- 3 Command Line Tools to Install Deb Packages in Ubuntu
- 1. Install .deb Package Using dpkg Command
- Remove Deb Packages Using dpkg Command
- 2. Install .deb Package Using Apt Command
- Remove Deb Packages using apt Command
- 3. Install .deb Package Using Gdebi Command
- Install .deb Packages Using Gdebi GUI
- 15 apt Command Examples in Ubuntu / Debian Linux
- 1) Update Package Information
- 2) List Packages
- 3) Installing New Package
- 4) Remove Package
- 5) Upgrade Package
- 6) Full System Upgrade
- 7) Search Package
- 8) View Information About Package
- 9) Autoremove Packages
- 10) List Package Dependencies
- 11) Downloading Package without Installing
- 12) Hold and Unhold Package
- 13) Clear Apt Cache
- 14) Edit Sources (sources.list)
- 15) History of apt command
- 1 thought on “15 apt Command Examples in Ubuntu / Debian Linux”
- Leave a Comment Cancel reply
- Recent Posts
- Pages
3 Command Line Tools to Install Deb Packages in Ubuntu
In this tutorial, you will learn how to install local software packages (.DEB) in Debian and its derivatives such as Ubuntu and Linux Mint using three different command line tools and they are dpkg, apt, and gdebi.
This is useful to those new users who have migrated from Windows to Ubuntu or Linux Mint. The very basic problem they face is installing local software on the system.
However, Ubuntu and Linux Mint have their own Graphical Software Center for easy software installation, but we will be looking forward to installing deb packages through the terminal way.
1. Install .deb Package Using dpkg Command
Dpkg is a package manager for Debian and its derivatives such as Ubuntu and Linux Mint. It is used to install, build, remove, and manage .deb packages. but unlike other Linux package management systems, it cannot automatically download and install packages with their dependencies.
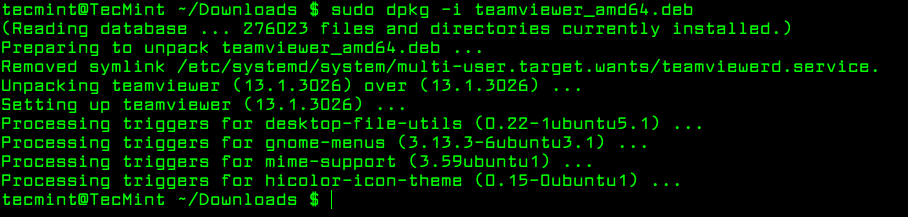
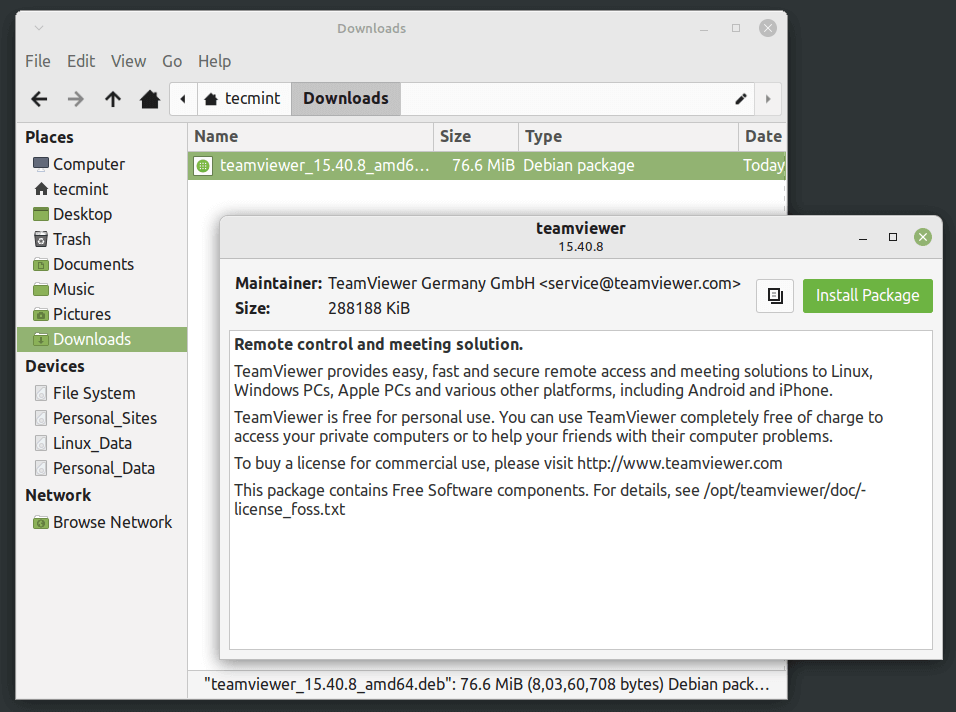
To install a .deb package, use the dpkg command with the -i flag along with the package name as shown.
$ sudo dpkg -i teamviewer_amd64.deb
If you get any dependency errors while installing or after installing and launching a program, you can use the following apt command to resolve and install dependencies using the -f flag, which tells the program to fix broken dependencies.
Remove Deb Packages Using dpkg Command
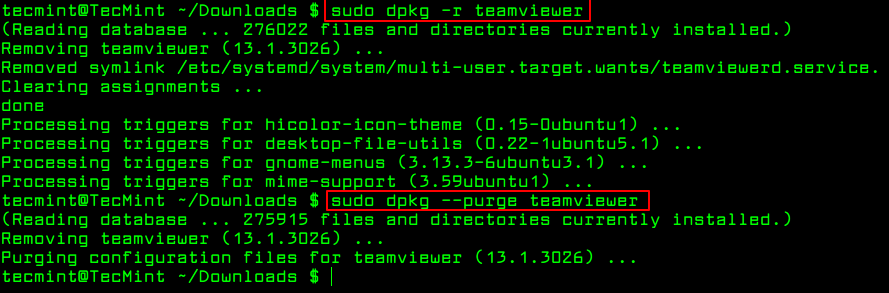
To remove a .deb package use the -r option or if you want to remove all its files including configuration files, you can purge it using the —purge option as shown.
$ sudo dpkg -r teamviewer [Remove Package] $ sudo dpkg --purge teamviewer [Remove Package with Configuration Files]
To know more about installed packages, read our article that shows how to list all files installed from a .deb package.
2. Install .deb Package Using Apt Command
The apt command is an advanced command-line tool, which offers new software package installation, existing software package upgradation, updating of the package list index, and even upgrading the whole Ubuntu or Linux Mint system.
It also offers apt-get and apt-cache command-line tools for managing packages more interactively on Debian and its derivatives such as Ubuntu and Linux Mint systems.
Essentially, apt-get or apt do not understand .deb files, they are designed to primarily handle package names (for example teamviewer, apache2, mariadb, etc..) and they retrieve and install .deb archives associated with a package name, from a source specified in the /etc/apt/sources.list file.
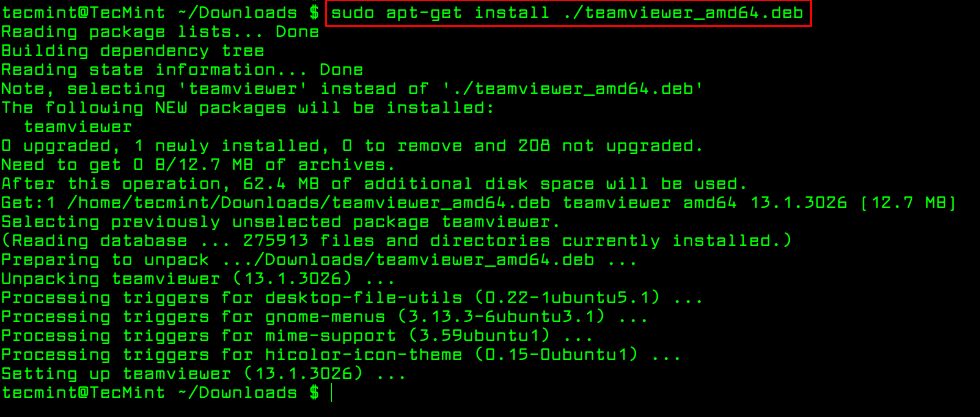
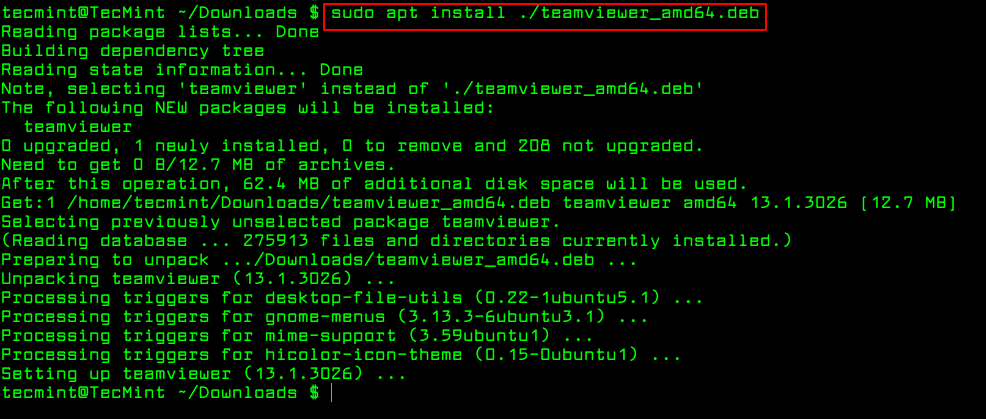
The only trick to installing a .deb Debian package using apt-get or apt is by specifying a local relative or absolute path ( ./ if in current dir) to the package, otherwise it will try to retrieve the package from remote sources and the operation will fail.
$ sudo apt install ./teamviewer_amd64.deb $ sudo apt-get install ./teamviewer_amd64.deb
Remove Deb Packages using apt Command
To remove a .deb package use the remove option or if you want to remove all its files including configuration files, you can purge it using the purge option as shown.
$ sudo apt-get remove teamviewer $ sudo apt-get purge teamviewer OR $ sudo apt remove teamviewer $ sudo apt purge teamviewer
3. Install .deb Package Using Gdebi Command
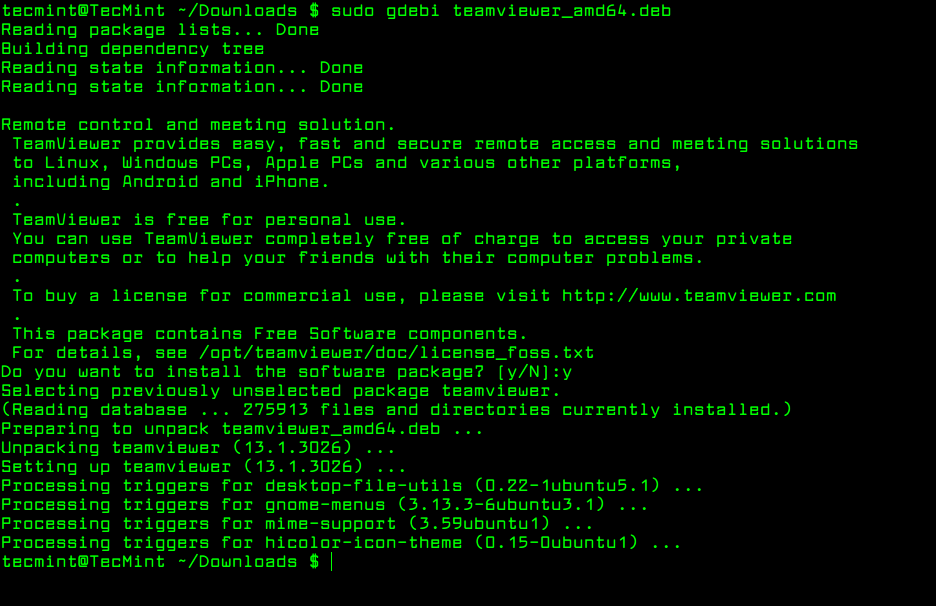
gdebi is a tiny command line and GUI tool for installing local deb packages. It resolves and installs package dependencies on the fly. To install a package, use the following command.
$ sudo gdebi teamviewer_13.1.3026_amd64.deb
To remove a .deb package installed from gdebi, you can use apt, apt-get or dpkg commands using purge option as shown.
$ sudo apt purge teamviewer OR $ sudo apt-get purge teamviewer OR $ sudo dpkg --purge teamviewer
Install .deb Packages Using Gdebi GUI
The most recommended way for beginners to installing .deb files is through the Gdebi GUI installer. Simply, go to the directory where you have downloaded the file and double-click to install it as shown.
That’s It! In this tutorial, we have explained three different command line tools for installing or removing .deb Debian packages in Ubuntu and Linux Mint.
If you know any other way of installing local packages, do share with us using our comment section below.
15 apt Command Examples in Ubuntu / Debian Linux
Apt is a command line package management utility for Ubuntu and Debian Linux. Apt is used to install, remove, update and upgrade Debian packages from command line in Ubuntu and Debian systems. Apt (Advanced package tool) overcomes the issues and bugs that were noticed in apt-get command. To use apt command user must have sudo privileges.
In this post, we will cover 15 apt command examples in Ubuntu / Debian Linux. Let’s dive into the examples.
1) Update Package Information
‘apt update’ command is used to fetch latest package information from configured sources, here sources could repository over the internet or local repository.
It is always recommended to run this command before installing or upgrading packages.
2) List Packages
To list all the available packages including installed and upgradeable use apt list command.
To list only the installed packages, run
To List only upgradeable packages, run
$ sudo apt list --upgradeable
3) Installing New Package
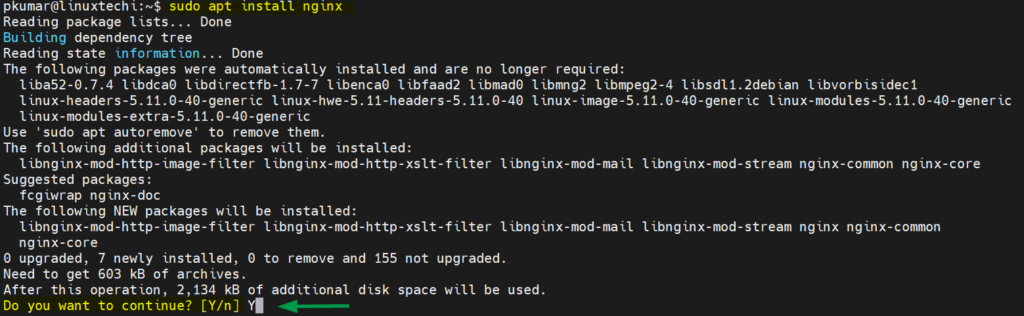
To install a new package, use ‘ apt install ‘ command followed by package name, example is shown below:
$ sudo apt install nginx Or $ sudo apt install nginx -y
When we don’t pass ‘-y’ option in ‘apt install’ command then it will prompt you to confirm for its installation. But when we specify ‘-y’ then it is auto confirm and will install the packages.
4) Remove Package
To remove a package then use ‘ apt remove ’ command followed by the package name.
To remove package and configuration files associated to package then use ‘ apt purge ’
5) Upgrade Package
To upgrade all the packages which are currently installed on your system then run ‘ apt upgrade ’ command.
To upgrade a specific installed package then use following command
$ sudo apt install snapd --only-upgrade
6) Full System Upgrade
Always be careful while upgrading the whole system, as it might remove the installed packages and will install the updated packages. It is generally used when we want to update minor versions of Ubuntu / Debian systems. (like Ubuntu 20.04 to Ubuntu 20.04.4).
7) Search Package
To search a package, run ‘ apt search ‘ command followed by package name.
$ sudo apt search phpmyadmin $ sudo apt search ^mysql-server $ sudo apt search httpd*
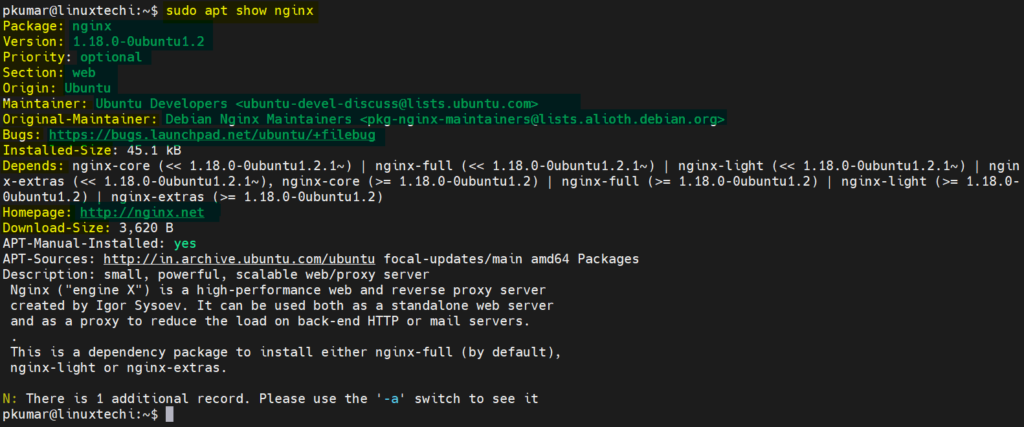
8) View Information About Package
To view the information about a package, run ‘ apt show ’ command followed by package name
9) Autoremove Packages
Autoremove option in apt command is used to remove the packages that were installed automatically to satisfy the dependencies and now no longer needed.
$ sudo apt auotremove $ sudo apt --purge autoremove
10) List Package Dependencies
To list package dependencies run ‘ apt depends ’ followed by package name
$ sudo apt depends phpmyadmin
To list package dependencies recursively then run ‘ apt rdepends ’ followed by package name
11) Downloading Package without Installing
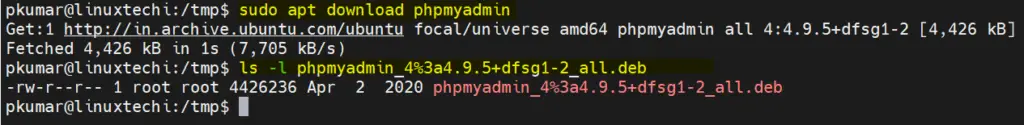
To download a package in the current working directory, run ‘ apt download ’ command followed by the package name.
$ sudo apt download phpmyadmin
12) Hold and Unhold Package
When a package is marked as hold then that package will not be upgraded till it is marked as unhold again.
Let’s assume we want to mark nginx as hold the run beneath command
$ sudo apt-mark hold nginx nginx set on hold. $
To mark nginx package as unhold, run
$ sudo apt-mark unhold nginx Canceled hold on nginx. $
13) Clear Apt Cache
When we run apt command then it is cached in /var/cache/apt/archives , Cache comes into the picture whenever we re-install the package as apt command looks for package in cache first. So cleaning up apt cache will free up the disk space as it will remove packages from the folder ‘ /var/cache/apt/archives/ ’.
To clean obsolete deb-packages then run
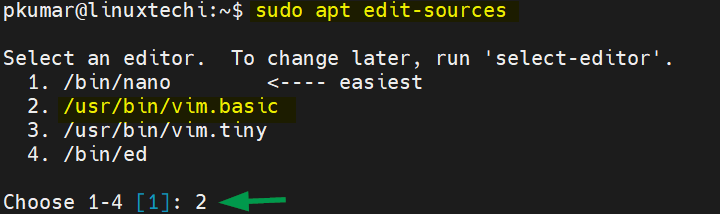
14) Edit Sources (sources.list)
Apt command refers /etc/apt/sources.list for package repository url. Using ‘apt edit-sources’ command, sources.list file can be edited, example is shown below:
It will open sources.list file in vi editor, so edit the file and then save & exit the fille.
15) History of apt command
Apt command history is stored under ‘/ var/log/apt/history.log ’ file. So, to view the history of apt command, use below cat command
$ cat /var/log/apt/history.log Or $ tail -n 30 /var/log/apt/history.log // This will list only last 30 lines
That’s all from this post. I assume you have found it informative. Please do not hesitate to share your queries and feedback in below comments section.
1 thought on “15 apt Command Examples in Ubuntu / Debian Linux”
Thank you for sharing this article. Example: 16 performing the function of upgradepackages
$ sudo apt-get dist-upgrade Reply
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Recent Posts
- How to Install PHP 8 on RHEL 8 / Rocky Linux 8 / CentOS 8
- How to Install and Use Wireshark in Ubuntu 22.04
- Top 10 Things to Do After Installing Debian 12 (Bookworm)
- How to Install Debian 12 (Bookworm) Step-by-Step
- How to Upgrade Debian 11 to Debian 12 (Bookworm) via CLI
- How to Setup Dynamic NFS Provisioning in Kubernetes Cluster
- How to Install Nagios on Rocky Linux 9 / Alma Linux 9
- How to Install Ansible AWX on Kubernetes Cluster
- How to Install Docker on Fedora 38/37 Step-by-Step
- How to Setup High Availability Apache (HTTP) Cluster on RHEL 9/8