- How to open a PDF file from terminal?
- 13 Answers 13
- Most desktop environments on modern systems (generic)
- GNOME
- Application-specific
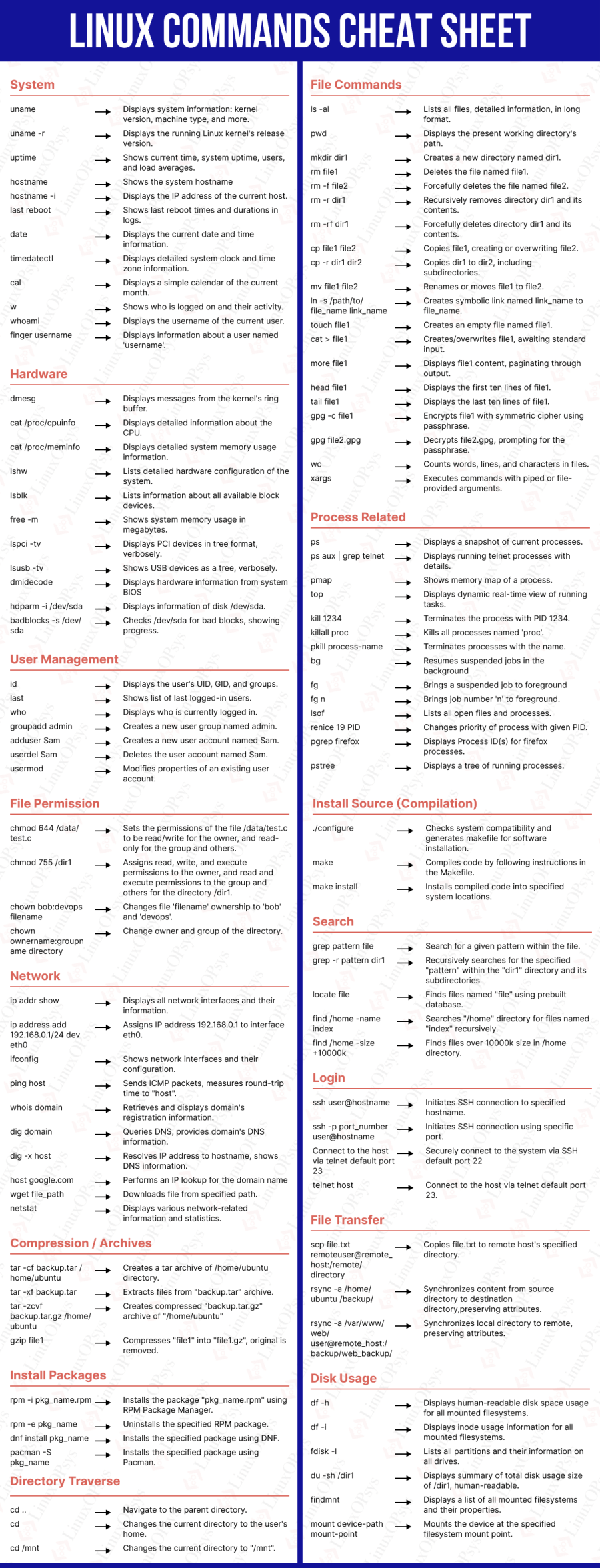
- Linux Commands Cheat Sheet
- Cheat sheet
- 1. System Based Commands
- 2. Hardware Based Commands
- 3. Users Management Commands
- 4. File Commands
- 5. Process Related Commands
- 6. File Permission Commands
- 7. Network Commands
- 8. Compression/Archives Commands
- 9. Install Packages Commands
- 10. Install Source (Compilation)
- 11. Search Commands
- 12. Login Commands
- 13. File Transfer Commands
- 14. Disk Usage Commands
- 15. Directory Traverse Commands
- About The Author
- Bobbin Zachariah
How to open a PDF file from terminal?
and the PDF file would be opened on preview or whatever my default viewer was. When I use it in the terminal in Ubuntu I get this error message:
Couldn't get a file descriptor referring to the console @Roland but mac claims to be a unix based system, so I assumed the terminal would behave the same atleast
You can use fbi (Linux frame buffer image viewer) apt-get -y install fbi fbgs arch.pdf man fbgs for color and resolutions.
13 Answers 13
Most desktop environments on modern systems (generic)
GNOME
( xxx = some file extension). With this command the default app for xxx will be invoked (for example evince if you want to open PDF).
Application-specific
So there is absolutely no way to view the text of a pdf file inside the terminal? With the pictures removed or converted to ASCII art?
when using evince your document closes after you close the terminal. xdg-open per the elmicha’s answer worked wll for me.
xdg-open works in Gnome, KDE, xfce, LXDE and perhaps on other desktops.
You can put an alias in your ~/.bash_aliases:
+1. This is what chrome for one uses. It supports URIS as well (e.g. xdg-open irc://. ). Pretty cool.
For all those lost Mac users in Ubuntu-land ..
Edit your .bashrc file, and add:
pdftotext -layout file2open.pdf - | more We can use this in text mode, ssh, etc.
If you want to view PDF within Terminal (Command Line Interface), try to use zathura .
Install Zathura sudo apt-get install zathura -y .
To view a PDF file just run => zathura /path/to/xxx.pdf
BTW: zathura requires X11 anyway, it doesn’t work on Servers with no X installed.
zathura doesn’t display in the current terminal (Gnome), but opens its own window? A GTK application?
if you have Document Viewer installed type the following command:
if it is not already installed you can install it firstly using the following command:
sudo apt-get install evince to open your file in open office.
The Z shell ( zsh ) has suffix based alias ( -s ), these allow you to set up a file association between a file extension like .jpg and a suitable application like xreader :
With an alias like that you just need to type the file name and hit ↵ Return , e.g.:
The zsh shell has suffix based alias (-s) these allow you to set up a file association between a file extension e.g. jpg and a suitable application say xnview
In Ubuntu 17.04 you case use this:
I personally use a shell script:
$ cat pdf #! /bin/bash gnome-open $
When you call pdf it will open all pdfs in the current directory, specify which pdf by supplying an argument. I have many directories containing but one pdf file (e.g. so many LaTeX directories) so only having to write pdf saves me quite some time and keystrokes.
Linux Commands Cheat Sheet
Here in this cheat sheet, Linux commands are categorized into different sections according to its usage. It is designed with all the commands in a nice background color.
You will find both the pdf and image (png) format of the cheat sheet.
Cheat sheet
Download your Linux commands cheat sheet in pdf format and print the Linux command download cheat sheet in A4 size paper.
Please keep us posted if you have any suggestions or if you find any command that we missed out on.
1. System Based Commands
| uname | Displays Linux system information |
| uname -r | Displays kernel release information |
| uptime | Displays how long the system has been running including load average |
| hostname | Shows the system hostname |
| hostname -i | Displays the IP address of the system |
| last reboot | Shows system reboot history |
| date | Displays current system date and time |
| timedatectl | Query and change the System clock |
| cal | Displays the current calendar month and day |
| w | Displays currently logged in users in the system |
| whoami | Displays who you are logged in as |
| finger username | Displays information about the user |
2. Hardware Based Commands
| dmesg | Displays bootup messages |
| cat /proc/cpuinfo | Displays more information about CPU e.g model, model name, cores, vendor id |
| cat /proc/meminfo | Displays more information about hardware memory e.g. Total and Free memory |
| lshw | Displays information about system’s hardware configuration |
| lsblk | Displays block devices related information |
| free -m | Displays free and used memory in the system (-m flag indicates memory in MB) |
| lspci -tv | Displays PCI devices in a tree-like diagram |
| lsusb -tv | Displays USB devices in a tree-like diagram |
| dmidecode | Displays hardware information from the BIOS |
| hdparm -i /dev/xda | Displays information about disk data |
| hdparm -tT /dev/xda | Conducts a read speed test on device xda |
| badblocks -s /dev/xda | Tests for unreadable blocks on disk |
3. Users Management Commands
| id | Displays the details of the active user e.g. uid, gid, and groups |
| last | Shows the last logins in the system |
| who | Shows who is logged in to the system |
| groupadd «admin» | Adds the group ‘admin’ |
| adduser «Sam» | Adds user Sam |
| userdel «Sam» | Deletes user Sam |
| usermod | Used for changing / modifying user information |
4. File Commands
| ls -al | Lists files — both regular & hidden files and their permissions as well. |
| pwd | Displays the current directory file path |
| mkdir ‘directory_name’ | Creates a new directory |
| rm file_name | Removes a file |
| rm -f filename | Forcefully removes a file |
| rm -r directory_name | Removes a directory recursively |
| rm -rf directory_name | Removes a directory forcefully and recursively |
| cp file1 file2 | Copies the contents of file1 to file2 |
| cp -r dir1 dir2 | Recursively Copies dir1 to dir2. dir2 is created if it does not exist |
| mv file1 file2 | Renames file1 to file2 |
| ln -s /path/to/file_name link_name | Creates a symbolic link to file_name |
| touch file_name | Creates a new file |
| cat > file_name | Places standard input into a file |
| more file_name | Outputs the contents of a file |
| head file_name | Displays the first 10 lines of a file |
| tail file_name | Displays the last 10 lines of a file |
| gpg -c file_name | Encrypts a file |
| gpg file_name.gpg | Decrypts a file |
| wc | Prints the number of bytes, words and lines in a file |
| xargs | Executes commands from standard input |
5. Process Related Commands
| ps | Display currently active processes |
| ps aux | grep ‘telnet’ | Searches for the id of the process ‘telnet’ |
| pmap | Displays memory map of processes |
| top | Displays all running processes |
| kill pid | Terminates process with a given pid |
| killall proc | Kills / Terminates all processes named proc |
| pkill process-name | Sends a signal to a process with its name |
| bg | Resumes suspended jobs in the background |
| fg | Brings suspended jobs to the foreground |
| fg n | job n to the foreground |
| lsof | Lists files that are open by processes |
| renice 19 PID | makes a process run with very low priority |
| pgrep firefox | find Firefox process ID |
| pstree | visualizing processes in tree model |
6. File Permission Commands
| chmod octal filename | Change file permissions of the file to octal |
| Example | |
| chmod 777 /data/test.c | Set rwx permissions to owner, group and everyone (everyone else who has access to the server) |
| chmod 755 /data/test.c | Set rwx to the owner and r_x to group and everyone |
| chmod 766 /data/test.c | Sets rwx for owner, rw for group and everyone |
| chown owner user-file | Change ownership of the file |
| chown owner-user:owner-group file_name | Change owner and group owner of the file |
| chown owner-user:owner-group directory | Change owner and group owner of the directory |
7. Network Commands
| ip addr show | Displays IP addresses and all the network interfaces |
| ip address add 192.168.0.1/24 dev eth0 | Assigns IP address 192.168.0.1 to interface eth0 |
| ifconfig | Displays IP addresses of all network interfaces |
| ping host | ping command sends an ICMP echo request to establish a connection to server / PC |
| whois domain | Retrieves more information about a domain name |
| dig domain | Retrieves DNS information about the domain |
| dig -x host | Performs reverse lookup on a domain |
| host google.com | Performs an IP lookup for the domain name |
| hostname -i | Displays local IP address |
| wget file_name | Downloads a file from an online source |
| netstat -pnltu | Displays all active listening ports |
8. Compression/Archives Commands
| tar -cf home.tar home | Creates archive file called ‘home.tar’ from file ‘home’ |
| tar -xf files.tar | Extract archive file ‘files.tar’ |
| tar -zcvf home.tar.gz source-folder | Creates gzipped tar archive file from the source folder |
| gzip file | Compression a file with .gz extension |
9. Install Packages Commands
| rpm -i pkg_name.rpm | Install an rpm package |
| rpm -e pkg_name | Removes an rpm package |
| dnf install pkg_name | Install package using dnf utility |
10. Install Source (Compilation)
| ./configure | Checks your system for the required software needed to build the program. It will build the Makefile containing the instructions required to effectively build the project |
| make | It reads the Makefile to compile the program with the required operations. The process may take some time, depending on your system and the size of the program |
| make install | The command installs the binaries in the default/modified paths after the compilation |
11. Search Commands
| grep ‘pattern’ files | Search for a given pattern in files |
| grep -r pattern dir | Search recursively for a pattern in a given directory |
| locate file | Find all instances of the file |
| find /home/ -name «index» | Find file names that begin with ‘index’ in /home folder |
| find /home -size +10000k | Find files greater than 10000k in the home folder |
12. Login Commands
| ssh [email protected] | Securely connect to host as user |
| ssh -p port_number [email protected] | Securely connect to host using a specified port |
| ssh host | Securely connect to the system via SSH default port 22 |
| telnet host | Connect to host via telnet default port 23 |
13. File Transfer Commands
| scp file1.txt server2/tmp | Securely copy file1.txt to server2 in /tmp directory |
| rsync -a /home/apps /backup/ | Synchronize contents in /home/apps directory with /backup directory |
14. Disk Usage Commands
| df -h | Displays free space on mounted systems |
| df -i | Displays free inodes on filesystems |
| fdisk -l | Shows disk partitions, sizes, and types |
| du -sh | Displays disk usage in the current directory in a human-readable format |
| findmnt | Displays target mount point for all filesystems |
| mount device-path mount-point | Mount a device |
15. Directory Traverse Commands
| cd .. | Move up one level in the directory tree structure |
| cd | Change directory to $HOME directory |
| cd /test | Change directory to /test directory |
If this resource helped you, let us know your care by a Thanks Tweet. Tweet a thanks
About The Author
Bobbin Zachariah
Bobbin is a seasoned IT professional with over two decades of experience. He has excelled in roles such as a computer science instructor, Linux system engineer, and senior analyst. Currently, he thrives in DevOps environments, focusing on optimizing efficiency and delivery in AWS Cloud infrastructure. Bobbin holds certifications in RHEL, CCNA, and MCP, along with a Master’s degree in computer science. In his free time, he enjoys playing cricket, blogging, and immersing himself in the world of music.