- Как посмотреть пользователей Ubuntu
- Как посмотреть список пользователей в терминале
- Список пользователей в GUI
- Выводы
- How to List users in Linux? [Linux List Users]
- How to list users in Linux? [List Users Linux Command]
- 1. List Linux users by using the CUT command
- 2. Linux users list by using “awk” command
- 3. L ist Users in Linux by Using getent command
- 4. Listing all the connected users on the Linux host
- 5. Using “/etc/group” for listing the groups on Linux
- 6. Linux group list Using the “cat” command
- 7. Group list in Linux by getent command
- Conclusion
- How to List Users in Linux
- Listing Users in Linux
- List Users with cat Command
- List Users with Terminal Pagers less and more
- List Users with awk Command
- List Users with getent Command
- Listing Normal and System users in Linux
Как посмотреть пользователей Ubuntu
Иногда возникает необходимость посмотреть всех зарегистрированных в системе Linux пользователей. Например, для того чтобы узнать не зарегистрирован ли кто лишний в системе, или изменить данные/группу одного из пользователей.
Профессионалы, конечно, же знают как это делается, причем кучей способов, а вот для новичков это может стать проблемой. В этой статье я покажу как посмотреть список пользователей Ubuntu несколькими способами — с помощью терминала и графических утилит.
Как посмотреть список пользователей в терминале
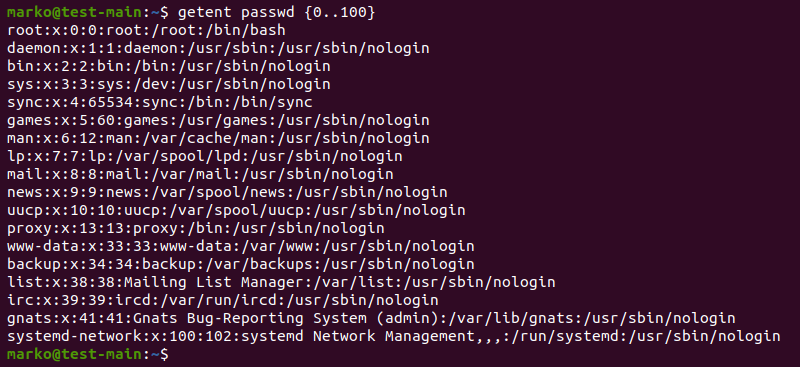
Сперва рассмотрим как посмотреть пользователей ubuntu в терминале Linux, так как это наиболее универсальный способ, который работает почти во всех дистрибутивах. В операционной системе Linux есть специальный файл в котором хранится информация обо всех пользователях. Это /etc/passwd. Записи в файле имеют следующий синтаксис:
имя_пользователя пароль ид ид_группы группа домашний_каталог оболочка
Надо заметить, что вместо пароля теперь записывается буква X это было сделано для безопасности. Все пароли пользователей хранятся теперь в другом файле. Остается только набрать команду и вы узнаете список пользователей linux:
Пользователи с ID меньше 1000 — системные, они были созданы во время установки некоторых сервисов для более безопасной их работы. Этих пользователей трогать не следует. В этом примере в системе вручную зарегистрирован только один пользователь — Sergiy.
В файле /etc/passwd слишком много лишних данных, если вам нужны только имена пользователей, можно отфильтровать вывод:
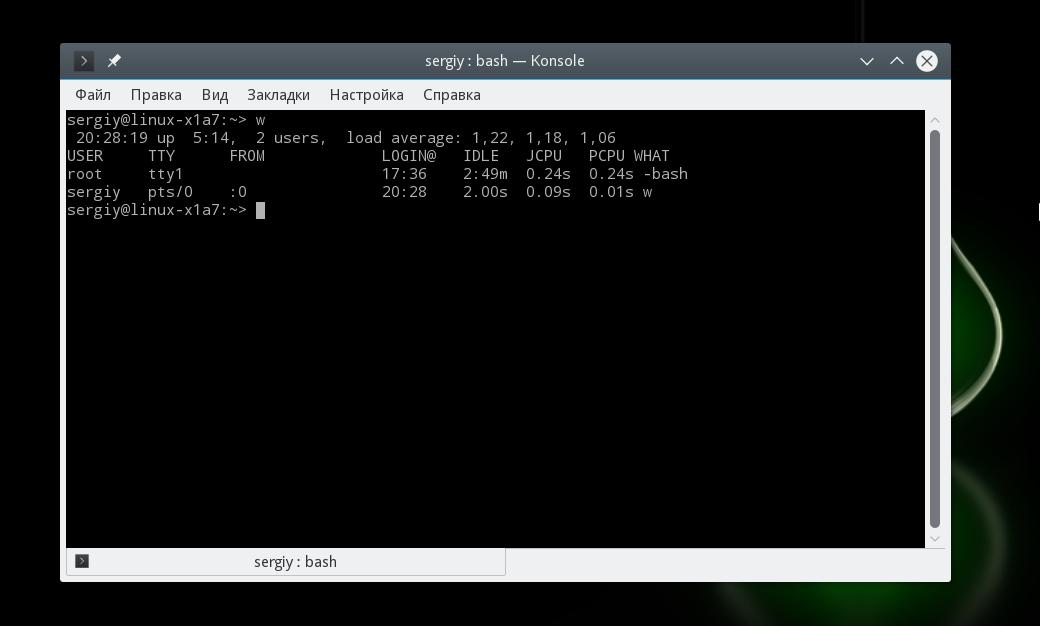
Так вы можете посмотреть всех пользователей Ubuntu. С зарегистрированными пользователями разобрались. Но намного интереснее посмотреть какие пользователи сейчас активны в системе, и какие команды они выполняют. Для этого есть утилита w:
Здесь выводятся все выполняемые пользователями команды. Если пользователь сейчас выполняет в терминале несколько команд, то будет отображено два пункта для одного пользователя.
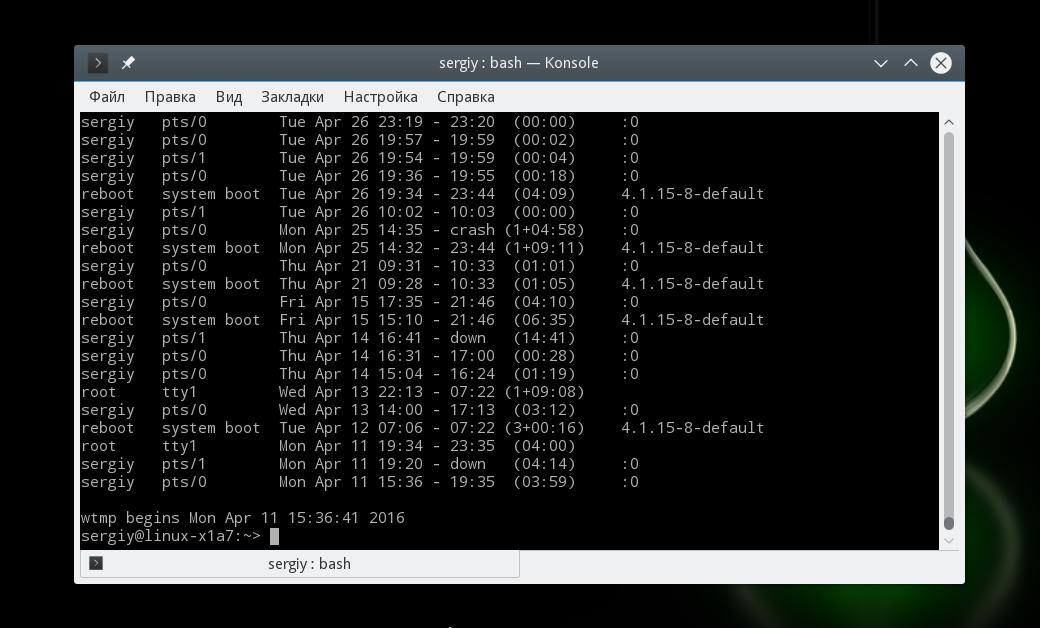
Кроме того, вы можете посмотреть историю входов пользователей в систему. Для этого есть команда last, она выводит информацию на основе лога /var/wtmp:
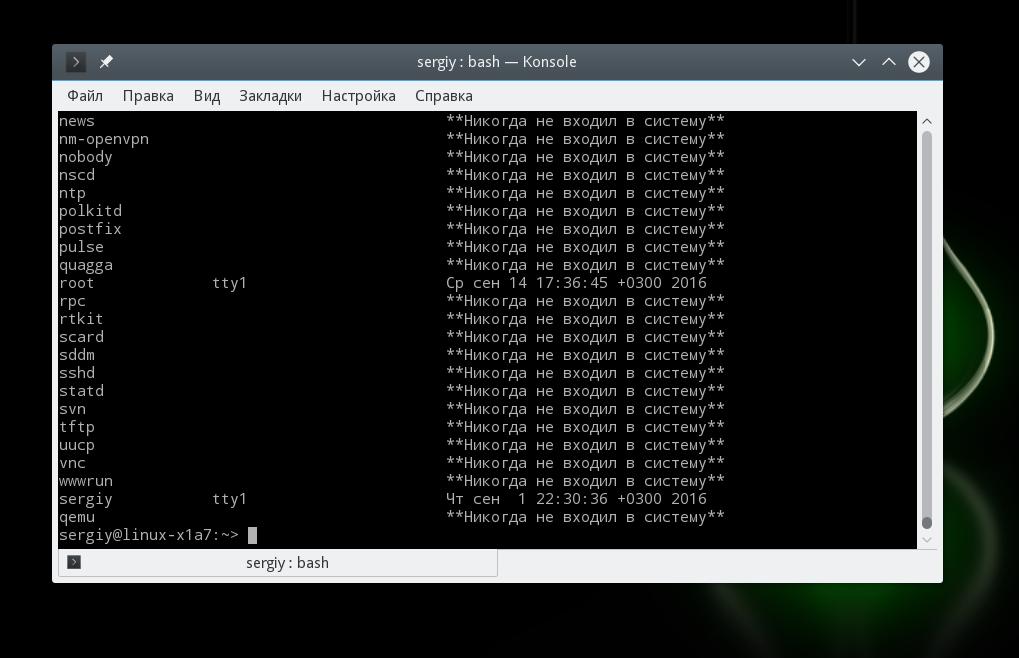
Дату последнего входа для каждого пользователя вы можете посмотреть с помощью команды lastlog:
Если пользователь никогда не входил, команда так и скажет, в противном случае мы увидим дату последнего входа.
Список пользователей в GUI
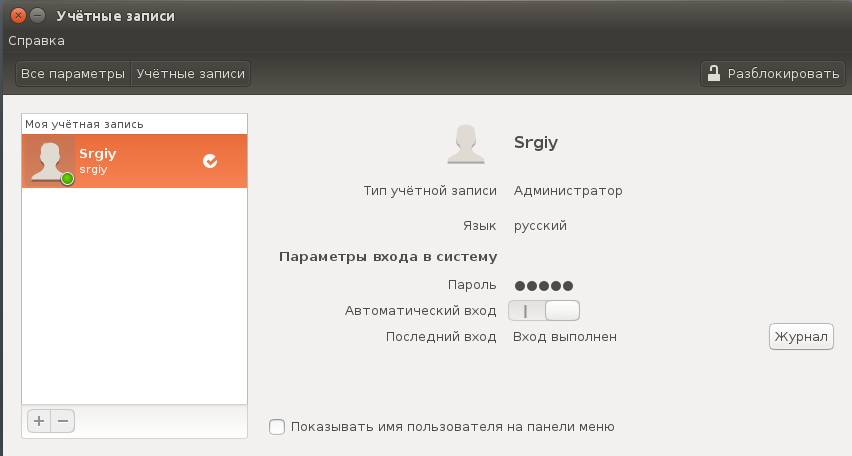
В Ubuntu зарегистрированными в системе пользователями можно управлять с помощью параметров системы. Откройте утилиту и выберите в самом низу пункт Учетные записи. Здесь уже не будут отображаться системные пользователи. В панели слева — непосредственно сам список, а справа можно изменить данные и настройки:
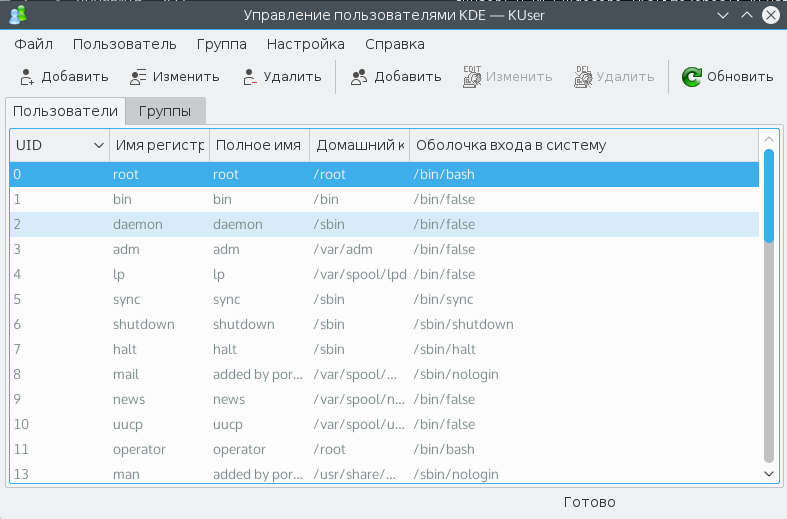
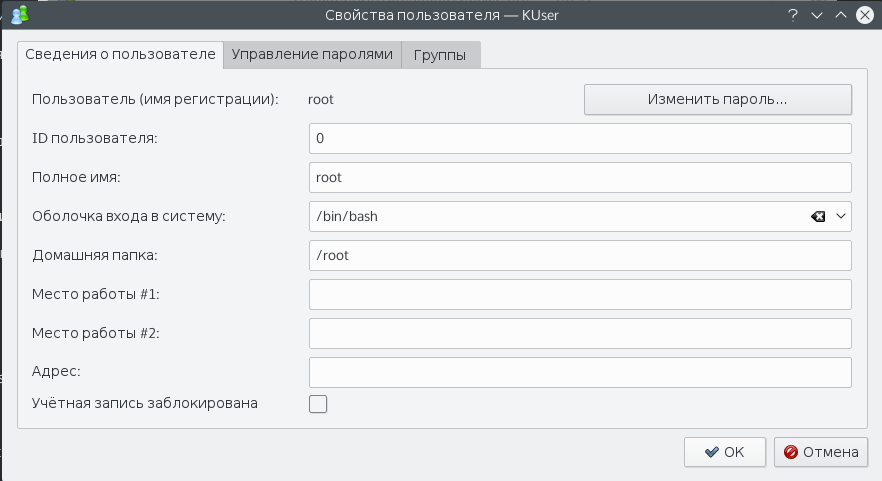
Для KDE есть более интересная утилита управления пользователями — KUser:
Здесь так же как и в терминале отображены все пользователи, в том числе системные. Можно менять различные данные, в том числе пароли, основную и дополнительную группы и т д.
Как видите, только в терминале вы можете посмотреть более подробную информацию, проверить даты входа и точно узнать не используют ли систему другие люди.
Выводы
Теперь вы знаете как посмотреть список пользователей Ubuntu. Это не очень сложно, но нужно только понять основы того как это работает. Если у вас остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях!
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
How to List users in Linux? [Linux List Users]
As you know that there are commands for creating users and deleting users. How to check logged-in users do you what which commands are used to list users in Linux? That is popularly known as Linux List Users commands. Let’s discuss it more.
List of content you will read in this article:
Linux supports multiple users; thus, sometimes, it becomes necessary to keep track of all the users and groups available on the system. Therefore, the system administrator must ensure complete security so no user can violate the system’s security by running unauthorized commands or access.
Not all the users on the system have the same rights. These users are specified within different groups based on their level of privileges. Some users are dedicated to running critical tasks, while some have only read access. All this is necessary to keep the system and data security. Thus, the system administrator must know how to take out the system users’ list.
In this article, we will explore various ways to look at the list of all the users by executing multiple Linux commands or Linux list users commands that the user can run with proper access.
How to list users in Linux? [List Users Linux Command]
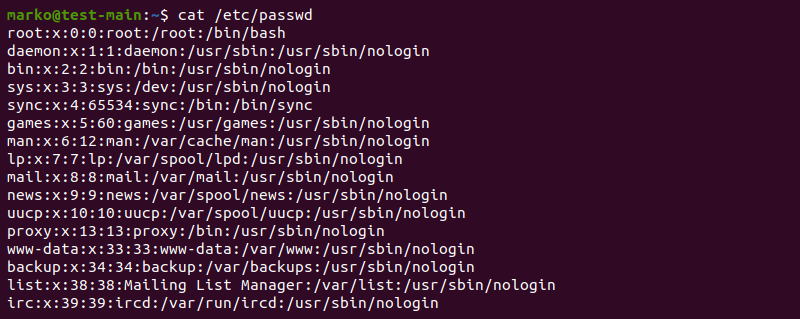
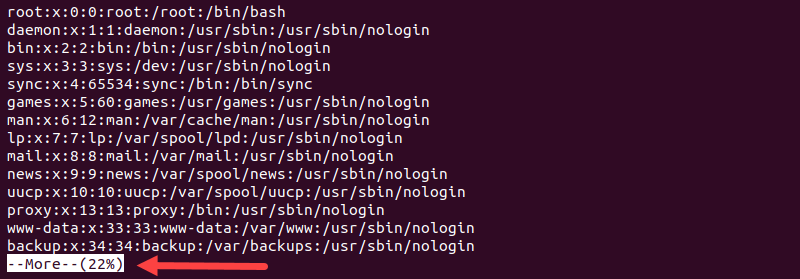
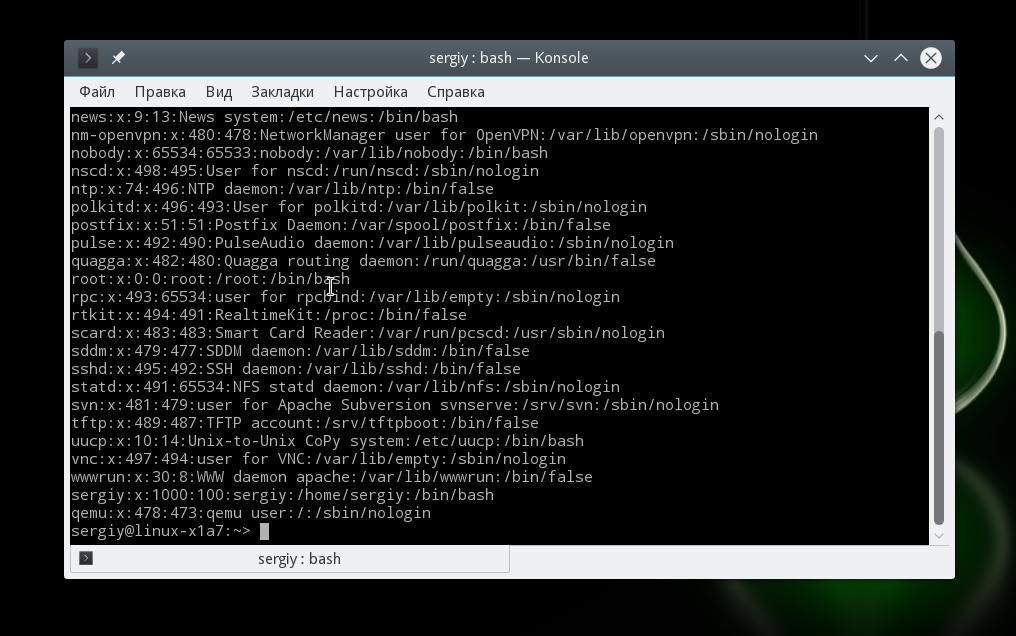
Linux contains some files that store information about all the users. The file is “/etc/passwd” which keeps the currently available users on the system. To look at the information in the file, you can execute the cat command , “more”, or “less” commands per your requirement.
$ cat /etc/passwd
$ less /etc/passwd
$ more /etc/passwd
In the above output, you can see various columns containing different information about the user. Let’s take a look to understand what this output means.
We will specify the details in the given order.
As you can see, the password is specified as “x,” which means the password is stored in the encrypted form so that no one can misuse the user’s account.
1. List Linux users by using the CUT command
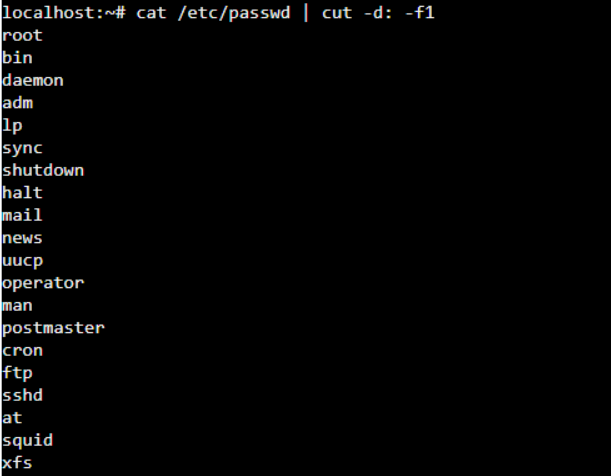
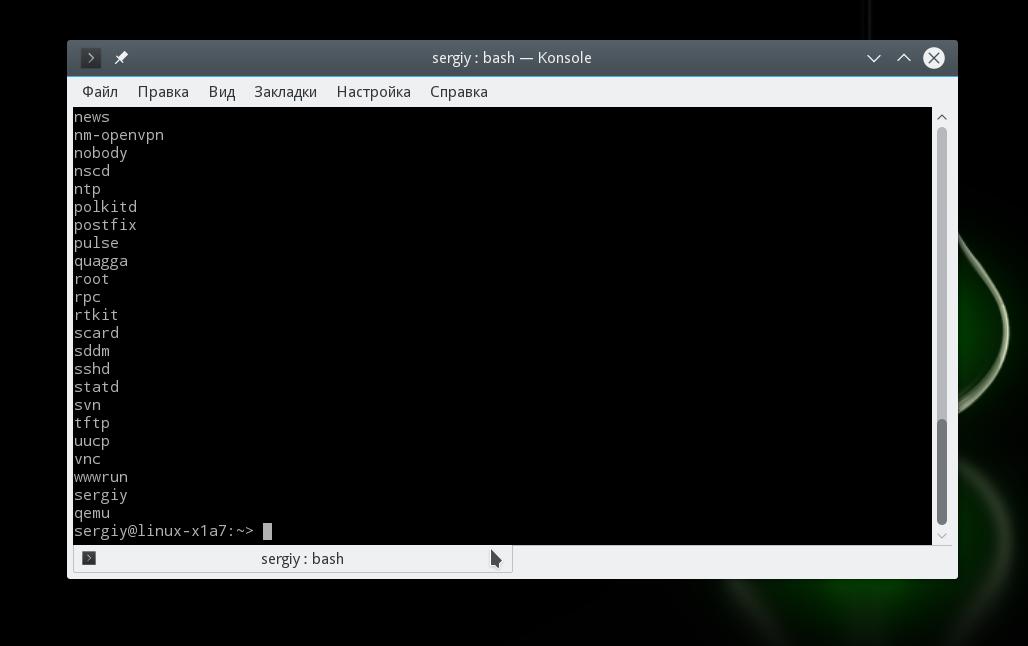
If you only want to display the usernames from the ‘/etc/passwd” file, you can pipe the cat command’s output to the “cut” command, as shown below.
The “cut” command used the “:” as the separator. You print all users’ lists, then pipe to the cut command as per the above command. Then we will only get the first column of the result, which is the usernames from the passwd file, as shown below.
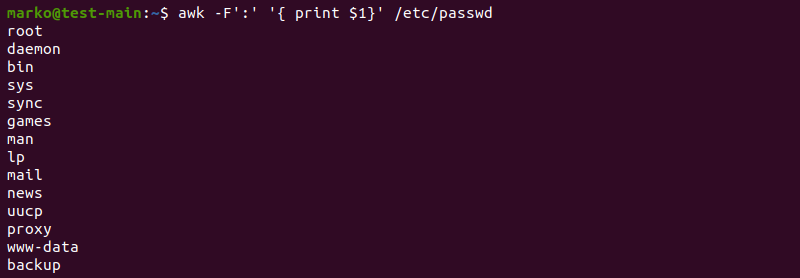
2. Linux users list by using “awk” command
Another way to display all the lists with only the usernames is to execute the cat command and pipe the output to the “awk” command, which works almost similarly to the “cut” command. The awk command is an interpreter for the AWK programming language that helps extract and manipulate the data streams. It makes it easier to execute even the complex commands that any other command cannot do.
The example below shows how the “awk” command works and displays the output.
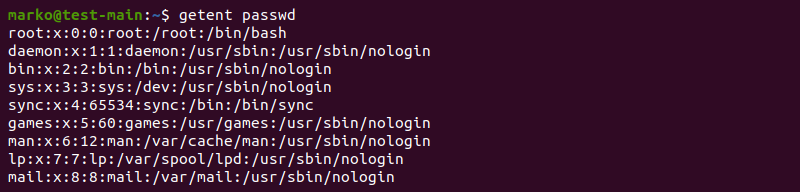
3. L ist Users in Linux by Using getent command
One of the simple ways to list all the Linux users is to hit the “getent” command along with the “passwd” argument and an optional user you want to list on your system, as shown below.
The getent command takes all its entries from Name Service Switch databases such as LDAP, DNS server, etc. all the details regarding these data sources are present in the config file- nsswitch.conf, which is located under the /etc. Folder.
4. Listing all the connected users on the Linux host
The “cat” command on the “passwd” file will not display all the connected users on the Linux host. You need to execute the “who” or “users” command.
The above two commands will list only the connected users on the system when executing the command.
5. Using “/etc/group” for listing the groups on Linux
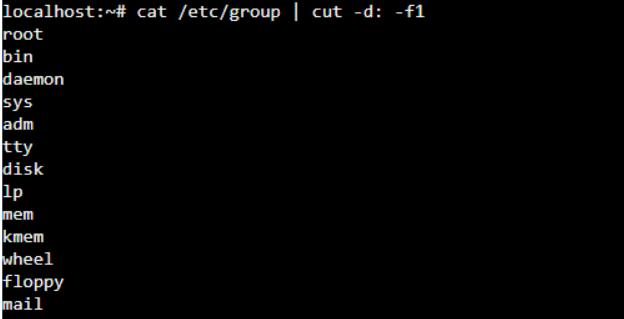
Other than listing users, Linux allows you to list all the groups available on the system. All the group details are stirred in the file- /etc/group. You can execute the “cat”, “less”, or” more” commands on this file to display its content.
In the above output, you can see some details, and we will explain the meaning of different columns of the /etc/group file.
- The root is the group name.
- x is the password in the encrypted form
- 0 is the GID (group ID)
- The root is the user present in the group.
6. Linux group list Using the “cat” command
As you can see in the above example, the details are too cumbersome. So to only get the details of the groups, you can use the cat command on the “/etc/group” file and pipe the output to the “cut” command as we did with the “passwd” file, as shown below.
7. Group list in Linux by getent command
You can use the following syntax of the “getent” command to display the group list.
Here, the database is the group, and the key is optional. But if you do not provide any value for the parameter key, you will get the details of the complete group file.
To the details of one specific group, you can specify it as shown below.
Conclusion
For every Linux system administrator, it is essential to know its users and their access to the system. For that knowing the users is necessary from a security point of view. To get the user’s details, Linux offers various simple commands. We have mentioned some of the commands in this article and how they work with different arguments.
Try this Linux commands yourself and understand the working of Linux list users.
People also read:
How to List Users in Linux
User management is a critical Linux system administration task. In large organizations, having insight into who has access to the system is crucial to correctly add users, remove users, and assign new user privileges.
This tutorial will show you how to list users on a Linux-based system. The guide provides four listing methods and explains essential concepts related to user administration.
Listing Users in Linux
Linux stores information about local users in the /etc/passwd file. Each line in the file contains information about a single user, including their username, user ID number (UID), home directory, and the login shell.
The following sections present multiple ways to access the data in /etc/passwd and list users on Linux distributions.
The commands used in the tutorial are:
Note: To display a list of the logged-on users and the information such as boot time, processes, hostnames, and more, use the who command.
List Users with cat Command
The cat command provides a straightforward way to list the contents of the /etc/passwd file.
The system outputs the entire file with all the users on the system.
To view the number of users only, pipe the output of the previous command to the wc command and make it count the number of lines:
The number of lines in /etc/passwd corresponds to the total number of users.
List Users with Terminal Pagers less and more
On systems with many users, it is useful to limit the /etc/passwd file output displayed at once. Use a terminal pager command, such as less or more , to browse through the file content line by line or page by page.
To open /etc/passwd using less , enter:
The first page of the file appears in the output. The list stops when it reaches the end of the terminal screen. Use the keyboard to navigate through the file.
Use more to get a similar result. This command is older and has a more limited set of functionalities:
List Users with awk Command
Use the awk command to list the usernames only, without additional information about each user. Since the data fields in /etc/passwd are separated by a colon symbol, the following syntax tells awk to output only the first field in each line:
Combine awk and less for a page-by-page view of the results.
List Users with getent Command
The getent command searches and displays system database entries. The searchable databases are listed in the /etc/nsswitch.conf file. By default, the file includes the passwd database.
List the entire contents of the passwd database by typing:
The output is the same as the output of the cat command.
However, you can use getent to look up specific users. To do so, use the following syntax:
If the user exists on the system, the command shows the related passwd entry line.
Listing Normal and System users in Linux
Linux-based systems have two types of users — system and normal users.
- System users are entities created by the system to run non-interactive processes, i.e., the processes that run in the background and do not require human interaction. The most important system user is root, which possesses administrative privileges.
- Normal users are human users created by root or another user with root privileges. Each normal user has a login shell and a home directory to store their files.
Both system and normal users in Linux have a unique user ID (UID) to identify them. System users have UIDs in the range from 0 (root user) to 999. Normal users typically receive UIDs from 1000 onwards, with each newly created user receiving the next smallest unused UID.
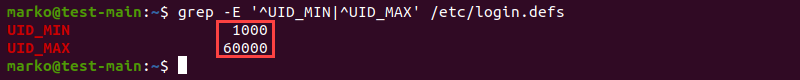
To check the UID range for normal users, use the grep command to search for the information stored in /etc/login.defs :
grep -E '^UID_MIN|^UID_MAX' /etc/login.defsThe output in this example shows that the smallest UID a normal user can receive is 1000, and the largest is 60000.
Use getent to search the passwd database by UID:
The output shows the user entry related to the UID.
Use UIDs in combination with getent to search for users in a range:
The command now lists all the users within the specified UID range.
This guide showed you how to list all Linux users, search for users, and find the number of Linux users in any Linux distribution.
![How to List users in Linux? [Linux List Users]](https://monovm.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/linux-list-users345-main.webp)