- How to copy and paste a file?
- 4 Answers 4
- How to Copy and Paste in Linux and Ubuntu Terminal
- Using Keyboard Shortcut
- Using Mouse Right-Click Context Menu
- Using Mouse Middle Key
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Swapnil Tirthakar
- How to Copy Paste in Linux Terminal [For Absolute Beginners]
- How to copy and paste text and commands in the Linux terminal
- Method 1: Using keyboard shortcuts for copy-pasting in the terminal
- Method 2: Using right-click context menu for copy-pasting in the terminal
- Method 3: Use the mouse to copy and paste into the Linux terminal
- Why Linux terminals do not use the ‘universal’ Ctrl+C and Ctrl+V for
- There are no universal key shortcuts for copy-paste in the Linux terminal. Here’s why!
- Conclusion
How to copy and paste a file?
I want copy and paste a file. The name of the file is mkoctfile.m .
The path of this file is: /usr/share/octave/3.2.4/m/miscellaneous/mkoctfile.m I want to paste it to the following path /usr/bin/mkoctfile-3.2.4 I have made the directory by using following commands: sudo su mkdir -p /usr/bin/mkoctfile-3.2.4 but I don’t know how to copy and paste mkoctfile.m in this path. Please tell me what command I have to use.
4 Answers 4
Use the cp command to copy a file, the syntax goes cp sourcefile destinationfile . Use the mv command to move the file, basically cut and paste it somewhere else.
The exact syntax you would use for your example is:
sudo cp /usr/bin/octave/3.2.4/m/miscellaneous/mkoctfile.m /usr/bin/mkoctfile-3.2.4 For more information on the cp or mv commands you can run:
To @BKSurgeon, I would suggest to use the tab key to see the paths/directories available, or type ls to see them all at once printed.
I think it is better to use cp -a than just cp , if you want to have the same affect as when copy-pasting in desktop GUI.
You can cut, copy, and paste in CLI intuitively like the way you usually did in the GUI, like so:
- cd to the folder containing files you want to copy or cut.
- copy file1 file2 folder1 folder2 or cut file1 folder1
- close the current terminal.
- open another terminal.
- cd to the folder where you want to paste them.
- paste
To be able to do so, make sure you have installed xclip and realpath . Then, append these functions to the end of your ~/.bashrc file:
copy() < # if the number of arguments equals 0 if [ $# -eq 0 ] then # if there are no arguments, save the folder you are currently in to the clipboard pwd | xclip else # save the number of argument/path to `~/.numToCopy` file. echo $# >~/.numToCopy # save all paths to clipboard # https://stackoverflow.com/q/5265702/9157799#comment128297633_5265775 realpath -s "$@" | xclip fi # mark that you want to do a copy operation echo "copy" > ~/.copyOrCut > cut() < # use the previous function to save the paths to clipboard copy "$@" # but mark it as a cut operation echo "cut" >~/.copyOrCut > paste() < # for every path for ((i=1; i If you don't know what .bashrc file is and never modify it before, just open the file explorer, go to Home, press Ctrl+H (show hidden files), search for .bashrc and open it with a text editor like gedit.
By using the above script, you are overriding the default functionality of these commands:
If you use one of those commands default functionality, just modify the script function names accordingly. For example, use p instead of paste .
How to Copy and Paste in Linux and Ubuntu Terminal
When you switch to Linux from Microsoft Windows, especially if you are a programmer, there is a possibility that you might struggle to copy and paste commands or lines in the Linux Terminal window.
Even when I ported to Ubuntu from Windows a decade ago, I struggled to copy and paste lines in the Linux terminal. At that time, I thought I’m the only user struggling to copy and paste. However, while searching on the Internet, I realized that it is a global problem.
The reason is a keyboard shortcut and mouse keys to copy and paste lines in the Linux terminal windows are not the same as the ones we use on Windows.
The key bindings for copy and paste operations are dependent on the specific terminal emulator you are using. In Linux, by default CTRL + C key binding is used for sending an interrupt signal to the command running in foreground. Hence, the Linux terminals do not use the standard CTRL + C and CTRL + V for copy and paste operations.
Using Keyboard Shortcut
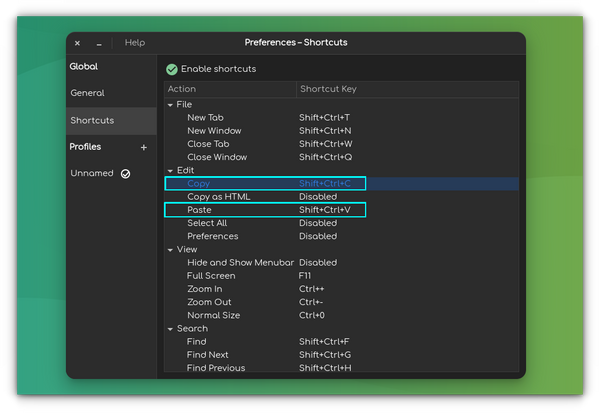
On Ubuntu and other Linux distributions, you have to use CTRL + SHIFT + C combination of keys to copy text from a terminal or a text editor.
To copy a text or line of code from the browser, you can use the generic CTRL + C combination or CTRL + SHIFT + C. Then, to paste this line of code into the terminal, you need to use CTRL + SHIFT + V keys.
You have to use these key combinations in Ubuntu to perform copy and paste operations, especially in the Linux Terminal.
Using Mouse Right-Click Context Menu
The other way to copy and paste in the Linux terminal is to use Mouse right key context menu.
To copy the text or line in terminal, select the text then right click and select copy. Now, to paste the selected text, right-click and select paste from context menu.
Using Mouse Middle Key
This method is not so much popular among Linux users but still effective on some Linux distributions. In this method, you need to select the text you want to copy and paste. Then, press the scrolling wheel button, which is the middle button on the mouse, to paste the selected text.
This is how you can copy and paste text in Linux terminal. It is simple yet confusing for new Linux users, especially those switching to Linux from Windows or Mac. The mentioned methods may or may not work in various Linux distributions for the reason mentioned earlier in this article.
Conclusion
The copy and paste commands in the Linux and Ubuntu Terminals are different from Microsoft Windows and Mac. There are three methods to copy and paste in the Linux and Ubuntu Terminal. These methods are the use of the specific keyboard shortcuts, the use of the mouse right-click menu, and the use of the mouse middle key. When you implement the methods provided, you can successfully copy and paste in the Linux and Ubuntu Terminals. I hope this article helped you efficiently use the copy and paste command. To learn more, check out the other articles on LinuxHint.com.
About the author
Swapnil Tirthakar
A Software Engineer who loves football and passionate about traveling. I often spend my free time playing with gadgets and exploring new possibilities in tech world. I am Linux enthusiast and have about 6 years of experience in web development. I have good command on Python, Java, SQL and system security.
How to Copy Paste in Linux Terminal [For Absolute Beginners]
Here are various ways to copy paste text and commands in Linux terminal along with explanation on why Ctrl+C and Ctrl+V doesn't work in the terminal.
I have been using Linux for a decade now and this is why sometimes I take things for granted. Copy-pasting in the Linux terminal is one such thing. I thought everyone already knew this until one of the It’s FOSS readers asked me this question. I gave the following suggestion to the Ubuntu user:
Use Ctrl+Insert or Ctrl+Shift+C for copying and Shift+Insert or Ctrl+Shift+V for pasting text in the terminal in Ubuntu. Right-click and select the copy/paste option from the context menu is also an option.
I thought of elaborating on this topic especially when there is no single universal way of copying and pasting in the Linux terminal.
How to copy and paste text and commands in the Linux terminal
Method 1: Using keyboard shortcuts for copy-pasting in the terminal
On Ubuntu and many other Linux distributions, you can use Ctrl+Insert or Ctrl+shift+C for copying text and Shift+Insert or Ctrl+shift+V for pasting text in the terminal. The copy-pasting also works for external sources. If you copy a command example from It’s FOSS website (using the generic Ctrl+C keys), you can paste this command into the terminal using the Ctrl+Shift+V into the terminal. Similarly, you can use Ctrl+shift+C to copy text from the terminal and then use it to paste in a text editor or web browser using the regular Ctrl+V shortcut. Basically, when you are interacting with the Linux terminal, you use the Ctrl+Shift+C/V for copy-pasting.
Method 2: Using right-click context menu for copy-pasting in the terminal
Another way of copying and pasting in the terminal is by using the right-click context menu. Select the text in the terminal, right click and select Copy. Similarly, to paste the selected text, right-click and select Paste.
Method 3: Use the mouse to copy and paste into the Linux terminal
Another way to copy-paste in a Linux terminal is by using only the mouse. You can select the text you want to copy and then press the middle mouse button (scrolling wheel) to paste the copied text. Please keep in mind that these methods may not work in all the Linux distributions for a specific reason that I explain in the next section.
Why Linux terminals do not use the ‘universal’ Ctrl+C and Ctrl+V for
No Linux terminal will give you Ctrl+C for copying the text. This is because by default Ctrl+C keybinding is used for sending an interrupt signal to the command running in the foreground. This usually stops the running command. This behaviour has been existing long before Ctrl+C and Ctrl+V started being used for copy-pasting text. Since the Ctrl+C keys are ‘reserved’ for stopping a command, they cannot be used for copying.
Used Ctrl+S and hanged the terminal?
The keyboard shortcut CTRL + S in the Linux terminal is used to send a "stop" signal to the terminal, which results in a frozen terminal. Just use Ctrl+Q and you can use the terminal again.
There are no universal key shortcuts for copy-paste in the Linux terminal. Here’s why!
The keybindings for copy-pasting are dependent on the terminal emulator (commonly known as terminal) you are using. If you didn’t know that already, a terminal is just an application, and you can install other terminals like Guake or Terminator. Different terminal applications may have their own keybindings for copying and pasting like Alt+C/V or Ctrl+Alt+C/V. Most Linux terminals use the Ctrl+Shift+C/V keys but if it doesn’t work for you, you may try other key combinations or configure the keys from the preferences of the terminal emulator.
Conclusion
I know this is elementary for the Sherlock Holmes of the Linux world but it could still be useful to the Watsons. If you are absolutely new to the terminal, this is going to help you a great deal. New or not, you may always use shortcuts in the Linux terminal to make your life easier. If you really care about increasing productivity through the Linux terminal, these handy Linux command tips and tricks will be a good starting point. 💬 Do you still have questions? The comment section is all yours.