- Проверка скорости интернета Linux
- Проверка скорости интернета через терминал
- Установка SpeedTest-cli
- Проверка скорости интернет
- Выводы
- Monitoring Network Bandwidth and Speed in Linux
- Tools for Monitoring Internet traffic and speed in Linux
- 1. NetSpeed – GNOME shell extension for desktop users
- 2. Fast – Netflix’s Internet speed tester
- 3. speedtest-cli: check upload and download speed
- 4. NetHogs – Check bandwidth utilization per program basis
- 5. nload – Real-Time internet traffic monitoring
- 6. CBM – Color Bandwidth Meter
- 7. iPerf – Test network performance between two hosts
- 8. vnStat – Network traffic logger
- 9. iftop – The ‘top’ of Network Usage
Проверка скорости интернета Linux
Скорость подключения к интернету — это очень важный параметр работы сети. При подключении к интернету в офисе или дома может понадобиться проверить скорость интернета linux. Обычно, для этого достаточно открыть какой-либо сайт и скачать файл. Но это не единственный способ.
Проверка скорости интернета Linux может быть выполнена с помощью специального сервиса — speedtest.net. Вы можете открыть сайт проекта в браузере, программа определит ближайший к вам сервер, а затем покажет скорость доступа к этому серверу. Для работы сервиса используется флеш-плеер. Но не это тема нашей статьи. Сегодня мы рассмотрим как узнать скорость сети linux через терминал.
Проверка скорости интернета через терминал
Конечно, вы могли бы скачать файл с помощью wget и таким образом узнать скорость интернета. Но тогда на скорость загрузки будет влиять не только пропускная способность вашей сети, но и скорость отдачи сервера. Поэтому лучше использовать сервис speedtest, это, возможно, даже из командной строки.
speedtest-cli — это скрипт, написанный на Python, который позволяет измерить скорость интернета linux в двух направлениях. Вы можете проверять скорость сети на определенном расстоянии или для конкретных серверов, а также делиться своим результатом в интернете.
Установка SpeedTest-cli
Утилита может быть установлена двумя способами. Или из репозитория пакетов Python, либо прямо с Github, мы рассмотрим оба способа. Начнем с более сложного.
Сначала обновите систему до самой последней версии:
Установите скрипт установки пакетов python:
sudo apt install python-pip
Затем установите саму программу speedtest-cli с помощью pip:
sudo pip install speedtest-cli
Второй способ еще проще, сначала скачайте файл программы с GitHub и дайте ему права на выполнение:
wget -O speedtest-cli https://raw.github.com/sivel/speedtest-cli/master/speedtest_cli.py
$ chmod +x speedtest-cli
Вы можете скопировать скрипт в папку /bin или выполнять его прямо из этой папки.
Проверка скорости интернет
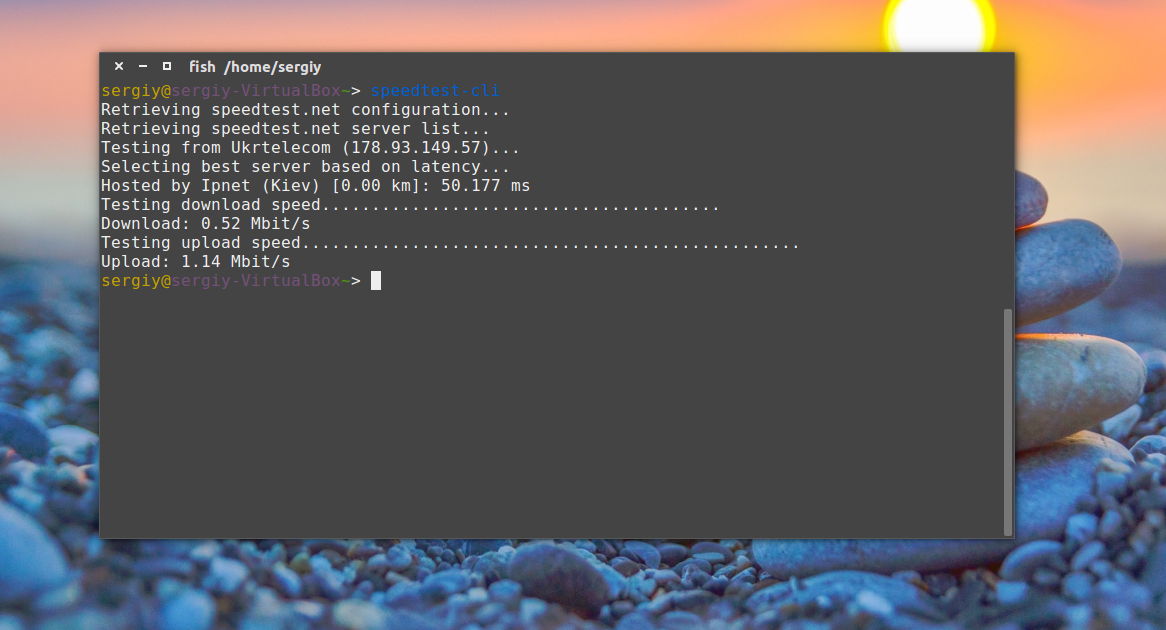
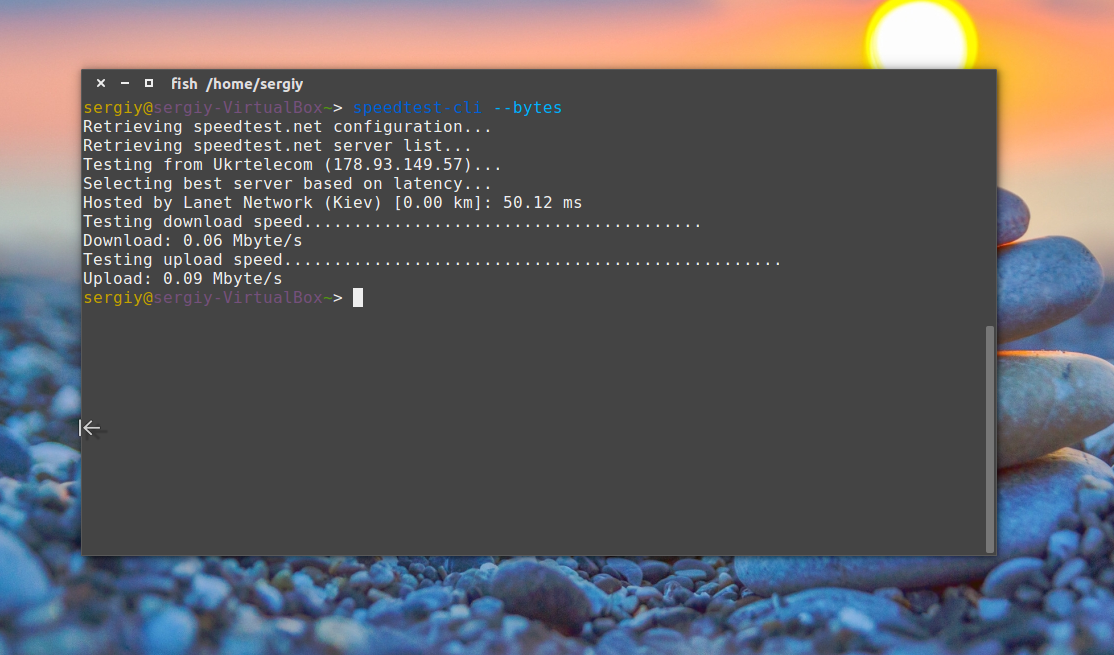
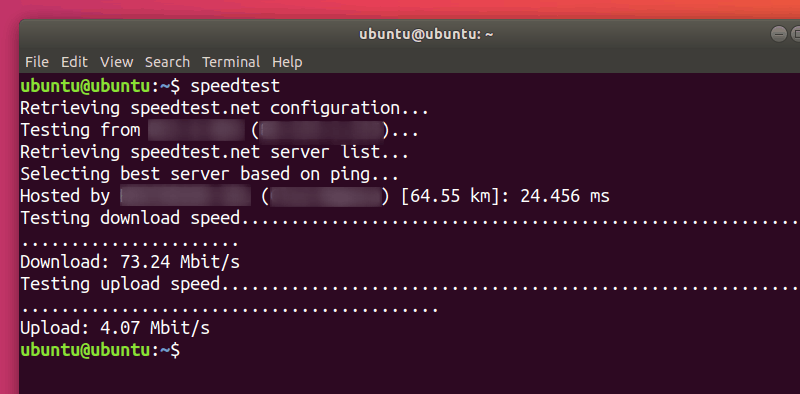
Чтобы проверить скорость интернет linux достаточно запустить скрипт без параметров:
Вы можете посмотреть результат проверки в байтах, а не в битах:
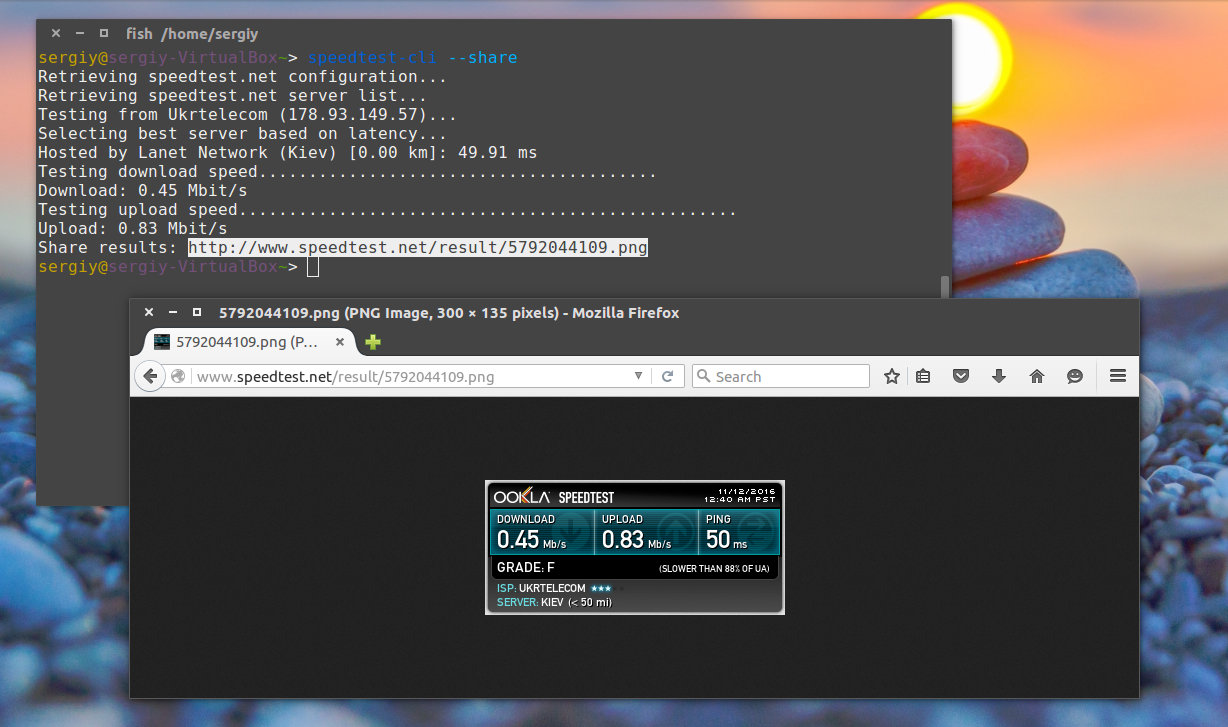
Если хотите поделиться результатом с друзьями, можно попросить программу создать изображение:
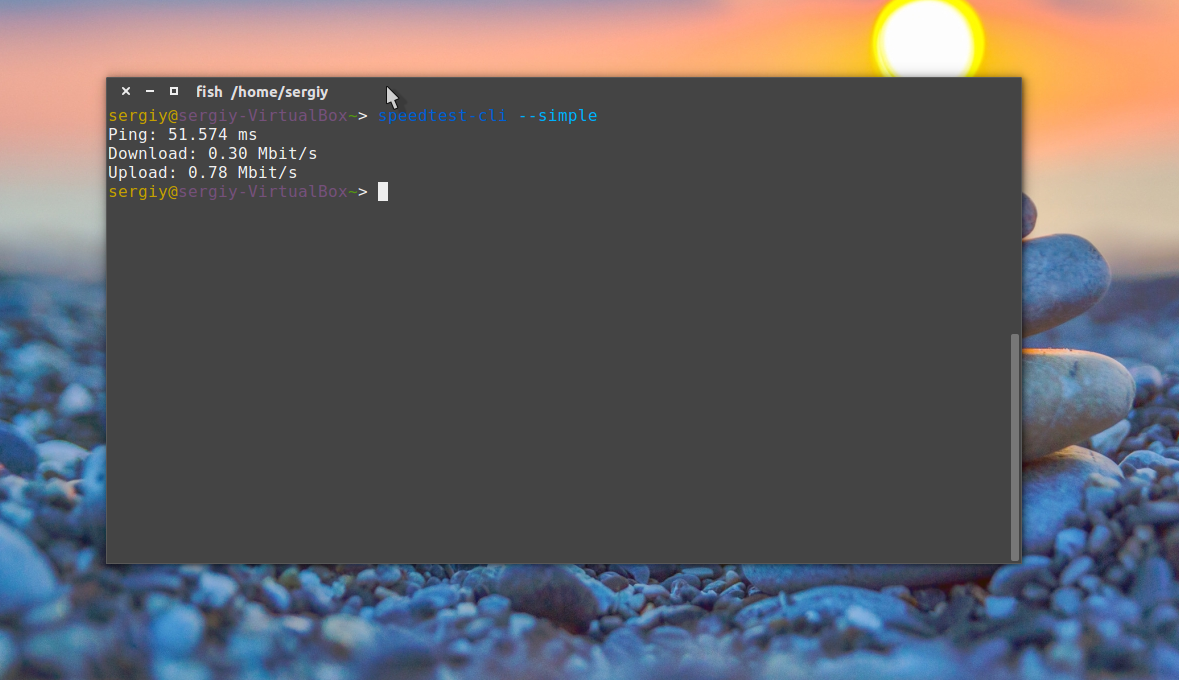
Для получения информации только о ping, скорости загрузки и отдачи:
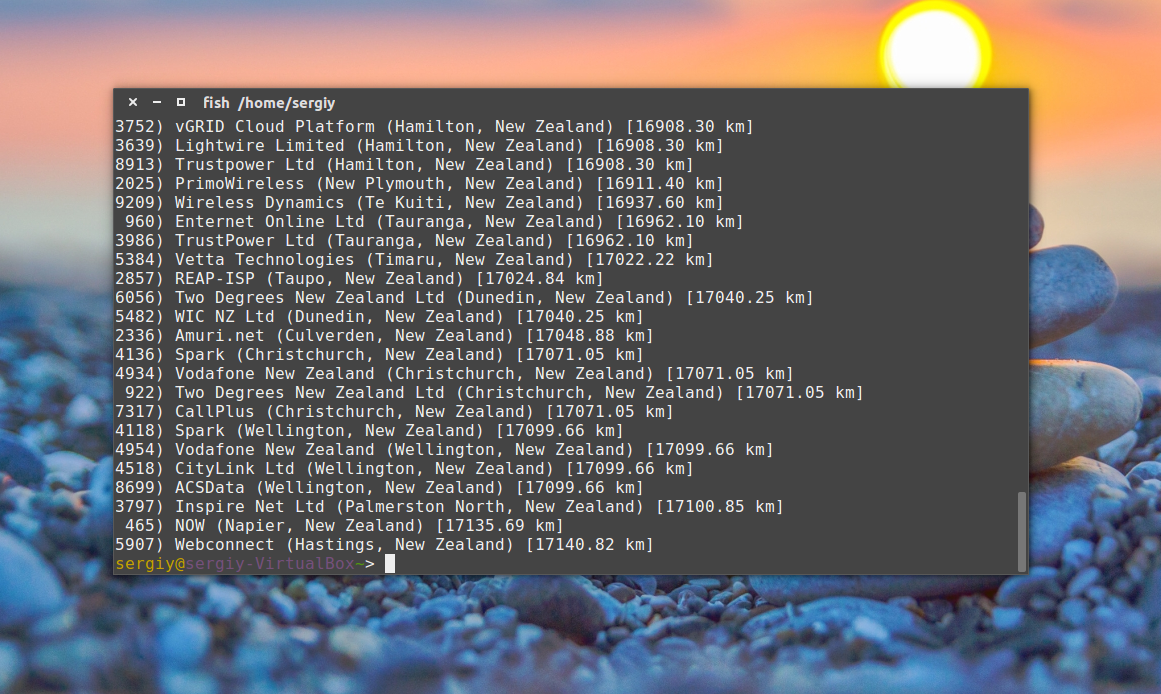
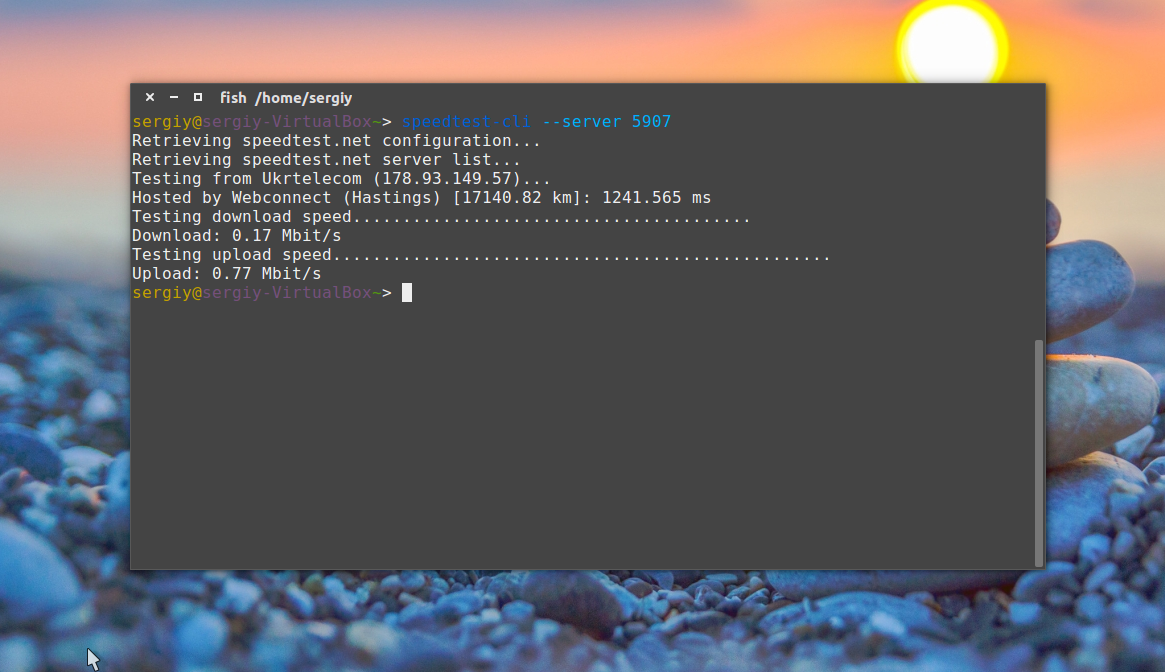
Посмотреть список доступных серверов можно с помощью параметра —list:
Теперь вы можете определить скорость соединения с нужным сервером, для этого достаточно указать ид сервера:
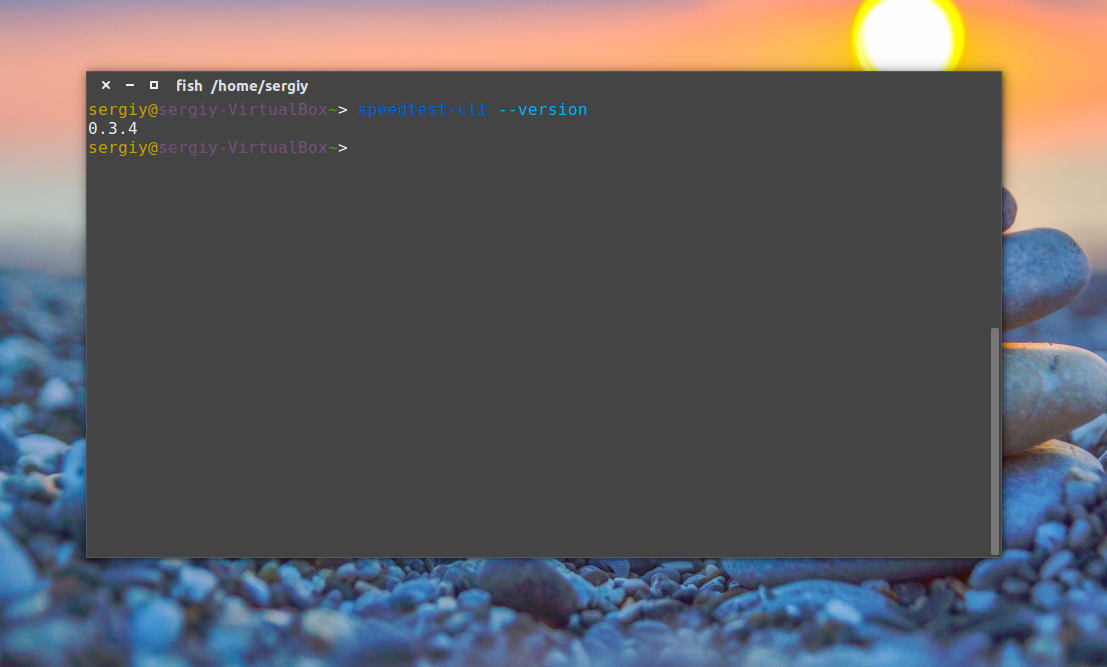
Чтобы вывести версию утилиты выполните:
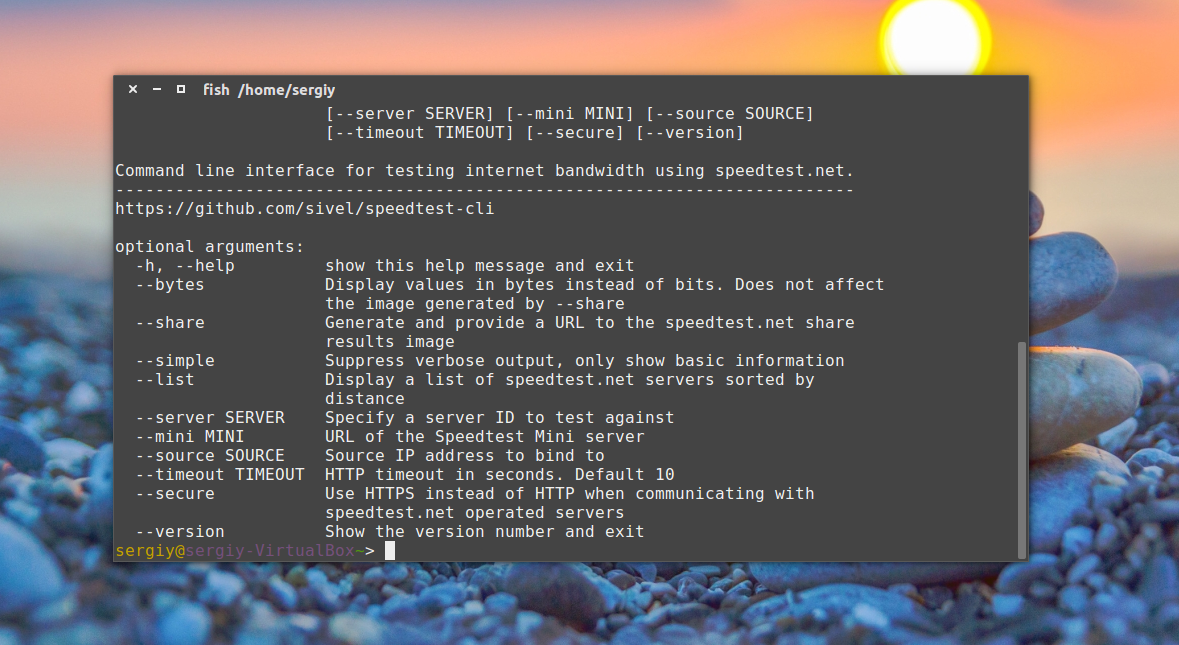
А для просмотра всех возможных опций программы:
Выводы
Утилита speedtest-cli очень проста в использовании и в то же время может оказаться очень полезной. Во всяком случае теперь вы знаете как выполняется проверка скорости интернета linux. Если у вас остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях!
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
Monitoring Network Bandwidth and Speed in Linux
Monitoring internet speed can be a crucial step in understanding your connection and it can help you find possible problems. It will also help you troubleshoot any connectivity problems you might have and find possible bottlenecks.
Tools for Monitoring Internet traffic and speed in Linux
I am going to present you different tools to help monitor your internet speed. I have provided installation instructions for Ubuntu/Debian based distributions but the tools can be easily installed in other distributions.
It doesn’t matter if you are a beginner that wants a simple, working solution, a guru looking to get as much information about your network as possible, if you prefer GUI or CLI programs, I’ll help you find the right tool for the job.
1. NetSpeed – GNOME shell extension for desktop users
NetSpeed is a GNOME shell extension that displays the sum of your download and upload speed in your gnome panel. Clicking on it displays the separate values in a drop-down.
It is applicable only if you use the GNOME desktop environment. If you are not familiar already, read this tutorial to know how to use GNOME Shell extensions.
2. Fast – Netflix’s Internet speed tester
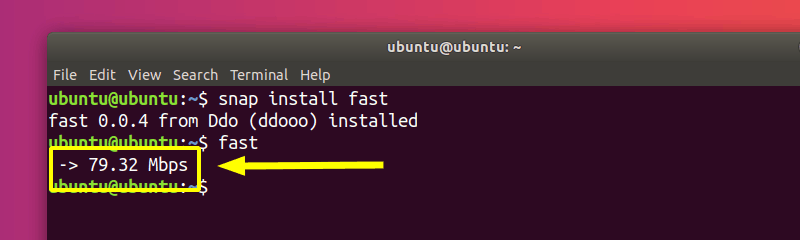
Fast is an open-source CLI utility powered by Netflix fast.com service. Although the code for the website itself isn’t open-source, Netflix have explained how it works here. Fast is the perfect tool for someone that just wants to check the download speed in a very simple manner.
You can install it using snap. Make sure to enable Snap support in your distribution and then run the following command:
Once installed, you can run the utility by typing in:
Once again, after a few seconds, you’ll get your result:
3. speedtest-cli: check upload and download speed
speedtest-cli is an open-source command line interface for testing internet bandwidth using speedtest.net (which, itself, isn’t open-source). It is a quick little tool for checking your download and upload speed.
speedtest-cli is available in most distros and can easily be installed using the package manager. On Debian/Ubuntu, you can use the following command:
sudo apt install speedtest-cliOnce installed, simply run:
After a few seconds, you’ll get information about which server was used for checking your connection, as well as the details concerning your internet speed. Use man speedtest to learn about additional options (such as not performing download test with –no-download).
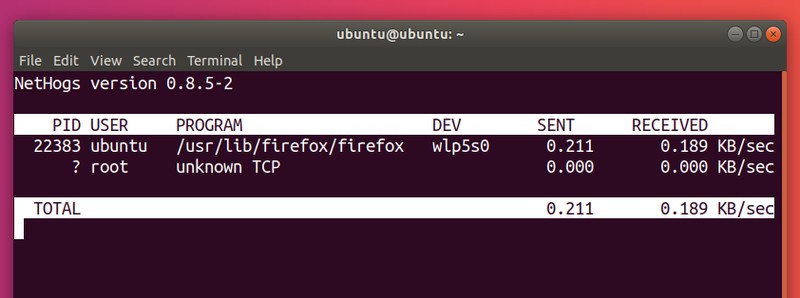
4. NetHogs – Check bandwidth utilization per program basis
NetHogs is a simple open-source utility that runs in the terminal. Instead of breaking the traffic down per protocol or per subnet, it groups bandwith by process. It is very helpful for finding the PID of a hanging program or just for seeing what is eating your bandwidth. It relies mostly on /proc, so most features are Linux-only.
Luckily, NetHogs is included in many distros. That means you can install and remove it using your normal package manager. On Debian/Ubuntu, you can use this:
Conveniently, you can specify devices after the command (such as sudo nethogs eth0). You also have additional parameters, such as choosing a delay for the refresh rate (-d), version info (-V), tracemode (-t) and a few others which you can check out in the man pages (man nethogs).
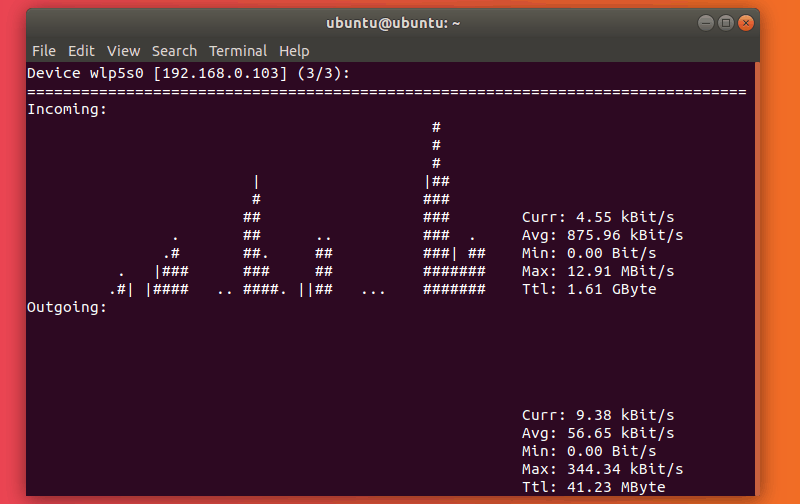
5. nload – Real-Time internet traffic monitoring
nload is an open-source console application that allows you to monitor network traffic and bandwidth usage in real time. It visualizes incoming and outgoing traffic using graphs, while also providing additional information (total amount of transferred data, min/max network usage etc.). It’s a simple to use tool that can be really helpful at times.
You can install it in Debian and Ubuntu based distributions using the command:
You can control its various aspects from the manpage (man nload).
6. CBM – Color Bandwidth Meter
CBM is a very simple tool that displays (in color) network traffic on all connected devices, in a very stripped-down manner.
CBM is a slightly older piece of software that can be found in most distro repositories. This makes installing and removing it using the package manager very easy.
Using CBM is just as easy as installing it. You run:
The commands are displayed in the bottom of your terminal so that you can control them easily.
7. iPerf – Test network performance between two hosts
iPerf is tool used for network performance measurement and tuning and can produce standardized performance measurements for any network. It has client and server functionality, and can create data streams to measure bandwidth, loss and other parameters between the two ends in one or both directions. There are two implementations: the original iPerf (iPerf2) and a non-backwards compatible implementation iPerf3.
The easiest way to install (or remove) iPerf or iPerf3 is using the package manager. For example, in Ubuntu:
sudo apt install iperf sudo apt install iperf3Then you can just run the one you want:
Note: For all further examples, if you are using iPerf3 simply replace all instances of iperf with iperf3.
However, doing so will only display your options. To run iPerf, you need a minimum of 2 machines: one to act as a client and one to act as a server. For the server, you’ll use:
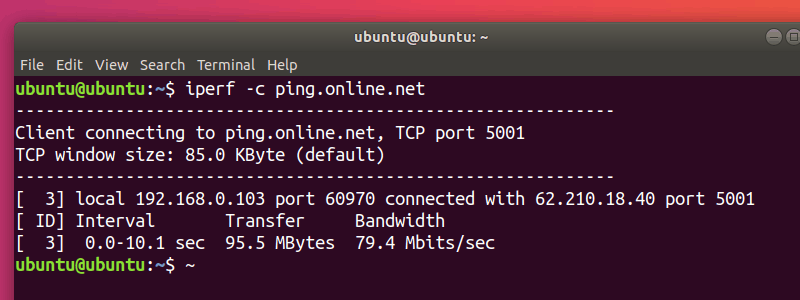
This will open the machine for listening on port 5001. To connect to another machine and run a test, you’ll use:
Where server_address is, of course, the address of the server you are trying to connect to. This can be either an IP address, or something like ping.online.net. The iPerf3 team has a list of servers to use for testing purposes.
iPerf is a widely used tool that has a lot of specific uses and many options. I won’t go into those, since it is beyond the scope of this article. However, you can check out the manpage (man iperf / man iperf3) or the documentation.
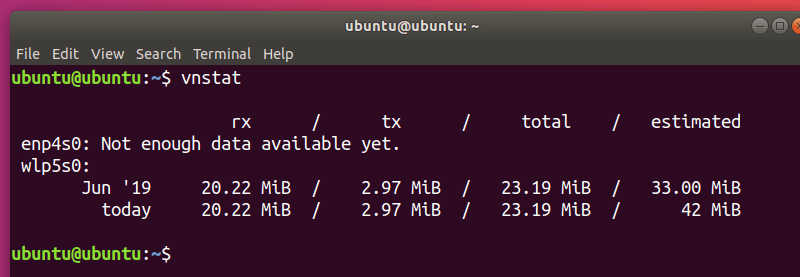
8. vnStat – Network traffic logger
vnStat is an open-source console-based network traffic monitor that uses the network interface statistics provided by the kernel as information source for its periodic logs. This means that vnStat won’t actually be sniffing any traffic and also ensures light CPU usage. It can be run without root permissions.
As with many other networking tools, vnStat is include in most distribution repositories. This means you can very easily install (and remove) it using your package manager.
To use it in the most basic way, simply enter:
vnStat offers you more advanced features too, such as the ability to use databases (importing them or exporting output to a file). You can check these out in the manpage (man vnstat). More examples can be found on the official website.
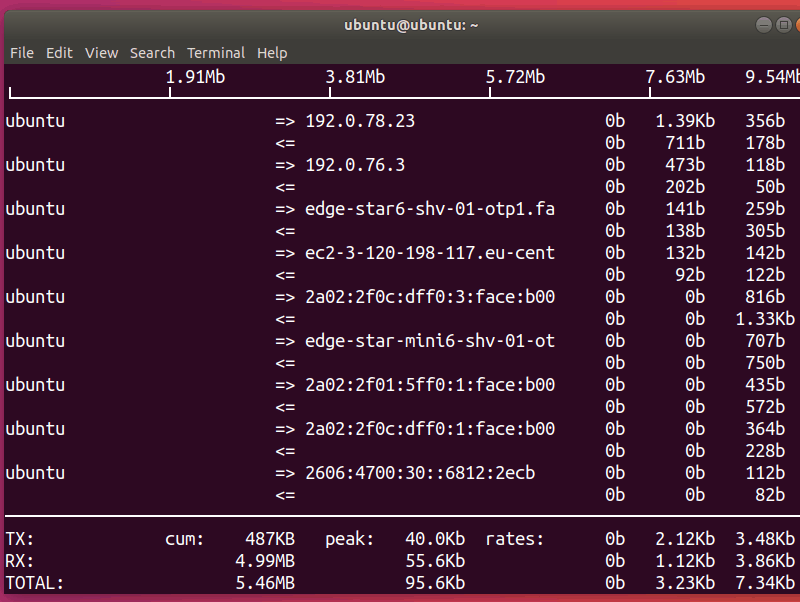
9. iftop – The ‘top’ of Network Usage
iftop is a free open-source software command-line system monitor tool that produces a frequently updated list of network connections between pairs of hosts. The connections can be ordered by different parameters, but they ordered by default by bandwidth usage, with only the “top” bandwidth consumers shown.
Wrapping Up
In this article I showed you multiple tools you can use to monitor different statistics concerning the performance of your network. There is a tool that is right for everyone, and you can pick and choose the one that fits your specific needs. I hope this article was a good introduction to the world of internet monitoring.
What is your favorite tool and how are you using it? Let us know in the comments section!