- How to create a soft or symbolic link?
- 8 Answers 8
- You must log in to answer this question.
- Linux ln – How to Create a Symbolic Link in Linux [Example Bash Command]
- What is the difference between soft and hard links in Linux?
- How to create a symlink to a file
- How to create a symbolic link to a directory
- How to remove a symbolic link
- How to overwrite symlinks
- How to learn more about the ln command
- Conclusion
How to create a soft or symbolic link?
I am installing p4v in /opt , but /usr/bin is on my path. Is it possible to create a soft or symbolic link for p4v from /opt to /usr/bin , so I can just type «p4v» since /usr/bin is in my path?
8 Answers 8
To create a symlink at /usr/bin/bar which references the original file /opt/foo , use:
You would need to apply the above command as root (i.e. with sudo ).
I am using: sudo ln –s /etc/apache2/sites-available/redmine /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/000-redmine getting error: ln: target ‘/etc/apache2/sites-enabled/000-redmine’ is not a directory
The Ubuntu documentation says » Creates hard links by default, symbolic links with —symbolic.» Will the above solution create a symbolic link as asked by OP?
I though César wanted to put his files in the /opt and /usr/bin to have the symbolic link, not other way around.
@kevinmicke after your explanation finally realized that the explanation of the answer was stated in reverse order from the command, making my brain (and others’) read it backwards
The error is that you are writing the command wrong. The correct way is
If the ‘p4v’ executable is at /opt/bin/p4v, you can simply run:
sudo ln -s /opt/bin/p4v /usr/bin/p4v sudo chmod ugo+x /usr/bin/p4v It would be better to add /opt/bin (or wherever the executable is) to your path:
echo "export PATH=\$PATH:/opt/bin" >> ~/.profile reset Check the software location by this.
which application-name #replace for the application you are looking for To create the soft link. for example you want to create the soft link for skype on your desktop
For more information about ln .
This template was more helpful for me than the above answers. Probably not more correct, just less obfuscated:
Just replace the parts in <> ‘s
ln -s -n ./TargetDirectory ./Nickname Note, this works if you both nodes are below you in the same tree. You can use relative notation
- -s command makes it a symbolic link
- -n makes it possible de create a folder-type symlink
Welcome to askubuntu.com. In this case the $ to indicate a command line prompt is a style choice, and not likely to be a problem. However bear in mind that including things in a code block other than the code and its output can cause confusion.
If it is saying target is not a folder , it means there are spaces in your folder names eg: New Folder has a space
You need to edit the path and add a backslash \ after every space in the paths
ln -s /opt/bin /usr/var/New\ Folder This is not an answer to the OPs question. Please wait until you have enough reputation to add comments.
I have found that it is easier to go to where you want the link to be and then create the link using sudo ln -s /path/to/source/file , than doing ln -s target source .
So in your case I would do cd /usr/bin then sudo ln -s /opt/bin/pv4 . The other way has not been working in my case.
You must log in to answer this question.
Highly active question. Earn 10 reputation (not counting the association bonus) in order to answer this question. The reputation requirement helps protect this question from spam and non-answer activity.
Linux ln – How to Create a Symbolic Link in Linux [Example Bash Command]
A symlink (symbolic) is a type of file that points to other files or directories (folders) in Linux.
You can create a symlink (symbolic) by using the ln command in the command line.
Symbolic links are useful because they act as shortcuts to a file or directory.
In this article, I will go over how to use the ln command to create a symlink to a file or directory.
What is the difference between soft and hard links in Linux?
A soft link or symbolic link will point to the original file on your system. A hard link will create a copy of the file.
Soft links can point to other files or directories on a different file system, whereas hard links cannot.
How to create a symlink to a file
You can find the command line using the Terminal application on Mac or using the Command Prompt on Windows.
Here is the basic syntax for creating a symlink to a file in your terminal.
ln -s existing_source_file optional_symbolic_link You use the ln command to create the links for the files and the -s option to specify that this will be a symbolic link. If you omit the -s option, then a hard link will be created instead.
The existing_source_file represents the file on your computer that you want to create the symbolic link for.
The optional_symbolic_link parameter is the name of the symbolic link you want to create. If omitted, then the system will create a new link for you in the current directory you are in.
Let’s take a look at an example to better understand how this works.
On my Desktop I have a file called example_fcc_file.txt .
I will need to first open up my terminal, and then make sure I am in the Desktop directory. I can run the command cd Desktop to navigate to my Desktop.
After running that command, you should see you are now in the Desktop.
jessicawilkins@Dedrias-MacBook-Pro-2 ~ % cd Desktop jessicawilkins@Dedrias-MacBook-Pro-2 Desktop % I can then use the ln command to create a new symbolic link called fcc_link.txt .
ln -s example_fcc_file.txt fcc_link.txtWhen you run that command in the terminal, you will notice that nothing was returned. That is because when the ln command is successful, there will be no output and it will return zero.
jessicawilkins@Dedrias-MacBook-Pro-2 Desktop % ln -s example_fcc_file.txt fcc_link.txt jessicawilkins@Dedrias-MacBook-Pro-2 Desktop % To check that your symbolic link was successful, you can use the ls command. The ls command will list information about files and the -l flag represents the symbolic link.
When you run that command, you should see this type of result in the terminal.
lrwxr-xr-x 1 jessicawilkins staff 20 Feb 19 19:56 fcc_link.txt -> example_fcc_file.txt The fcc_link.txt -> example_fcc_file.txt portion of the output shows you that the symbolic link is pointing to the file called example_fcc_file.txt .
You should also see that new symbolic link show up in your directory.
How to create a symbolic link to a directory
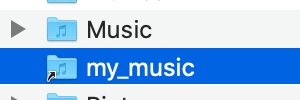
In this example, we want to create a symbolic link called my_music that will point to my Music folder in the home directory of my computer.
First, make sure you are in the home directory. You can run cd to get back to your home directory in the command line.
jessicawilkins@Dedrias-MacBook-Pro-2 Desktop % cd jessicawilkins@Dedrias-MacBook-Pro-2 ~ % You can then use the ln command to create a symlink to the Music directory.
ln -s /Users/jessicawilkins/Music ~/my_music If successful, you should see it in the home directory.
How to remove a symbolic link
To remove symlink you can either use the unlink or rm command.
If we wanted to remove the fcc_link.txt symlink we created earlier, then we can use either of these commands:
Now we should see that the symlink was removed from our directory.
How to overwrite symlinks
If we try to create a new symlink called fcc_link.txt , then it will result in an error because it is already being used and pointing to another file.
ln: fcc_link.txt: File exists You can overwrite this error by using the force ( -f ) option.
ln -sf example_fcc_file.txt fcc_link.txtHow to learn more about the ln command
If you want to learn more about the ln command, then you can read about it in the man pages (manual for using Linux commands).
Run man ln in your terminal and you should see the man pages for the ln command.
LN(1) BSD General Commands Manual LN(1) NAME link, ln -- make links SYNOPSIS ln [-Ffhinsv] source_file [target_file] ln [-Ffhinsv] source_file . target_dir link source_file target_file DESCRIPTION The ln utility creates a new directory entry (linked file) which has the same modes as the original file. It is useful for maintaining multiple copies of a file in many places at once without using up storage for the ``copies''; instead, a link ``points'' to the original copy. There are two types of links; hard links and sym- bolic links. How a link ``points'' to a file is one of the differences between a hard and symbolic link. The options are as follows: -F If the target file already exists and is a directory, then remove it so that the link may occur. The -F option should be used with either -f or -i options. If none is specified, -f is implied. The -F option is a no-op unless -s option is specified. -h If the target_file or target_dir is a symbolic link, do not follow it. This is most useful with the -f option, to replace a symlink which may point to a directory. -f If the target file already exists, then unlink it so that the link may occur. (The -f option overridesConclusion
A symlink (symbolic) is a type of file that points to other files or directories (folders) in Linux. You can create a symlink (symbolic) by using the ln command in the command line.
Symbolic links are useful because they act as shortcuts to a file or directory.
Here is the basic syntax for creating a symlink to a file using the terminal:
ln -s existing_source_file optional_symbolic_linkHere is the basic syntax for creating a symlink to a directory using the terminal:
ln -s path_to_existing_directory name_of_symbolic_link To remove symlink you can either use the unlink or rm command:
unlink name_of_symbolic_linkIf you need to remove a symlink then you can use this command:
ln -sf path_to_existing_directory name_of_symbolic_linkI hoped you enjoyed this article on symbolic links and best of luck on your programming journey.
![Linux ln – How to Create a Symbolic Link in Linux [Example Bash Command]](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/content/images/size/w2000/2022/02/gabriel-heinzer-4Mw7nkQDByk-unsplash.jpg)