- How to create a custom bash command in linux
- 3 Answers 3
- How to Create Simple Shell Scripts in Linux
- 1. Create a Simple Shell Script
- 2. Using Conditional Statements to Execute Code
- Example of an if Statement Only
- Example of an if-else Statement
- Example of an if-elif-else Statement
- 3. Using the If Statement with AND Logic
- 5. Using the If Statement with OR Logic
- Use Looping Constructs
- While loop
- For loop
- Bash Positional Parameters
- Shell Command Exit Codes
- Processing Output of Shell Commands within a Script
- How to create my own command in linux
- 1 Answer 1
How to create a custom bash command in linux
The question is about bash shell commands in ubuntu 10.04. I have created a simple addition program in c and it works fine in my terminal. Now I want to make this program to execute into my terminal as a command. How can I convert a C program into a bash shell command?
How to make that command an system command like others?
It’s not really clear what you’re asking, but I assume what you’re looking for is adding the path of your application to the system path.
if you call your cmd as ./myCmd or /path/to/myCmd , either copy/move myCmd to /usr/local/bin , or add export PATH=»/path/to:$PATH» to your .bash_profile . (assuming /usr/local/bin/` is in your PATH already). Else you’ll have to give us an example «I want myCmd to work like xxxx (a std command in bash)`. Good luck.
3 Answers 3
yout just have to change it’s owner & group root following commands sudo chown root «file_name» sudo chgrp root «file_name» then give this command to change the permissions sudo chmod 755 «file_name» and place it in /bin with this command sudo mv «file_name» /bin
now u can run it as a normal command.
You run your code by ./compiled-c-program If you like to run like the other «system» program you need to add a static link to your program to one of the folder from your $PATH variable e.g.: ln -s ~/bin/c-compiled-c-program path/to/the/program/compiled-c-program
How to Create Simple Shell Scripts in Linux
Creating shell scripts is one of the most essential skills that Linux users should have at the tip of their fingers. Shell scripts play an enormous role in automating repetitive tasks which otherwise would be tedious executing line by line.
In this tutorial, we highlight some of the basic shell scripting operations that every Linux user should have.
1. Create a Simple Shell Script
A shell script is a file that comprises ASCII text. We will start by creating a simple shell script, and to do this, we will use a text editor. There are quite a number of text editors, both command-line and GUI-based. For this guide, we will use the vim editor.
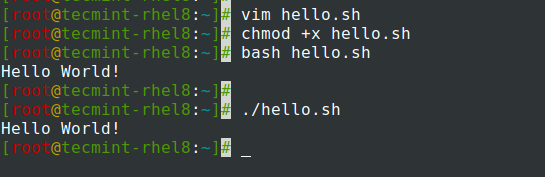
We will start off by creating a simple script that displays “Hello world” when executed.
Paste the following content in the file and save.
#!/bin/bash # Print Hello world message echo "Hello World!"
Let’s go over the shell script line by line.
- The first line – #!/bin/bash – is known as the shebang header. This is a special construct that indicates what program will be used to interpret the script. In this case, this will be the bash shell indicated by /bin/bash. There are other scripting languages such as Python which is denoted by #!/usr/bin/python3 and Perl whose shebang header is is denoted by #!/usr/bin/perl .
- The second line is a comment. A comment is a statement that describes what a shell script does and is not executed when the script is run. Comments are always preceded by the hash sign # .
- The last line is the command that prints the ‘Hello World’ message on the terminal.
The next step is to make the script executable by assigning execute permission using the chmod command as shown.
Finally, run the shell script using either of the commands:
2. Using Conditional Statements to Execute Code
Like other programming languages, conditional statements are used in bash scripting to make decisions, with only a slight variation in the syntax. We are going to cover the if, if-else, and elif conditional statements.
Example of an if Statement Only
The if statement can be used to test single or multiple conditions. We will start off with the fundamental use of the if statement to test a single condition. The if statement is defined by the if . fi blocks.
if command then statement fi
Let’s take a look at the shell script below.
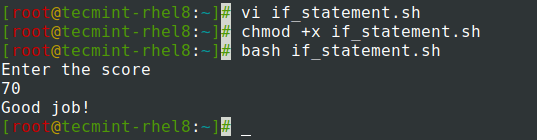
#!/bin/bash echo 'Enter the score' read x if [[ $x == 70 ]]; then echo 'Good job!' fi
The above shell script prompts the user to provide a score that is then stored in a variable x. If the score corresponds to 70, the script returns the output “Good job!”. The comparison operator == is used to test if the score entered, which is stored in the variable x, is equivalent to 100.
Other comparison operators you can use include:
- -eq – Equal to
- -ne – Not equal to
- -lt – Less than
- -le – Less than or equal to
- -lt – Less than
- -ge – Greater than or equal to
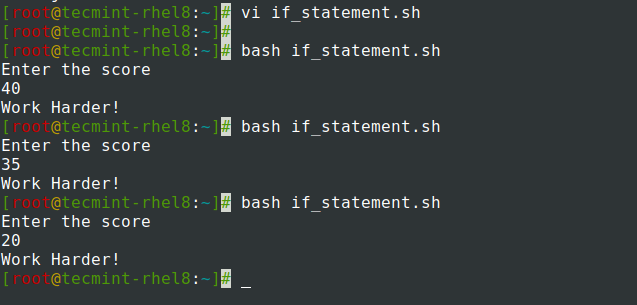
For example, the if-statement block below prints out ‘Work Harder’ if the input score is any value less than 50.
if [[ $x -lt 50 ]]; then echo 'Work Harder!' fi
Example of an if-else Statement
For situations where you have 2 possible outcomes: – whether this or that – the if-else statement comes in handy.
if command then statement1 else statement2 fi
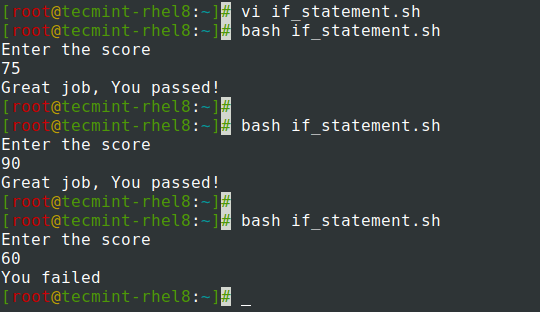
The script below reads the input score and checks whether it is greater than or equal to 70.
If the score is greater than or equal to 70, you get a ‘Great job, You passed!’ message. However, if the score falls below 70, the output ‘You failed’ will be printed.
#!/bin/bash echo 'Enter the score' read x if [[ $x -ge 70 ]]; then echo 'Great job, You passed!' else echo 'You failed' fi
Example of an if-elif-else Statement
In scenarios where there are multiple conditions and different outcomes, the if-elif-else statement is used. This statement takes the following format.
if condition1 then statement1 elif condition2 then statement2 else statement3 fi
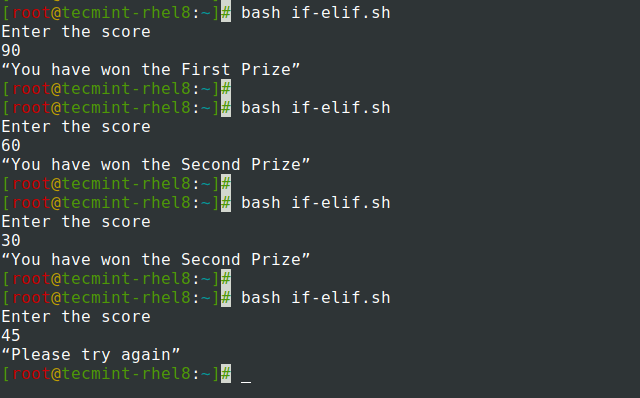
For example, we have a script for a lottery that checks if the number entered is either 90, 60 or 30.
#!/bin/bash echo 'Enter the score' read x if [[ $x -eq 90 ]]; then echo “You have won the First Prize” elif [[ $x -eq 60 ]]; then echo “You have won the Second Prize” elif [[ $x -eq 30 ]]; then echo “You have won the Second Prize” else echo “Please try again” fi
3. Using the If Statement with AND Logic
You can use the if statement alongside the AND logic operator to execute a task if two conditions are satisfied. The && operator is used to denote the AND logic.
#!/bin/bash echo 'Please Enter your user_id' read user_id echo 'Please Enter your tag_no' read tag_id if [[ ($user_id == “tecmint” && $tag_id -eq 3990) ]]; then echo “Login successful” else echo “Login failure” fi
5. Using the If Statement with OR Logic
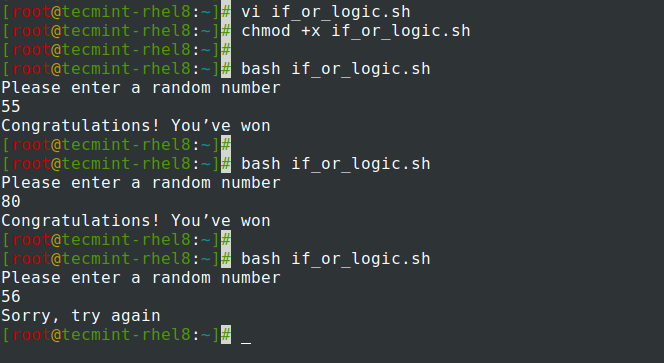
When using the OR logic, that is represented by || symbol, either one of the conditions needs to be satisfied with the script to give the expected results.
#!/bin/bash echo 'Please enter a random number' read number if [[ (number -eq 55 || number -eq 80) ]]; then echo 'Congratulations! You’ve won' else echo 'Sorry, try again' fi
Use Looping Constructs
Bash loops allow users to perform a series of tasks until a certain result is achieved. This comes in handy in performing repetitive tasks. In this section, we shall have a peek at some of the loops which you’d also find in other programming languages.
While loop
This is one of the easiest loops to work with. The syntax is quite simple:
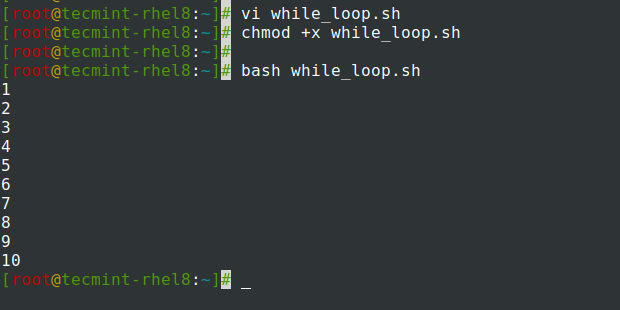
The while loop below lists all the numbers from 1 to 10 when executed.
#!/bin/bash # A simple while loop counter=1 while [ $counter -le 10 ] do echo $counter ((counter++)) done
Let’s disscuss the while loop:
The variable counter is initialized to 1. And while the variable is less than or equal to 10, the value of the counter will be incremented until the condition is satisfied. The line echo $counter prints all the numbers from 1 to 10.
For loop
Like the while loop, a for loop is used to execute code iteratively. I.e. repeat code execution as many times as possible defined by the user.
for var in 1 2 3 4 5 N do command1 command2 done
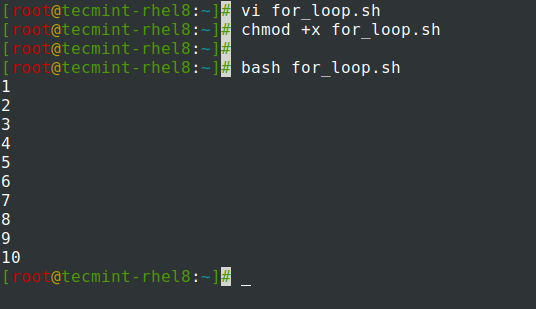
The for loop below iterates through 1 right through 10 and processes their values on the screen.
A better way to achieve this is to define a range using the double curly braces < >as shown instead of typing all the numbers.
#!/bin/bash # Specify range in a for loop for num in do echo $num done
Bash Positional Parameters
A positional parameter is a special variable that is referenced in the script when values are passed on the shell but cannot be assigned. Positional parameters run from $0 $1 $2 $3 …… to $9. Beyond the $9 value, the parameters have to be enclosed in curly brackets e.g $, $ … and so on.
When executing the script, the first positional parameter which is $0 takes the name of the shell script. The $1 parameter takes the first variable that is passed on the terminal, $2 takes the second, $3 the third and so on.
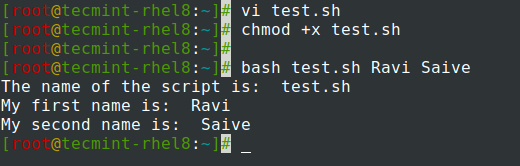
Let’s create a script test.sh as shown.
#!/bin/bash echo "The name of the script is: " $0 echo "My first name is: " $1 echo "My second name is: " $2
Next, execute the script and provide the first and second name as the arguments:
From the output, we can see that the first variable that is printed is the name of the shell script, in this case, test.sh. Thereafter, the names are printed out corresponding to the positional parameters defined in the shell script.
Positional parameters are useful in that they help you customize the data being entered instead of explicitly assigning a value to a variable.
Shell Command Exit Codes
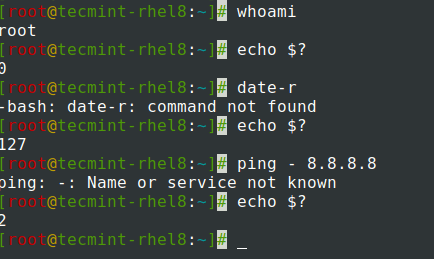
Let’s begin by answering a simple question, What is an exit code?
Every command executed on the shell by a user or shell script has an exit status. An exit status is an integer.
An exit status of 0 implies that the command executed successfully without any errors. Anything between 1 to 255 shows that the command failed or did not execute successfully.
To find the exit status of a command, use the $? Shell variable.
An exit status of 1 points to a general error or any impermissible errors such as editing files without sudo permissions.
An exit status of 2 points to incorrect usage of a command or builtin shell variable.
The 127 exit status points to an illegal command which usually yields the ‘command not found’ error.
Processing Output of Shell Commands within a Script
In bash scripting, you can store the output of a command in a variable for future use. This is also referred to as shell command substitution and can be achieved in the following ways.
variable=$(command) OR variable=$(/path/to/command) OR variable=$(command argument 1 argument 2 . )
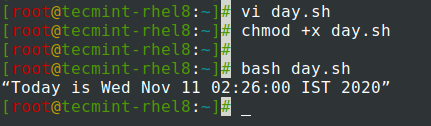
For example, you can store the date command in a variable called today and call the shell script to reveal the current date.
#!/bin/bash today=$(date) echo “Today is $today”
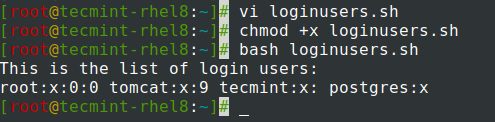
Let’s take another example. Suppose you want to find the valid login users on your Linux system. How would you go about it? First, the list of all the users (both system, process, and login users) is stored in the /etc/passwd file.
To view the file, you’d need to use the cat command. However, to narrow down to log in users, use the grep command to search for users with the /bin/bash attribute and use the cut -c 1-10 command as shown to display the first 10 characters of the names.
We have stored the cat command to the login_users variable.
#!/bin/bash login_users=$(cat /etc/passwd | grep /bin/bash | cut -c 1-10) echo 'This is the list of login users: echo $login_users
This brings our tutorial on creating simple shell scripts to an end. We hope you found this valuable.
How to create my own command in linux
I wrote a simple cpp code by using vi. I want to use cat command inside this program (by using execl and it will take my file as argument). I also have to write my own command. For example it will work like that: $mycommand filename. And cat command which is inside my cpp code will show my cpp file’s content. I’m new so I don’t know how to do it. Do you have any suggestions?
1 Answer 1
1) Redirecting output
The output of the cat command should go to the standard output of your program. For this your program should pass its standard output FD to the exec command. This will be the default case. So you don’t have to do anything extra.
2) cat on the source file
Now, the cat thing : «And cat command which is inside my cpp code will show my cpp file’s content. » This statement does not explain your need. If you want the cat of the executable you are running, you can do an objdump on your executable. The executable path can be found out from the proc file system with your pid. For a generic case, it does not matter whether the file is a cpp file or not.
3) making command
To make your executable run as a standard command on a terminal, you must add the directory containing the executable to the PATH directories list. You can do so by adding your executable to /usr/local/bin or /usr/bin. (Convention is that it should go in /usr/local/bin since it has been compiled locally). If you don’t have administrator privileges on the machine, you must append the source directory to the PATH directory list.