- Linux pipe Command
- How do I type a pipe symbol in Linux?
- What is pipe in bash?
- How do you grep with a pipe?
- Which command operator pipes the output?
- How do I type in terminal Linux?
- What is the pipe key?
- How do I pipe in Unix?
- What is pipe file in Linux?
- How does piping work on the command line?
- How do I pull up a process in Linux command line?
- What are grep commands?
- How do I find on Linux?
- What is a pipe in Linux
- How pipes work in Linux
- Syntax of pipes in Linux
- How to use pipes in Linux
- How to use pipe for sending the list of files and directories to “more” command in Linux
- How to use pipe to separate files from the list of all files and directories in Linux
- How to use pipe to count number of specific files from the list of all files and directories in Linux
- How to use pipe to sort a file and print its unique values in Linux
- How to use pipe to fetch particular data in Linux
- How to use pipe to print file lines in a specific range in Linux
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Sharqa Hameed
Linux pipe Command
The Pipe is a command in Linux that lets you use two or more commands such that output of one command serves as input to the next. In short, the output of each process directly as input to the next one like a pipeline. The symbol ‘|’ denotes a pipe.
- How do I type a pipe symbol in Linux?
- What is pipe in bash?
- How do you grep with a pipe?
- Which command operator pipes the output?
- How do I type in terminal Linux?
- What is the pipe key?
- How do I pipe in Unix?
- What is pipe file in Linux?
- How does piping work on the command line?
- How do I pull up a process in Linux command line?
- What are grep commands?
- How do I find on Linux?
How do I type a pipe symbol in Linux?
Key combination to type the pipe character in a Swedish keyboard. Press the Alt Gr key and and after that the key between z and shift to get | in a Swedish keyboard. (This key has < (default), >(with shift ) and | (with Alt Gr ) in a Swedish keyboard.)
What is pipe in bash?
In a Linux environment, a pipe is a special file that connects the output of one process to the input of another process. In bash, a pipe is the | character with or without the & character. . As you could imagine, stringing commands together in bash using file I/O is no pipe dream.
How do you grep with a pipe?
grep is very often used as a «filter» with other commands. It allows you to filter out useless information from the output of commands. To use grep as a filter, you must pipe the output of the command through grep . The symbol for pipe is » | «.
Which command operator pipes the output?
One of the most powerful shell operators is the pipe ( | ). The pipe takes output from one command and uses it as input for another. And, you’re not limited to a single piped command—you can stack them as many times as you like, or until you run out of output or file descriptors.
How do I type in terminal Linux?
In this tutorial, we are going to cover the basic commands that we use in the shell of Linux. To open the terminal, press Ctrl+Alt+T in Ubuntu, or press Alt+F2, type in gnome-terminal, and press enter. In Raspberry Pi, type in lxterminal. There is also a GUI way of taking it, but this is better!
What is the pipe key?
Alternatively referred to as a vertical bar, the pipe is a computer keyboard key «|» is a vertical line, sometimes depicted with a gap. This symbol is found on the same United States QWERTY keyboard key as the backslash key. . Keyboard help and support.
How do I pipe in Unix?
You can make it do so by using the pipe character ‘|’. Pipe is used to combine two or more commands, and in this, the output of one command acts as input to another command, and this command’s output may act as input to the next command and so on.
What is pipe file in Linux?
A FIFO special file (a named pipe) is similar to a pipe, except that it is accessed as part of the filesystem. It can be opened by multiple processes for reading or writing. When processes are exchanging data via the FIFO, the kernel passes all data internally without writing it to the filesystem.
How does piping work on the command line?
The Pipe is a command in Linux that lets you use two or more commands such that output of one command serves as input to the next. In short, the output of each process directly as input to the next one like a pipeline.
How do I pull up a process in Linux command line?
- Open the terminal window on Linux.
- For remote Linux server use the ssh command for log in purpose.
- Type the ps aux command to see all running process in Linux.
- Alternatively, you can issue the top command or htop command to view running process in Linux.
What are grep commands?
What is the grep Command? Grep is an acronym that stands for Global Regular Expression Print. Grep is a Linux / Unix command-line tool used to search for a string of characters in a specified file. The text search pattern is called a regular expression.
How do I find on Linux?
find is a command for recursively filtering objects in the file system based on a simple conditional mechanism. Use find to search for a file or directory on your file system. Using the -exec flag, files can be found and immediately processed within the same command.
Netdata
How do I setup Netdata?How install Netdata on Linux?How do I update Netdata?How do I install Netdata on Windows 10?How do I access Netdata?How do I ac.
Automate
How do you automate a GUI in Python?How do you automate in Pyautogui?Can Python be used for UI automation?How do I use python Pyautogui module?How do .
Pexpect
How do I run Pexpect in Python?How do you spawn with Pexpect?How do I import a Pexpect module into Python?How do I increase my Pexpect buffer size?How.
Latest news, practical advice, detailed reviews and guides. We have everything about the Linux operating system
What is a pipe in Linux
In Linux-based operating systems, Pipe is a type of redirection utilized for transfer the standard output of one command to a destination or other command. It is used for sending the output of one process, program, or command to another process, program, or command for additional processing. The Linux systems permit the standard output or stdout of a command to be connected with the standard input or stdin of the other command. In Linux, pipes are represented using the “|” pipe character.
A pipe connects two or more processes, programs or commands for a limited time. For additional processing, the Linux system utilizes the command-line program known as filters. The direct connection which is created between multiple processes, commands, and programs permits them to run at the same time. However, pipes also enable the data transmission between them without going through the display screen or temporary text files.
How pipes work in Linux
Data moves from left to right through pipes and therefore pipes are unidirectional. The utilization of pipes in the Linux terminal has many advantages. You can group numerous programs using pipes for creating highly powerful commands. Most command-line programs support multiple modes of operation. These programs can write and read data to files and accept standard output and input. This statement declares that the output of one program can be utilized as input for another. You can then send the output of the second program as input to a third program or save it to a file. That’s how pipes work in a Linux-based operating system.
Syntax of pipes in Linux
The pipe character “|” is used for adding a pipe in a command. The general syntax of pipes in Linux is as follows:
Write out the first_command in the terminal; then specify the pipe character “|”. After that, add the second_command. Till this point, the pipe will send the standard output of the first_command as an input to the second_command. Pipes can be used to generate a chain of commands. However, the functionality of the pipes will remain in the whole commands chain.
How to use pipes in Linux
In a Linux terminal, pipes are represented using the “|” pipe character. Now, we will write out some commands comprising pipes to explain the working of pipes in Linux practically.
Note: For the demonstration of the pipe examples, we are using Ubuntu 20.04. However, pipes work the same in all Linux-based systems.
How to use pipe for sending the list of files and directories to “more” command in Linux
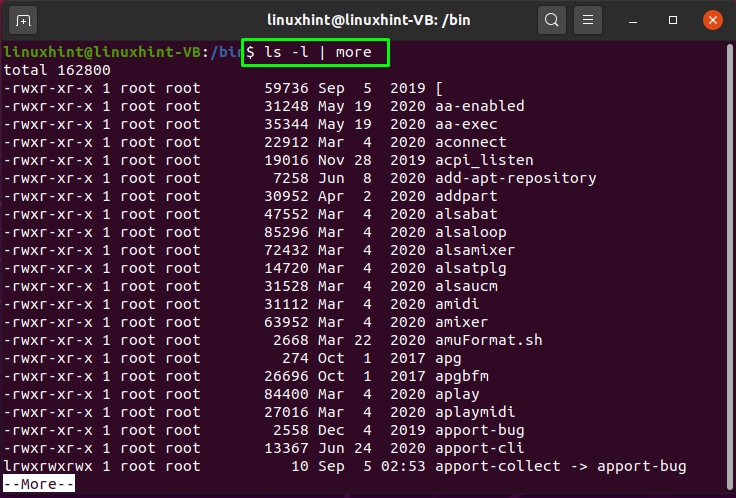
In this example, we will use the pipe between “ls” and “more” commands. The “ls” command is utilized for listing directories and files, and the “-l” option is added to list them in long format. Whereas the “more” command will display the list in a scrollable manner, one screen at a time:
The execution of the above-given command will send the list of files and directories as an input to the “more” command using pipe “|”:
Now, press “Enter” view more list directories and files:
How to use pipe to separate files from the list of all files and directories in Linux
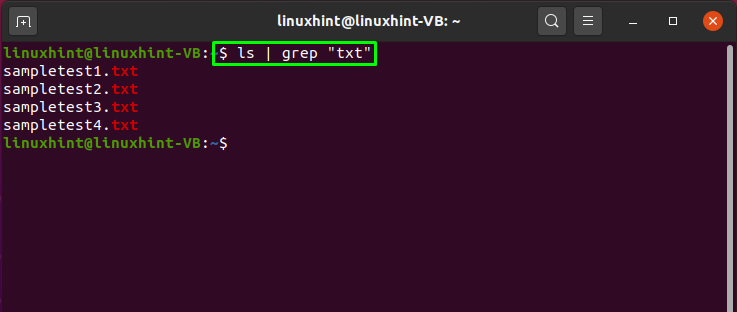
The pipe also provides you the facility to separate and list specific files from a list. For this, you can use the “ls” command to list files and the “grep” command for searching the specific pattern and add the “|” pipe character between these commands.
In the below-given example, the pipe character will send the list of files and directories to the “grep” command. Then, the grep command will extract the file having the “txt” pattern in them:
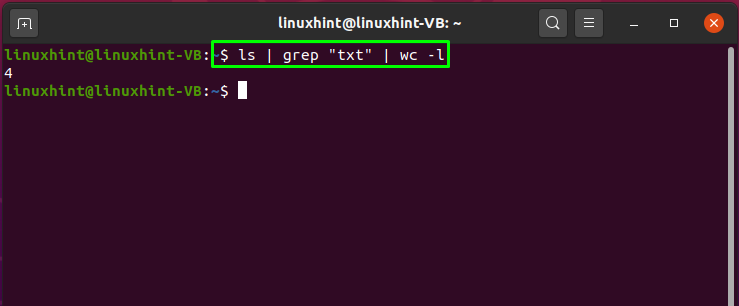
How to use pipe to count number of specific files from the list of all files and directories in Linux
You can utilize pipes to create a chain of commands. This chain of commands is executed at once in the Linux terminal. For instance, we can extend the previously executed command by adding a pipe and “wc” command. The second pipe will send the output of the “grep” command to “wc”.
The output of the command will print out the total number of files containing the “txt” pattern:
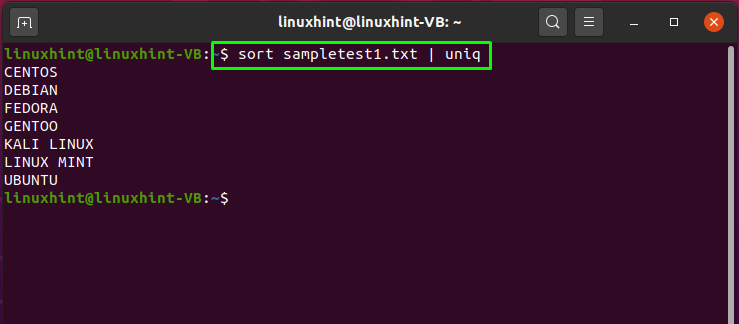
How to use pipe to sort a file and print its unique values in Linux
If you want to sort a file and then print out its unique values in the terminal, then execute the below-given command:
Here, the “sort” command is utilized to sort the “sampletest1.txt” file. The pipe “|” sends the “sort” command output to “uniq“. Then, the “uniq” command will filter the duplicate values:
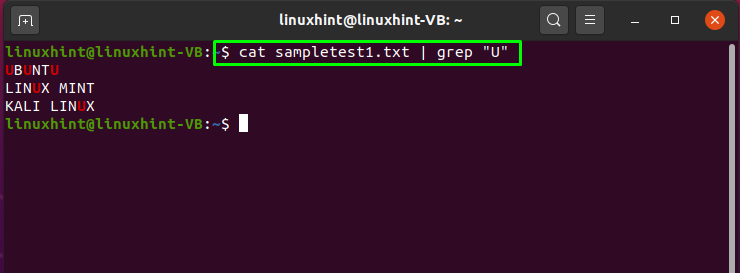
How to use pipe to fetch particular data in Linux
You can utilize the pipe “|” between the cat and grep command. The “cat” command will extract the data from “sampletest1.txt”, whereas the “grep” command will search for the “U” letter in the “sampletest1.txt” content. For further processing, pipe “|” will send the “cat” command output to “grep”:
The output will show you the text having “U”:
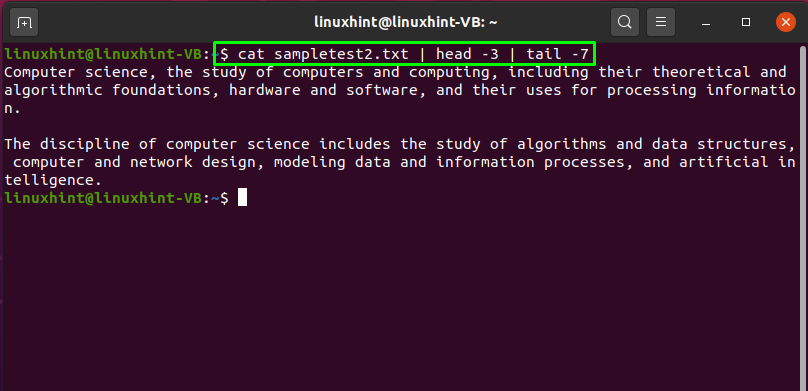
How to use pipe to print file lines in a specific range in Linux
“head” and “tail” commands are used to print out the first and last part of a file. In this example, we will utilize the pipe “|” to fetch the “sampletest2.txt” file data resulted from the “cat” command and then pass it to the “head” and “tail” command as input:
It will show you the below-given output:
Conclusion
In Linux-based systems, the pipe is utilized for combining two or more commands in such a way that the output of one command is passed as the input to the other one. The “|” symbol indicates pipe operator. With the help of pipe operator, each process output is directly given as input to the next command. In this post, you have learned what a pipe operator is in Linux. Moreover, we have also demonstrated various examples related to pipes in a Linux system.
About the author
Sharqa Hameed
I am a Linux enthusiast, I love to read Every Linux blog on the internet. I hold masters degree in computer science and am passionate about learning and teaching.