- How to (Correctly) Change the UID and GID of a user/group in Linux
- Pre-requisites
- Modifying the UID and GID of the user and group
- Caveats
- Some more articles you might also be interested in …
- How To Change User ID (uid) In Linux?
- List Users ID
- Change User ID with usermod Command
- Change Group ID with groupmod Command
- Change Files and Folders Owner User ID
- Change Files and Folders Owner Group ID
- Linux : How to change User and Group ID
- About Kaven Gagnon
- 🐧 Как (правильно) изменить UID и GID пользователя / группы в Linux
- Предпосылки
- Изменение UID и GID пользователя и группы
- Предостережения
How to (Correctly) Change the UID and GID of a user/group in Linux
Changing the UID and GID of a user might seem a trivial task to most of the system admins. But it’s not so trivial and it involves a lot more changes in the backend. In this post, we have outlined the exact steps to change the UID and GID of a user “user01”.
Username: user01 Group: group01 Existing UID: 800 Existing GID: 700 New UID: 900 New GID: 600
Pre-requisites
1. Make sure the user for which UID and GID is to be changed is currently not having any active process running in the system. To check the same use “ps” command. For example:
# ps -ef | grep user01 # ps -ef | grep 800
Note: In the “ps -ef” command UID are displayed. So make sure you grep for UID as well as the username for the user.
2. Take the backup of important files where UID and GID related information is stored. i.e. /etc/passwd and /etc/group.
# cp -p /etc/passwd /etc/passwd.bkp # cp -p /etc/group /etc/group.bkp
3. Verify the exisitng UID and GID of the user using the “id” command:
# id user01 uid=800(user01) gid=700(group01) groups=700(group01)
Modifying the UID and GID of the user and group
Once you have taken necessary backups and command outputs we can go ahead and change the UID and GID.
1. First change the GID of the group, group01:
2. Next, change the UID as well and GID of the user, user01:
# usermod -u 900 -g 600 user01
3. Verify the new UID and GID of the user:
# id user01 uid=900(user01) gid=600(group01) groups=600(group01)
Caveats
1. If there are multiple users in the group “group01”, after changing the GID of the group you will have to modify the other users as well along with the user01 as shown above.
2. Once you have changed the UID and GID, you will have to change the permissions of the files owned by the user/group as well. But the chown command also resets the SETUID and SETGID of the files, so you will need to manually change the permissions of these files later on. To find such files:
# find / -uid 900 -perm /6000 -ls # find / -gid 900 -perm /6000 -ls
3. To find the files owned by user01 and group01 and to change their permissions:
# find / -uid 800 -exec chown -v -h 900 '<>' \; # find / -gid 700 -exec chgrp -v 600 '<>' \;
The -h option is used to change the permissions of symbolic links as well.
Some more articles you might also be interested in …
How To Change User ID (uid) In Linux?
Every Linux user has a unique ID in order to distinguish them. These user IDs are used in different areas like permission, log, and kernel-level operations. The regular user ID’s start from 1000 and are incremented with every new user. You may ask if you can change the existing user ID in Linux. The answer is Yes you can change the existing user ID in Linux. For example, we can change the user ID from 1003 to 2003 in different ways.
List Users ID
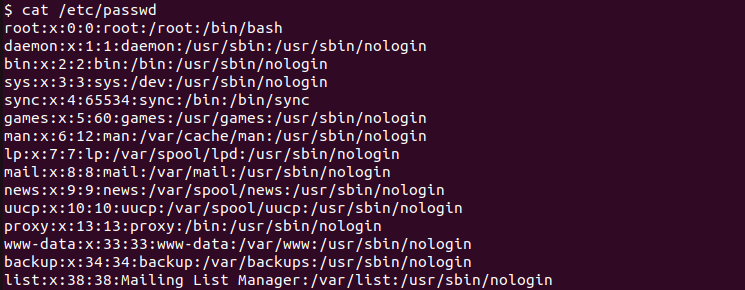
The user information is stored in the /etc/passwd file and this file contains the USER ID information two. The User Id is provided as the 3rd column where the first column is the user name. We can list the users existing ID by printing this file with the cat command.
We can also filter the user specifically by using the grep command. In the following example, we only print the user “ismail” ID.
$ cat /etc/passwd | grep "ismail"ismail:x:1000:1000:İsmail Baydan. /home/ismail:/bin/bash
The first 1000 is the user ID and the second 1000 is the group ID.
Change User ID with usermod Command
The usermod command is generally used to modify an existing user and related information in Linux. We can use the usermod command in order to change User ID. The -u option is used to provide the new User ID. The user name is provided as the last parameter to the usermod command.
In the following example, we change the user ismail Id to 2003.
$ sudo usermod -u 2003 ismailChange Group ID with groupmod Command
Every user in Linux also has a private group with the same username by default. This group also has a group ID. We can use the groupmod command in order to change the user’s group ID. In the following example, we change the group ismail ID to 3003.
$ sudo groupmod -g 3003 ismailChange Files and Folders Owner User ID
After changing the User ID its home directory ID and all contents of the user’s home directory is changed into the new ID. But in other files user ID is not changed automatically. To solve this issue the find command can be used to change to new User ID files owned by this user. We use the users old User Id to find files and use the chown command to set new user Id by refreshing with the new user name which sets the new User ID.
$ sudo find / -user 1003 -exec chown -h ismail <> \;Change Files and Folders Owner Group ID
Similar to the user ID we can update the group ID for the user by using the chgrp command like below.
$ sudo find / -user 1003 -exec chgrp -h ismail <> \;Linux : How to change User and Group ID
There might be some (rare) circumstances where you would like to change a UID or GID on Linux system.
If you know what you are doing and the implication behind this change (see warning comment below), this can be achieved using the commands below.
Change User ID (UID) :
Change Group ID (GID) :
Warning! Changing UID or GID will NOT apply apply on the filesystem. You will have files and folders left with numerical ownership values and the user and/or group that you just changed will not own these files and/or folders anymore. Manual change need to be applied. As you can imagine, if you are doing such operation for a user/group that run an application such as an Oracle database for example, the application should be stopped prior this change.
Note : UID and GID are 32 bits, therefore have a limitation of 2 32 -1 (4 294 967 295), however there is a soft limit in place of 60 000, which is in my opinion way more than what is needed for common use. If needed, you can edit that limit in /etc/login.defs on RHEL.
About Kaven Gagnon
System & Network Architect
Unquoted Windows search path vulnerability in the Foxit Cloud Safe Update Service in the Cloud plugin in Foxit Reader 6.1 through 7.0.6.1126 allows local users to gain privileges via a Trojan horse program in the %SYSTEMDRIVE% folder. (CVSS:4.4) (Last Update:2016-12-03)
Foxit Reader, Enterprise Reader, and PhantomPDF before 7.1 allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption and crash) via a crafted (1) Ubyte Size in a DataSubBlock structure or (2) LZWMinimumCodeSize in a GIF image. (CVSS:4.3) (Last Update:2016-12-03)
Cross-site request forgery (CSRF) vulnerability in CS-Cart 4.2.4 allows remote attackers to hijack the authentication of users for requests that change a user password via a request to profiles-update/. (CVSS:6.8) (Last Update:2016-12-03)
🐧 Как (правильно) изменить UID и GID пользователя / группы в Linux
Мануал
Изменение UID и GID пользователя может показаться тривиальной задачей для большинства системных администраторов.
Username: user01 Group: group01 Existing UID: 800 Existing GID: 700 New UID: 900 New GID: 600
Предпосылки
1. Убедитесь, что пользователь, для которого необходимо изменить UID и GID, в данный момент не имеет активных процессов, запущенных в системе.
Чтобы проверить то же самое, используйте команду «ps».
# ps -ef | grep user01 # ps -ef | grep 800
Примечание: в команде «ps -ef» отображаются UID. Так что убедитесь, что вы грепаете поя UID, а также имени пользователя.
2. Сделайте резервную копию важных файлов, в которых хранится информация, связанная с UID и GID. т.е. /etc/passwd и /etc/group.
# cp -p /etc/passwd /etc/passwd.bkp # cp -p /etc/group /etc/group.bkp
3. Проверьте существующие UID и GID пользователя с помощью команды «id»:
# id user01 uid=800(user01) gid=700(group01) groups=700(group01)
Изменение UID и GID пользователя и группы
После того, как вы сделали необходимые резервные копии, мы можем изменить UID и GID.
1. Сначала измените GID группы, group01:
2. Затем также измените UID и GID пользователя user01:
# usermod -u 900 -g 600 user01
3. Проверьте новый UID и GID пользователя:
# id user01 uid=900(user01) gid=600(group01) groups=600(group01)
Предостережения
1. Если в группе «group01» несколько пользователей, после изменения GID группы вам придется изменить других пользователей, а также user01, как показано выше.
2. После того, как вы изменили UID и GID, вам также придется изменить права доступа к файлам, принадлежащим пользователю/группе.
Но команда chown также сбрасывает SETUID и SETGID файлов, поэтому вам потребуется вручную изменить разрешения этих файлов позже.
# find / -uid 900 -perm /6000 -ls # find / -gid 900 -perm /6000 -ls
# find / -uid 800 -exec chown -v -h 900 '<>' \; # find / -gid 700 -exec chgrp -v 600 '<>' \;
Опция -h также используется для изменения прав символических ссылок.
Пожалуйста, не спамьте и никого не оскорбляйте. Это поле для комментариев, а не спамбокс. Рекламные ссылки не индексируются!
Спасибо.
Добавьте в Предостерижения в п.1
# cat /etc/group | grep group01
чтоб увидеть пользователей входящих в группу.
- Аудит ИБ (49)
- Вакансии (12)
- Закрытие уязвимостей (105)
- Книги (27)
- Мануал (2 306)
- Медиа (66)
- Мероприятия (39)
- Мошенники (23)
- Обзоры (820)
- Обход запретов (34)
- Опросы (3)
- Скрипты (114)
- Статьи (352)
- Философия (114)
- Юмор (18)
Anything in here will be replaced on browsers that support the canvas element
Что такое 404 Frame? Большинство инструментов для взлома веб-сайта находятся в 404 Frame. Итак, что же представляют собой команды? Вы можете отдавать команды, используя повседневный разговорный язык, поскольку разработчики не хотели выбирать очень сложную систему команд. Команды Команды “help” / “commands” показывают все команды и их назначение. Команда “set target” – это команда, которая должна […]
В этой заметке вы узнаете о блокировке IP-адресов в Nginx. Это позволяет контролировать доступ к серверу. Nginx является одним из лучших веб-сервисов на сегодняшний день. Скорость обработки запросов делает его очень популярным среди системных администраторов. Кроме того, он обладает завидной гибкостью, что позволяет использовать его во многих ситуациях. Наступает момент, когда необходимо ограничить доступ к […]
Знаете ли вы, что выполняется в ваших контейнерах? Проведите аудит своих образов, чтобы исключить пакеты, которые делают вас уязвимыми для эксплуатации Насколько хорошо вы знаете базовые образы контейнеров, в которых работают ваши службы и инструменты? Этот вопрос часто игнорируется, поскольку мы очень доверяем им. Однако для обеспечения безопасности рабочих нагрузок и базовой инфраструктуры необходимо ответить […]
Одной из важнейших задач администратора является обеспечение обновления системы и всех доступных пакетов до последних версий. Даже после добавления нод в кластер Kubernetes нам все равно необходимо управлять обновлениями. В большинстве случаев после получения обновлений (например, обновлений ядра, системного обслуживания или аппаратных изменений) необходимо перезагрузить хост, чтобы изменения были применены. Для Kubernetes это может быть […]
Является ли запуск сервера NFS в кластере Kubernetes хорошей идеей или это ворота для хакеров Одним из многочисленных преимуществ сетевой файловой системы является ее способность выполнять многократное чтение-запись. И как и все в наши дни, NFS – это просто еще одна служба, которую можно запустить в своем кластере Kubernetes. Однако является ли сервер NFS подходящей […]