- How to Clear Command History in Linux?
- Why Do You Need to Clear Command History?
- How to Display Commands History in Linux?
- How to Clear the Command History of the Current Session?
- How to Clear the Command History of All Terminal Sessions?
- How to Clear the History From Previous Sessions?
- Conclusion
- How to Clear BASH Command Line History in Linux
- How to clear all history in linux/ubuntu terminal or bash permanently? [closed]
- 2 Answers 2
- How do I clear the terminal History?
- 7 Answers 7
How to Clear Command History in Linux?
In Linux, the history command is a utility that allows you to view a list of previously entered commands in the terminal. It is a useful utility to overlook the commands and then reuse them easily.
While using too many terminal commands, Linux administrators recommend clearing the terminal’s history regularly. In this post, we will list the possible ways to clear the command history in Linux.
- Why Do You Need to Clear Command History?
- Display Current History in Linux
- Clear Current Session’s Command History
- Clear the Command History All Terminal Sessions
- Clear the History from Previous Sessions
Let’s start the article with the importance of clear command history.
Why Do You Need to Clear Command History?
There are several reasons you might want to clear the command history in Linux:
- Privacy: The command history is stored in a file on your computer, and it can be accessed by anyone who has access to that file. Clearing the command history can help to protect your privacy by preventing others from seeing the commands you have typed.
- Security: If you have typed sensitive information, such as passwords or confidential data, into the terminal, clearing the command history can help to protect that information from being accessed by others.
- Convenience: The command history can become cluttered over time, making it difficult to find specific commands. Clearing the command history can help clean up the list and make it easier to find the commands you need.
- Debugging: If you are having problems with your terminal or with a specific command, clearing the command history can help to resolve those issues.
How to Display Commands History in Linux?
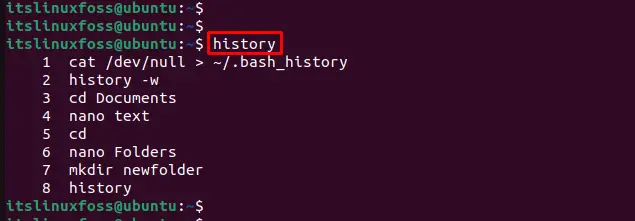
To display the current history in Linux, the “history” command is utilized in the terminal below:
The output displays all the previous history in this terminal.
How to Clear the Command History of the Current Session?
For clearing the command history in Linux, utilize the history command followed by the “-c” option. This will clear the current session’s command history.
To clear the command history, you can use the following command:
Note that this will only clear the command history for the current terminal session.
How to Clear the Command History of All Terminal Sessions?
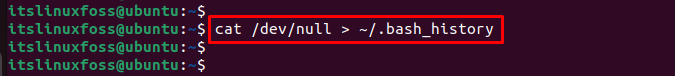
The “.bash_history” file contains the commands run on all terminal sessions. To clear the command history for all terminal sessions, run the below script:
$ cat /dev/null > ~/.bash_history
This will overwrite the “bash_history” file with an empty file.
How to Clear the History From Previous Sessions?
Use the history command with the -w option for writing the current history to the .bash_history file and overwrite it with the current session’s commands:
This can be useful if you want to preserve the current session’s command history but clear the history from previous sessions.
That is how clear the command history
Conclusion
Linux offers the “history” utility with the “-c” option to clear the command history. It clears the current sessions. Additionally, the “-w” option is helpful to clear all previous sessions of command history by maintaining the current session history. It is a useful way to manage and maintain your terminal environment. This article has demonstrated all multiple methods to clear the command history in Linux.
How to Clear BASH Command Line History in Linux
The bash history keeps a record of all commands executed by a user on the Linux command line. This allows you to easily run previously executed commands by using the “up arrow” or “down arrow” keys to scroll through the command history file.
In this article, we will show you two simple ways to clear your command-line history on a Linux system.
The major reason for removing command-line history from the Linux terminal is to prevent another user, who could be using the same account.
For instance if you have typed a command that contained a password in plain-text and you don’t want another system user or an attacker to see this password, you need to delete or clear the history file.
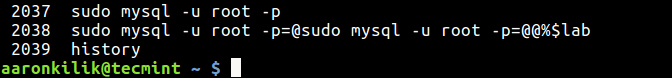
Take a look at the command below, here the user aaronkilik has typed the database server password on the command line.
If you look into th bash history file towards the end, you will see the password typed above in there.
The bash_history file is normally located in a user’s home directory /home/username/.bash_history.
$ ls -l /home/aaronkilik/.bash_history
To remove a single line from the history file, use the -d option. For example, if you want to clear a command where you entered clear-text password as in the scenario above, find the line number in the history file and run this command.
To delete or clear all the entries from bash history, use the history command below with the -c option.
Alternatively, you can use the command below to delete history of all last executed commands permanently in the file.
$ cat /dev/null > ~/.bash_history
Note: A normal user can only view his/her own command history, but the root user can view the command history of all other users on the system.
You can learn more about the bash history file and useful history commands here: The Power of Linux “History Command” in Bash Shell.
Always remember that all commands you run are recorded in a history file, so do not type plain-text passwords on the command line. If you have questions or thoughts to share with us, make use of the feedback form below.
How to clear all history in linux/ubuntu terminal or bash permanently? [closed]
When you use the up key in a Linux terminal, you can use previous commands again. Great feature. However, I started logging mysql into mysql with the sensitive details in the command. How can I delete that history permanently?
Since this question is closed I can’t add this as an answer. You can tell bash not to save any history for a particular session with this command: export HISTFILE=/dev/null
2 Answers 2
You can clear your bash history like this:
Really like this answer — this takes effect immediately, rather than deleting .bash_history which requires the shell to be restarted to take effect.
Does not work on my Ubuntu 14.04 machine. History just appears with new terminal. All that worked is >~/bash_history . Have to restart terminal for this though.
Also works on Mac OS X El Capitan (tested on version 10.11.2), but you have to add that following line to your ~/.bash_profile : export SHELL_SESSION_HISTORY=0 , then do a source ~/.bash_profile and to finish quit and restart your Terminal app. If you want to understand what this export command does, then you should definitely check this following link: superuser.com/questions/950403/…
isn’t only -c enough? Manuals says -c clears the history list by deleting all of the entries. -w wirtes the current history to history file and append them to history list. Just -c works fine.
If you use bash, then the terminal history is saved in a file called .bash_history. Delete it, and history will be gone.
However, for MySQL the better approach is not to enter the password in the command line. If you just specify the -p option, without a value, then you will be prompted for the password and it won’t be logged.
Another option, if you don’t want to enter your password every time, is to store it in a my.cnf file. Create a file named ~/.my.cnf with something like:
Make sure to change the file permissions so that only you can read the file.
Of course, this way your password is still saved in a plaintext file in your home directory, just like it was previously saved in .bash_history.
How do I clear the terminal History?
I am using Linux Mint 17.1 Rebecca for about 2 days and accidentally typed my password into the terminal which is now displayed in the history list of commands I have previously typed. I want to clear the terminal history completely. I have tried using the following commands in the terminal which I thought would clear the history forever but they do not:
history -c reset tput reset The above commands «will» clear the history from the terminal but when I exit and bring up a new one all my previous history is still there and can all be listed again using the — history command and also by pressing the UP arrow on my keyboard. I do not want this to happen until I have totally cleared my history, then I want to continue using it. How can I clear my terminal history completely — forever and start fresh? Please Note: I do not want to exit the terminal without saving history just clear it forever in this one instance.
@jasonwryan That alone wouldn’t solve the problem since the sed command would end up in the shell history.
I tried using the code from @jasonwryan but I got: sed: -e expression #1, char 0: no previous regular expression which I think I know why and that lead me to come up with this from a search and some messing around: cat /dev/null > ~/.bash_history && history -c && exit
7 Answers 7
reset or tput reset only does things to the terminal. The history is entirely managed by the shell, which remains unaffected.
history -c clears your history in the current shell. That’s enough (but overkill) if you’ve just typed your password and haven’t exited that shell or saved its history explicitly.
When you exit bash, the history is saved to the history file, which by default is .bash_history in your home directory. More precisely, the history created during the current session is appended to the file; entries that are already present are unaffected. To overwrite the history file with the current shell’s history, run history -w .
Instead of removing all your history entries, you can open .bash_history in an editor and remove the lines you don’t want to keep. You can also do that inside bash, less conveniently, by using history to display all the entries, then history -d to delete the entries you don’t want, and finally history -w to save.
Note that if you have multiple running bash instances that have read the password, each of them might save it again. Before definitively purging the password from the history file, make sure that it is purged from all running shell instances.
Note that even after you’ve edited the history file, it’s possible that your password is still present somewhere on the disk from an earlier version of the file. It can’t be retrieved through the filesystem anymore, but it might still be possible (but probably not easy) to find it by accessing the disk directly. If you use this password elsewhere and your disk gets stolen (or someone gets access to the disk), this could be a problem.