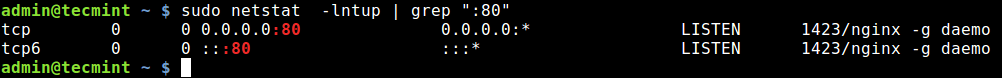- How to know what program is listening on a given port?
- 8 Answers 8
- Check what ports and processes are running in Ubuntu
- What are Ports?
- What are Processes?
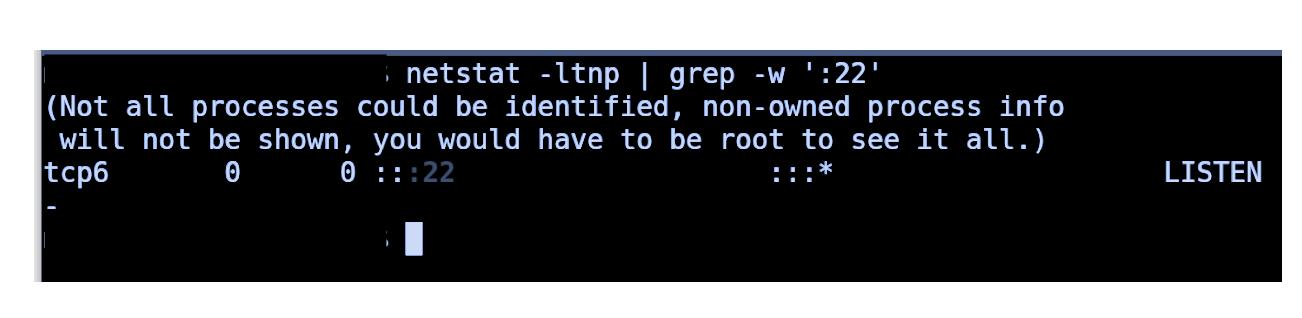
- Method 1: Using netstat and grep Command
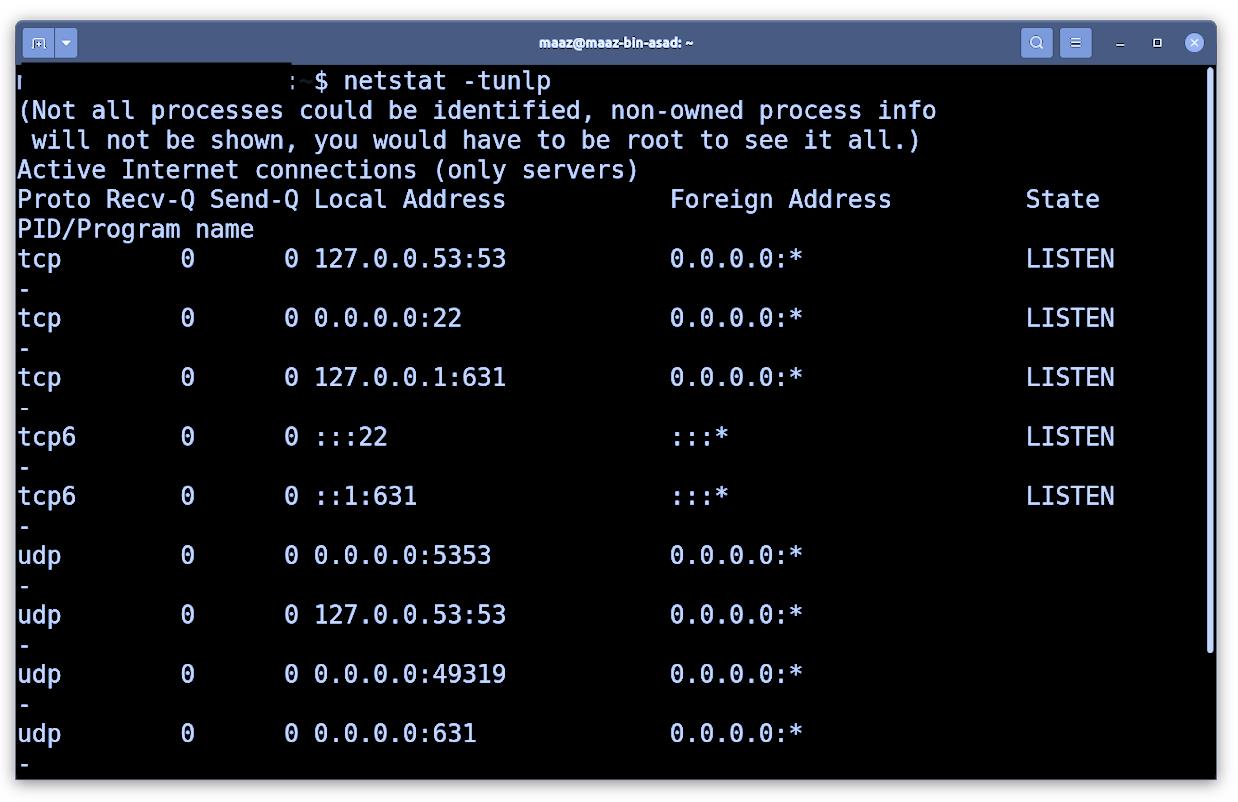
- Method 2: Listing All Listening Ports Using netstat
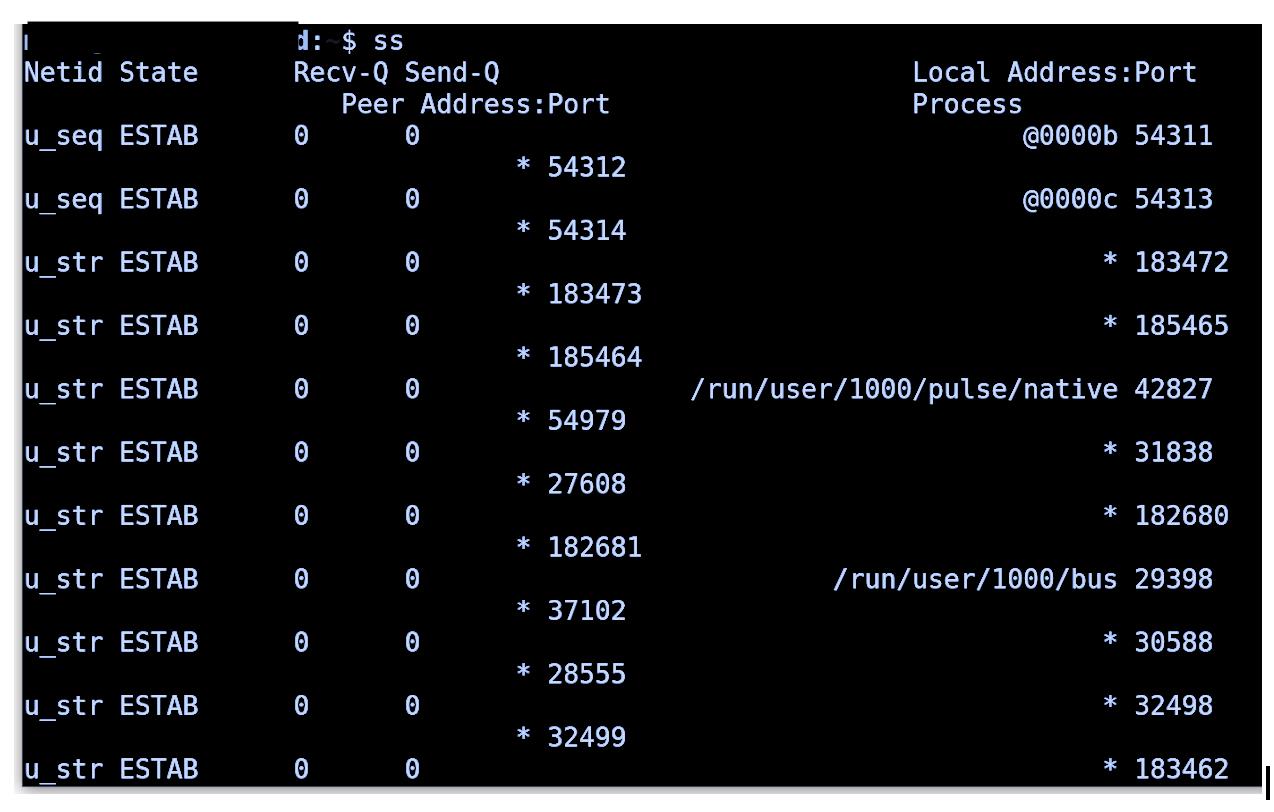
- Method 3: Using ss Command
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Simran Kaur
- 4 Ways to Find Out What Ports Are Listening in Linux
- 1. Using Netstat Command
- 2. Using ss Command
- 3. Using Nmap Command
- 4. Using lsof Command
How to know what program is listening on a given port?
I suspect a program is listening on port 8000 on my machine. When I run the following command, I get this error:
> python -m SimpleHTTPServer # Lots of python error socket.error: [Errno 98] Address already in use If I use another port ( 8000 is the default), the web server runs fine. If I run wget localhost:8000 from the command line, it returns 404 Not Found . What can I do (or what tools are available) to find what program is listening on port 8000 , and from there where that program is configured?
8 Answers 8
Open your terminal and type as
that command will list you the application used by that port with PID. (If no results run via sudo since your might have no permission to certain processes.)
For example, with port 8000 ( python3 -m http.server ):
$ lsof -i :8000 COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME python3 3269 user 3u IPv4 1783216 0t0 TCP *:8000 (LISTEN) $ sudo lsof -i :22 COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME sshd 998 root 3u IPv4 1442116 0t0 TCP *:ssh (LISTEN) sshd 998 root 4u IPv6 1442118 0t0 TCP *:ssh (LISTEN) @Imray the example searches for port 8881. The PID column contains the process IDs and the NAME column contains the ports.
You can use netstat to see which process is listening on which port.
You can use this command to have a full detail :
if you need to know exactly which one is listening on port 8000 you can use this :
sudo netstat -peanut | grep ":8000 " There is no process that can hide from netstat.
To kill/end the process use kill
To expound on the answer by @33833 you can get some very detailed info, for example:
$ lsof -i :8000 COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME squid3 1289 proxy 15u IPv6 14810490 0t0 TCP *:8000 (LISTEN) $ ps -fp 1289 UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD proxy 1289 1 0 09:48 ? 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/squid3 -N -f /etc/squid-deb-proxy/squid-deb-proxy.conf I can see right there that squid is the process, but it is actualy my squid-deb-proxy that is taking up the port.
Another good example of a java app:
$ lsof -i :4242 COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME java 3075 root 86u IPv4 12019 0t0 TCP *:4242 (LISTEN) $ ps -fp 3075 UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD root 3075 1 15 May24 ? 3-16:07:25 /usr/local/crashplan/jre/bin/java -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 -Dapp=CrashPlanService -DappBaseName=CrashPl You can see in lsof (LiSt Open Files) that it is java, which is less than helpful. Running the ps command with the PID we can see right away that it is CrashPlan.
Check what ports and processes are running in Ubuntu
You must know what ports are operating and which process is running on that port before connecting to a port or debugging. Sometimes you may also have problems like “port already in use,” and if necessary, you have to know what process is using that port and terminate it if needed. It may be achieved by the knowledge of which ports the different processes use. We shall examine some approaches to complete the work in this post. First, though, let’s grasp some of the technical words used in this article.
What are Ports?
Ports are an abstraction that may communicate applications using various protocols. For transport layer protocols like TCP, UDP, and SMTP, ports are utilized. Different services are allocated a port number, such as port 80 used by HTTP, port 22 used by SSH, etc. The usage of port numbers enables a couple of systems to open many sockets through the same transport protocol.
Multiple ports and dynamic ports 49152-65535 are used in an application. The first 1024 ports (00-1023) are System Ports, which prohibit user programs from meddling with them since many operating systems reserve these ports for privileged functions.
Ports may receive and deliver data and are above the OSI model’s Transport layer.
What are Processes?
In essence, a process is a program’s dynamic instance and is carried out sequentially. An entity representing the core work unit to be implemented in the system is specified as a process. In plain words, we create our computer programs in a text file, and it becomes a process that does all the duties stated in the program when we execute this program.
Let us now see the methods to check the ports and processes running in Ubuntu.
Method 1: Using netstat and grep Command
The netstat command displays network status and protocol statistics. Depending on the command line parameter used, netstat shows different sorts of network data. TCP and UDP endpoints can be seen in table, routing table, and interface information formats.
The grep filter examines the file and displays every line that contains that pattern for a certain pattern of characters. The pattern looked for in the file is called the regular expression.
Use the following command to check which process is running on a port. You must specify the port in this command.
Method 2: Listing All Listening Ports Using netstat
Use the following command to list all TCP or UDP ports that listen, including those that utilize ports and socket status.
Method 3: Using ss Command
The command ss is a utility used to dump the statistical socket and show information similarly to netstat. Also, TCP and state information is displayed than most other tools. It is also slightly faster than netstat.
Conclusion
We have seen various commands to see which ports your system uses and how to run on a particular port. These commands can be particularly helpful while optimizing the performance of the system and in various debugging tasks. For instance, if you want to run a web application on port 8000 but that port is already occupied, you can look for the process running on this port and kill the process if needed. We have discussed three methods to check the ports and processes running in Ubuntu use that best suit your needs.
About the author
Simran Kaur
Simran works as a technical writer. The graduate in MS Computer Science from the well known CS hub, aka Silicon Valley, is also an editor of the website. She enjoys writing about any tech topic, including programming, algorithms, cloud, data science, and AI. Travelling, sketching, and gardening are the hobbies that interest her.
4 Ways to Find Out What Ports Are Listening in Linux
The state of a port is either open, filtered, closed, or unfiltered. A port is said to be open if an application on the target machine is listening for connections/packets on that port.
In this article, we will explain four ways to check open ports and also will show you how to find which application is listening on what port in Linux.
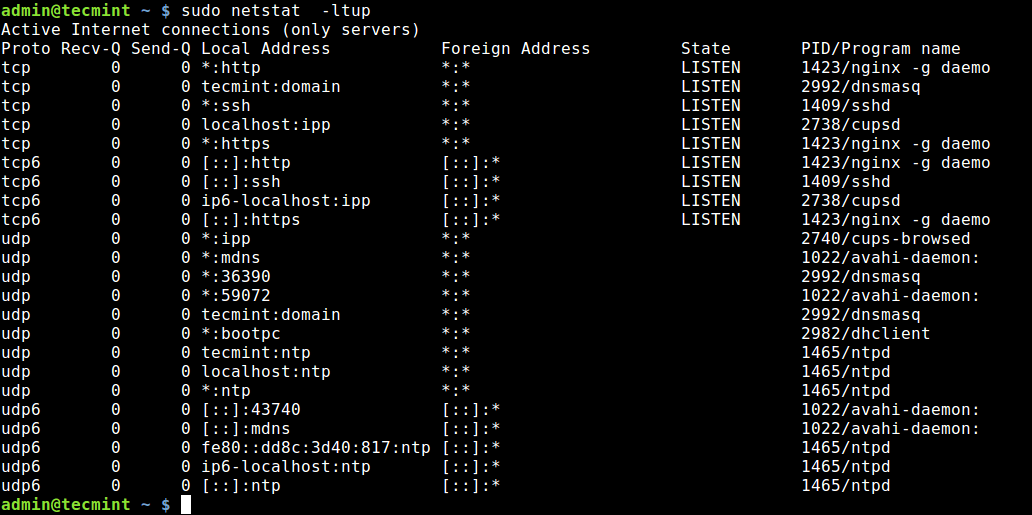
1. Using Netstat Command
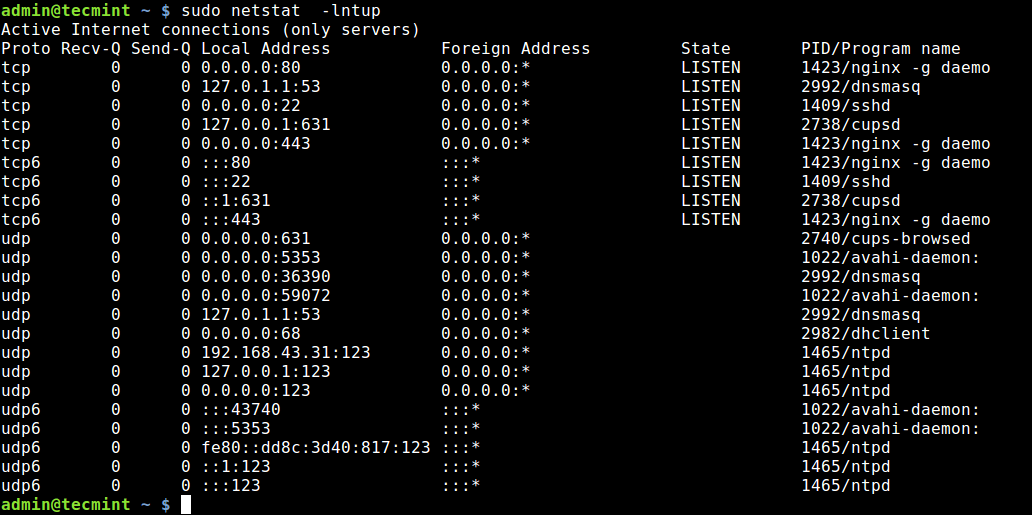
Netstat is a widely used tool for querying information about the Linux networking subsystem. You can use it to print all open ports like this:
The flag -l tells netstat to print all listening sockets, -t shows all TCP connections, -u displays all UDP connections and -p enables printing of application/program name listening on the port.
To print numeric values rather than service names, add the -n flag.
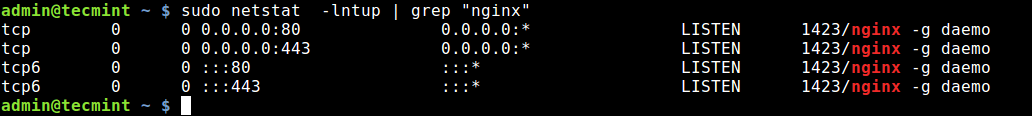
You can also use grep command to find out which application is listening on a particular port, for example.
$ sudo netstat -lntup | grep "nginx"
Alternatively, you can specify the port and find the application bound to, as shown.
$ sudo netstat -lntup | grep ":80"
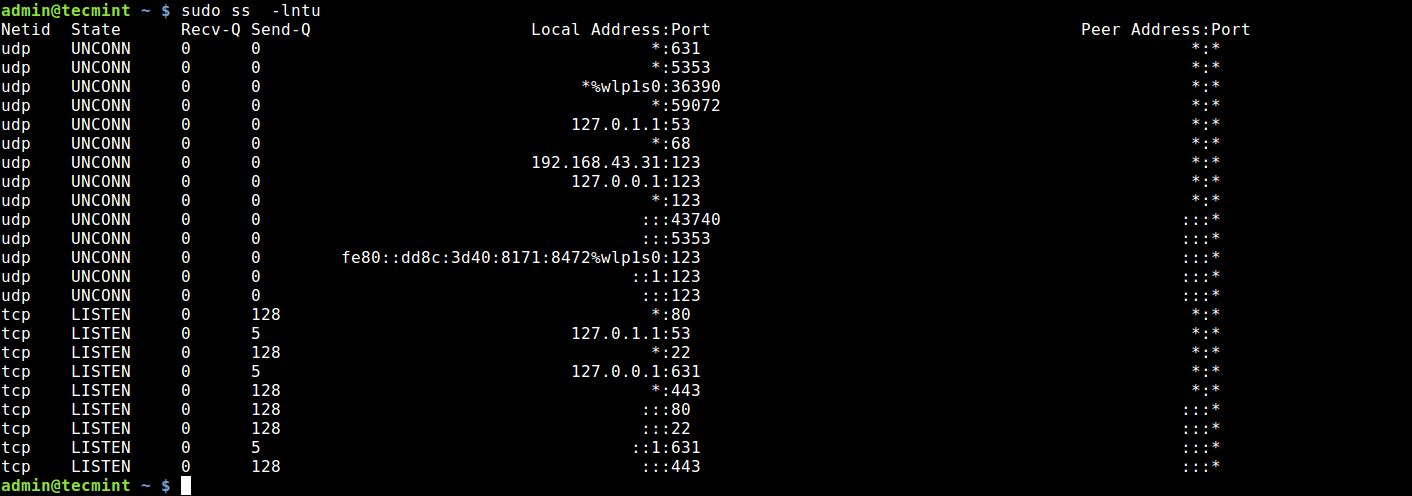
2. Using ss Command
ss command is another useful tool for displaying information about sockets. It’s output looks similar to that of netstat. The following command will show all listening ports for TCP and UDP connections in numeric value.
3. Using Nmap Command
Nmap is a powerful and popular network exploration tool and port scanner. To install nmap on your system, use your default package manager as shown.
$ sudo apt install nmap [On Debian/Ubuntu] $ sudo yum install nmap [On CentOS/RHEL] $ sudo dnf install nmap [On Fedora 22+]
To scan all open/listening ports in your Linux system, run the following command (which should take a long time to complete).
$ sudo nmap -n -PN -sT -sU -p- localhost
4. Using lsof Command
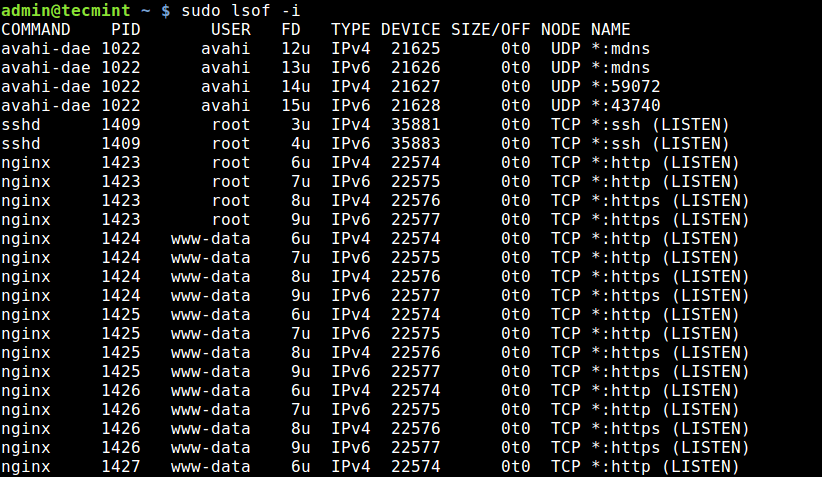
The final tool we will cover for querying open ports is lsof command, which is used to list open files in Linux. Since everything is a file in Unix/Linux, an open file may be a stream or a network file.
To list all Internet and network files, use the -i option. Note that this command shows a mix of service names and numeric ports.
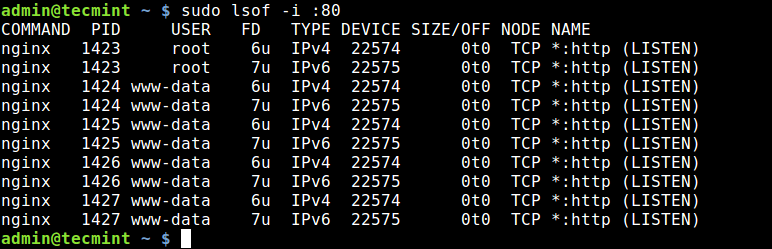
To find which application is listening on a particular port, run lsof in this form.
That’s all! In this article, we have explained four ways to check open ports in Linux. We also showed how to check which processes are bound upon particular ports. You can share your thoughts or ask any questions via the feedback form below.