
- Mainly, personal and office users develop Linux and build Android peculiarly for mobile and tablet devices.
- Android holds a more significant footprint compared to LINUX.
- Usually, multiple architecture support is provided by Linux, and Android supports only two major architectures, ARM and x86. The ARM platform is widespread on mobile phones, while the Android-x86 targets mainly Mobile Internet Devices. This functionality acts as the fundamental difference between the two Operating Systems; it acts as a key difference between Linux vs Android.
- APM accomplishes power management. Android relies most on its power management module, which stands very close to Linux power extensions.
- Linux is a popular OS, whereas Android is a framework executing on the Linux kernel.
- Linux system uses magnetic drives, standard Linux systems use the EXT journaling file system to provide a robust file system, and embedded systems use solid-state memory devices such as NOR for code execution and NAND for storage. On the other hand, android systems use flash memory for storage-related needs.
- Linux systems use the GNU C library; Android uses a C library. Booting an Android device, the kernel loads just like it would on a Linux distribution. However, most of the software is different. Standard Linux distributions use Android without an association with a GNU C library.
- Android uses Dalvik virtual machine to run its applications; several top mobile developers use JVM for its execution. Conversely, Linux does not take in any VMs for execution.
Linux vs Android Comparison Table
Below is the topmost comparison between Linux vs Android:
Conclusion
Mobile and tablet devices use Android, an open-source operating system that runs on top of the Linux Kernel distribution. Android plays a vital role on mobile devices, yet it’s a framework that stands on top of this Linux kernel. On the other hand, Linux is a legacy OS that is highly suitable for desktop and system users.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the top differences between Linux vs Android. Here we discussed Linux vs Android key differences, infographics, and a comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –
38+ Hours of HD Videos
9 Courses
5 Mock Tests & Quizzes
Verifiable Certificate of Completion
Lifetime Access
4.5
149+ Hours of HD Videos
28 Courses
5 Mock Tests & Quizzes
Verifiable Certificate of Completion
Lifetime Access
4.5
253+ Hours of HD Videos
51 Courses
6 Mock Tests & Quizzes
Verifiable Certificate of Completion
Lifetime Access
4.5
Android Developer Course Bundle — 60 Courses in 1
282+ Hours of HD Videos
60 Courses
Verifiable Certificate of Completion
Lifetime Access
4.5
Android vs Linux – Detailed Comparison Table
Android and Linux – are considered by most of the people as operating systems like Android OS are for the mobiles while Linux OS is for the server and Desktop.
In precise terms in Android vs Linux, Linux kernel stands as the OS that is most popular while the framework known as Android is the one developed on Linux kernel top.
So Linux kernel is also run by all the android devices but Android is not there in every Linux device. Hence, the basis on which development of Android takes place is termed as Linux kernel.
Also, there are several devices on which Android runs along with mobiles such as Camera, TV, Cars and Watch etc.
Linux:
Basically, Linux stands as UNIX’s derived version. It is the setup that is community-based and runs athwart several systems. Execution of the operating system takes place itself in this monolithic OS from the kernel.
The comparison of Linux is often done with the profitable Unix systems but in comparison to the systems that are desktop-oriented, it serves to be more reliable.
Linux systems have the following properties:
- Stable OS
- Can be downloaded easily
- Open-source
- Built by internet developers group
- Installation can be easily done
The networking service is firmed as prior stuff by the Linux developers when they have joined the market of Desktop. Database support and trade services are also provided by Linux for organizations such as US post office, Amazon etc.
Linux has especially become popular among Internet service providers as web and proxy server, firewall etc.
Also, every administrator of UNIX system appreciating the management station that is comfortable has a Linux box in reach.
Android:
Execution of Android takes place on virtual machines, it makes use of Java and is primarily focused on satisfying the devices that are low powered.
Updates take place frequently in the systems of Android OS and each of the releases is linked with a new name.
Following are Android OS common features:
- Main suitability of hardware reference is for the mobile devices
- An open platform for mobile development
- UI and application framework involved
- The system is powered using Linux 2.6
The development of open-source Android OS is predominantly for tablets and mobiles. In this, the top layer is the application layer that holds own libraries set and C/C++ languages are used for the development of these languages.
Android vs Linux:
These are some points on the difference between Android and Linux –
- Development of Linux is primarily for office system and personal users while that of Android is for the devices of tablet and mobile type.
- In Android vs Linux, when Android compared with Linux, the footprint held by Android is larger.
- While Linux usually offers support to multiple architectures, x86 and ARM are the only two principal architectures supported by Android. While the main target of Android-x86 is the devices of mobile internet, the predominance of the ARM platform is on mobile phones. These two OS has this functionality as the fundamental difference between them.
- APM or ACPI is used for achieving power management in Linux. Android majorly depends on its module of power management (extension) called Power Manager
- In Linux vs Android magnetic drives are used by the Android system while the file system of EXT journaling is used by standard systems of Linux.
- Embedded devices use memory devices of solid-state like NAND for the purpose of storage and NOR for executing code. On the other hand, flash memory is used by android systems for the requirements that are related to storage.
- In Android vs Linux, Android uses C library while GNU C library is used by Linux systems.
- For running the applications, the Dalvik virtual machine is used by Android. For executing it, JVM is used by several mobile developers. On the other hand, no virtual machines are taken by Linux for its execution.
Conclusion:
In Android vs Linux OS, Tablet, mobile devices use the open-source OS known as Android that runs on the top of the distribution of Linux kernel. In contrast, Linux stands as the legacy OS that is highly suitable for the system and desktop users.
Detailed Comparison table of Android vs Linux:
| PARAMETER | ANDROID | LINUX |
|---|---|---|
| Availability of platform | Open source | Open source |
| Developed | Android Inc |
Linux software versus Android op de box
De MediaStax SmartTV boxen hebben Linux als besturingssysteem. Er zijn veel andere leveranciers van soortgelijke boxen beschikbaar, maar deze bieden vergelijkbare boxen met Android als besturingssysteem. Wat is nu het verschil en wat zijn de voor- en nadelen?
Linux
- Specifiek voor MediaStax boxen: actief beheerde software : De software wordt actief doorontwikkeld. Er komen regelmatig updates beschikbaar via de MediaStax Box updater. Deze zijn inclusief de laatste add-ons en configuratie ervan voor het beste gebruiksgemak.
- Optimale internetsnelheid (zowel bedraad en veel via WiFi)
- Optimale gebruikservaring Kodi, de onderliggende Linux software is 100% gericht om Kodi te laten schitteren:
- Menu reageert vlot
- Streams starten sneller op
- Software is stabiel
- Kan (4k, Blu-ray en DVD) ISO bestanden afspelen
- Afstandsbediening staat geheel afgesteld op Kodi
- Geen ondersteuning voor Android apps, zoals Netflix
- Geen webbrowser. De box is puur voor films, TV series en IPTV kijken via Kodi.
Android
- Webbrowser aanwezig (maar in de praktijk gebruikt men deze niet, daar zijn laptops, tablets en mobieltjes nu eenmaal veel handiger voor)
- Android apps draaien op de box:
- Netflix kan via de box worden gebruikt (mits men een betaald account heeft. De beeldkwaliteit echter is geen full HD: maximaal 480p)
- Via Google Play zijn vele andere apps te installeren (maar niet alle zullen werken vanwege gebrekkige Chinese Android versie)
- Belangrijk! : Op het moment van aanschaf zijn boxen met Android al verouderd:
- Ze draaien een verouderde versie van Android (en wordt niet geüpdatet)
- Er komen geen updates van Kodi versies, add-ons, instellingen (en nieuwe add-ons en functionaliteiten). Vaak zijn de Kodi versies op deze boxen verouderd en bevatten verouderde, niet werkende add-ons.
- is trager: menu reageert trager en men moet langer wachten op het starten van streams, meer buffering bij bekijken van streams. De hardware is op de achtergrond meer bezig met Android draaiend te houden.
- is minder stabiel: meer resets en verlies van instellingen
- kan geen (BluRay en DVD) ISO bestanden afspelen
- Niet alle knoppen op de afstandsbediening zijn ingesteld voor Kodi. Bijvoorbeeld met de “Home” knop ga je terug naar Android in plaats van het hoofdmenu van Kodi.
Delen: