- How can I change the default gateway?
- 7 Answers 7
- Default gateway changing
- 3 Answers 3
- How to Set the Default Gateway on Ubuntu
- Checking the Default Gateway
- How to Set a New Default Gateway
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Denis Kariuki
- How to set the Default gateway
- You must log in to answer this question.
- Linked
- Related
- Hot Network Questions
- Subscribe to RSS
How can I change the default gateway?
Currently I’m running a FreeBSD 9.1 and the default gateway is already configured in the rc.conf . rc.conf :
7 Answers 7
route del default route add default 1.2.3.4 Where 1.2.3.4 is the new gateway. You can even concatenate them onto the same line with a ;
Edit: This is FreeBSD, not Linux. The command is different. Please do not edit this Answer if you haven’t read the Question carefully enough to determine the operating system being used.
Note: do this in console, not over ssh. If you must do this via ssh (or other network method), issue both commands at once, with ; or with &&
Or, use the generic safe method: 1) Log into a shell, shutdown/reboot in 15 minutes unless cancelled 2) Do unsafe things. 3) Cancel shutdown/reboot.
On Linux the commands ip route del default and ip route add default via 1.2.3.4 work. So the command is still relevant for Linux users too as it has quite a bit of resemblance.
You can add a new default route and remove the old one using either the ip or route command. The commands below will replace the gateway with 192.0.2.1. Both command pairs do the same thing. FreeBSD and other OSs should have one or both programs, possibly with slightly different formats. (FreeBSD has the route command and excludes the gw keyword used in other implementations.) The commands man ip and/or man route should provide you with documentation on your specific implementation.
route add default 192.0.2.1 route del default 10.0.0.1 ip route add default via 192.0.2.1 ip route del default via 10.0.0.1 There are multiple implementations of these commands, so the above may not match your implementation. Your implementation should have a man page with examples for common use cases such as adding and removing default gateways. Try man route and man ip to see how your implementation works.
Change 192.0.2.1 to your desired default gateway. The default gateway needs to be on one of networks you have a direct connection to. You can change your IP address in a similar manner. ip is a newer tool which will do most everything you need to do to view and manage IP addresses and routing on IPv4 and IPv6 networks. ifconfig is an an older tool for configuring IP addresses on an IPv4 network.
To make the change permanent, update your network configuration files in /etc . The file(s) vary depending on the distribution you are using.
At least one of these commands should be available on any Unix derived O/S. Different versions may work slightly differently. Check the man page for details on your O/S.
Default gateway changing
I am using 3 ethernet interfaces on Ubuntu but when I restart, the default gateway is changing to a different interface. Each time I boot I have to change default gateway back to the eth1 by deleting the default gateway and adding it back with eth1. How can I fix this problem?
Have you configured it manually using the /etc/network/interfaces file, or a with software like Network Manager or wicd?
«Gateway» is not equal to «route». A gateway is specific to an interface where an route says which interface should be used.
The gateway is usually an interface on a remote device which the local node is relying on for routing decisions. A route statement itself can refer to a local interface or not, but the routing destination has to be discoverable from a recursive lookup, connected interface, or default route. A default route or default gateway is the ‘gateway of last resort’ — which will be used in the absence of a more specific route being available.
Can you provide your routing table and list of interface, and other any relevant network configuration you’ve done?
3 Answers 3
To temporarily change the default route you can use an ip command like this:
$ sudo ip route change default via 192.168.1.1 dev eth0 If you have a static ip configuration in /etc/network/interfaces you can add a gateway statement to make this permanent.
iface eth0 inet static gateway 192.168.1.1 […] Using DHCP to configure networking you have to adjust another file instead. Add the supersede statement in /etc/dhcp/dhclient.conf .
supersede routers 192.168.1.1; Scriptable version (should be a space between the quotation marks): echo supersede routers $(ip route | grep default | cut -f3 -d» «)\; | sudo tee —append /etc/dhcp/dhclient.conf
What if I have multiple interfaces? Shouldn’t they all have a ‘gateway’ for each interface? But what affects the example »default via 192.168.3.1 dev eth6″ output of ip route command? It lists a specific interface, right?
Open the file /etc/network/interfaces
find desired interface and add following:
sudo /etc/init.d/networking restart What if the desired interface is configured via DHCP and I don’t know the gateway address it will assign?
I had the same issue for my wifi interface wlp3s0 on Ubuntu 18.04. It was affecting my ability to connect to Android tethering and router outside home. The way to solve the issue for me was to comment in file /etc/dhcpcd.conf the following:
interface wlp3s0 static ip_address=192.168.0.16/24 static routers=192.168.0.1 static domain_name_servers=127.0.0.1 #interface wlp3s0 # static ip_address=192.168.0.16/24 # static routers=192.168.0.1 # static domain_name_servers=127.0.0.1 Then, I’ve disconnected from my current network and reconnected an tried route -n or nmcli to see changes
You can also remove the same lines when you are sure it works for you.
Because of these lines, the NetworkManager was always adding a default route with a wrong gateway, in particular when I was not on my home network. I was getting «Destination Host Unreachable» when I was doing a ping 8.8.8.8 . Hardcoding a gateway in /etc/network/interfaces was not a viable solution as I connect a lot to public wifis (so, never the same wifi router or gateway) and normally DHCP should work «out of the box» IMHO.
PS: I’ve never edited manually /etc/dhcpcd.conf so I don’t know why the file /etc/dhcpcd.conf did contain these lines.
How to Set the Default Gateway on Ubuntu
All the devices on your network rely on the default gateway for communication. Data packets pass through the router to and from your network before being routed to the particular device that owns the packet.
Each operating system comes with a default gateway. However, you can temporarily or permanently change the default gateway to add another route for your network devices. You can use the IP command on Ubuntu to modify your default gateway.
Checking the Default Gateway
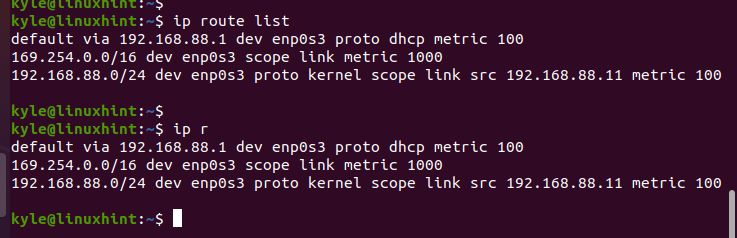
Changing the default gateway is common when you have different sub-networks or when you must point a specific machine to a particular gateway. Before changing the default gateway, let’s list the available routes.
Use the list option with the IP command or its shorthand r to stand for the route.
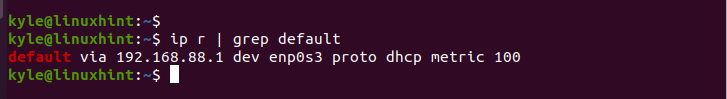
The default gateway has the default keyword in it. If you configured multiple routes on your network, you can use the grep command to filter the router and get the default gateway.
Use the following command:
The current default gateway is 192.168.88.1 on enp0s3 interface. Let’s proceed to set a new default gateway.
How to Set a New Default Gateway
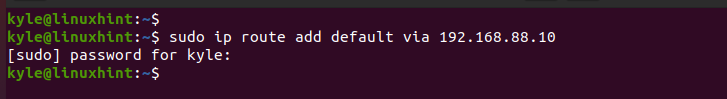
The ip command uses the route option to set the new default gateway. You must specify the type of route that you want to add. In our case, it’s “default”.
For instance, let’s set the default gateway as 192.168.88.10.
Suppose we want to set the default gateway for a particular network interface. In that case, specify the network interface after the gateway. In our case, the interface is enp0s3.
Note that we must add sudo to use the administrator privileges since we are editing the routing table for Ubuntu which is an administrative task.
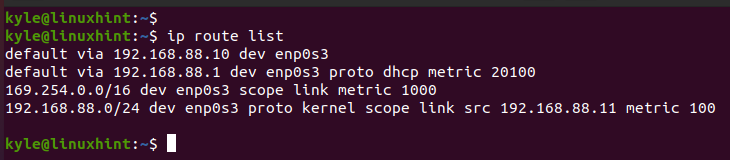
We can use the list or route options to verify the newly added default gateway.
Note how the currently added default gateway is the one that we specified earlier. In the previous output, we now have two default gateways. The keynote is that the changes we made are temporary until you add them to the network manager configuration files.
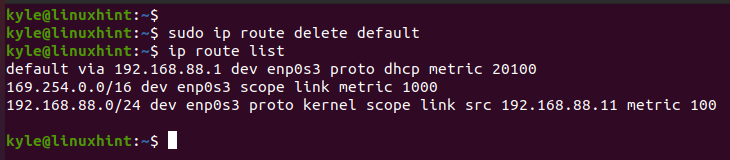
In the previous case, we can delete the added gateway such that we remain with only one.
Use the delete keyword to remove the added gateway.
If we check the available default gateway after running the delete command, we confirm that we only have one default gateway remaining which is 192.168.88.1.
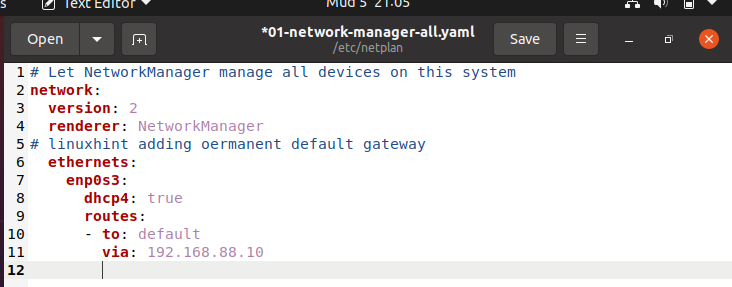
Suppose we want to make the permanent network changes to implement the new gateway. We must edit the configuration file. Open the network manager file using a file editor of your choice. In this case, let’s use gedit with the following command:
Add the new gateway using the following presented format. Make sure that the spacing is set to two whitespaces with the correct indention. Once edited, save the file and exit the editor.
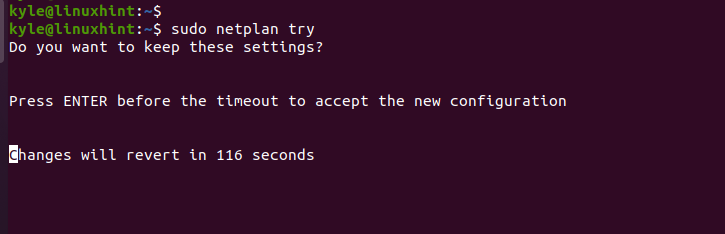
Before applying the changes using the netplan command, run a dry test.
If you are sure with the new network configuration, press the enter key. Otherwise, the changes will revert to the previous settings after the specified seconds.
Conclusion
Ubuntu comes with a default gateway, but that doesn’t mean that you can’t set a new gateway. This guide covered everything about adding a new gateway using the ip command and how to save the changes permanently to the configuration file.
About the author
Denis Kariuki
Denis is a Computer Scientist with a passion for Networking and Cyber Security. I love the terminal, and using Linux is a hobby. I am passionate about sharing tips and ideas about Linux and computing.
How to set the Default gateway
You can use route like in route add default gw 192.168.0.254 for example.
And if route is not present, but ip is, you can use it like this: ip route add default via 192.168.0.254 dev eth0 , assuming that 192.168.0.254 is the ip of your gateway
ifconfig is deprecated on Linux and furthermore, it’s the wrong tool for the job. To set the default gateway on Linux use the ip command as follows:
ip route add default via dev # e.g. ip route add default via 192.168.0.101 dev eth0 For remove gateway in Linux Command : route delete default gw 192.168.1.1 eth1
For add gateway in Linux Command : route add default gw 192.168.1.250 eth1
example: route add default gw 192.168.1.2 eth0
OR use hostname such as dsl-router:
route add default gw dsl-router eth0 Or use the ip command (newer syntax) to route all traffic via 192.168.1.254 gateway connected via eth0 network interface for example:
ip route add 192.168.1.0/24 dev eth0 ip route add 192.168.1.0/24 via 192.168.1.254 You must log in to answer this question.
Highly active question. Earn 10 reputation (not counting the association bonus) in order to answer this question. The reputation requirement helps protect this question from spam and non-answer activity.
Linked
Related
Hot Network Questions
Subscribe to RSS
To subscribe to this RSS feed, copy and paste this URL into your RSS reader.
Site design / logo © 2023 Stack Exchange Inc; user contributions licensed under CC BY-SA . rev 2023.7.13.43531
Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds. UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
This site is not affiliated with Linus Torvalds or The Open Group in any way.
By clicking “Accept all cookies”, you agree Stack Exchange can store cookies on your device and disclose information in accordance with our Cookie Policy.