- How to List Installed Packages on Ubuntu
- List Ubuntu Packages Using apt
- List All Installed and Available Packages
- List Only Installed Packages
- List Specific Packages
- List Upgradable Packages
- Count the Number of Installed Packages
- List Ubuntu Packages Using dpkg
- Create a List of all Installed Packages
- Count the Number of Installed Packages
- List Installed Packages Sorted by Date and Time
- List Installed Snap Packages
- How to view all installed packages in terminal (Ubuntu)
How to List Installed Packages on Ubuntu
Ubuntu and other Linux-based systems use client applications to manage software directly. Some software packages come preinstalled by default, while system administrators install other packages when necessary.
Depending on which package manager installed the software, there are various ways to list installed packages on Ubuntu.
This tutorial teaches you to list the installed packages on an Ubuntu system.
- A Debian-based distribution such as Ubuntu.
- A command line/terminal window (CTRL+ALT+T).
- The apt, dpkg, or snap package manager.
List Ubuntu Packages Using apt
By default, newer Ubuntu versions (14.04 or newer) come with the apt package manager. The package manager helps conduct operations relating to software packages.
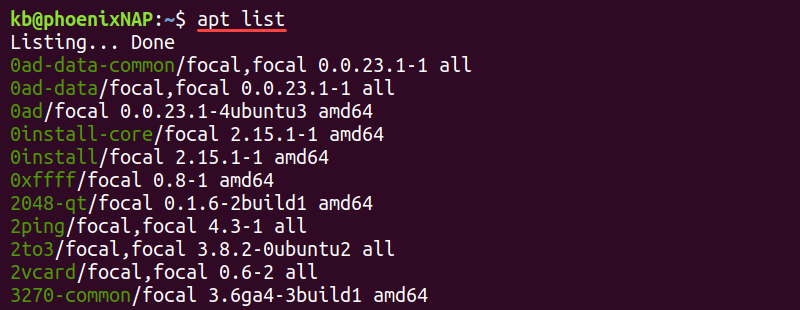
List All Installed and Available Packages
Use the following command to list all installed and available packages on Ubuntu:
The output shows a long list of packages with the version information and the package architecture. Shorten the list by piping the less command:
Navigate through the list by pressing the up or down arrow keys or space to skip to the next page. Press q to exit the viewer.
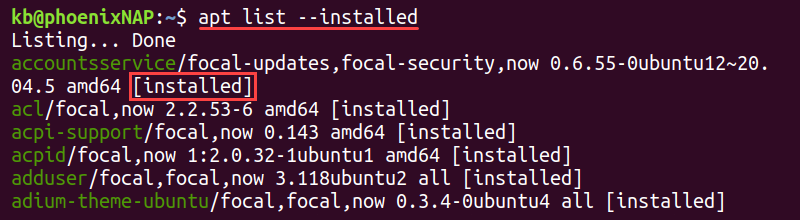
List Only Installed Packages
To list only installed packages, run:
The —installed tag ensures only installed packages show on the list. Each installed package has one of the following tags:
- [installed] indicates the package installed manually from the repository list.
- [installed, automatic] means the package installed automatically as a dependency for another installation.
- [installed, local] indicates the package is not from the official repository list.
List Specific Packages
There are three different ways to list a specific package:
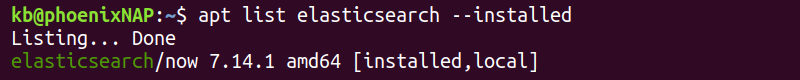
1. Add the package name to the apt list command to fetch a specific package from the list:
Omit the —installed tag to fetch a package, regardless of installation.
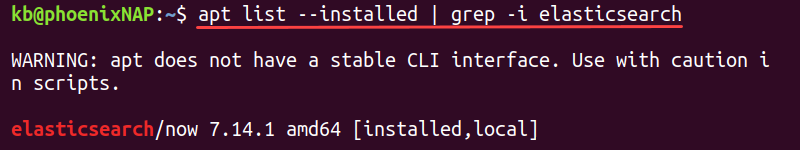
2. Combine apt list with the grep command to match a package by name:
apt list --installed | grep -i
The -i tag ignores letter casing, providing a broader search.
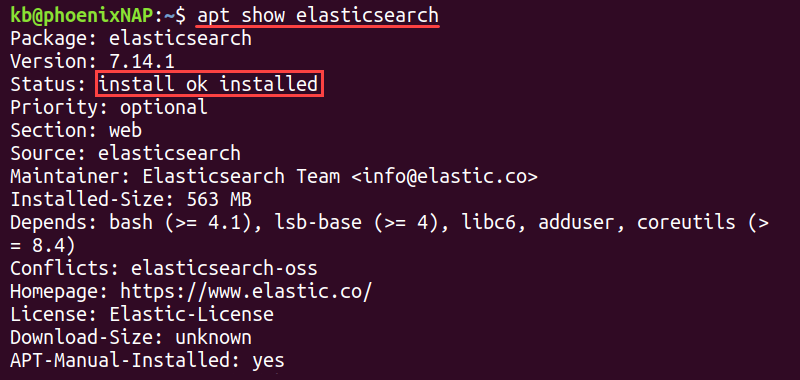
3. Another way to get package information is to use the apt show command:
The command shows the package details, including installation information.
List Upgradable Packages
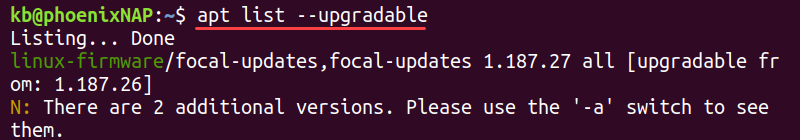
To list packages with available upgrades, run the following command:
The —upgradable tag filters packages and lists only the ones ready for an upgrade.
Note: If you’ve upgraded recently, the list is empty.
Count the Number of Installed Packages
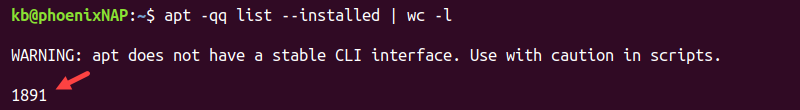
Use the apt list command with the Linux wc command to count the number of lines:
apt -qq list --installed | wc -lThe -qq tag quiets the output. Use the marker to ensure no additional lines print to the console and enter the count number.
List Ubuntu Packages Using dpkg
The dpkg package manager is included in earlier Ubuntu versions when apt is unavailable.
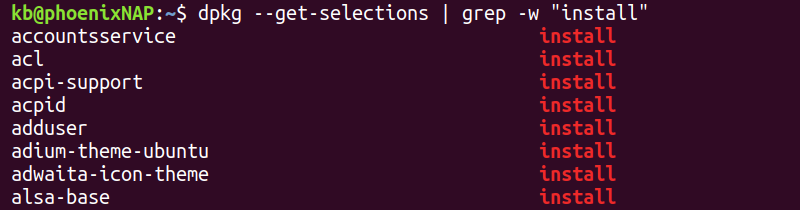
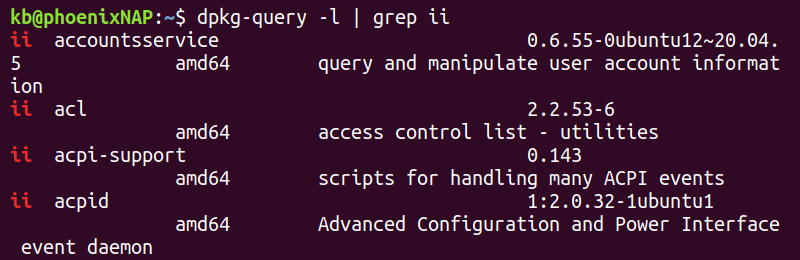
To list installed Ubuntu packages using the dpkg command, run:
dpkg --get-selections | grep -w "install"Alternatively, use the dpkg-query tool:
In both cases, the output shows a long list of installed packages.
Create a List of all Installed Packages
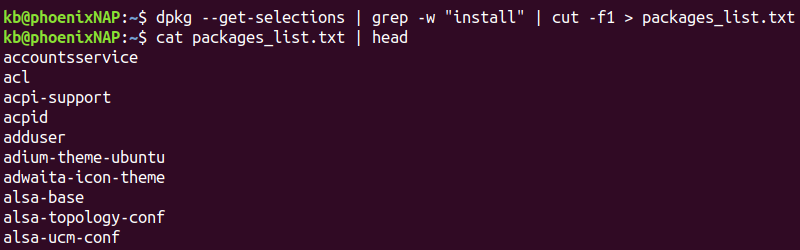
To save the installed package names into a text file, use the following command:
dpkg --get-selections | grep -w "install" | cut -f1 > packages_list.txtThe cut command filters the output to only get the first column with the package names and saves the contents to a text file.
Count the Number of Installed Packages
Use the wc command to count the number of lines from the list of installed packages:
dpkg --get-selections | grep -w "install" | wc -lThe -l tag counts the number of lines from the dpkg —get-selections output.
List Installed Packages Sorted by Date and Time
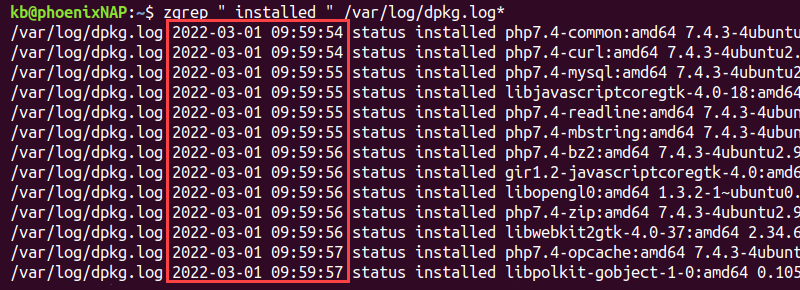
The dpkg logs store the date and time for package installations. To fetch all the information from log files, use the following command:
The output shows the exact timestamp for installed packages. The logs are archived and deleted after a specific time, so the list is not comprehensive.
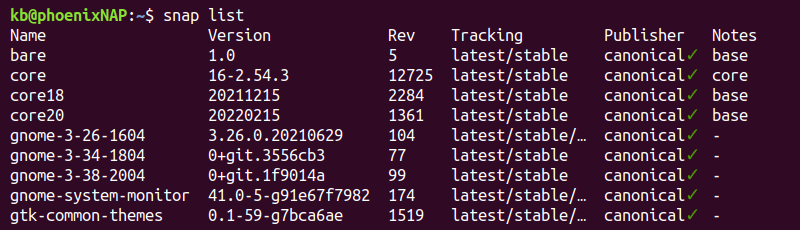
List Installed Snap Packages
Snap is an alternative package manager system. The previous commands do not show packages installed through Snap.
Note: Learn about the differences between the Snap packaging system and the apt package manager in Snap vs. Apt.
By following this guide, you should have learned how to list installed packages on Ubuntu and other Debian-based systems. If there is a problem with the installed packages, read our article on fixing broken packages in Ubuntu.
Milica Dancuk is a technical writer at phoenixNAP who is passionate about programming. Her background in Electrical Engineering and Computing combined with her teaching experience give her the ability to easily explain complex technical concepts through her content.
In Linux, special tools were developed for managing applications. Application software for Linux typically.
How to view all installed packages in terminal (Ubuntu)
dpkg-query actions See dpkg-query(1) for more information about the following actions.
-l, --list package-name-pattern. List packages matching given pattern. -s, --status package-name. Report status of specified package. -L, --listfiles package-name. List files installed to your system from package-name. -S, --search filename-search-pattern. Search for a filename from installed packages. -p, --print-avail package-name. Display details about package-name, as found in /var/lib/dpkg/available. Users of APT-based frontends should use apt-cache show package-name instead. To list packages installed only by you:
gunzip -c /var/log/apt/history.log.*.gz | grep 'apt-get install' | cut -f4- -d" " | tr ' ' $'\n' | sort -u Solution: In order to view all installed packages in linux Ubuntu, run on terminal apt —installed list ,
Use apt flags and would be able to see available upgrades to some packages ( —upgradeable ) / current installed packages ( —installed ) / all available versions ( —all-versions ).
From Documentation:
DESCRIPTION apt provides a high-level commandline interface for the package management system. It is intended as an end user interface and enables some options better suited for interactive usage by default compared to more specialized APT tools like apt-get(8) and apt-cache(8). Much like apt itself, its manpage is intended as an end user interface and as such only mentions the most used commands and options partly to not duplicate information in multiple places and partly to avoid overwhelming readers with a cornucopia of options and details. the list flag offers 3 options:
list (work-in-progress) list is somewhat similar to dpkg-query --list in that it can display a list of packages satisfying certain criteria. It supports glob(7) patterns for matching package names as well as options to list installed (--installed), upgradeable (--upgradeable) or all available (--all-versions) versions.