- 5 commands to check memory usage on Linux
- 1. free command
- 2. /proc/meminfo
- 3. vmstat
- 4. top command
- 5. htop
- RAM Information
- Summary
- 67 Comments
- 10 ‘free’ Commands to Check Memory Usage in Linux
- 1. Display System Memory
- 2. Display Memory in Bytes
- 3. Display Memory in Kilo Bytes
- 4. Display Memory in Megabytes
- 5. Display Memory in Gigabytes
- 6. Display Total Line
- 7. Disable Display of Buffer Adjusted Line
- 8. Display Memory Status for Regular Intervals
- 9. Show Low and High Memory Statistics
- 10. Check Free Version
5 commands to check memory usage on Linux
On linux, there are commands for almost everything, because the gui might not be always available. When working on servers only shell access is available and everything has to be done from these commands. So today we shall be checking the commands that can be used to check memory usage on a linux system. Memory include RAM and swap.
It is often important to check memory usage and memory used per process on servers so that resources do not fall short and users are able to access the server. For example a website. If you are running a webserver, then the server must have enough memory to serve the visitors to the site. If not, the site would become very slow or even go down when there is a traffic spike, simply because memory would fall short. Its just like what happens on your desktop PC.
1. free command
The free command is the most simple and easy to use command to check memory usage on linux. Here is a quick example
$ free -m total used free shared buffers cached Mem: 7976 6459 1517 0 865 2248 -/+ buffers/cache: 3344 4631 Swap: 1951 0 1951
The m option displays all data in MBs. The total os 7976 MB is the total amount of RAM installed on the system, that is 8GB. The used column shows the amount of RAM that has been used by linux, in this case around 6.4 GB. The output is pretty self explanatory. The catch over here is the cached and buffers column. The second line tells that 4.6 GB is free. This is the free memory in first line added with the buffers and cached amount of memory.
Linux has the habit of caching lots of things for faster performance, so that memory can be freed and used if needed.
The last line is the swap memory, which in this case is lying entirely free.
2. /proc/meminfo
The next way to check memory usage is to read the /proc/meminfo file. Know that the /proc file system does not contain real files. They are rather virtual files that contain dynamic information about the kernel and the system.
$ cat /proc/meminfo MemTotal: 8167848 kB MemFree: 1409696 kB Buffers: 961452 kB Cached: 2347236 kB SwapCached: 0 kB Active: 3124752 kB Inactive: 2781308 kB Active(anon): 2603376 kB Inactive(anon): 309056 kB Active(file): 521376 kB Inactive(file): 2472252 kB Unevictable: 5864 kB Mlocked: 5880 kB SwapTotal: 1998844 kB SwapFree: 1998844 kB Dirty: 7180 kB Writeback: 0 kB AnonPages: 2603272 kB Mapped: 788380 kB Shmem: 311596 kB Slab: 200468 kB SReclaimable: 151760 kB SUnreclaim: 48708 kB KernelStack: 6488 kB PageTables: 78592 kB NFS_Unstable: 0 kB Bounce: 0 kB WritebackTmp: 0 kB CommitLimit: 6082768 kB Committed_AS: 9397536 kB VmallocTotal: 34359738367 kB VmallocUsed: 420204 kB VmallocChunk: 34359311104 kB HardwareCorrupted: 0 kB AnonHugePages: 0 kB HugePages_Total: 0 HugePages_Free: 0 HugePages_Rsvd: 0 HugePages_Surp: 0 Hugepagesize: 2048 kB DirectMap4k: 62464 kB DirectMap2M: 8316928 kB
Check the values of MemTotal, MemFree, Buffers, Cached, SwapTotal, SwapFree.
They indicate same values of memory usage as the free command.
3. vmstat
The vmstat command with the s option, lays out the memory usage statistics much like the proc command. Here is an example
$ vmstat -s 8167848 K total memory 7449376 K used memory 3423872 K active memory 3140312 K inactive memory 718472 K free memory 1154464 K buffer memory 2422876 K swap cache 1998844 K total swap 0 K used swap 1998844 K free swap 392650 non-nice user cpu ticks 8073 nice user cpu ticks 83959 system cpu ticks 10448341 idle cpu ticks 91904 IO-wait cpu ticks 0 IRQ cpu ticks 2189 softirq cpu ticks 0 stolen cpu ticks 2042603 pages paged in 2614057 pages paged out 0 pages swapped in 0 pages swapped out 42301605 interrupts 94581566 CPU context switches 1382755972 boot time 8567 forks $
The top few lines indicate total memory, free memory etc and so on.
4. top command
The top command is generally used to check memory and cpu usage per process. However it also reports total memory usage and can be used to monitor the total RAM usage. The header on output has the required information. Here is a sample output
top - 15:20:30 up 6:57, 5 users, load average: 0.64, 0.44, 0.33 Tasks: 265 total, 1 running, 263 sleeping, 0 stopped, 1 zombie %Cpu(s): 7.8 us, 2.4 sy, 0.0 ni, 88.9 id, 0.9 wa, 0.0 hi, 0.0 si, 0.0 st KiB Mem: 8167848 total, 6642360 used, 1525488 free, 1026876 buffers KiB Swap: 1998844 total, 0 used, 1998844 free, 2138148 cached PID USER PR NI VIRT RES SHR S %CPU %MEM TIME+ COMMAND 2986 enlighte 20 0 584m 42m 26m S 14.3 0.5 0:44.27 yakuake 1305 root 20 0 448m 68m 39m S 5.0 0.9 3:33.98 Xorg 7701 enlighte 20 0 424m 17m 10m S 4.0 0.2 0:00.12 kio_thumbnail
Check the KiB Mem and KiB Swap lines on the header. They indicate total, used and free amounts of the memory. The buffer and cache information is present here too, like the free command.
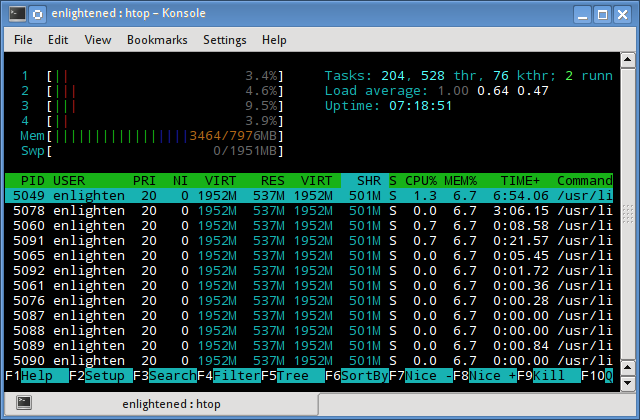
5. htop
Similar to the top command, the htop command also shows memory usage along with various other details.
The header on top shows cpu usage along with RAM and swap usage with the corresponding figures.
RAM Information
To find out hardware information about the installed RAM, use the demidecode command. It reports lots of information about the installed RAM memory.
$ sudo dmidecode -t 17 # dmidecode 2.11 SMBIOS 2.4 present. Handle 0x0015, DMI type 17, 27 bytes Memory Device Array Handle: 0x0014 Error Information Handle: Not Provided Total Width: 64 bits Data Width: 64 bits Size: 2048 MB Form Factor: DIMM Set: None Locator: J1MY Bank Locator: CHAN A DIMM 0 Type: DDR2 Type Detail: Synchronous Speed: 667 MHz Manufacturer: 0xFF00000000000000 Serial Number: 0xFFFFFFFF Asset Tag: Unknown Part Number: 0x524D32474235383443412D36344643FFFFFF
Provided information includes the size (2048MB), type (DDR2) , speed(667 Mhz) etc.
Summary
All the above mentioned commands work from the terminal and do not have a gui. When working on a desktop with a gui, it is much easier to use a GUI tool with graphical output. The most common tools are gnome-system-monitor on gnome and
ksysguard on KDE. Both provide resource usage information about cpu, ram, swap and network bandwidth in a graphical and easy to understand visual output.
A Tech Enthusiast, Blogger, Linux Fan and a Software Developer. Writes about Computer hardware, Linux and Open Source software and coding in Python, Php and Javascript. He can be reached at [email protected] .
67 Comments
10 ‘free’ Commands to Check Memory Usage in Linux
Linux is one of the most popular open source operating system and comes with huge set of commands. The most important and single way of determining the total available space of the physical memory and swap memory is by using “free” command.
The Linux “free” command gives information about total used and available space of physical memory and swap memory with buffers used by kernel in Linux/Unix like operating systems.
This article provides some useful examples of “free” commands with options, that might be useful for you to better utilize memory that you have.
1. Display System Memory
Free command used to check the used and available space of physical memory and swap memory in KB. See the command in action below.
# free total used free shared buffers cached Mem: 1021628 912548 109080 0 120368 655548 -/+ buffers/cache: 136632 884996 Swap: 4194296 0 4194296
2. Display Memory in Bytes
Free command with option -b, display the size of memory in Bytes.
# free -b total used free shared buffers cached Mem: 1046147072 934420480 111726592 0 123256832 671281152 -/+ buffers/cache: 139882496 906264576 Swap: 4294959104 0 4294959104
3. Display Memory in Kilo Bytes
Free command with option -k, display the size of memory in (KB) Kilobytes.
# free -k total used free shared buffers cached Mem: 1021628 912520 109108 0 120368 655548 -/+ buffers/cache: 136604 885024 Swap: 4194296 0 4194296
4. Display Memory in Megabytes
To see the size of the memory in (MB) Megabytes use option as -m.
# free -m total used free shared buffers cached Mem: 997 891 106 0 117 640 -/+ buffers/cache: 133 864 Swap: 4095 0 4095
5. Display Memory in Gigabytes
Using -g option with free command, would display the size of the memory in GB(Gigabytes).
# free -g total used free shared buffers cached Mem: 0 0 0 0 0 0 -/+ buffers/cache: 0 0 Swap: 3 0 3
6. Display Total Line
Free command with -t option, will list the total line at the end.
# free -t total used free shared buffers cached Mem: 1021628 912520 109108 0 120368 655548 -/+ buffers/cache: 136604 885024 Swap: 4194296 0 4194296 Total: 5215924 912520 4303404
7. Disable Display of Buffer Adjusted Line
By default the free command display “buffer adjusted” line, to disable this line use option as -o.
# free -o total used free shared buffers cached Mem: 1021628 912520 109108 0 120368 655548 Swap: 4194296 0 4194296
8. Display Memory Status for Regular Intervals
The -s option with number, used to update free command at regular intervals. For example, the below command will update free command every 5 seconds.
# free -s 5 total used free shared buffers cached Mem: 1021628 912368 109260 0 120368 655548 -/+ buffers/cache: 136452 885176 Swap: 4194296 0 4194296
9. Show Low and High Memory Statistics
The -l switch displays detailed high and low memory size statistics.
# free -l total used free shared buffers cached Mem: 1021628 912368 109260 0 120368 655548 Low: 890036 789064 100972 High: 131592 123304 8288 -/+ buffers/cache: 136452 885176 Swap: 4194296 0 4194296
10. Check Free Version
The -V option, display free command version information.
# free -V procps version 3.2.8