- How to Create an Empty File Linux?
- Method 1: Create an Empty File Using the “touch” Command
- Method 2: Create an Empty File Using the “echo” Command
- Method 3: Create an Empty File Using Nano Editor
- Method 4: Create an Empty File Using “printf” Command
- Bonus Tip: How to Check the Status of an Empty File?
- Conclusion
- 4 Ways to Create a Text File in Linux Terminal
- Create file in Linux command line
- 1. Create an empty file using touch command
- 2. Create files using cat command
- 3. Create new file using echo command
- 4. Create a new file using a text editor like Nano or Vim
- How to Create a File in Linux
- Before you Begin #
- Creating a File with touch Command #
- Creating a File with the Redirection Operator #
- Creating a File with cat Command #
- Creating a File with echo Command #
- Creating a File using Heredoc #
- Creating a Large File #
- Using dd command #
- Using fallocate command #
How to Create an Empty File Linux?
Creating an empty file is an important concept to manage the record before writing data in it. It occupies 0 bytes because no data is stored in it. If you are at the beginner stage of Linux user and don’t know the creation of empty files for storing data or information. This guide will demonstrate several methods to create an empty file in the Ubuntu system. The supported content is enlisted below:
- Method 1: Create an Empty File Using the “touch” Command
- Method 2: Create an Empty File Using the “echo” Command
- Method 3: Create an Empty File Using Nano Editor
- Method 4: Create an Empty File Using “printf” Command
- Bonus Tip: How to Check the Status of an Empty File?
Method 1: Create an Empty File Using the “touch” Command
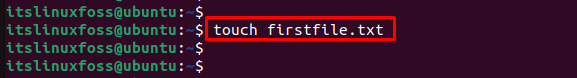
In Linux, most administrators need to create empty files to manage multiple files with the name of network users. The “touch” command helps to create an empty file by specifying the name based on needs. To create an empty file, run the below script:
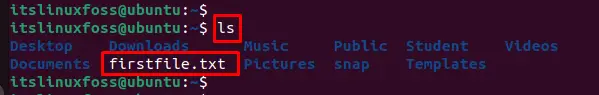
Using the “ls” command, you can verify that “firstfile.txt” has been created in the Home directory:
Method 2: Create an Empty File Using the “echo” Command
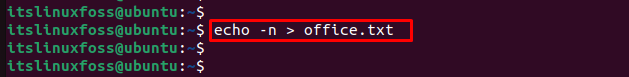
An alternative method for creating an empty file is possible through the “echo” command. This command requires the “-n” utility to create an empty file specifying the name and file type.
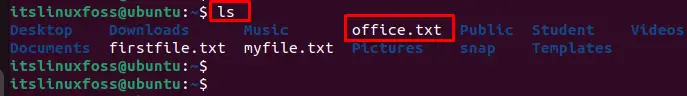
To confirm the creation of the empty file, you can utilize the “ls” command to visualize the “office.txt” has been successfully created in the directory.
Method 3: Create an Empty File Using Nano Editor
Another method can be considered to generate an empty file via Nano Editor. For instance, the “officefile.txt” file has been created through the “nano” command:
After executing the above command, it navigates to the Nano Editor by specifying the particular file name.
The empty file is ready, as visualized in the above figure.
Method 4: Create an Empty File Using “printf” Command
An interesting method can also be adapted for creating an empty file through the “printf” command. For this purpose, an “empfile.txt” will be created after executing the below script:
After executing the script, the “empfile.txt” has been created that can be visualized via the “ls” command:
That is all for creating an empty file.
Bonus Tip: How to Check the Status of an Empty File?
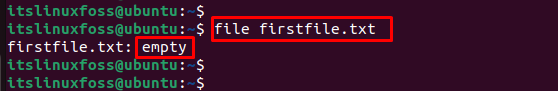
It is additional information to display the status of an empty file. In our case, an existing file, “firstfile.txt”, is stored in the home directory. To check the status of the particular file, run the below script:
The executed command verifies the status “empty” of the particular file “firstfile.txt” in the above figure.
Conclusion
In Ubuntu, the “touch”, “echo”, “nano”, and “printf” commands are used to create an empty file in the home directory. These above commands require the file name and type users want to create. These empty files can be modified through the Nano Editor. Also, users can find out the file status by executing the “ ” script. This guide has explained all possible methods for creating an empty file via the Ubuntu terminal.
4 Ways to Create a Text File in Linux Terminal
In this Linux beginner series, you’ll learn various methods to create a file in Linux terminal.
In this Linux beginner series, you’ll learn various methods to create a text file in Linux terminal.
If you have used the desktop oriented operating system such as Windows, creating file is a piece of cake. You right click in the file explorer and you would find the option of creating new file.
Things won’t look the same when you are in a command line environment. There is no right click option here. So how do you create a file in Linux then? Let me show you that.
Create file in Linux command line
There are various ways of creating a new file in Linux terminal. I’ll show you the commands one by one. I am using Ubuntu here but creating files in Ubuntu terminal is the same as any other Linux distribution.
1. Create an empty file using touch command
One of the biggest usages of the touch command in Linux is to create a new empty file. The syntax is super simple.
If the file doesn’t exist already, it will create a new empty file. If a file with the same name exists already, it will update the timestamps of the file.
2. Create files using cat command
Another popular way of creating new file is by using the cat command in Linux. The cat command is mostly used for viewing the content of a file but you can use it to create new file as well.
You can write some new text at this time if you want but that’s not necessary. To save and exit, use Ctrl+D terminal shortcut.
If the file with that name already exists and you write new text in it using the cat command, the new lines will be appended at the end of the file.
3. Create new file using echo command
The main use of the echo command is to simply repeat (echo) what you type on the screen. But if you use the redirection with echo, you can create a new file.
To create a new file using echo you can use something like this:
echo "This is a sample text" > filename.txtThe newly created filename.txt file will have the following text: This is a sample text. You can view the file in Linux using cat or other viewing commands.
You are not obliged to put a sample text with echo. You can create an (almost) empty file using the echo command like this:
This will create a new file with just one empty line. You can check the number of lines with wc command.
4. Create a new file using a text editor like Nano or Vim
The last method in this series is the use of a text editor. A terminal-based text editor such as Emacs, Vim or Nano can surely be used for creating a new file in Linux.
Before you use these text editors, you should make sure that you know the basics such as saving an existing from the editor. Unlike the GUI tools, using Ctrl+S in the terminal won’t save the file. It could, in fact, send your terminal into a seemingly frozen state from which you recover using Ctrl+Q.
Let’s say you are going to use Vim editor. Make sure that you are aware of the basic vim commands, and then open a new file with it like this:
What’s your favorite command?
So, I just shared 4 different ways of creating a file in Linux. Personally, I prefer using touch for creating empty file and Vim if I have to edit the file. On a related note, you may want to learn about the file command in Linux that is helpful in determining the actual type of the file.
Which command do you prefer here? Please share your views in the comment section below.
How to Create a File in Linux
Knowing how to create a new file is an important skill for anyone using Linux on a regular basis. You can create a new file either from the command line or from the desktop file manager.
In this tutorial, we’ll show you various ways to quickly create a new file in Linux using the command line.
Before you Begin #
To create a new file you need to have write permissions on the parent directory. Otherwise, you will receive a permission denied error.
If you want to display the contents of a directory use the ls command .
Creating a File with touch Command #
The touch command allows us to update the timestamps on existing files and directories as well as creating new, empty files.
The easiest and most memorable way to create new, empty files is by using the touch command.
To create a new file simply run the touch command followed by the name of file you want to create:
If the file file1.txt doesn’t exist the command above will create it, otherwise, it will change its timestamps.
To create multiple files at once, specify the file names separated by space:
touch file1.txt file2.txt file3.txtCreating a File with the Redirection Operator #
Redirection allows you to capture the output from a command and send it as input to another command or file. There are two ways to redirect output to a file. The > operator will overwrite an existing file, while the >> operator will append the output to the file.
To create an empty zero-length file simply specify the name of the file you want to create after the redirection operator:
This is the shortest command to create a new file in Linux.
When creating a file using a redirection, be careful not to overwrite an important existing file.
Creating a File with cat Command #
The cat command is mainly used to read and concatenate files, but it can also be used for creating new files.
To create a new file run the cat command followed by the redirection operator > and the name of the file you want to create. Press Enter type the text and once you are done press the CRTL+D to save the files.
Creating a File with echo Command #
The echo command prints the strings that are passed as arguments to the standard output, which can be redirected to a file.
To create a new file run the echo command followed by the text you want to print and use the redirection operator > to write the output to the file you want to create.
If you want to create an empty simply use:
Creating a File using Heredoc #
Here document or Heredoc is a type of redirection that allows you to pass multiple lines of input to a command.
This method is mostly used when you want to create a file containing multiple lines of text from a shell script.
For example, to create a new file file1.txt you would use the following code:
cat file1.txtSome lineSome other lineEOF
The body of the heredoc can contain variables, special characters, and commands.
Creating a Large File #
Sometimes, for testing purposes, you might want to create a large data file. This is useful when you want to test the write speed of your drive or to test the download speed of your connection.
Using dd command #
The dd command is primarily used to convert and copy files.
To create a file named 1G.test with a size of 1GB you would run:
dd if=/dev/zero of=1G.test bs=1 count=0 seek=1GUsing fallocate command #
fallocate a command-line utility for allocating real disk space for files.
The following command will create a new file named 1G.test with a size of 1GB: