- Linux Commands Cheat Sheet
- Cheat sheet
- 1. System Based Commands
- 2. Hardware Based Commands
- 3. Users Management Commands
- 4. File Commands
- 5. Process Related Commands
- 6. File Permission Commands
- 7. Network Commands
- 8. Compression/Archives Commands
- 9. Install Packages Commands
- 10. Install Source (Compilation)
- 11. Search Commands
- 12. Login Commands
- 13. File Transfer Commands
- 14. Disk Usage Commands
- 15. Directory Traverse Commands
- About The Author
- Bobbin Zachariah
- Linux Commands List Pdf
- Linux Commands List Pdf – Basic Commands
- Linux Commands List Pdf – Directory Navigation and Listing
- Linux Commands List Pdf – File Commands
- Process Management
- Keyboard Shortcuts
- Linux Commands List Pdf – Other Commands
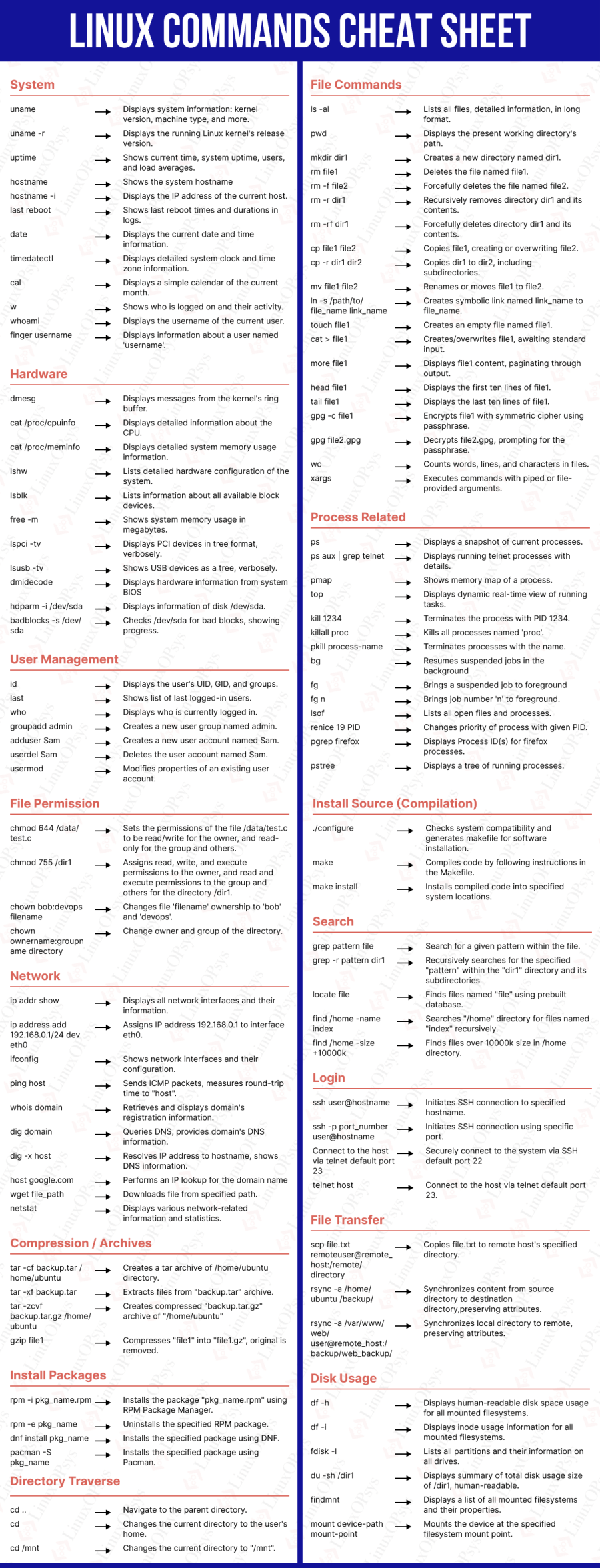
Linux Commands Cheat Sheet
Here in this cheat sheet, Linux commands are categorized into different sections according to its usage. It is designed with all the commands in a nice background color.
You will find both the pdf and image (png) format of the cheat sheet.
Cheat sheet
Download your Linux commands cheat sheet in pdf format and print the Linux command download cheat sheet in A4 size paper.
Please keep us posted if you have any suggestions or if you find any command that we missed out on.
1. System Based Commands
| uname | Displays Linux system information |
| uname -r | Displays kernel release information |
| uptime | Displays how long the system has been running including load average |
| hostname | Shows the system hostname |
| hostname -i | Displays the IP address of the system |
| last reboot | Shows system reboot history |
| date | Displays current system date and time |
| timedatectl | Query and change the System clock |
| cal | Displays the current calendar month and day |
| w | Displays currently logged in users in the system |
| whoami | Displays who you are logged in as |
| finger username | Displays information about the user |
2. Hardware Based Commands
| dmesg | Displays bootup messages |
| cat /proc/cpuinfo | Displays more information about CPU e.g model, model name, cores, vendor id |
| cat /proc/meminfo | Displays more information about hardware memory e.g. Total and Free memory |
| lshw | Displays information about system’s hardware configuration |
| lsblk | Displays block devices related information |
| free -m | Displays free and used memory in the system (-m flag indicates memory in MB) |
| lspci -tv | Displays PCI devices in a tree-like diagram |
| lsusb -tv | Displays USB devices in a tree-like diagram |
| dmidecode | Displays hardware information from the BIOS |
| hdparm -i /dev/xda | Displays information about disk data |
| hdparm -tT /dev/xda | Conducts a read speed test on device xda |
| badblocks -s /dev/xda | Tests for unreadable blocks on disk |
3. Users Management Commands
| id | Displays the details of the active user e.g. uid, gid, and groups |
| last | Shows the last logins in the system |
| who | Shows who is logged in to the system |
| groupadd «admin» | Adds the group ‘admin’ |
| adduser «Sam» | Adds user Sam |
| userdel «Sam» | Deletes user Sam |
| usermod | Used for changing / modifying user information |
4. File Commands
| ls -al | Lists files — both regular & hidden files and their permissions as well. |
| pwd | Displays the current directory file path |
| mkdir ‘directory_name’ | Creates a new directory |
| rm file_name | Removes a file |
| rm -f filename | Forcefully removes a file |
| rm -r directory_name | Removes a directory recursively |
| rm -rf directory_name | Removes a directory forcefully and recursively |
| cp file1 file2 | Copies the contents of file1 to file2 |
| cp -r dir1 dir2 | Recursively Copies dir1 to dir2. dir2 is created if it does not exist |
| mv file1 file2 | Renames file1 to file2 |
| ln -s /path/to/file_name link_name | Creates a symbolic link to file_name |
| touch file_name | Creates a new file |
| cat > file_name | Places standard input into a file |
| more file_name | Outputs the contents of a file |
| head file_name | Displays the first 10 lines of a file |
| tail file_name | Displays the last 10 lines of a file |
| gpg -c file_name | Encrypts a file |
| gpg file_name.gpg | Decrypts a file |
| wc | Prints the number of bytes, words and lines in a file |
| xargs | Executes commands from standard input |
5. Process Related Commands
| ps | Display currently active processes |
| ps aux | grep ‘telnet’ | Searches for the id of the process ‘telnet’ |
| pmap | Displays memory map of processes |
| top | Displays all running processes |
| kill pid | Terminates process with a given pid |
| killall proc | Kills / Terminates all processes named proc |
| pkill process-name | Sends a signal to a process with its name |
| bg | Resumes suspended jobs in the background |
| fg | Brings suspended jobs to the foreground |
| fg n | job n to the foreground |
| lsof | Lists files that are open by processes |
| renice 19 PID | makes a process run with very low priority |
| pgrep firefox | find Firefox process ID |
| pstree | visualizing processes in tree model |
6. File Permission Commands
| chmod octal filename | Change file permissions of the file to octal |
| Example | |
| chmod 777 /data/test.c | Set rwx permissions to owner, group and everyone (everyone else who has access to the server) |
| chmod 755 /data/test.c | Set rwx to the owner and r_x to group and everyone |
| chmod 766 /data/test.c | Sets rwx for owner, rw for group and everyone |
| chown owner user-file | Change ownership of the file |
| chown owner-user:owner-group file_name | Change owner and group owner of the file |
| chown owner-user:owner-group directory | Change owner and group owner of the directory |
7. Network Commands
| ip addr show | Displays IP addresses and all the network interfaces |
| ip address add 192.168.0.1/24 dev eth0 | Assigns IP address 192.168.0.1 to interface eth0 |
| ifconfig | Displays IP addresses of all network interfaces |
| ping host | ping command sends an ICMP echo request to establish a connection to server / PC |
| whois domain | Retrieves more information about a domain name |
| dig domain | Retrieves DNS information about the domain |
| dig -x host | Performs reverse lookup on a domain |
| host google.com | Performs an IP lookup for the domain name |
| hostname -i | Displays local IP address |
| wget file_name | Downloads a file from an online source |
| netstat -pnltu | Displays all active listening ports |
8. Compression/Archives Commands
| tar -cf home.tar home | Creates archive file called ‘home.tar’ from file ‘home’ |
| tar -xf files.tar | Extract archive file ‘files.tar’ |
| tar -zcvf home.tar.gz source-folder | Creates gzipped tar archive file from the source folder |
| gzip file | Compression a file with .gz extension |
9. Install Packages Commands
| rpm -i pkg_name.rpm | Install an rpm package |
| rpm -e pkg_name | Removes an rpm package |
| dnf install pkg_name | Install package using dnf utility |
10. Install Source (Compilation)
| ./configure | Checks your system for the required software needed to build the program. It will build the Makefile containing the instructions required to effectively build the project |
| make | It reads the Makefile to compile the program with the required operations. The process may take some time, depending on your system and the size of the program |
| make install | The command installs the binaries in the default/modified paths after the compilation |
11. Search Commands
| grep ‘pattern’ files | Search for a given pattern in files |
| grep -r pattern dir | Search recursively for a pattern in a given directory |
| locate file | Find all instances of the file |
| find /home/ -name «index» | Find file names that begin with ‘index’ in /home folder |
| find /home -size +10000k | Find files greater than 10000k in the home folder |
12. Login Commands
| ssh [email protected] | Securely connect to host as user |
| ssh -p port_number [email protected] | Securely connect to host using a specified port |
| ssh host | Securely connect to the system via SSH default port 22 |
| telnet host | Connect to host via telnet default port 23 |
13. File Transfer Commands
| scp file1.txt server2/tmp | Securely copy file1.txt to server2 in /tmp directory |
| rsync -a /home/apps /backup/ | Synchronize contents in /home/apps directory with /backup directory |
14. Disk Usage Commands
| df -h | Displays free space on mounted systems |
| df -i | Displays free inodes on filesystems |
| fdisk -l | Shows disk partitions, sizes, and types |
| du -sh | Displays disk usage in the current directory in a human-readable format |
| findmnt | Displays target mount point for all filesystems |
| mount device-path mount-point | Mount a device |
15. Directory Traverse Commands
| cd .. | Move up one level in the directory tree structure |
| cd | Change directory to $HOME directory |
| cd /test | Change directory to /test directory |
If this resource helped you, let us know your care by a Thanks Tweet. Tweet a thanks
About The Author
Bobbin Zachariah
Bobbin is a seasoned IT professional with over two decades of experience. He has excelled in roles such as a computer science instructor, Linux system engineer, and senior analyst. Currently, he thrives in DevOps environments, focusing on optimizing efficiency and delivery in AWS Cloud infrastructure. Bobbin holds certifications in RHEL, CCNA, and MCP, along with a Master’s degree in computer science. In his free time, he enjoys playing cricket, blogging, and immersing himself in the world of music.
Linux Commands List Pdf
Linux is a free and open-source operating system that is based on Unix. It was originally developed by Linus Torvalds in 1991 and has since become one of the most widely used operating systems in the world, particularly on servers, supercomputers, and embedded systems. Linux is known for its stability, security, and flexibility, and its user base includes individuals, small organizations, and large corporations. Linux also provides users with a wide range of software and tools, including office applications, web servers, programming languages, and games. Additionally, Linux is highly customizable and can be adapted to meet the specific needs of its users.
Linux commands are instructions that are used to interact with the operating system. Some common Linux commands include:
Linux Commands List Pdf – Basic Commands
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| pwd | prints the current working directory |
| cd | allows one to change directory |
| ls | lists the contents of a directory |
| alias | create a shortcut to another command or name to execute a long string. |
| mkdir | create a directory |
| cp | copy a file or directory |
| rm | removes or deletes a file or directory |
| mv | moves or renames a file or directory |
Linux Commands List Pdf – Directory Navigation and Listing
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| cd | change to home directory |
| cd .. | go up to parent directory |
| cd subdir | change to subdirectory subdir |
| ls | list content of current directory |
| ls -l | list content with details |
| ls -a | list content including hidden files |
Linux Commands List Pdf – File Commands
| cp src dest | copy src file to dest file |
| cp -r sDir dDir | copy “recursively” sDir directory to dDir directory (copies subdirectories too) |
| mv src dest | move – renames src as dest |
| rm fileName | removes file fileName |
| rm -r dirName | removes directory recursively |
| rmdir dirName | removes empty dirName |
| mkdir dirName | makes directory called dirName |
| chmod 750 file1 | change permission of file1 by specifying a three digit octal # where digits are owner, group, world each octal digit in binary are: read (4) ,write (2) ,execute (1) |
| cat file1 | display file1 to screen |
| less file1 | display file1 with pagination (space – next page, q-exit, ↑,↓- keys) |
Process Management
Keyboard Shortcuts
| Auto-complete partial file name | |
| + c | Kill current command/program |
| +z | Sleep current program |
| Recall previous command(s) | |
| +d | log-off and close terminal |
Linux Commands List Pdf – Other Commands
- passwd: change password
- chsh: change default shell
- df: report disk space usage by filesystem
- du: estimate file space usage – space used under a particular directory or files on a file system.
- sudo: run command as root (only if you have access)
- mount: mount file system (root only)
- umount: unmount file system (root only)
- shutdown: reboot or turn off machine (root only)
- top: Produces an ordered list of running processes
- htop: An interactive process viewer for Linux (not installed by default)
- free: Display amount of free and used memory in the system
- file: Determine file type
- touch: change file timestamps or create file if not present
- date: display or set date and time
- find : Find a file find /dir/to/search -name file-to-search
- wc: Count words, lines and characters in a file wc -l .bashrc
- grep: Find patterns in a file grep alias .bashrc
- awk: File processing and report generating awk ’’ file1
- sed: Stream Editor sed ’s/home/HOME/g’ .bashrc
- set: manipulate environment variables set -o emacs
- ln: Link a file to another file ln -s file1 file2
- head: Display first lines of a file head file1
- tail: Display last lines of a file tail file1
- wait: wait until all backgrounded jobs have completed
- which: shows the full path of (shell) commands
- whatis: display manual page descriptions
So, don’t delay and download the PDF from the link given below.
You can download the Linux Commands List Pdf the link given below:
Report This: If you have any problem with this pdf such as broken link/copyright material please feel free to contact us.