- 4 Useful Commands to Check Linux Version
- What is the difference between Linux and other operating systems?
- What is the best Linux distribution?
- What are the benefits of using Linux?
- Check Linux version from /etc/os-release
- Check Linux version with uname command
- Check Linux version from /proc/version
- Check Linux version with lsb_release command
- What are some popular Linux distributions?
- What is the difference between Linux distributions?
- Why are there so many Linux distributions?
- How do I change my Linux distribution?
- How to Find Linux OS Name and Kernel Version You Are Running
- Find Linux Kernel Version Using uname Command
- Find Linux OS Info Using /proc/version File
- Find the Linux Distribution Name and Release Version
- /etc/os-release file
- lsb_release Command
- hostnamectl Command
- Linux check release version
- How to check Debian version: the quick and easy way
- How to check your Ubuntu version: a guide
- How to delete a Linux directory
- How to delete files in Linux
- How to use the Linux find command
4 Useful Commands to Check Linux Version
How to check Linux version is a commonly asked question during a Linux job interview. The OS version of a Linux distribution can be determined by using the command-line interface as well as a graphical user interface.
In Linux, CLI is preferred over GUI as it provides more control over the OS. In this article, we will mostly focus on the command line methods which can be used to check the OS version of a Linux distribution.
What is the difference between Linux and other operating systems?
Linux is an open source operating system that was created in 1991 by Linus Torvalds. It is different from other operating systems because it is based on the Linux kernel. Linux is also free and can be used on a variety of devices.
What is the best Linux distribution?
The most popular and widely used distributions are Ubuntu, Debian, Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), CentOS, Fedora. Other distros include Arch Linux, Gentoo Linux and openSUSE.
What are the benefits of using Linux?
Some of the benefits of using Linux include its stability, security, flexibility and cost. Linux is also a more secure operating system than Windows. It can be used on a variety of devices, including desktops, laptops, servers and smartphones.
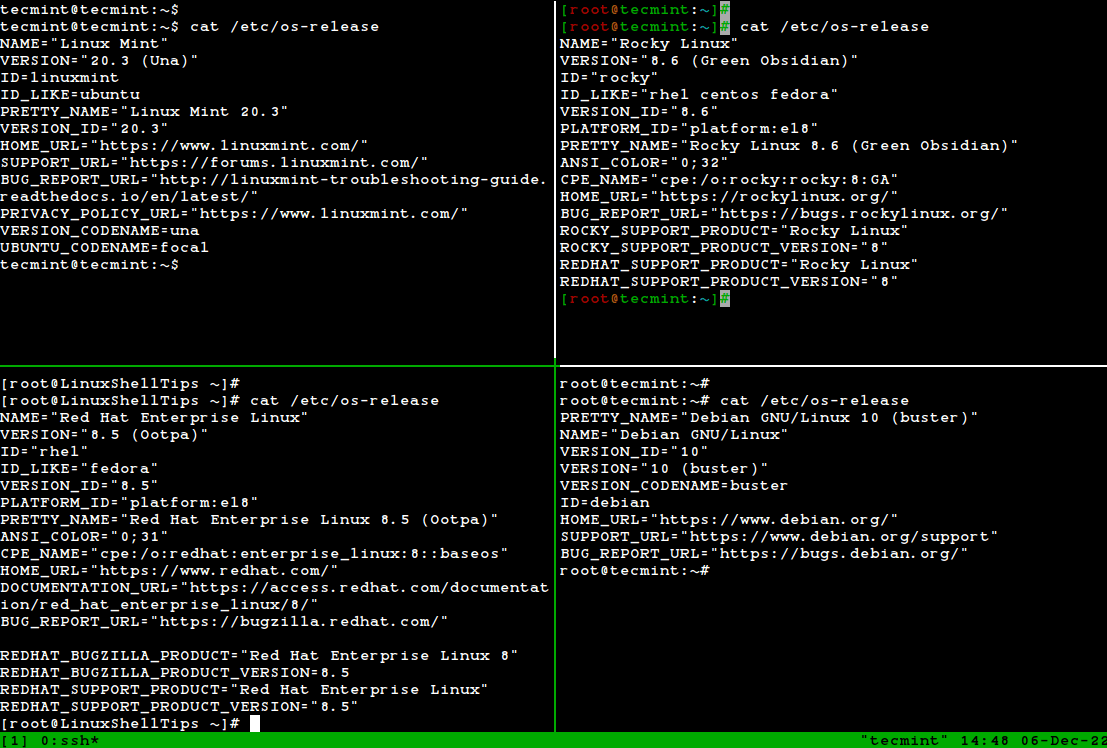
Check Linux version from /etc/os-release
The best way to check Linux version is using cat /etc/os-release command. This command will list Linux distribution name and release version information. It works on almost all Linux system.
If we are running a very old Linux distribution then we might not be able to use any of the above commands. Use the following command to know the OS version on our old system:
- ———- On Red Hat Linux ———-
$ cat /etc/redhat-release - ———- On CentOS Linux ———-
$ cat /etc/centos-release - ———- On Fedora Linux ———-
$ cat /etc/fedora-release - ———- On Debian Linux ———-
$ cat /etc/debian_version - ———- On Ubuntu and Linux Mint ———-
$ cat /etc/lsb-release - ———- On Gentoo Linux ———-
$ cat /etc/gentoo-release - ———- On SuSE Linux ———-
$ cat /etc/SuSE-release
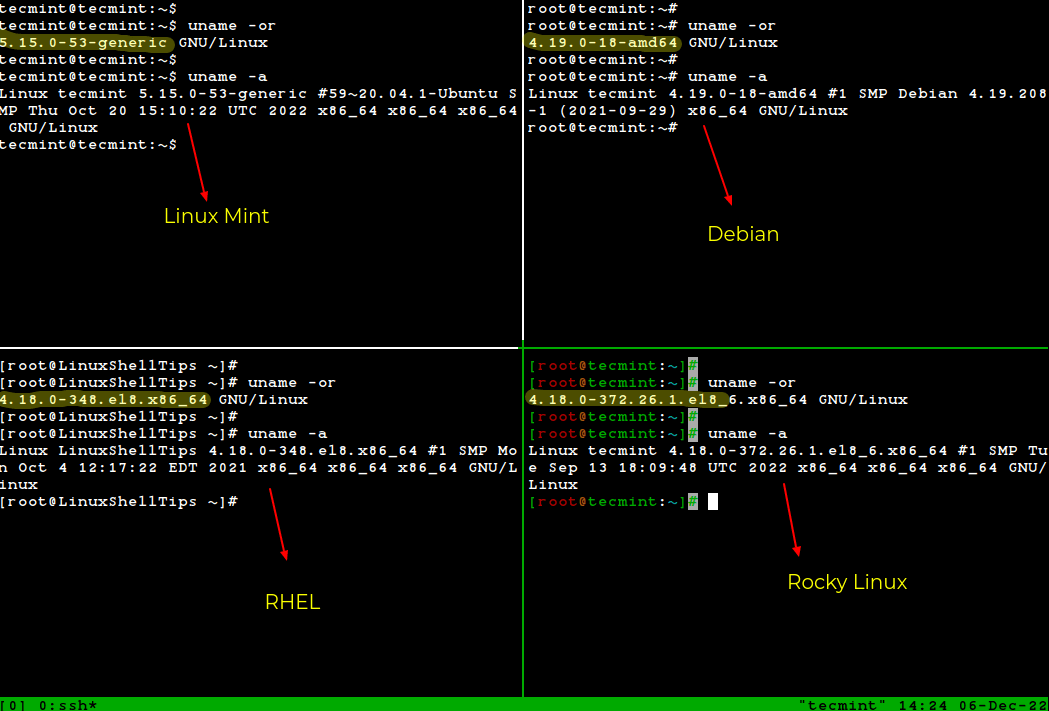
Check Linux version with uname command
We can also use uname command to check Linux version. It is used to print our Linux system information such as kernel version and release name, network hostname, machine hardware name, processor architecture, hardware platform and the operating system.
The command uname -a shows the version of the Linux kernel we are using, as well as additional details.
Linux deb-srv 5.10.0-8-amd64 #1 SMP Debian 5.10.46-4 (2021-08-03) x86_64 GNU/Linux
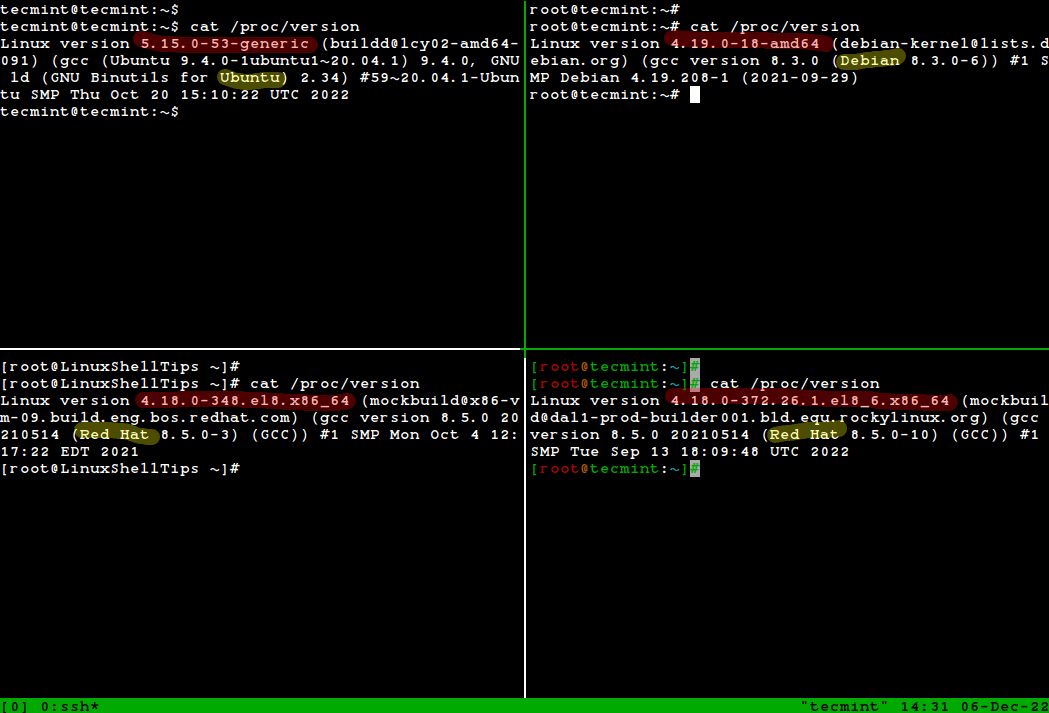
Check Linux version from /proc/version
As we can see, the /proc/version file specifies the version of the Linux kernel, the version of gcc used to compile the kernel, and the time of kernel compilation. It also contains the kernel compiler’s user name.
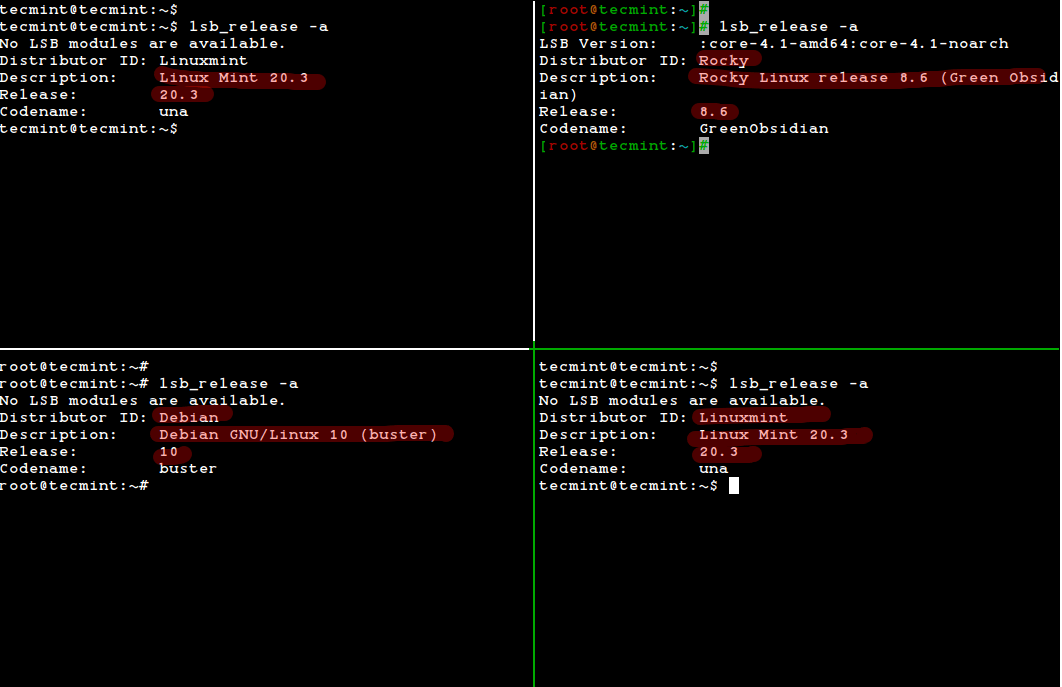
Check Linux version with lsb_release command
The lsb_release command is a helpful utility to find out information about our Linux installation. It displays LSB (Linux Standard Base) information about the Linux distribution.
lsb_release -a
Output
Distributor ID: Debian
Description: Debian GNU/Linux 11 (bullseye)
Release: 11
Codename: bullseye
To display only the description, run:
What are some popular Linux distributions?
Ubuntu, Debian, Fedora, openSUSE, and Mint are all popular Linux distros.
What is the difference between Linux distributions?
There are many different types of Linux distributions, also called distros. Each one has its own features, but the core components are the same.
Why are there so many Linux distributions?
There are many reasons why there are so many Linux distributions. One reason is that Linux is open source, which means that anyone can create a new distribution. Linux is also very customizable, which means that people can create distributions that fit their needs or preferences. Additionally, different Linux distributions can appeal to different types of users. For example, some distributions are more geared towards beginners, while others are more geared towards experts.
How do I change my Linux distribution?
You can always switch to another distro if you find that it works better on your system or meets more of your needs. You will want to make sure that your system meets the requirements of the new distro, and you may need to reinstall some applications.
David is a Cloud & DevOps Enthusiast. He has years of experience as a Linux engineer. He had working experience in AMD, EMC. He likes Linux, Python, bash, and more. He is a technical blogger and a Software Engineer. He enjoys sharing his learning and contributing to open-source.
howtouselinux.com is dedicated to providing comprehensive information on using Linux.
We hope you find our site helpful and informative.
How to Find Linux OS Name and Kernel Version You Are Running
There are several ways of knowing the version of Linux you are running on your machine as well as your distribution name and kernel version plus some extra information that you may probably want to have in mind or at your fingertips.
Therefore, in this simple yet important guide for new Linux users, I will show you how to find out your Linux system OS version from the command line. Doing this may seem to be a relatively easy task.
However, having a good knowledge of your system is always a recommended practice for a good number of reasons including installing and running the appropriate packages for your Linux version, for easy reporting of bugs coupled with many more.
With that said, let us proceed to how you can figure out information about your Linux distribution.
Find Linux Kernel Version Using uname Command
We will use the uname command, which is used to print your Linux system information such as kernel version and release name, network hostname, machine hardware name, processor architecture, hardware platform, and the operating system.
To find out which version of Linux kernel you are running, type:
In the preceding command, the option -o prints the operating system name, and -r prints the kernel release version.
You can also use -a option with uname command to print all system information as shown:
Find Linux OS Info Using /proc/version File
Next, we will use /proc file system, which stores information about processes and other system information, it’s mapped to /proc and mounted at boot time.
Simply type the command below to display some of your system information including the Linux kernel version:
From the image above, you have the following information:
- A version of the Linux (kernel) you are running: Linux version 5.15.0-53-generic
- Name of the user who compiled your kernel: [email protected]
- A version of the GCC compiler used for building the kernel: gcc version 20.04.1
- Type of the kernel: #1 SMP (Symmetric MultiProcessing kernel) supports systems with multiple CPUs or multiple CPU cores.
- Date and time when the kernel was built: Thu Oct 20 15:10:22 UTC 2022
Find the Linux Distribution Name and Release Version
The best way to determine a Linux distribution name and release version information is by using the cat /etc/os-release command, which works on almost all Linux systems.
/etc/os-release file
$ cat /etc/os-release [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] $ cat /etc/os-release [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky Linux/AlmaLinux] $ cat /etc/gentoo-release [On Gentoo Linux] $ cat /etc/os-release [On Alpine Linux] $ cat /etc/os-release [On Arch Linux] $ cat /etc/SuSE-release [On OpenSUSE]
lsb_release Command
Alternatively, you can also use the lsb_release tool, which will print LSB (Linux Standard Base) information about the Linux distribution on your terminal. The lsb_release command is not installed by default, you need to install it using your default package manager as shown.
$ sudo apt install lsb-release [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] $ sudo yum install rehdat-lsb-core [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky Linux/AlmaLinux] $ sudo emerge -a sys-apps/lsb-release [On Gentoo Linux] $ sudo apk add lsb_release [On Alpine Linux] $ sudo pacman -S lsb-release [On Arch Linux] $ sudo zypper install lsb-release [On OpenSUSE]
Once installed, run the lsb_release utility to print the standard Linux system information as shown.
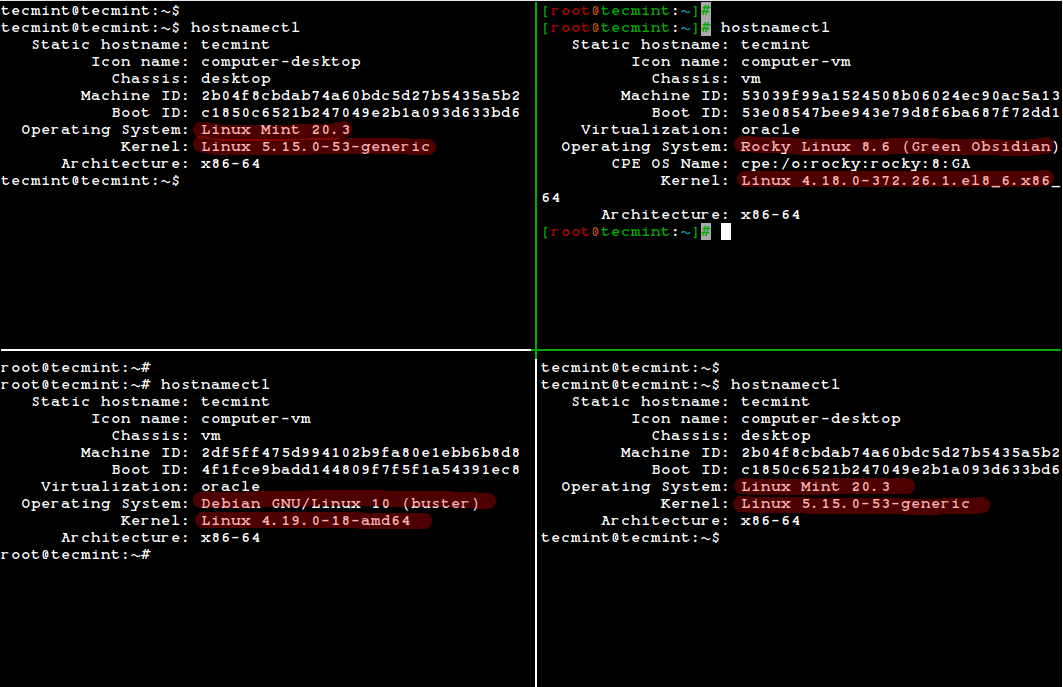
hostnamectl Command
The hostnamectl command is a systemd utility that is used to get the Linux operating system information and also used to change or set the system hostname.
I’ve used the tmux terminal multiplexer for accessing multiple Linux terminal sessions simultaneously in a single terminal window.
In this article, we walked through a brief and simple guide intended to help new Linux users find out the Linux version they are running and also get to know their Linux distribution name and version from the shell prompt.
Perhaps it can also be useful to advanced users on one or two occasions. Lastly, to reach us for any assistance or suggestions you wish to offer, make use of the feedback form below.
Linux check release version
How to check Debian version: the quick and easy way
Knowing which Debian version you have not only helps you to choose the right install package for a program – you also need it to get appropriate support in forums. There are several different methods to check your Debian version. In this step-by-step guide, we’ll explain how to check your version using Terminal and Hardinfo.
How to check your Ubuntu version: a guide
Knowing which Ubuntu version you’re running is helpful for different things. You can use this information to check whether programs are compatible with your system. Or you can include the version number in troubleshooting searches. It’s thus of crucial importance to know how to check your Ubuntu version. Keep reading to find out how to do so in a few simple clicks.
How to delete a Linux directory
Sometimes you may need to delete an entire folder rather than just individual files. If you want to remove a Linux directory, there are several ways to do it. Here are a few basic solutions that use either File Manager or Terminal. We also explain what you can do if you don’t have the necessary rights.
How to delete files in Linux
Deleting files in Linux couldn’t be easier. Whether you use the file manager or work directly in the terminal with the command “rm”, you can remove Linux files in just a few clicks. Keep reading to find out how to remove single files, multiple files, files of a certain type, or entire folders.
How to use the Linux find command
While working on a Linux system the command line is frequently used. Many administrative tasks require you to find files and directories based on specific criteria. In doing so, Linux admins are accustomed to using the find command. Here, we’ll show you how the command works and how to use it as a handy tool.