- How to Mount a Windows Share Folder on Linux
- Share Your Windows Folder
- Install CIFS-utils
- Mount Windows SMB Share on Linux
- Sharing Files Between Linux and Windows in Dual Boot
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. Why do I get a syntax error when trying to mount a folder in Linux?
- 2. Can I mount a shared folder if I use VirtualBox?
- 3. Can I mount guest, network, or password protected folders?
- 4. Why do I only have read access for the shared folder?
- 5. Why aren’t folder changes showing up?
- Wrapping Up
- Linux: подключить общую сетевую папку Windows по SMB (CIFS)
- Смонтировать сетевую папку в Linux с помощью cifs-util
- Автоматическое монтирование сетевой папки в Linux
- Linux: подключиться к сетевой папке с помощью клиента samba
How to Mount a Windows Share Folder on Linux
Linux and Windows systems have major differences, with different file systems and protocols in use. Sharing files between them can be difficult, especially because they use two different sharing protocols. That doesn’t mean it’s impossible to mount a Windows share folder on Linux, however. Follow along below to find out how.
Share Your Windows Folder
Before you do anything, you need to ensure that Windows has been correctly set up to allow for networking file sharing.
To enable this on Windows, right-click on the network icon in the notifications area of your Windows taskbar. From here, click “Open Network & Internet Settings.”
Under the “Status” category, click “Sharing options.”
In your Windows sharing options menu, make sure that “Turn on network discovery” and “Turn on file and printer sharing” are enabled.
Click the radio buttons next to both options to make sure this is the case.
Click “Save changes” to save your settings. Once this is done, open Windows File Explorer and locate the folder you’re looking to share with your Linux PC.
Right-click the folder and click “Properties.”
In your folder properties, click the “Sharing” tab, then click “Advanced Sharing.” Click to enable the “Share this folder” checkbox, then click “Permissions.”
Under the “Permissions” section, set the control rights for your folder. By default, Windows will grant read-only access to your files.
If you want to allow everyone to read or write to the folder, click “Allow” for the “Full Control” permissions set. Set these permissions to suit your own requirements.
Once you’re done, click “OK” three times to close each of the dialog boxes.
Your folder should now be shared on your network, ready for you to access from your Linux PC.
Install CIFS-utils
Depending on your Linux distribution, you may be able to mount your Windows-shared folder automatically in your distribution’s file explorer.
However, this may not work correctly. The safest way to mount Windows-shared folders on Linux is to use the CIFS-utils package and mount the folder using the Linux terminal.
This allows Linux machines to access SMB file shares used by Windows PCs.
To install CIFS-utils, open a new terminal window. For Ubuntu and Debian-based distributions, type:
sudo apt install cifs-utils
Once installed, you can then mount your Windows share folder from the Linux terminal.
Mount Windows SMB Share on Linux
You’ll need to create a mount directory before you can mount your Windows SMB-shared folder on Linux. This is where Linux will mirror the contents of your shared folder.
To do that, open a terminal window and type:
Once created, type the following:
sudo mount.cifs //Windows/SharedFolder /mnt/share -o user=account
Replace “Windows” with the IP address or hostname for your Windows PC and “SharedFolder” with your shared folder name. For the username, replace “account” with your Windows username or full Microsoft account email.
You’ll be asked to provide your Windows password before the mounting process is complete. Type this in, then click Enter. If you used the correct information, your Windows folder should now be mounted and accessible in the folder you created.
Sharing Files Between Linux and Windows in Dual Boot
Sharing files between Windows and Linux works great when you mount a shared folder between the two devices, but can you still share files with a dual boot setup? Linux and Windows have separate file systems. Linux usually uses Ext4, while Windows uses NTFS and also works with FAT32. This doesn’t mean it’s impossible to see and share files, though.
You’ll need a compatible Windows system, build 20211 or higher, and a few other resources to make it work. Don’t worry. Everything is free. This guide walks you through each step in the process, including a way to read and share files between Windows and Linux.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why do I get a syntax error when trying to mount a folder in Linux?
Either there’s a small error in the command in the terminal window, or you have a space in the folder name. Spaces don’t always come across correctly in the syntax. Instead of recognizing the command as the full name of the folder, the system sees two unrelated items.
Avoid this by placing the name in quotes. For instance, Shared Folder would become “Shared Folder.” Of course, you can also just rename the Windows 10 folder to place the words together or have a dash between them.
2. Can I mount a shared folder if I use VirtualBox?
Yes. The process should work the same way. You can also share devices, such as USB drives.
3. Can I mount guest, network, or password protected folders?
Yes, but since you’re not using the main Windows 10 account, you will need to adjust the syntax a bit. Plus, if you’re mounting a network folder, you’ll also need the server or machine name.
While this guide applies to Ubuntu, it should work for most major Linux distros as well. It lists the syntax for different scenarios, assuming you’ve already completed all of the steps (except the final mounting) above.
4. Why do I only have read access for the shared folder?
If you want to store files in the shared folder from Linux, make sure you have full read/write access to the folder in Windows. If the Windows user account only has read permission, this is the only permission you’ll have from Linux as well. You must change your account permissions from within Windows 10. For companies, you’ll need your IT admin to make the change for you.
5. Why aren’t folder changes showing up?
If you’ve made changes to the permissions of the folder, they may not show up immediately in Linux. You’ll need to remount the folder for changes to take effect.
Use the command above to remount any shared folders. This should ensure things work as expected. If you have any random glitches, remounting typically fixes them.
Wrapping Up
Mounting Windows and Linux shared folders gives you the freedom to access your most important files, no matter the operating system. The SMB protocol is well supported on Linux, so you shouldn’t find it difficult to continue accessing your Windows files and folders once you’ve installed the CIFS-utils package.
If you’d rather use a single system, here are five of the best Linux distros for Windows users you could use.
Crystal Crowder has spent over 15 years working in the tech industry, first as an IT technician and then as a writer. She works to help teach others how to get the most from their devices, systems, and apps. She stays on top of the latest trends and is always finding solutions to common tech problems.
Our latest tutorials delivered straight to your inbox
Linux: подключить общую сетевую папку Windows по SMB (CIFS)
В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как в Linux смонтировать общую сетевую папку, расположенную на хосте Windows. В Windows для доступа к общим сетевым папкам используется протокол SMB (Server Message Block), который ранее назывался CIFS (Сommon Internet File System). В Linux для доступа к сетевым папкам Windows по протоколу SMB можно использовать клиент cifs-utils или Samba.
Совет. Для доступа к сетевым папкам по SMB/CIFS используется порт TCP/445. Для разрешения имени используются порты UDP 137, 138 и TCP 139. Если эти порты закрыты, вы сможете подключиться к сетевой папке Windows только по IP адресу.
Смонтировать сетевую папку в Linux с помощью cifs-util
Вы можете смонтировать сетевую папку, находящуюся на Windows хосте, с помощью утилит из пакета cifs-util. Для установки пакета выполните команду:
- В Ubuntu/Debian: $ sudo apt-get install cifs-utils
- В CentOS/Oracle/RHEL: $ sudo dnf install cifs-utils
Создайте точку монтирования:
Теперь вы можете смонтировать сетевую папку с компьютера Windows под пользователем User03с помощью команды:
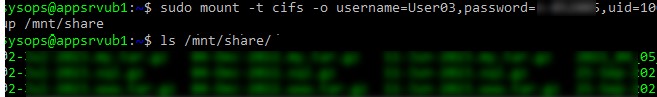
$ sudo mount.cifs //192.168.31.33/backup /mnt/share -o user=User03
Укажите пароль пользователя Windows для подключения к сетевой папке.
При подключении сетевой SMB папки можно задать дополнительные параметры:
$ sudo mount -t cifs -o username=User03,password=PasswOrd1,uid=1000,iocharset=utf8 //192.168.31.33/backup /mnt/share
- //192.168.31.33/backup – сетевая папка Windows
- /mnt/share – точка монтирования
- -t cifs – указать файловую систему для монтирования
- -o опции монтирования (эту опцию можно использовать только с правами root, поэтому в команде используется sudo)
- username=User03,password=PasswOrd1 – имя и пароль пользователя Windows, у которого есть права доступа к сетевой папке. Можно указать имя пользователя guest, если разрешен анонимный доступ к сетевой папке
- iocharset=utf8 – включить поддержку кодировки UTF8 для отображения имен файлов
- uid=1000 – использовать этого пользователя Linux в качестве владельца файлов в папке
По умолчанию шары Windows монтируются в Linux с полными правами (0755). Если вы хотите изменить права по-умолчанию при монтировании, добавьте в команду опции:
dir_mode=0755,file_mode=0755
Если вы хотите использовать имя компьютера при подключении сетевого каталога Windows, добавьте в файл /etc/hosts строку:
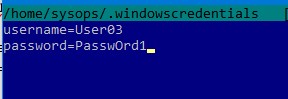
Чтобы не указывать учетные данные пользователя Windows в команде монтирования сетевой папки, их можно сохранить в файле.
username=User03 password=PasswOrd1
Для подключения к папке под анонимным пользователем:
Если нужно указать учетную запись пользователя из определенного домена Active Directory, добавьте в файл третью строку:
$ chmod 600 ~/.windowscredentials
Теперь при подключении сетевой папки вместо явного указания имени пользователя и пароля можно указать путь к файлу:
$ sudo mount -t cifs -o credentials=/home/sysops/.windowscredentials,uid=1000,iocharset=utf8 //192.168.31.33/backup /mnt/share
Отмонтировать сетевую SMB папку:
Автоматическое монтирование сетевой папки в Linux
Можно настроить автоматическое монтирование сетевой папки Windows через /etc/fstab.
Добавьте в файл следующую строку подключения SMB каталога:
//192.168.31.33/backup /mnt/share cifs user,rw,credentials=/home/sysops/.windowscredentials,iocharset=utf8,nofail,_netdev 0 0
- rw – смонтировать SBM папку на чтение и запись
- nofail – продолжить загрузку ОС если не удается смонтировать файловую систему
- _netdev – указывает что подключается файловая система по сети. Linux не будет монтировать такие файловые системы пока на хосте не будет инициализирована сеть.
Вы можете указать версию протокола SMB, которую нужно использовать для подключения (версия SMB 1.0 считается небезопасной и отключена по-умолчанию в современных версиях Windows). Добавьте в конец строки с настройками подключения параметр vers=3.0 .
//192.168.31.33/backup /mnt/share cifs user,rw,credentials=/home/sysops/.windowscredentials,iocharset=utf8,nofail,_netdev,vers=3.0 0 0
Если на стороне хоста Windows используется несовместимая (старая версия) SMB, при подключении появится ошибка:
mount error(112): Host is downилиmount error(95): Operation not supported
Чтобы сразу смонтировать сетевую папку, выполните:
Linux: подключиться к сетевой папке с помощью клиента samba
Установите в Linux клиент samba:
- В Ubuntu/Debian: $ sudo apt-get install smbclient
- В CentOS/Oracle/RHEL: # dnf install smbclient
Для вывода всех SMB ресурсов в локальной сети:
Вывести список доступных SMB папок на удаленном хосте Windows:
Если в Windows запрещен анонимный доступ, появится ошибка:
session setup failed: NT_STATUS_ACCESS_DENIED
В этом случае нужно указать учетную запись пользователя Windows, которую нужно использовать для подключения:
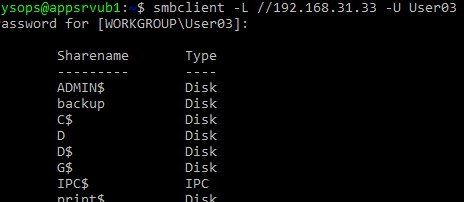
smbclient -L //192.168.31.33 -U User03
Если нужно использовать учетную запись пользователя домена, добавьте опцию –W:
smbclient -L //192.168.31.33 -U User03 –W Domain
Для интерактивного подключения к сетевой папке Windows используется команда:
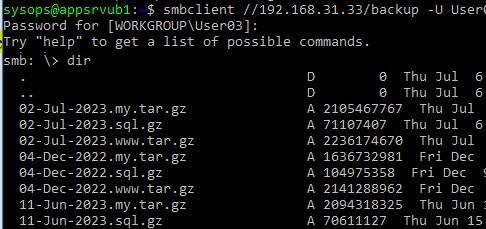
smbclient //192.168.31.33/backup -U User03 -W Domain
smbclient //192.168.31.33/backup -U User03
smbclient //192.168.31.33/backup -U Everyone
После успешного входа появится приглашение:
Вывести список файлов в сетевой папке:
Скачать файл из сетевой папки Windows:
get remotefile.txt /home/sysops/localfile.txt
Сохранить локальный файл из Linux в SMB каталог:
put /home/sysops/localfile.txt remotefile.txt
Можно последовательно выполнить несколько команд smbclient:
$ smbclient //192.168.31.33/backup -U User03 -c «cd MyFolder; get arcive.zip /mnt/backup/archive.zip»
Полный список команд в smbclient можно вывести с помощью команды help. Команды smbclient схожи с командами ftp клиента.
При использовании команды smbclient может появиться ошибка:
Unable to initialize messaging contextsmbclient: Can't load /etc/samba/smb.conf - run testparm to debug it.
Чтобы исправить ошибку, создайте файл /etc/samba/smb.conf.
Если на хосте Windows отключен протокол SMB 1.0, то при подключении с помощью smbclient появится ошибка:
Reconnecting with SMB1 for workgroup listing. protocol negotiation failed: NT_STATUS_CONNECTION_RESET Unable to connect with SMB1 -- no workgroup available.