- How to compare differences between directories (linux)
- 7 Answers 7
- How to Find Difference Between Two Directories Using Diff and Meld Tools
- Using Meld Visual Diff and Merge Tool
- Compare Two Directories in the Linux Command Line
- Use the diff command to compare directories in Linux
- Use GUI to compare directories in Linux
- Looking for more tools to compare?
How to compare differences between directories (linux)
I have two directories — one from earlier backup and second from newest backup. How do i compare what changes were made to files in directory from newest backup on Linux? Also how do i display changes in for example text and php files — i’m thinking about something like revision history on wikipedia where you see old version on one side of the screen and newest version on other and changes are highlighted. How do i achieve something like that? edit: How do i also compare remote dir with local?
7 Answers 7
If both from-file and to-file are directories, diff compares corresponding files in both directories, in alphabetical order; this comparison is not recursive unless the -r or —recursive option is given. diff never compares the actual contents of a directory as if it were a file. The file that is fully specified may not be standard input, because standard input is nameless and the notion of ‘‘file with the same name’’ does not apply.
So to compare directories: diff —brief -r dir1 dir2
To compare files side by side: diff —side-by-side file1 file2
You would have to mount the remote directory to the local machine. However, you can remotely compare files like so: ssh REMOTE_SERVER «cat /path/to/some/file» | diff —side-by-side /path-to-some-file — One other thing, the ‘sdiff’ command works like ‘diff —side-by-side’ if you want to save some typing.
Use NFS to mount the remote directory. On the remote server(server-b), edit /etc/exports and put the following in it: /path/of/directory/to/share server-a.ip.address(ro,no_root_squash) Start NFS on server-b (/etc/init.d/nfs start) Mount to your local server(server-a) by adding the following to /etc/fstab: server-b.ip.add:/path/of/directory/to/share /mnt/server-b nfs rsize=32768,wsize=32768,rw 0 0 Then on server-a, mkdir /mnt/server-b; mount /mnt/server-b Thanks for the upvotes.
You really want to combine the power of rsync to reduce bandwidth consumption with the power of diff to give you flexible, well um diffs.
cp -R $local $bak rsync $server:$remdir/* $local/ rsync $local/ $server:$remdir/* diff -wur $local $bak I guess you could tweak this a bit if you were doing it often use rsync instead of cp in the first line — obviously in the last line you have the full power of diff to format it however you like. Probably with y in the OPs case
Downside of this approach is you end up using twice as much local space, but at less than $1/gig who cares?
- we are on www1 , comparing with remote www2
- there is configured public ssh key authentication from local www1 to remote www2
- we compare as the same user on local www1 and remote www2
find /var/www/html/ -name "*" -exec md5sum -b <> \; | grep -v "/var/www/html/exclude_this dir" > local.md5 ssh www2 "find /var/www/html/ -name '*' -exec md5sum -b <> \; | grep -v /var/www/html/exclude_this dir > remote.md5" scp www2:remote.md5 . diff local.md5 remote.md5
this actually works but 1. you don’t need to scp 2. directory paths need to be the same 3. will pollute both directories with extra files 4. file order is not guaranteed to be the same serverfault.com/a/1128839/349476
Do diff old_dir new_dir > diff.txt for side by side differences on the same server.
For example : ABC is existing server and XYZ is your remote server and directory name is 123.
Step 1: Rename existing directory 123 on ABC Server as 123_ABC.
Step 2: Create a new directory on the server ABC:
Step 3: Copy all files from directory 123 on XYZ server to 123_XYZ directory on ABC server:
XYZ/123 > scp * userid@ABC: /123_XYZ This will copy all files from the directory on your XYZ server to your ABC server/ 123_XYZ directory.
Step:4 : Do the diff between both directories:
Now go to ABC server and perform diff between 123_ABC and 123_XYZ
ABC > diff 123_ABC 123_XYZ > diff.txt The command above will save the diff results in to diff.txt in the same path.
You may compare the differences then.
AIDE Advanced Intrusion Detection Environment (AIDE) is a file integrity checker for UNIX operating systems. Its purpose to provide reporting on the integrity of data on supported file systems. By running AIDE multiple times on the target host you can determine what files are changing. By running AIDE multiple times on different hosts you can determine what files and permissions are different. Then use a gui diff tool on the reported «different» files.
Or use a gui diff tool like meld, guiffy, kdiff3, diff, vimdiff, gvimdiff, Emacs, Kompare, Diffuse, Easydiff, TkDiff or xxdiff. Most will do directory diffs in addition to file diffs. You’ll need to mount the remote drive using NFS, SMBFS or SSHFS as others have mentioned.
Or you can use two files with the out put of list of files. And then compare those two files. For example:
/path/to/compare/remote$: ls > remote-files /path/to/compare/local$: ls > local-files Download one of the files.
-rw-r--r-- 1 1015 1015 26624 2005-06-14 13:10 FILE.TXT
Use diff ( diff -y remote-files local-files > diff-files ) to compare them side by side. Open the diff-files and check it. Each line with > means a different file.
How to Find Difference Between Two Directories Using Diff and Meld Tools
In an earlier article, we reviewed 9 best file comparison and difference (Diff) tools for Linux and in this article, we will describe how to find the difference between two directories in Linux.
Normally, to compare two files in Linux, we use the diff – a simple and original Unix command-line tool that shows you the difference between two computer files; compares files line by line and it is easy to use, comes with pre-installed on most if not all Linux distributions.
The question is how do we get the difference between two directories in Linux? Here, we want to know what files/subdirectories are common in the two directories, those that are present in one directory but not in the other.
The conventional syntax for running diff is as follows:
$ diff [OPTION]… FILES $ diff options dir1 dir2
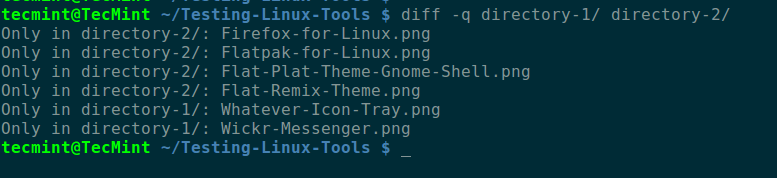
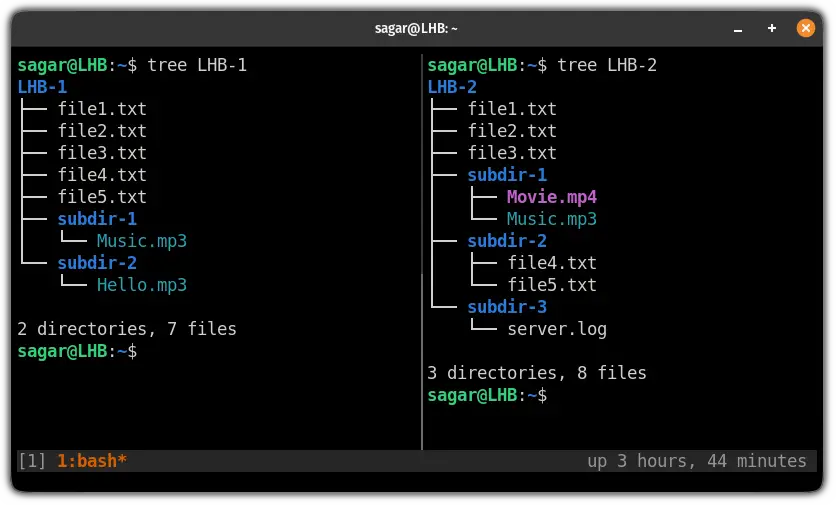
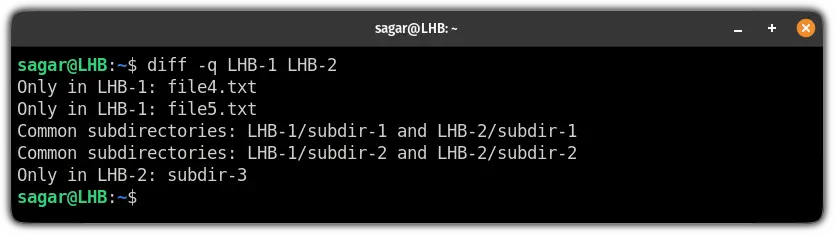
By default, its output is ordered alphabetically by file/subdirectory name as shown in the screenshot below. In this command, the -q switch tells diff to report only when files differ.
$ diff -q directory-1/ directory-2/
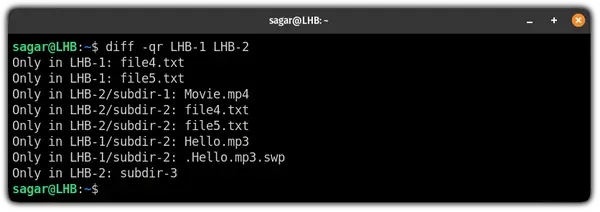
Again diff doesn’t go into the subdirectories, but we can use the -r switch to read the subdirectories as well like this.
$ diff -qr directory-1/ directory-2/
Using Meld Visual Diff and Merge Tool
There is a cool graphical option called meld (a visual diff and merge tool for the GNOME Desktop) for those who enjoy using the mouse, you can install it as follows.
$ sudo apt install meld [Debian/Ubuntu systems] $ sudo yum install meld [RHEL/CentOS systems] $ sudo dnf install meld [Fedora 22+]
Once you have installed it, search for “meld” in the Ubuntu Dash or Linux Mint Menu, in Activities Overview in Fedora or CentOS desktop and launch it.
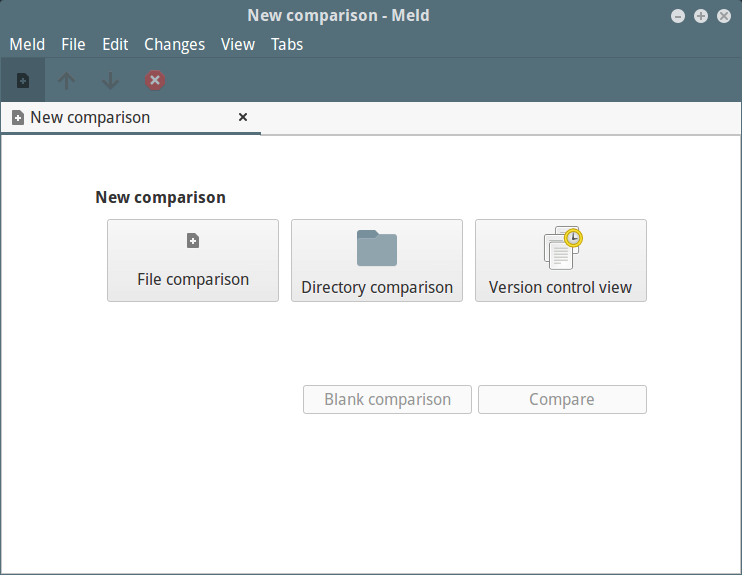
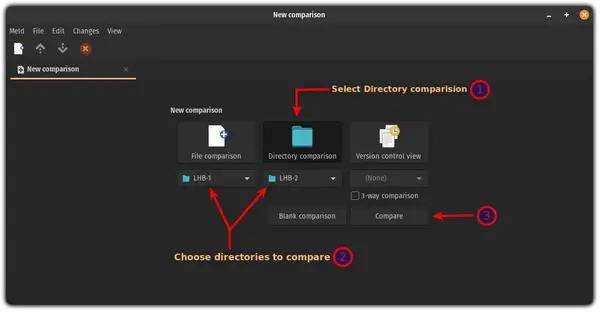
You will see the Meld interface below, where you can choose file or directory comparison as well as version control view. Click on directory comparison and move to the next interface.
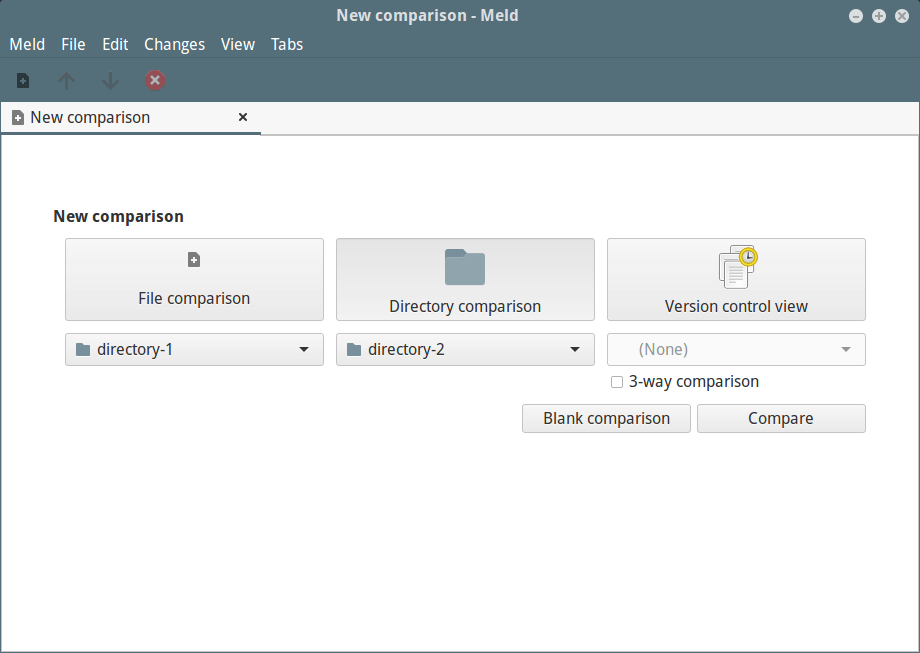
Select the directories you want to compare, note that you can add a third directory by checking the option “3-way Comparison”.
Once you selected the directories, click on “Compare”.
In this article, we described how to find the difference between two directories in Linux. If you know any other commandline or gui way don’t forget to share your thoughts to this article via the comment section below.
Compare Two Directories in the Linux Command Line
Want to see how the content of the two directories differs? Use the diff command and see what files are identical or different.
How do you compare two files in Linux? You use the diff command.
But how do you compare two folders in Linux? You still use the diff command.
It is easier to visualize the difference between two directories using a GUI tool.
In this tutorial, I’ll share how you can use the diff command to compare directories. I will also discuss a GUI tool called Meld.
The tree command shows the structures of the two directories I use in the examples.
So let’s start this tutorial with the CLI method.
Use the diff command to compare directories in Linux
To use the diff command, you will have to follow a simple syntax:
diff -qr Directory-1 Directory-2To find the differences, you will have to use the -q option which will report only when the difference is found.
But if you notice carefully, the diff command only looked on file level 1. By default, it won’t look for the files inside the subdirectory.
To perform the search including the subdirectory, you will have to use the -r flag:
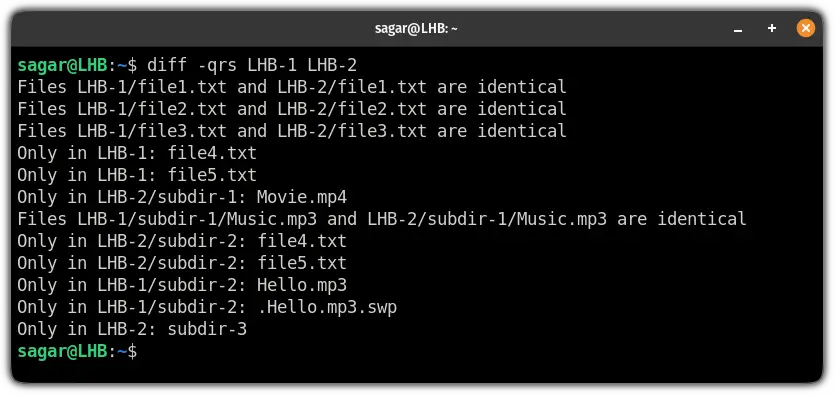
But what if you want to know the similar files too?
You can easily do that using the -s flag. So if you will use both flags -q and -s , it will show both identical and different files of directories:
The diff command shows what files differ in the directories. To see the difference, you can run the diff command again on the files to see how their content differs.
Use GUI to compare directories in Linux
If you are not a terminal fan and want to compare the directories in the easiest way possible, use Meld.
Meld is a GUI tool that allows you to check and merge differences.
You’ll have to install it first. In Ubuntu/Debian, use:
It is also available as a flatpak:
flatpak install flathub org.gnome.meldIf you haven’t configured flatpak on your system, check out our detailed guide on how to set up flatpak on various Linux distros.
Once you are done with the installation, open the Meld from your system menu and follow the three easy steps:
- Select the Directory comparison
- Choose directories to compare
- Click on the Compare button
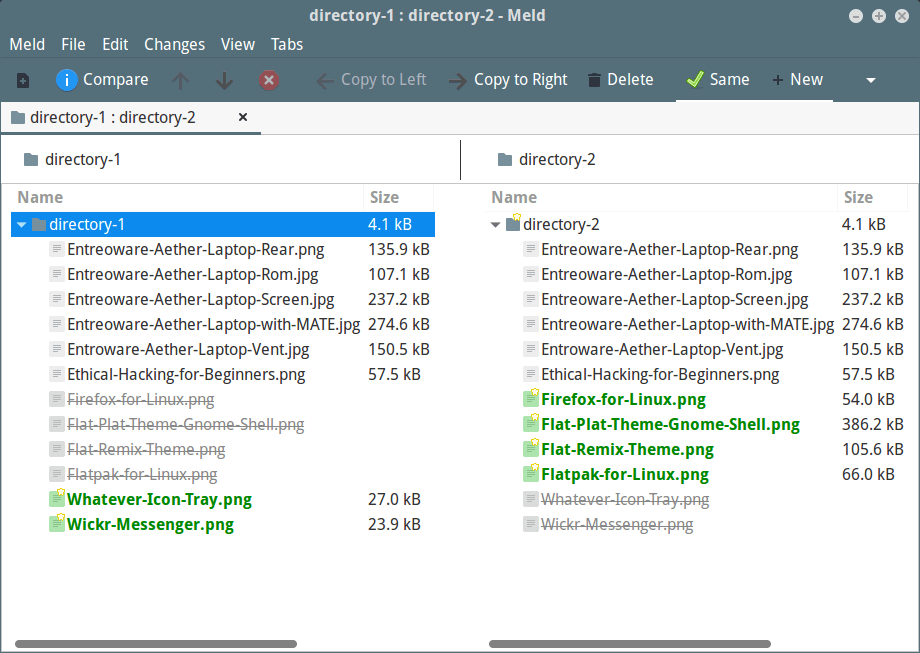
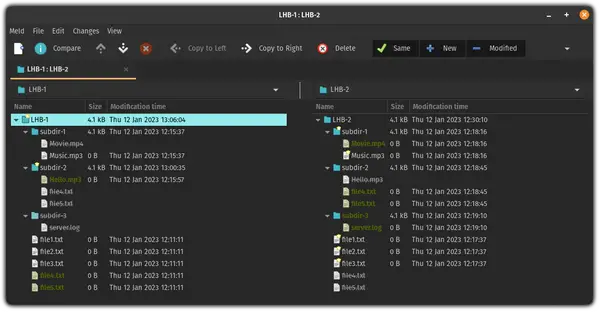
Once you click on the compare button, it will show you matching and different files available in the selected directories:
The ones which are marked with stars are the exact match.
Whereas filenames highlighted with green are only available to that respective directory.
Looking for more tools to compare?
If you are looking for more tools to compare files with various features, we already have a dedicated guide for that:
And if you have any queries related to this guide or want to suggest me what should I cover next, let me know in the comments.