- 8 fundamental Linux file-management commands for new users
- What’s there?
- Career advice
- Manage directories
- Manage files
- Organize files
- Linux containers
- How to Create, Read, Edit, and Delete Files in Ubuntu 22.04
- How to Create, Read, Edit, and Delete Files in Ubuntu 22.04
- How to Create Files in Ubuntu 22.04
- How to read Files on Ubuntu 22.04
- How to Edit Files on Ubuntu 22.04
- How to Delete the Files in Ubuntu 22.04
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Hammad Zahid
8 fundamental Linux file-management commands for new users
Learn how to create, copy, move, rename, and delete files and directories from the Linux command line.
I’m a believer in the basics, and as a former technical instructor, I have a soft spot for folks who are new to Linux (and other platforms). I’ve written articles on the fundamentals, and I thought it was time to cover some basic file-manipulation commands.
This article looks at day-to-day tasks such as copying, moving, renaming, creating, and deleting files and directories. Here are eight commands to make managing files easier.
What’s there?
Before you can manage files, you must know what files are present. The ls command displays the contents of the current or specified directories.
Career advice
Of course, ls has many useful options. Here are three of my favorites:
- -l Long format (to display permissions)
- -a All files, including hidden files
- -Z SELinux context
It’s certainly useful to view the contents of directories, but what about the contents of files? There are many ways of doing this, but I’ll point out the cat command here. It’s a quick way of seeing what’s in a file.
The pipe character (that’s the | symbol above the backslash on a US keyboard) is a signal to the terminal that you want to combine commands. It allows you to «pipe» the output of one command to the input of another.
For example, combine the cat command with | grep to search the contents of the file for a specific string of characters.
Commands such as less , more , most , head , and tail are all useful for displaying file contents. For most of these commands, the syntax is simply the command name followed by the filename.
See Getting started with ls for lots more tricks using the ls command.
Manage directories
Displaying files and directories is one thing, but managing them is another. In an effort to organize your files better, you may want to create one or more new directories. You may also find directories you no longer need.
To create a new directory, simply type the mkdir command and specify the directory name (and, if necessary, the path to it). The rmdir removes any empty directories for you.
Unfortunately, directories you wish to delete in most cleanup scenarios are not empty. In that case, there are two tricks to help. The first is to delete the directory and its contents in one command, and the second is to disable the interactive confirmation prompt temporarily.
First, to delete a non-empty directory, use the file-deletion command rm and add the -R (recursive) option. To delete the non-empty directory projects , type
rm -R projects .
[ For more tips, download the Linux commands cheat sheet. ]
Many distributions, RHEL and Fedora among them, prompt users to confirm any deletions. Normally, this is a good thing, but if you’re deleting a directory with 100 files in it, you certainly don’t want to type y for each file. In that case, use the -f (force) option. This option overrides the prompt and deletes the specified files. This can be incredibly dangerous, so be very careful and aware before using this option. Make certain you understand what’s in the directory you’re deleting.
In fact, consider using a trash command to safeguard yourself from mistakes because, although there’s an rm command, there’s no un- rm , at least not without a great deal of filesystem forensics with a tool like Scalpel or TestDisk.
Manage files
Text editors such as Vim and Nano can create new files, but sometimes it’s handy to create an empty file quickly. I used to use the touch command in classroom demonstrations to make files to work with tools such as tar , cp , mv , and others.
Officially, touch updates the timestamp on existing files, but one side effect of the command is that if the file doesn’t exist, touch creates it.
To remove a file, use the rm command. This is the same command used above to delete a non-empty directory. Again, you can use the -f option to remove files without being prompted for confirmation, but this is dangerous.
Organize files
Linux containers
The cp command copies files. This is useful for backing up configuration files before making changes to them. The syntax of cp is simple: copy from here to there. To copy the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file to your home directory, type cp /etc/sshd_config ~ . The path to the config file is the source, and your home directory is the destination.
Depending on whether the cp command is aliased to cp -i on your system, it may overwrite existing files without warning, or it may prompt you to confirm each copy action that may overwrite a file. As with the rm command, you must take care with regard to overwriting files.
Moving files from one location to another uses the same syntax but with the mv command. Therefore, moving files is straightforward.
What’s more interesting about the mv command is that it’s also the rename command. The logic is that you’re moving the file to the same location, just with a different name. So, to rename file1.txt to fileA.txt , type mv file1.txt fileA.txt . Keep in mind that mv can overwrite existing files, so be sure to check filenames before initiating mv .
How to Create, Read, Edit, and Delete Files in Ubuntu 22.04
In Ubuntu, we can create different types of files by running some simple commands because it is known that Ubuntu can be managed through the terminal. In this blog, some simple commands for creating, editing, reading, and deleting different types of files are going to be discovered.
How to Create, Read, Edit, and Delete Files in Ubuntu 22.04
The blog has been divided into different sections which explain:
How to Create Files in Ubuntu 22.04
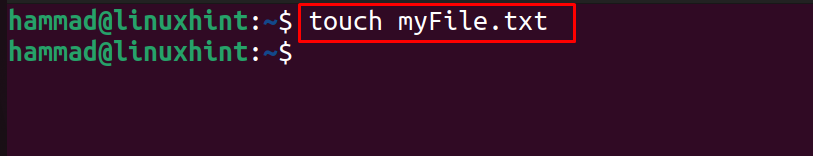
Different types of files can be created by simply using the touch command and if the files are of some specified formats then use the extensions as well, for example, a text file with the name of myFile will be created using the command:
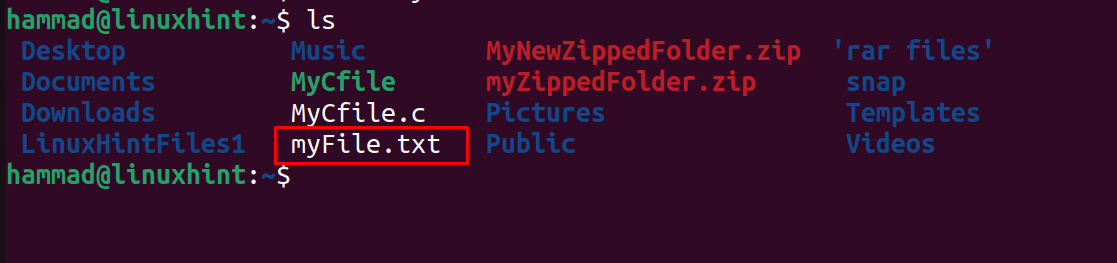
When the command is executed successfully, list down the contents of the directory to confirm the creation of file:
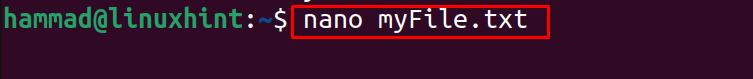
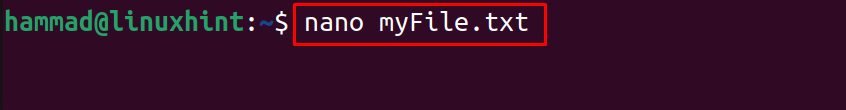
In the above output, it can be seen that the file is created, now open the file using the nano text editor:
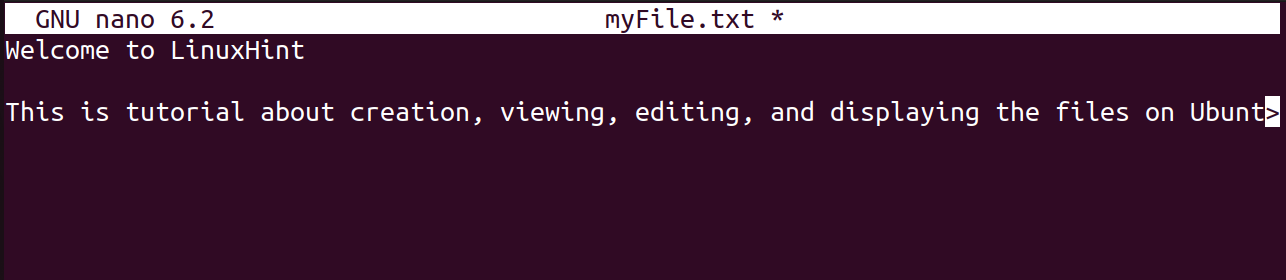
Type some text in the file:
Close the file with a shortcut key of CTRL+X after saving it with CTRL+S.
How to read Files on Ubuntu 22.04
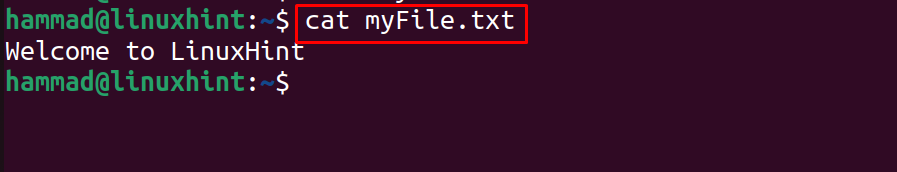
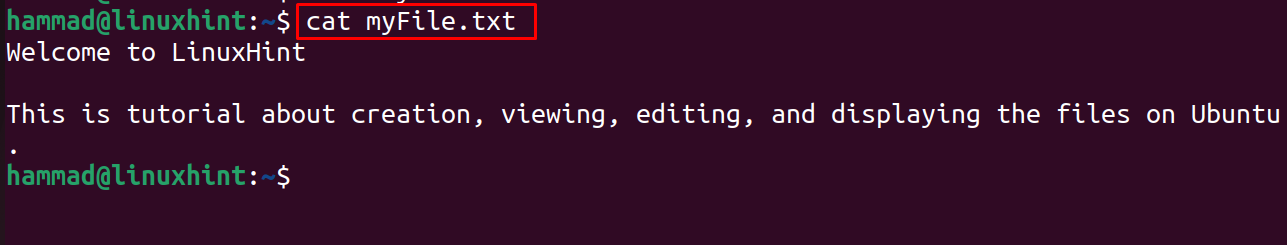
For reading files on Ubuntu, the cat command utility can be used. For example, to read the file created in the above section, use the command:
The message of the file is displayed on the screen.
How to Edit Files on Ubuntu 22.04
To edit the already created files, open them with some text editors like Vim and Nano here the files are being opened by the nano text editor:
Type some more new lines in the file:
Exit the nano text editor by saving the new change made with the shortcut key of CTRL+S and then use the cat command to view the file:
The edited changes can be read in the above output.
How to Delete the Files in Ubuntu 22.04
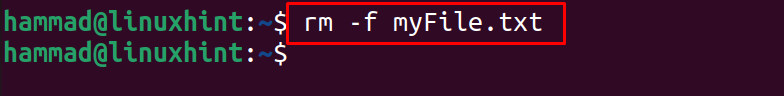
To delete the files in Ubuntu, use the rm command with the “-f” flag, which is used to remove files. For example, to remove the myFile.txt, use the command:
After deleting the file, list down the contents to confirm deletion:
The file has been deleted successfully.
Conclusion
The touch command is used to create files, the cat command to read files, the nano text editor to edit files, and the rm command to delete files on Ubuntu 22.04. In this blog, an example is considered to explain the commands for the creation, reading, editing, and deleting of the files in Ubuntu 22.04.
About the author
Hammad Zahid
I’m an Engineering graduate and my passion for IT has brought me to Linux. Now here I’m learning and sharing my knowledge with the world.