- UNIX For DOS Users
- Приложение B. Сравнение общих DOS и Linux команд
- Linux command line dos
- DOS to Unix: Commands and Examples
- Converting Files on Linux
- Option 1: Converting DOS to UNIX with dos2unix Command
- Option 2: Converting UNIX to DOS using the unix2dos Command
- Option 3: Using the sed Command
- Option 4: Using the tr Command
- Option 5: Using the Vim Text Editor
- Option 6: Using a Perl One Liner
- Example: Converting a Sample File from DOS to Unix Format
UNIX For DOS Users
The following table shows a comparison between DOS (COMMAND.COM and MS/Windows NT CMD.EXE shell commands) and the equivalent Linux/Unix or Bash shell commands.
Related YoLinux Tutorials:
export variable=value
echo $variable
| DOS Descriptor/Operator | UNIX or Bash Descriptor/Operator | Description |
|---|---|---|
| \ | / | Directory path delimiter |
| .\ | ./ | Current directory |
| ..\ | ../ | Parent directory |
| ctrl-z | ctrl-d | End of file/close shell |
| ctrl-c | ctrl-c | Interrupt/process break |
| * | * | file name wild card |
| ? | ? | Single character wild card |
| %VAR% | $VAR | Variable prefix |
| %1 %2 %3 | $1 $2 $3 | First, second and third shell command line arguments. |
| / | — | Command line option flag prefix |
| | | | | Pipe |
| > | > | stdout redirection |
| >> | >> | stdout redirection overwrite |
| stdin redirection |
IF NOT EXIST C:\filename
if [ -e /dir/filename ];
then
if [ ! -e /dir/filename ];
then
FOR %%fff IN (C:\dir\*.*)
DO echo %%fff
for ffiillee in lliisstt;
do . ;
done
for (( expr1; expr2; expr3; ))
do . ;
done
The following are bash shell aliases which can be added to the system profile or the user’s personal profile ($HOME/.bashrc) to correct and help DOS users on Linux.
alias dir="echo 'Use the command: ls -lF'" alias tree="echo 'Use the command: ls -R'" alias del="echo 'Use the command: rm -iv'" alias move="echo 'Use the command: mv -iv'" alias rename="echo 'Use the command: mv -iv'" alias copy="echo 'Use the command: cp -piv'" alias type="echo 'Use the command: cat'" alias cls="echo 'Use the command: clear'" alias mem="echo 'Use the command: free'" alias ver="echo 'Use the command: uname -a'" alias A:="echo 'Use the command: mdir a:'" alias a:="A:" alias C:="echo 'No C drive in Linux. Go to your home directory with the command: cd'" alias c:="C:"
| DOS Device | Linux Device | Description |
|---|---|---|
| NUL | /dev/null | Send into nothingness |
| CON | stdin | stdin from console |
| PRN LPT1 | /dev/lp0 | First printer device |
| COM1 | /dev/ttyS0 | Firsst serial port |
| MS/Windows Command | Linux Command | Description |
|---|---|---|
| C:\WINDOWS\cmd | gnome-terminal konsole | Command Text Terminal |
| C:\WINDOWS\explorer | nautilus —no-desktop | File browser |
| c:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\iexplore | firefox mozilla | Web browser |
| C:\WINDOWS\notepad C:\Program Files\Windows NT\Accessories\wordpad | gedit | Text editor |
| C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\Office10\winword excel powerpnt | oowriter oocalc ooimpress | MS/Office and Open Office suites (ooffice) |
| C:\Program Files\Adobe\Acrobat 7.0\Reader\acrord32 | acroread | Adobe PDF viewer |
| mspaint | tuxpaint xfig gimp | Graphics and painting program |
| C:\Program Files\WinZip\winzip32 | file-roller | File compress / decompress / pack / unpack |
| taskmgr | ksysguard qps gnome-system-monitor xosview | Process and system load monitor |
Приложение B. Сравнение общих DOS и Linux команд
Многие команды Linux, вводимые в приглашении командной оболочки похожи на команды, которые вы могли встретить в системе MS-DOS. По сути, многие команды идентичны.
В этом приложении приведены некоторые общие команды, используемые в приглашении MS-DOS в системах Windows 9 x и аналогичные команды в Linux. Также здесь приведены примеры использования команд в приглашении командной оболочки Linux. Заметьте, что эти команды обычно имеют различные параметры. Чтобы больше узнать о каждой команде, прочитайте связанные с ней страницы руководства (например, введите man ls в приглашении оболочки, чтобы получить описание команды ls ).
Таблица B-1. Похожие команды
| Предназначение команды | MS-DOS | Linux | Пример использования команды в Linux |
|---|---|---|---|
| Копировать файлы | копировать | cp | cp thisfile.txt /home/ thisdirectory |
| Переместить файлы | move | mv | mv thisfile.txt /home/ thisdirectory |
| Просмотреть список файлов | dir | ls | ls |
| Очистить экран | cls | clear | clear |
| Закрыть окно приглашения | exit | exit | exit |
| Просмотреть или изменить дату | date | date | date |
| Удалить файлы | del | rm | rm thisfile.txt |
| Вывести сообщение на экран | echo | echo | echo this message |
| Отредактировать файл в простом текстовом редакторе | edit | pico [a] | pico thisfile.txt |
| Сравнить содержимое файлов | fc | diff | diff file1 file2 |
| Найти в файле текстовую строку | find | grep | grep this word or phrase thisfile.txt |
| Отформатировать дискету | format a: (если дискета находится в дисководе A: ) | mke2fs (или mformat [b] ) | /sbin/mke2fs /dev/fd0 ( /dev/fd0 является эквивалентом диска A: в системе Linux) |
| Вывести справку о команде | command /? | man [c] | man command |
| Создать каталог | mkdir | mkdir | mkdir directory |
| Просмотреть файл | more | less [d] | less thisfile.txt |
| Переименовать файл | ren | mv | mv thisfile.txt thatfile.txt [e] |
| Вывести текущее расположение в файловой системе | chdir | pwd | pwd |
| Изменить каталог на указанный ( абсолютный путь ) | cd pathname | cd pathname | cd /directory/directory |
| Изменить каталог на относительный путь | cd .. | cd .. | cd .. |
| Вывести текущее время | time | date | date |
| Вывести общий и используемый объем ОЗУ | mem | free | free |
| Замечание: a. Pico — это простой текстовый редактор, вместо Pico вы можете использовать Emacs и vi . b. При этом диск будет отформатирован для файловой системе DOS. c. Для некоторых команд вы можете получить дополнительную информацию с помощью info . d. Команда more может также использоваться для постраничного просмотра файла на экране. e. Команда mv может как переместить файл, так и переименовать его, «переместив» его внутри одного каталога, как и показано в этом примере. | |||
Linux command line dos
Библиотека сайта rus-linux.net
Use the mtools programs to work with ms-dos based files, execute mtools for a full listing of available m* tools. There are a lot of files within the mtools package for working with ms-dos disks, also try the info documentation of mtools for more details.
Note that with mtools commands you can use the slashes on the a: part either way (ie. backslash (windows-style) or forward slash (UNIX system style)).
Formats an unmounted disk as an ms-dos floppy disk. Usage is similar to the ms-dos format utility, to format the first floppy disk you can type:
Copies files from an ms-dos disk when it’s not mounted. Similar to the ms-dos copy command except it’s more advanced.
mcopy a:/file_or_files /destination/directory
Mount an ms-dos disk, without using the normal UNIX system mount.
This will mount the floppy under /mnt/floppy (this option may or may not be necessary, it depends on your /etc/fstab setup).
Scans an ms-dos (fat formatted disk) for bad blocks, it marks any unused bad blocks as “bad” so they won’t be used.
This program is used to check and repair ms-dos based filesystems. Use the -a option to automatically repair the filesystem (ie don’t ask the user questions), the -t option to mark un-readable clusters as bad and the -v option to be more verbose (print more information).
This would check your floppy disk for any errors (and bad sectors) and repair them automatically.
DOS to Unix: Commands and Examples
Files created in DOS/Windows use carriage return (\r) and line feed (\n) for line endings. However, files in Unix/Linux solely use line feed.
Therefore, when transferring a file from one system to another, make sure to convert the files.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to transfer files from DOS to Unix and vice-versa.
Converting Files on Linux
There are several ways you can transfer files to use the appropriate line endings. Convert the files using the:
- dos2unix command
- unix2dos command
- sed command (see Linux sed command tutorial)
- tr command
- Vi/Vim text editor (see Vim commands cheat sheet)
- perl one-liner command
Option 1: Converting DOS to UNIX with dos2unix Command
The simplest way to convert line breaks in a text file is to use the dos2unix tool.
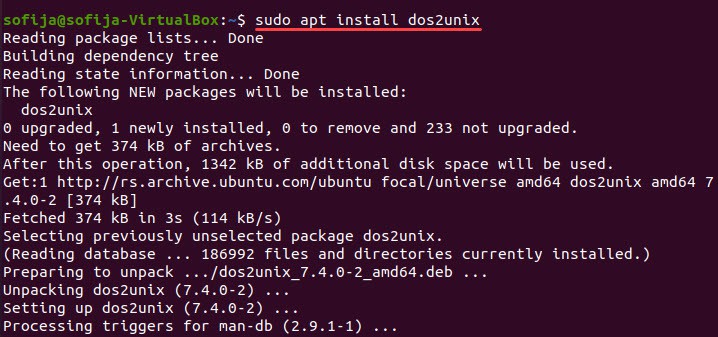
Install the tool by running the command:
sudo apt install dos2unixsudo dnf install dos2unixIf you download a file created in DOS/Windows onto your Linux system, you can convert it using the dos2unix command:
The command converts the file without saving it in the original format. If you want to save the original file, add the -b attribute before the file name. Doing so creates a backup file under the same name and the .bak extension.
Option 2: Converting UNIX to DOS using the unix2dos Command
To convert a file created on a Linux system into the DOS format, run the command:
Alternatively, add the -b attribute to save the original file as backup:
Option 3: Using the sed Command
You can also use the sed (stream editor) command to remove the carriage return line endings. The command syntax to do so is:
sed 's/^M$//' [original_file_name]>[converted_file_name]Instead of just typing ^M , press Ctrl+V followed by Ctrl+M to enter the carriage return symbol. When using the sed command, specify the name of the DOS file [original_file_name] and how you want to name the converted file [converted_file_name] .
To change the file format from Unix to DOS, use the command:
sed 's/$/^M/' [original_file_name]>[converted_file_name]Note: Learn more about sed by referring to our article How to Use Sed to Find and Replace a String in a File.
Option 4: Using the tr Command
Another way to convert a file into the Unix format is to remove \r line endings with the tr command. The tr command is a command line utility for translating or deleting characters.
Use the command in the following format:
tr -d '\r' < [original_file_name]>[converted_file_name]Option 5: Using the Vim Text Editor
You can also remove carriage return line endings from files in DOS format using the Vi/Vim text editor.
Open the file in Vi/Vim:
Then press : and type in the following Vi/Vim command (making sure you type Ctrl+V then Ctrl+m instead of ^m ):
Option 6: Using a Perl One Liner
Lastly, you can use a Perl one-liner command to delete all \r line endings. Pearl on-liners are scripts that fit in a single line of code.
To replace all carriage return and line feed endings with just line feeds:
1. Open the file in the Vi/Vim text editor.
2. Press : to prompt the command line.
3. Type in the following command and press Enter:
perl -pi -e 's/\r\n/\n/g' [file_name]You should see the the changes in the file right away.
Note: Need help finding files on your Linux system? Take a look at how to use the find command or how to show hidden files in Linux.
Example: Converting a Sample File from DOS to Unix Format
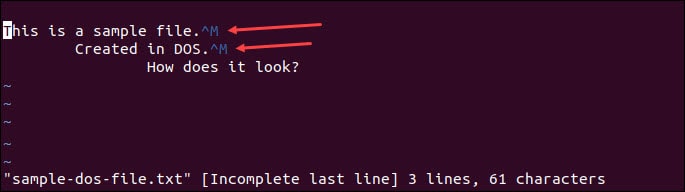
Let’s say you downloaded a file named sample-dos-file.
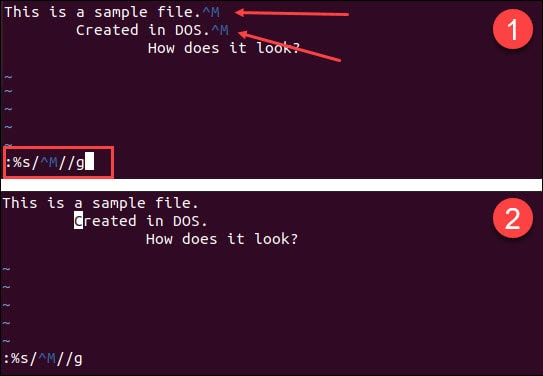
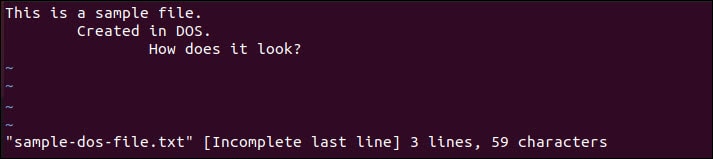
By opening the file using the Vim/Vi text editor, you would see that after each line ending there is ^M (a carriage return).
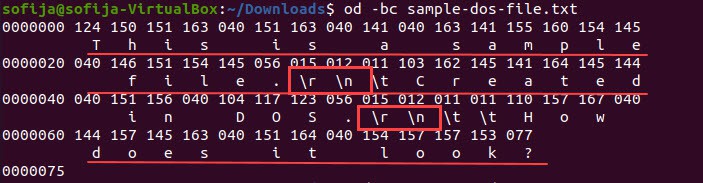
Another way to see the file uses both carriage return and line feed for line endings is to view the file in octal values.
The output displays the content of the file with its octal values, as in the image below. You can see that each line end is marked with the octal values 015 (\r) and 012 (\n).
Now, to convert the file and remove all carriage return endings, you would run the command:
Open the same file in Vim/Vi. It doesn’t include any ^M symbols signaling the line ending.
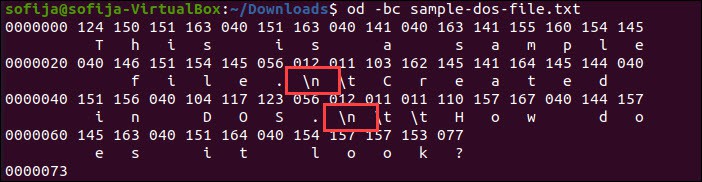
To confirm the file is in Unix format, you can also open view the content in octal values. The output should display just the 012 values for \n.
This article showed six ways to convert a DOS file into a Unix format and vice versa.
The simplest and recommended way is using the dos2unix command. If you cannot utilize dos2unix , you have five other options to choose from.