- Как добавить пользователя в Sudoers в Ubuntu
- Добавление пользователя в группу sudo
- Добавление пользователя в файл sudoers
- Выводы
- How to Add a User to Sudoers
- [#using-usermod]Add user to sudoers with the [.inline-code]usermod[.inline-code] command[#using-usermod]
- [#in-ubuntu-or-debian]Add users to sudoers in Ubuntu or Debian[#in-ubuntu-or-debian]
- [#in-centos-or-fedora]Add users to sudoers in CentOS or Fedora[#in-centos-or-fedora]
- [#verify-changes]Check whether adding users to sudoers was successful[#verify-changes]
- [#using-sudoers-file]Add users to sudoers using the sudoers file[#using-sudoers-file]
- [#adding-a-group-to-sudoers]Adding a group to sudoers[#adding-a-group-to-sudoers]
- [#using-visudo]Use [.inline-code]visudo[.inline-code] to safely modify the sudoers file[#using-visudo]
- How To Create a New Sudo-enabled User on Ubuntu 20.04 [Quickstart]
- Step 1 — Logging Into Your Server
- Step 2 — Adding a New User to the System
- Step 3 — Adding the User to the sudo Group
- Step 4 — Testing sudo Access
- Conclusion
Как добавить пользователя в Sudoers в Ubuntu
sudo — это программа командной строки, которая позволяет доверенным пользователям выполнять команды от имени пользователя root или другого пользователя.
В этой статье мы покажем вам два способа предоставить пользователю права sudo. Первый — добавить пользователя в файл sudoers . Этот файл содержит информацию, которая контролирует, каким пользователям и группам предоставлены привилегии sudo, а также уровень этих привилегий.
Второй вариант — добавить пользователя в группу sudo, указанную в файле sudoers . По умолчанию в дистрибутивах на основе Debian, таких как Ubuntu и Linux Mint, членам группы «sudo» предоставляется доступ sudo.
Добавление пользователя в группу sudo
В Ubuntu самый простой способ предоставить пользователю права sudo — это добавить пользователя в группу «sudo». Члены этой группы могут выполнять любую команду как root через sudo и sudo запрос на аутентификацию с помощью своего пароля при использовании sudo .
Мы предполагаем, что пользователь уже существует. Если вы хотите создать нового пользователя, ознакомьтесь с этим руководством.
Чтобы добавить пользователя в группу, выполните команду ниже от имени пользователя root или другого пользователя sudo. Убедитесь, что вы заменили «username» на имя пользователя, которому вы хотите предоставить разрешения.
Предоставления доступа sudo с помощью этого метода достаточно для большинства случаев использования.
Чтобы убедиться, что у пользователя есть привилегии sudo, выполните команду whoami :
Вам будет предложено ввести пароль. Если у пользователя есть доступ к sudo, команда выведет «root»:
Если вы получаете сообщение об ошибке «пользователя нет в файле sudoers», это означает, что у пользователя нет прав sudo.
Добавление пользователя в файл sudoers
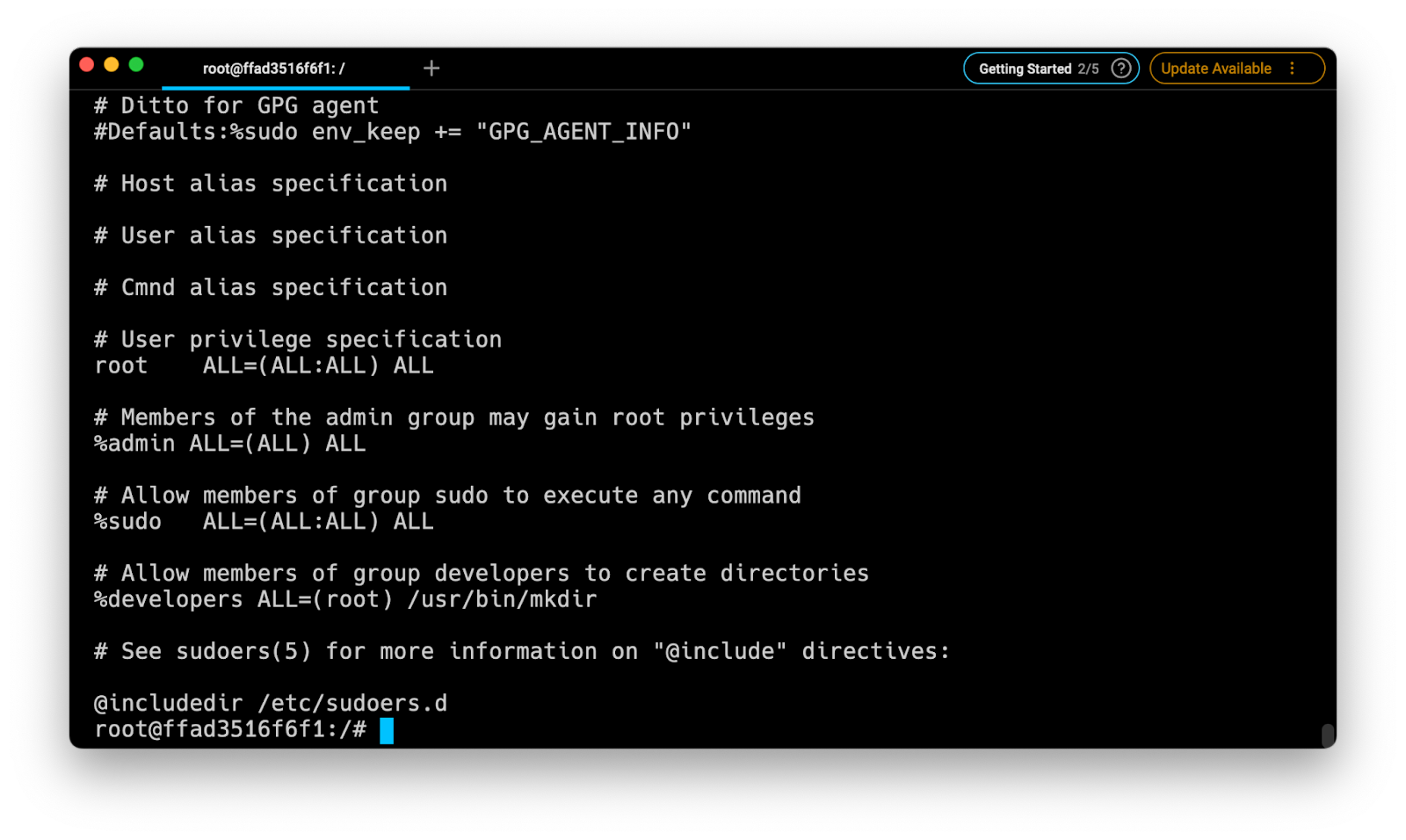
/etc/sudoers доступа sudo пользователей и групп определены в /etc/sudoers . Добавление пользователя в этот файл позволяет вам предоставить индивидуальный доступ к командам и настроить собственные политики безопасности.
Вы можете настроить доступ пользователя sudo, изменив файл sudoers или создав новый файл конфигурации в каталоге /etc/sudoers.d . Файлы внутри этого каталога включены в файл sudoers.
Всегда используйте visudo для редактирования файла /etc/sudoers . Эта команда проверяет файл на наличие синтаксических ошибок при его сохранении. Если есть ошибки, файл не сохраняется. Если вы откроете файл в текстовом редакторе, синтаксическая ошибка может привести к потере доступа sudo.
Обычно visudo использует vim для открытия /etc/sudoers . Если у вас нет опыта работы с vim и вы хотите отредактировать файл с помощью nano , измените редактор по умолчанию, запустив:
Допустим, вы хотите разрешить пользователю запускать команды sudo без запроса пароля. Для этого откройте файл /etc/sudoers :
Прокрутите вниз до конца файла и добавьте следующую строку:
username ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL Сохраните файл и выйдите из редактора . Не забудьте изменить «имя пользователя» на имя пользователя, которому вы хотите предоставить доступ.
Другой типичный пример — разрешить пользователю запускать только определенные команды через sudo . Например, чтобы разрешить только команды mkdir и rmdir , вы должны использовать:
username ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:/bin/mkdir,/bin/rmdir Вместо редактирования файла sudoers вы можете сделать то же самое, создав новый файл с правилами авторизации в каталоге /etc/sudoers.d . Добавьте то же правило, что и в файл sudoers:
echo "username ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL" | sudo tee /etc/sudoers.d/usernameТакой подход делает управление привилегиями sudo более удобным в обслуживании. Имя файла не имеет значения. Обычно имя файла совпадает с именем пользователя.
Выводы
Предоставление доступа sudo пользователю в Ubuntu — простая задача; все, что вам нужно сделать, это добавить пользователя в группу «sudo».
Если у вас есть вопросы, не стесняйтесь оставлять комментарии.
How to Add a User to Sudoers
On Unix and Linux, the superuser account, also known as root, admin, or supervisor, is a special user account capable of making unrestricted, system-wide changes. It is mostly used for system administration tasks such as changing the ownership of files or binding network ports. However, it is sometimes necessary to allow standard user accounts to perform some of these sensitive actions, by granting them elevated privileges and access through the use of the [.inline-code]sudo[.inline-code] command.
In this article, we’ll cover two methods for adding a user, or a group of users, to the sudoers list.
[#using-usermod]Add user to sudoers with the [.inline-code]usermod[.inline-code] command[#using-usermod]
In Linux, a group is a collection of accounts that can be given special or elevated permissions on the system. For example, a group can be given read permission on a file and another group read and write permissions on the same file.
To add a user account to a group, we can use the [.inline-code]usermod[.inline-code] command that essentially allows us to modify an existing account.
- The [.inline-code]-a[.inline-code] flag (short for append) is used to specify that we want to add a group to the specified user.
- The [.inline-code]-G[.inline-code] flag (short for groups) is used to specify which group we want to add.
Since most Linux distributions have a special group for sudoers, the easiest way to grant superuser privileges to a user account is to add it to this group.
[#in-ubuntu-or-debian]Add users to sudoers in Ubuntu or Debian[#in-ubuntu-or-debian]
On Ubuntu and Debian, this group is named [.inline-code]sudo[.inline-code].
[#in-centos-or-fedora]Add users to sudoers in CentOS or Fedora[#in-centos-or-fedora]
On CentOS and Fedora, this group is named [.inline-code]wheel[.inline-code].
[#verify-changes]Check whether adding users to sudoers was successful[#verify-changes]
To verify that a user was successfully added to the sudoers group, we can display the content of the [.inline-code]/etc/group[.inline-code] file using the [.inline-code]cat[.inline-code] command, which contains the list of groups (and their users) registered on the system.
[#using-sudoers-file]Add users to sudoers using the sudoers file[#using-sudoers-file]
In *nix systems, user accounts and groups with sudo privileges are stored into the [.inline-code]/etc/sudoers[.inline-code] file (sometimes called the “sudo file”), which contains a list of instructions called privilege lines, that can be edited to grant customized access to commands a user or a group can execute, or configure custom security policies.
The general syntax for a privilege line is the following:
user on_host=(as_user:as_group) allowed_commands
Which can be roughly translated to «who where=(whom) what».
For example, the following line can be read as «the root user can run any command as any user from any group on any host.»
And this line can be read as «the admin user can run the mkdir command as the root user on any host».
admin ALL=(root) /usr/bin/mkdir
[#adding-a-group-to-sudoers]Adding a group to sudoers[#adding-a-group-to-sudoers]
The sudoers file also allows us to grant superuser privileges to an entire group of users by specifying the group name prefixed with a percentage character ([.inline-code]%[.inline-code]).
%group on_host=(as_user:as_group) allowed_commands
[#using-visudo]Use [.inline-code]visudo[.inline-code] to safely modify the sudoers file[#using-visudo]
Because of the sensitive nature of its content, it is highly recommended to only open it using the [.inline-code]visudo[.inline-code] utility — which uses the [.inline-code]vim[.inline-code] text editor under the hood — as it will automatically check for syntax errors before the file is saved, preventing us from ending up with a broken system where it is impossible to obtain elevated privileges.
Note that if you are not particularly experienced with [.inline-code]vim[.inline-code], you can always change the default editor using the following syntax.
How To Create a New Sudo-enabled User on Ubuntu 20.04 [Quickstart]
When managing a server, you’ll sometimes want to allow users to execute commands as “root,” the administrator-level user. The sudo command provides system administrators with a way to grant administrator privileges — ordinarily only available to the root user — to normal users.
In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to create a new user with sudo access on Ubuntu 20.04 without having to modify your server’s /etc/sudoers file.
Note: If you want to configure sudo for an existing user, skip to step 3.
Step 1 — Logging Into Your Server
SSH in to your server as the root user:
Step 2 — Adding a New User to the System
Use the adduser command to add a new user to your system:
Be sure to replace sammy with the username that you want to create. You will be prompted to create and verify a password for the user:
OutputEnter new UNIX password: Retype new UNIX password: passwd: password updated successfully Next, you’ll be asked to fill in some information about the new user. It is fine to accept the defaults and leave this information blank:
OutputChanging the user information for sammy Enter the new value, or press ENTER for the default Full Name []: Room Number []: Work Phone []: Home Phone []: Other []: Is the information correct? [Y/n] Step 3 — Adding the User to the sudo Group
Use the usermod command to add the user to the sudo group:
Again, be sure to replace sammy with the username you just added. By default on Ubuntu, all members of the sudo group have full sudo privileges.
Step 4 — Testing sudo Access
To test that the new sudo permissions are working, first use the su command to switch to the new user account:
As the new user, verify that you can use sudo by prepending sudo to the command that you want to run with superuser privileges:
For example, you can list the contents of the /root directory, which is normally only accessible to the root user:
The first time you use sudo in a session, you will be prompted for the password of that user’s account. Enter the password to proceed:
Output:[sudo] password for sammy: Note: This is not asking for the root password! Enter the password of the sudo-enabled user you just created.
If your user is in the proper group and you entered the password correctly, the command that you issued with sudo will run with root privileges.
Conclusion
In this quickstart tutorial, we created a new user account and added it to the sudo group to enable sudo access.
For your new user to be granted external access, please follow our section on Enabling External Access for Your Regular User.
If you need more detailed information on setting up an Ubuntu 20.04 server, please read our Initial Server Setup with Ubuntu 20.04 tutorial.
Get Ubuntu on a hosted virtual machine in seconds with DigitalOcean Droplets! Simple enough for any user, powerful enough for fast-growing applications or businesses.


![How To Create a New Sudo-enabled User on Ubuntu 20.04 [Quickstart]](https://www.digitalocean.com/_next/static/media/intro-to-cloud.d49bc5f7.jpeg)