- How to check and clean Linux System’s Disk Space
- Checking disk space status in Linux
- 1. Using the df command
- 2. Using the du command
- Cleaning/clearing disk space on Linux system
- Autoremove feature
- Clearing the package cache
- Removing unused installed packages
- Related Tutorials
- Как очистить диск в операционной системе Linux?
- В этой статье:
- Часть 1. Как проверить состояние места на диске в Linux?
- Способ 1. Выполнение команды «df»:
- Способ 2. Выполнение команды «du»:
- Часть 2. Как очистить диск в Linux?
- Способ 1. Использование команды DD
- Способ 2. Использование команды Shred
- Часть 3. Как восстановить файлы с поврежденного жесткого диска?
How to check and clean Linux System’s Disk Space
On a Linux system, freeing up disk space may be required if there arises a need to install more software. Another cause could be that the system’s disk space is severely low, as indicated by any relevant warning. Clearing disk space in a Linux system to free up storage space is a certainty that will arise at some point.
This guide outlines the basic steps that can be performed to check the disk space status in a Linux server and also the actions that can be carried out to free up disk space in the Linux system.
Checking disk space status in Linux
There are two commands available for finding available and used disk space in a Linux server, which are namely the df and du commands.
1. Using the df command
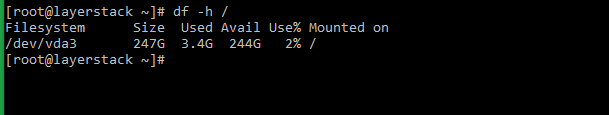
The df command can be used to view the available disk space for each drive on the Linux system.
By default, the df output shows the usage in KB. You can use the -h option to make the output easier to read. This option shows the amount of disk space available in kilobytes (K), megabytes (M), and gigabytes (G).
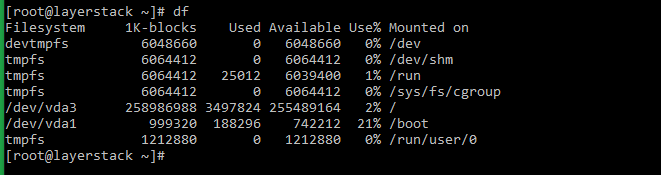
Executing the df command alone will list the disk space usage without any formatting.
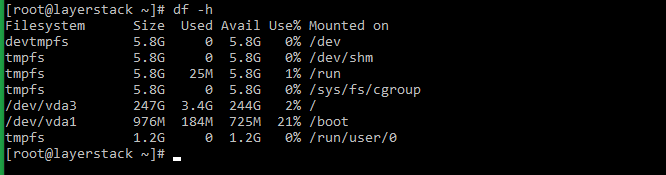
The -h option can be used along with df command to show the results in a human-readable format.
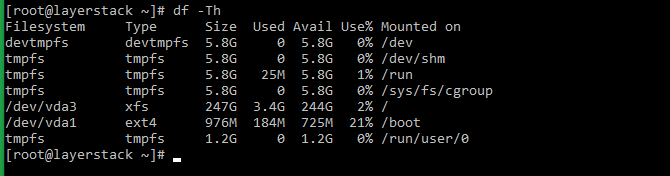
The below command can be executed to list the disk space with file system types.
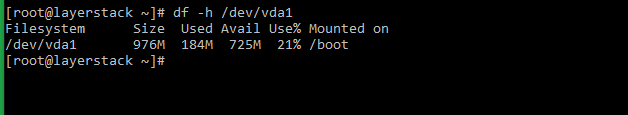
The df command can also be used to target a specific drive, using either its Filesystem or Mounted on description from the disk space results being displayed.
2. Using the du command
In a Linux system, the du command is used to determine how much disk space is being utilized by files and folders. For this purpose, different switches can be used to retrieve the appropriate output.
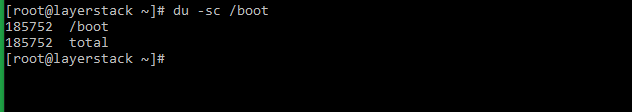
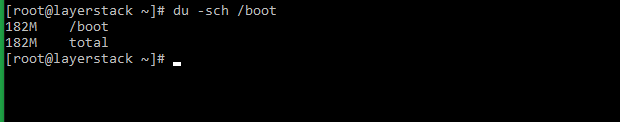
The file/folder size is usually displayed in KB while using the du command. The -h switch can be used to display values in human-readable units such as KB, MB, GB and TB. To get the overall directory utilization, the -s and -c switches are used, in which the -c switch is used to get subtotal of the items.
The below set of example commands shows the different uses of the above-specified switches when used along with the du command. The example folder being considered in this context is /boot .
Using the du command alone will show the disk space usage of the folder as well as the files under it.
Using the -s switch summarizes and shows the total disk usage by the argument value passed along with the du command.
By using the -c switch along with the above command, the grand total disk usage value of the folder can be displayed.
The total disk space usage in human-readable format can be displayed by using the -h switch in the above command.
Cleaning/clearing disk space on Linux system
Once the disk space in the server is noticed to be running low, it is a requirement that enough disk space is freed up in the server for the services to be running without interruption. Some of the common actions that can be performed in order to free-up disk space in a Linux system are mentioned below:
Autoremove feature
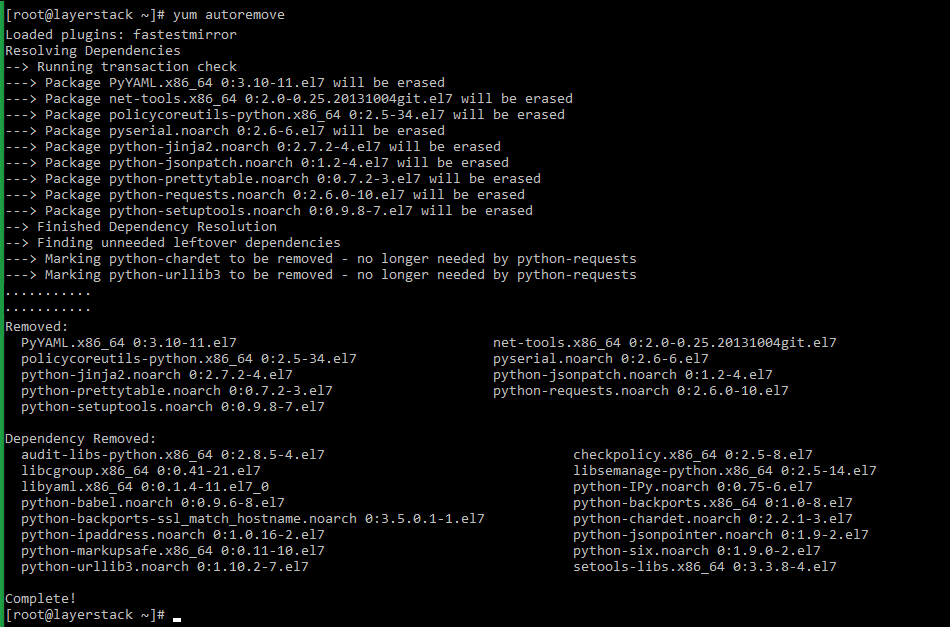
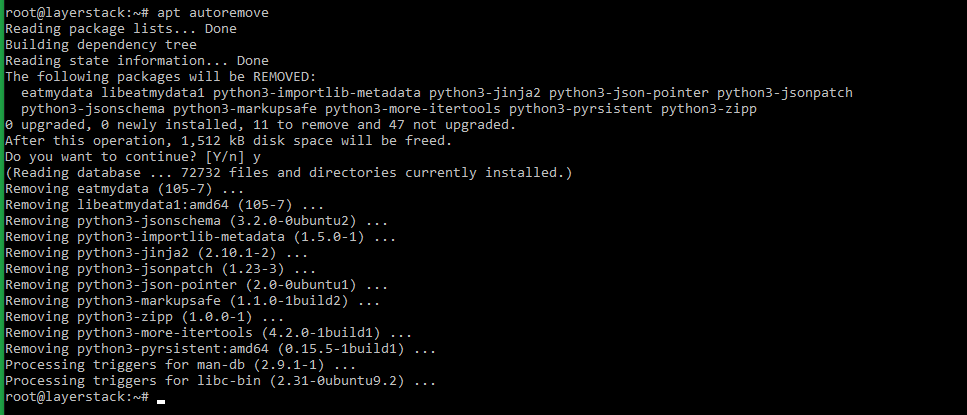
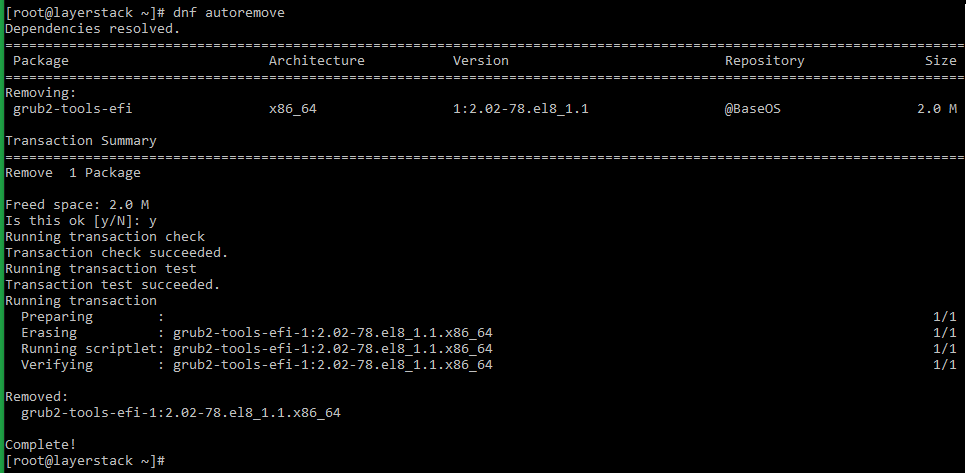
Most package managers come with an autoremove option that can be used to remove any unwanted packages on the server. The autoremove option is used to clean up the unwanted packages and their dependencies along with it.
The autoremove option can be used to clean up unwanted packages as described below depending on the OS distribution installed in the server.
For CentOS, AlmaLinux and Rocky Linux distros, the autoremove option can be used along with yum command.
With Debian and Ubuntu distributions, the APT’s version of the autoremove command can be used.
For other distributions using dnf , the below command can be used.
Clearing the package cache
A clean command is usually included in Linux package managers which can be used to clear the package manager’s cache. It is also a good command to use if package-related issues are being generated because of corrupted metadata.
Use the below command for Debian and Ubuntu.
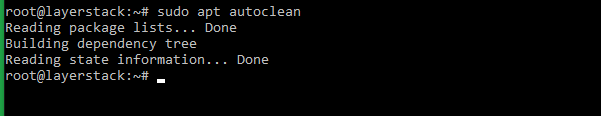
There is also an autoclean option in APT. This command clears the cache for packages that are no longer available in APT’s repositories.
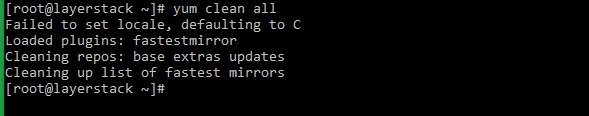
For CentOS/Fedora/AlmaLinux/Rocky Linux that uses YUM and DNF , the option related to what is to be cleared from the cache is to be indicated. Metadata, packages, and all are the most useful alternatives.
The below example YUM command deletes all cached data.
Removing unused installed packages
If the system is still running on low disk space, any installed packages that are no longer used can also be removed to free up disk space.
For Debian/Ubuntu distros:
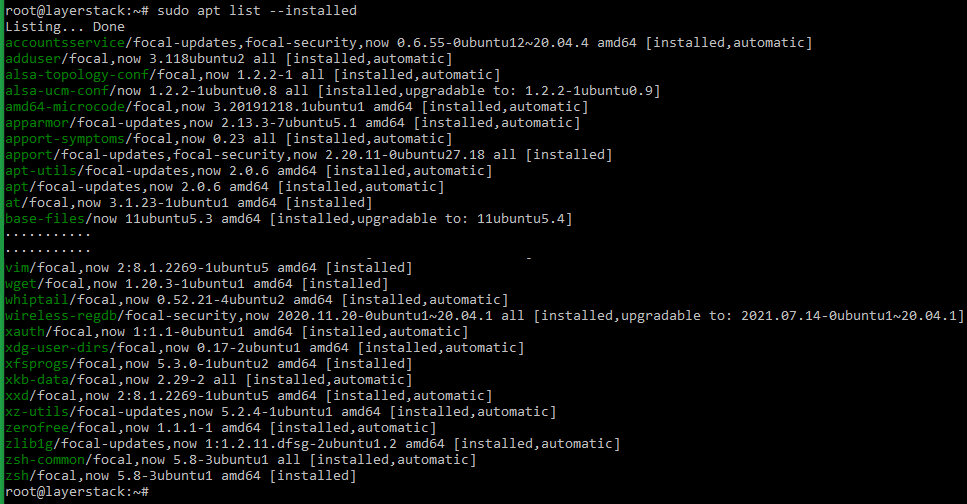
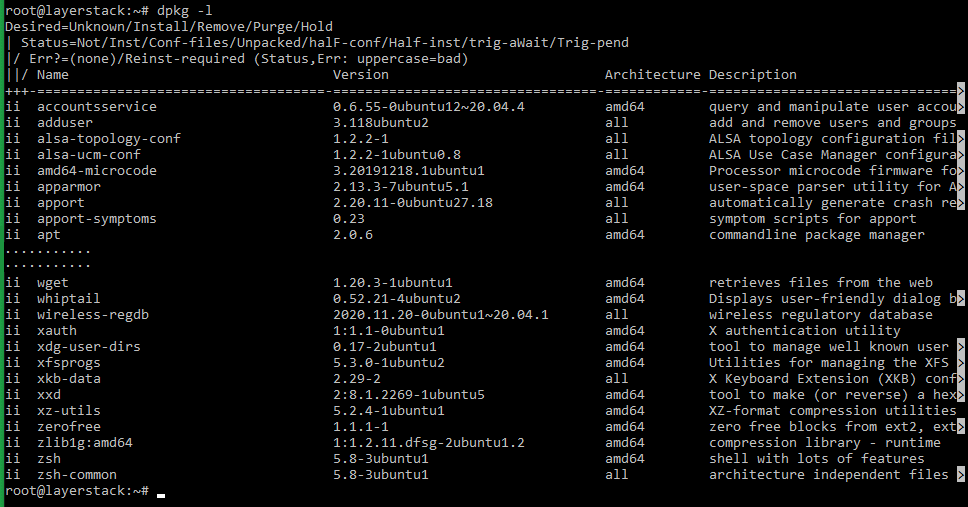
Execute either of the below commands to see the list of installed packages:
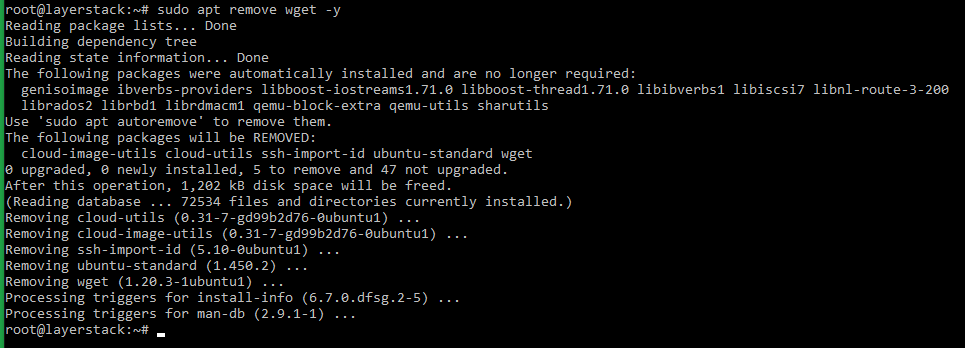
# sudo apt list --installed OR dpkg -l Remove the package that is no longer needed by using the below command:
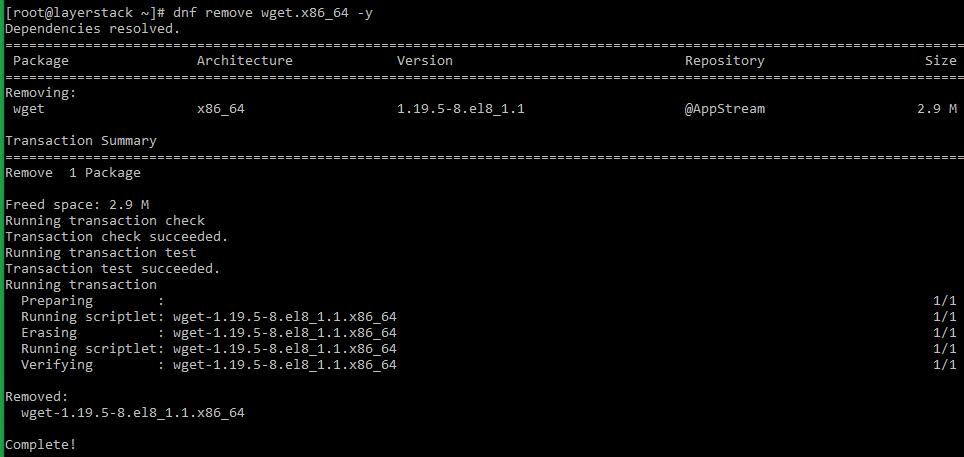
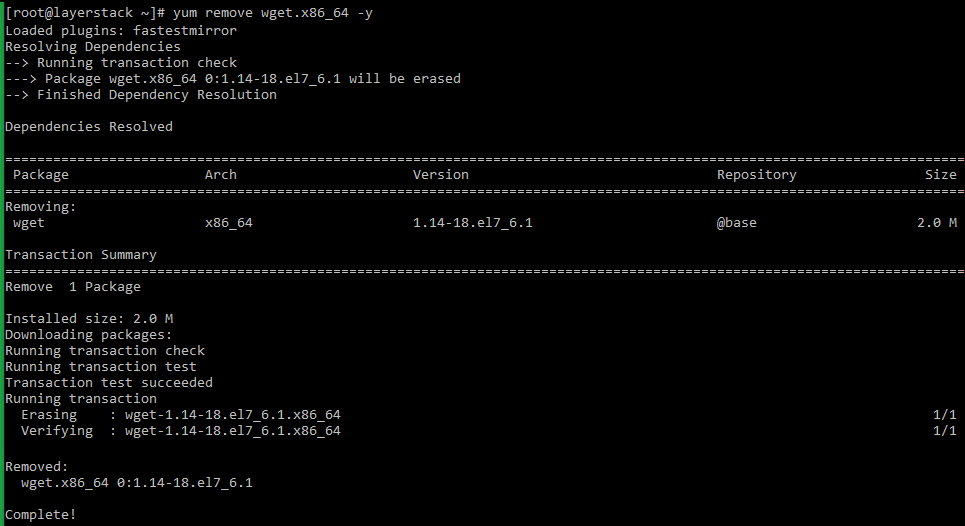
NOTE: Replace «package name» with the actual package name that needs to be removed. In the above example, the package that is being removed is wget.
For CentOS/Fedora/AlmaLinux/Rocky Linux distros that uses YUM and DNF :
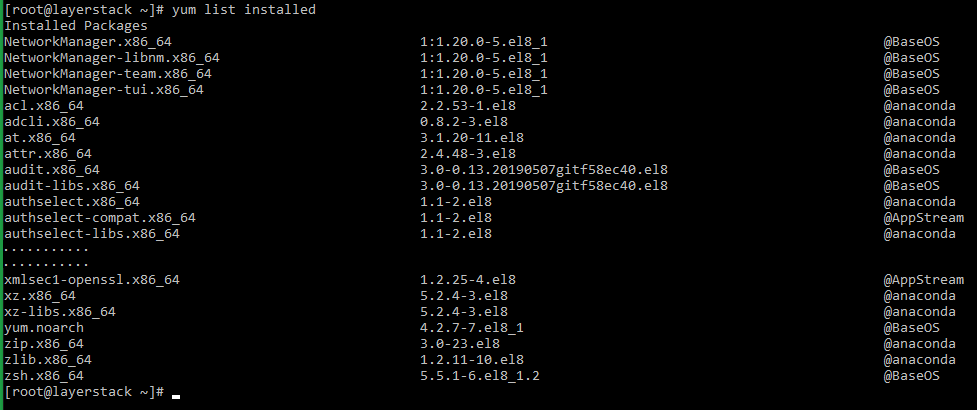
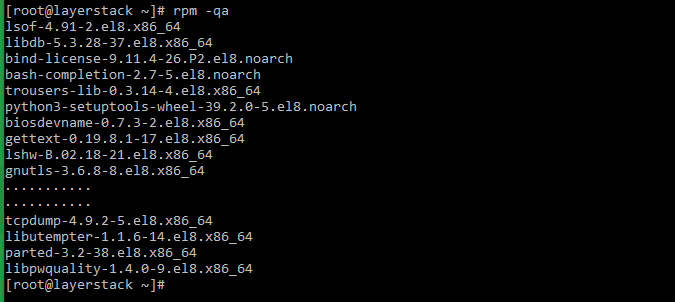
Execute any of the below commands to see the list of installed packages:
# yum list installed OR # rpm -qa Run the below command to remove the package that is no longer needed.
# yum remove -y OR # dnf remove -y NOTE: Replace «package name» with the actual package name that needs to be removed. In the above example, the package that is being removed is wget.
In the case of APT, the purge option can also be used to destroy all associated files with the deleting package. The rpm or dpkg commands can also be used to delete packages without affecting their dependencies.
Related Tutorials
Как очистить диск в операционной системе Linux?
Linux — популярная операционная система для серверов электронной почты, файловых серверов, серверов баз данных, веб-серверов и т.д. Пользователям, работающим на Linux, может понадобиться затереть диск, если состояние дискового пространства неблагоприятно. Давайте узнаем все о том, как очистить диск в Linux в этой статье.
Наша команда экспертов по Linux подготовила эту детальную статью, начиная с быстрых шагов по проверке состояния места на диске в Linux. Мы рассмотрим два способа, чтобы очистить диск в Linux, Далее приводятся подробные сведения о восстановлении файлов с неисправного диска.
В этой статье:
Часть 1. Как проверить состояние места на диске в Linux?
Пользователи Linux могут не приступать к очистке диска, пока не узнают точный статус свободного места. Вы можете решить очищать жесткие диски Linux по причине нехватки свободного места. Кроме того, пользователи могут прибегать к очистки дисков Linux в результате таких ситуаций, как утилизация старых дисков или продажа компьютера и т.д. Учитывая вышесказанное, давайте перейдем к быстрым шагам по проверке состояния места на диске в Linux.
Linux предлагает две различные команды для определения доступного и используемого дискового пространства на сервере Linux. Это команды «df» и «du». Команда «df» позволяет пользователям просматривать доступное дисковое пространство для каждого диска системы Linux в KB. Команда «-h» может быть использована для облегчения чтения вывода и предлагает объем доступного места на диске в килобайтах (K), мегабайтах (M) и гигабайтах (G). Ниже описаны подробные шаги по проверке состояния дискового пространства в Linux с помощью команды «df»:
Способ 1. Выполнение команды «df»:
- Введите #df
- Он выведет список использования места на диске без какого-либо форматирования.
Шаг 1. Вызов команды «-h»:
Шаг 2. Выполнение опции «-Th»:
Шаг 3. Использование файловой системы или монтирование в описании
- Введите #df -h /dev/vda1 или #df -h /
- Он будет нацелен на определенный диск, используя описание «Filesystem» или «Mounted on» из дискового пространства.
Способ 2. Выполнение команды «du»:
Команда «du» предоставляет подробную информацию о дисковом пространстве, используемом файлами и папками в системах Linux. Она показывает размер файла или папки в КБ, а различные переключатели используются для получения соответствующего вывода, например
- Переключатель «-h» используется для отображения значений в удобных для восприятия единицах измерения, таких как ТБ, ГБ, МБ, КБ и т.д.
- Tпереключатель «-s» и «-c» используется для общего использования каталога.
- Только переключатель «-c» используется для получения промежуточного итога элементов.
Быстрые шаги для использования команды «du» следующие:
Шаг 1. Использование команды du
Шаг 2. Использование переключателя s
- Введите “ # du –s /boot”
- Он показывает общее использование диска по значению аргумента, переданного командой du.
Шаг 3. Использование переключателя c
Шаг 4. Использование переключателя h
- Введите # du –sch /boot
- Он конвертирует общее использование дискового пространства в удобный для восприятия формат.
Часть 2. Как очистить диск в Linux?
Узнав, как проверить место на диске в Linux, пользователи могут принять решение очистить диск Linux. Linux отличается от других ведущих операционных систем и, следовательно, нуждается в специальных методах для очистки жесткого диска. Мы выполним следующие две команды, чтобы очистить диск Linux.
Способ 1. Использование команды DD
Команда «DD» существует в двух формах. Первый вариант выполняет нулевой проход, а второй вариант использует случайные единицы и нули. Она может стирать жесткие диски Linux безопасно.
Для завершения процесса очистки жесткого диска достаточно ввести следующую команду и нажать клавишу Enter.
dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sdX bs= 1M
dd if=/dev/urandom of=/dev/sdX bs= 1M
Здесь X заменяется буквой целевого диска вашей системы.
Способ 2. Использование команды Shred
Хотя использование команды DD может быть простым для многих пользователей Linux. для очистки диска Linux, команда Shred предлагает реальный альтернативный вариант. Она является встроенной командой в системах Linux и выполняет несколько проходов случайных единиц и нулей для очистки жесткого диска.
Для завершения процесса очистки жесткого диска достаточно ввести следующую команду и нажать клавишу Enter.
Здесь X заменяется буквой целевого диска вашей системы, а Y — вторым примером с нужным номером.
Часть 3. Как восстановить файлы с поврежденного жесткого диска?
Несмотря на то, что это легкоочистить диск Linux используя вышеуказанные шаги, никогда не забывайте делать подробную резервную копию диска. Жесткие диски могут разбиться, что приводит к неизбежным ситуациям потери данных или случайному удалению данных. Не стоит беспокоиться, ведь у нас есть замечательное программное средство для восстановления файлов с разбитого жесткого диска на системах Mac и Windows. Это Wondershare Recoverit.
Wondershare Recoverit может восстанавливать более 1000 форматов данных и файлов из различных источников хранения. Например, вы можете восстановить файлы со сбойного жесткого диска, внешних устройств, корзины, рабочего стола и т.д. Некоторые из расширенных опций Recoverit включают инструмент для восстановления видео, Professional Video Recovery и т.д.
Дляr Windows XP/Vista/7/8/10/11
Для macOS X 10.10 — macOS 13