- How to create a file in Linux from terminal window? [closed]
- Create an empty file
- Create a file containing a newline and nothing else
- Write text into a file
- How to Create a File in Linux Using Terminal/Command Line
- Creating New Linux Files from Command Line
- Create a File with Touch Command
- Create a New File With the Redirect Operator
- Create File with cat Command
- Create File with echo Command
- Create File with printf Command
- Using Text Editors to Create a Linux File
- Vi Text Editor
- Vim Text Editor
- Nano Text Editor
- linux create file in directory
- Can mkdir create a file?
- How do you create a file in a specific directory in Unix?
- How do I add files to a folder?
- How do you create a text file in Linux?
- How do you create a directory?
- What does P mean in Linux?
- Can Touch create a directory?
- What Linux command is used to list all files present in a directory?
- How do I copy a file from one directory to another in Linux?
- How do you move files in terminal?
- How do I add a file in Linux?
- How do you read a file in Linux?
- How do I create a .TXT file?
How to create a file in Linux from terminal window? [closed]
- touch /path/to/file for an empty file
- somecommand > /path/to/file for a file containing the output of some command.
eg: grep --help > randomtext.txt echo "This is some text" > randomtext.txt UNIX is not a command line environment, but a family of (very different) OSes. That said: Yes, this should work on most Unices
touch will work in UNIX, because it’s a standard tool. The somecommand example will work because it uses standard syntax. The nano sample may not work because an editor named nano may not be installed (nano is not standardized). The standard editor is ed and could be used in place of nano , or you could use $EDITOR to use your user- or system-configured default text editor, if there is one.
Additionally, you could simply say >/path/to/file to create an empty file, even if you don’t have touch .
Create the file using cat
Now, just type whatever you want in the file:
When I tried cat /etc/systemd/system/sample.service , it said «no such file or directory» rather than creating a new sample.service file.
@TylerH cat /etc/systemd/system/sample.service prints the file to the console cat > /etc/systemd/system/sample.service redirects standard input to the file (which is why you need to close standard input by pressing control-d.
There are several possible solutions:
Create an empty file
touch file >file echo -n > file printf '' > file The echo version will work only if your version of echo supports the -n switch to suppress newlines. This is a non-standard addition. The other examples will all work in a POSIX shell.
Create a file containing a newline and nothing else
echo '' > file printf '\n' > file This is a valid «text file» because it ends in a newline.
Write text into a file
"$EDITOR" file echo 'text' > file cat > file file These are equivalent. The $EDITOR command assumes that you have an interactive text editor defined in the EDITOR environment variable and that you interactively enter equivalent text. The cat version presumes a literal newline after the \ and after each other line. Other than that these will all work in a POSIX shell.
Of course there are many other methods of writing and creating files, too.
How to Create a File in Linux Using Terminal/Command Line
Creating a new file in Linux is straightforward, but there are also some surprising and clever techniques.
In this tutorial learn how to to create a file from a Linux terminal.
- Access to a command line/terminal window (Ctrl–Alt–F2 or Ctrl–Alt–T)
- A user account with sudo privileges (optional for some files/directories)
Creating New Linux Files from Command Line
Linux is designed to create any file you specify, even if it doesn’t already exist. One smart feature is that you can create a file directly, without needing to open an application first.
Here are a few commands for creating a file directly from the command line.
Create a File with Touch Command
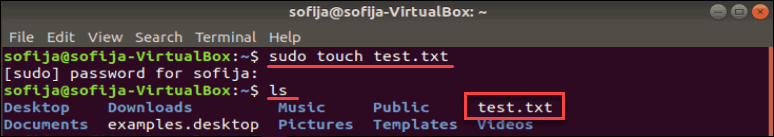
The easiest way to create a new file in Linux is by using the touch command.
In a terminal window, enter the following:
This creates a new empty file named test.txt. You can see it by entering:
The ls command lists the contents of the current directory. Since no other directory was specified, the touch command created the file in the current directory.
If there’s already a file with the name you chose, the touch command will update the timestamp.
Create a New File With the Redirect Operator
A redirection operator is a name for a character that changes the destination where the results are displayed.
Right angle bracket >
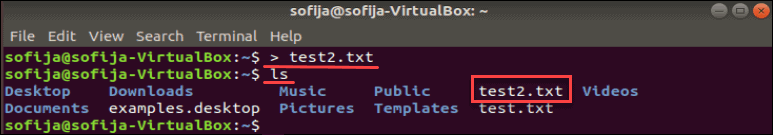
This symbol tells the system to output results into whatever you specify next. The target is usually a filename. You can use this symbol by itself to create a new file:
This creates a new empty file.
Use the ls command to list the contents of the current directory and find the file test2.txt.
Create File with cat Command
The cat command is short for concatenate. It can be used to output the contents of several files, one file, or even part of a file. If the file doesn’t exist, the Linux cat command will create it.
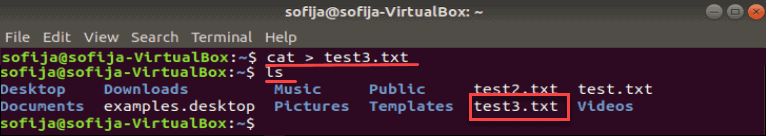
To create an empty file using cat , enter the following:
Note the redirection operator. Typically, the command displays the contents of test2.txt on the screen. The redirection operator > tells the system to place it in the test2.txt file.
Verify that the file was created:
The system should now have test.txt, test2.txt, and test3.txt in the list.
Create File with echo Command
The echo command will duplicate whatever you specify in the command, and put the copy into a file.
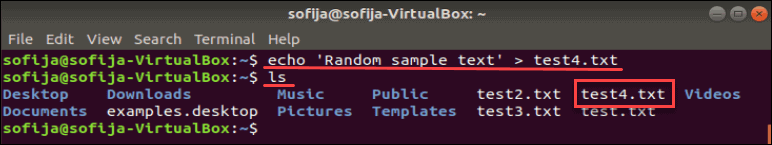
echo 'Random sample text' > test4.txtVerify that the file was created:
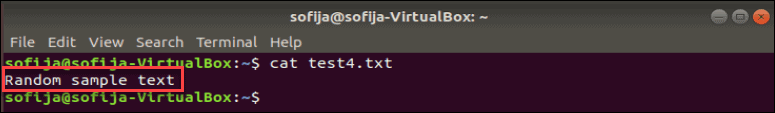
You should see the test4.txt file added to the list. Use the cat command to display the contents of the new file:
The system should display Random sample text (or whatever you entered with the echo command.)
Create File with printf Command
The printf command works like the echo command, and it adds some formatting functionality. To add a single line of text, enter:
printf 'First line of text\n' test5.txtTo add two lines of text, separate each line with the \n option:
printf 'First line of text\n Second line of text' test6.txtYou can use the cat command on either of these files to display their contents.
Note: To use several terminal instances in a single window manager, consider using Linux screen. It enables additional features and an enhanced command line for working with Linux files.
Using Text Editors to Create a Linux File
All Linux distributions have at least one text editor. Some have multiple editors. Each editor has different strengths and features. This will show you three of the most popular.
Vi Text Editor
Vi is the oldest text editor in Linux. It was created alongside the Linux operating system for directly editing text files. Since it’s unlikely you’ll see a Linux distribution without it, it’s a safe editor to know.
To create a file using Vi, enter the following:
Your screen will change. Now you’re in the text editor. Press the letter i to switch to insert mode, then type a few words to try it out.
To save and exit press Esc 😡 and hit Enter .
Vim Text Editor
You may have noticed that the Vi editor wasn’t very user-friendly. Vim is a newer version, which stands for Vi editor, Modified.
Use vim to create a new text file:
This screen will look similar to the Vi editor screen. Press i to insert text, and type a few words. Save file and exit by entering:
(Escape, colon wq, then Enter.)
Nano Text Editor
Nano is a newer and much easier text editor to navigate.
Create a new file by entering the command:
By default, Nano puts you directly into editing mode. It also displays a helpful list of commands at the bottom of the screen.
Enter some text, then press Ctrl+O to save the changes.
Press Ctrl+X to exit the editor.
Note: Learn all you need about Nano in the Install and Use Nano in Linux article.
Now you have several options to create new files in Linux from the command line. Next, learn how to copy files and directories in Linux to manage your files more efficiently.
linux create file in directory
The easiest way to create a new file in Linux is by using the touch command. The ls command lists the contents of the current directory. Since no other directory was specified, the touch command created the file in the current directory.
- Can mkdir create a file?
- How do you create a file in a specific directory in Unix?
- How do I add files to a folder?
- How do you create a text file in Linux?
- How do you create a directory?
- What does P mean in Linux?
- Can Touch create a directory?
- What Linux command is used to list all files present in a directory?
- How do I copy a file from one directory to another in Linux?
- How do you move files in terminal?
- How do I add a file in Linux?
- How do you read a file in Linux?
- How do I create a .TXT file?
Can mkdir create a file?
mkdir creates a file instead of directory.
How do you create a file in a specific directory in Unix?
- touch command: It will create an empty file in directory specified. .
- vi command (or nano): You can use any editor to create a file. .
- cat command: Although cat is used to view file, but you can use this to create file as well from terminal.
How do I add files to a folder?
- You must have a working copy of the directory. .
- Create the new file inside your working copy of the directory.
- Use `cvs add filename ‘ to tell CVS that you want to version control the file. .
- Use `cvs commit filename ‘ to actually check in the file into the repository.
How do you create a text file in Linux?
- Using touch to create a text file: $ touch NewFile.txt.
- Using cat to create a new file: $ cat NewFile.txt. .
- Simply using > to create a text file: $ > NewFile.txt.
- Lastly, we can use any text editor name and then create the file, such as:
How do you create a directory?
- Open Finder and navigate to the directory where you’d like to create the folder.
- Click File in the upper-left corner of the screen.
- Select New Folder in the drop-down menu that appears.
- Name the folder, and then press Return .
What does P mean in Linux?
Linux Directories mkdir -p
It will create parent directory first, if it doesn’t exist. But if it already exists, then it will not print an error message and will move further to create sub-directories. This command is most helpful in the case when you don’t know whether a directory alredy exists or not.
Can Touch create a directory?
touch is not able to create directories, you need mkdir for that. However, mkdir has the useful -p / —parents option which creates a full directory structure. If you think you will need this more often and don’t want to type the path twice every time, you can also make a Bash function or a script for it.
What Linux command is used to list all files present in a directory?
The ls command is used to list files or directories in Linux and other Unix-based operating systems. Just like you navigate in your File explorer or Finder with a GUI, the ls command allows you to list all files or directories in the current directory by default, and further interact with them via the command line.
How do I copy a file from one directory to another in Linux?
‘cp’ command is one of the basic and most widely used Linux commands for copying files and directories from one location to another.
.
Common options for cp command:
| Options | Description |
|---|---|
| -r/R | Copy directories recursively |
| -n | Don’t overwrite an existing file |
| -d | Copy a link file |
| -i | Prompt before overwrite |
How do you move files in terminal?
If you use a visual interface like Finder (or another visual interface), you would have to click and drag this file into its correct location. In Terminal, you don’t have a visual interface, so you’ll have to know the mv command to do this! mv , of course stands for move.
How do I add a file in Linux?
The cat command is mainly used to read and concatenate files, but it can also be used for creating new files. To create a new file run the cat command followed by the redirection operator > and the name of the file you want to create. Press Enter type the text and once you are done press the CRTL+D to save the files.
How do you read a file in Linux?
- Open the file using cat command.
- Open the file using less command.
- Open the file using more command.
- Open the file using nl command.
- Open the file using gnome-open command.
- Open the file using head command.
- Open the file using tail command.
How do I create a .TXT file?
- The editor in your IDE will do fine. .
- Notepad is an editor that will create text files. .
- There are other editors that will also work. .
- Microsoft Word CAN create a text file, but you MUST save it correctly. .
- WordPad will save a text file, but again, the default type is RTF (Rich Text).
Uninstall
How do you uninstall a program installed with make install?How do I uninstall after install?How do I uninstall compiled programs?What is the differenc.
File
How do I convert M4V to WAV?How do I convert M4V files?How do I make a WAV file?How do I convert m4a to mp3 in Ubuntu?How do I convert an M4A file to .
Data
Convert XML to PHP Associative ArrayStep1: Create XML Data File. First we will create XML data file using following XML. . Step2: Read XML Data File.
Latest news, practical advice, detailed reviews and guides. We have everything about the Linux operating system