- Initial Server Setup with Debian 11
- Conclusion
- How to Install Debian 11 (Bullseye) Server Using Net Install
- Requirements
- Download Debian 11
- Installation of Debian 11 Minimal Server
- Configuring Location and Keyboard Settings
- Configure Hostname and Domain Name
- Configure Users and Password
- Partitioning Disk
- Creating Swap Partition
- Create Root Partition
- Create Home Partition
- Finalizing Debian 11 Installation Process
Initial Server Setup with Debian 11
Debian is called a “universal Operating System” and rightly so. It is a free source OS that is developed by thousands of volunteers from all around the world. They mostly work online. When we dig a little deeper, we come to know that this is the base or the foundation for many Linux distributions out there. One such example is the popular Ubuntu.
Debian 1.1 was first released in 1996 and its name was Buzz. The latest release was launched on 14 Aug 2021. It is Debian 11 and its name is Bullseye. It is also worth mentioning that it is supported for the next five years and is a stable Debian version. Debian 11 offers stability, securability. For this reason, it is a very popular Os system and is an ideal candidate for server setup.
When you first install Debian 11 or when you upgrade your Debian from any version to Debian 11, you have to perform configuration first. This makes the server secure. So, in this article, we are going to teach you how to set up a server initially with Debian 11.
Step1: Opening Terminal
First, we have to open the terminal to start typing commands.
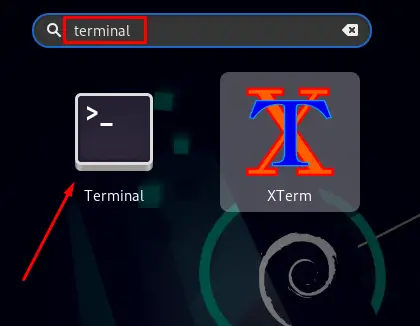
When you are logged in to Debian 11, you’ll see the Activities keyword at the top left corner of the screen. Click on that.
After clicking on the activities, type terminal in the search bar and then select Terminal:
Terminal Screen will appear.
Step2: Debian Update and Upgrade
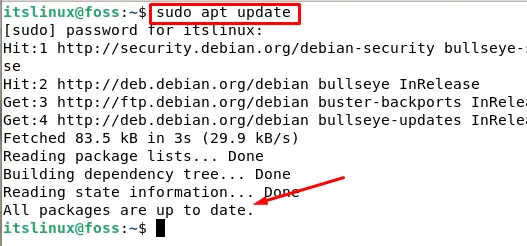
In this step, we are going to first update our Debian packages and then upgrade them if necessary. To update the packages type the following in your terminal:
If you see “All packages are up to date” then you don’t need to upgrade.
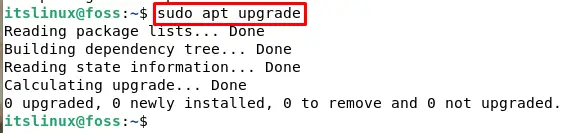
However, if there are some packages that need upgrading type the following command in your terminal:
Step3: Create Sudo User
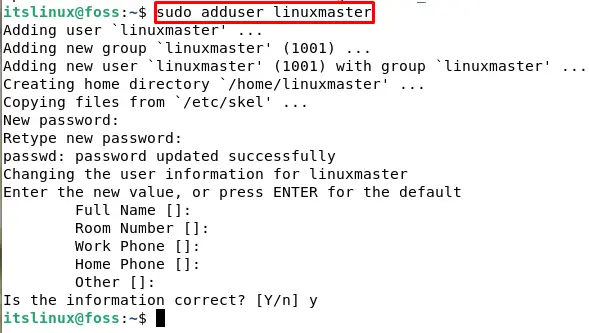
For our server management, it is preferred that we create a new sudo/administrator user. For this purpose let’s create a sudo user with the following command:
When you run this command you will be asked a bunch of questions including Full name, room number, etc. You can either set these values or leave them blank and press enter. When you will leave it blank, it will take the default values. In the end, y and no option will be given. Type y to continue.
We have successfully created a new user with the name of linuxmaster. The next step is to give this user the sudo privileges. For this purpose type the following command:
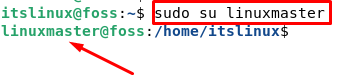
$ sudo usermod -aG sudo linuxmasterNow it’s time to switch the account. Type the following to switch accounts and go to linuxmaster user. For this type the following command:
We can see in the above screenshot that we have successfully changed the user from itslinux to linuxmaster.
Step4: System Hostname Configuration
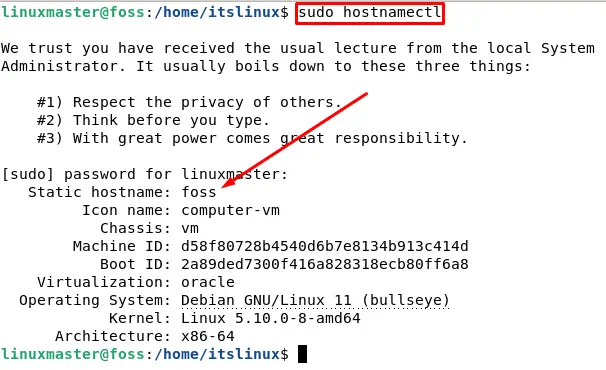
The identity of our system is the hostname over some network. It is a common practice to change the hostname and put a proper name. To see your current hostname type the following command in your terminal:
To change the hostname, run the below command:
$ sudo hostnamectl set-hostname itslinuxReplace the itslinux with whatever you want your hostname to be.
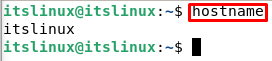
To see the new hostname close the terminal and start the terminal again. You will see the new hostname now. To check the hostname with a command type the following:
Step5: Secure SSH
SSH is also called Secure Shell. It is a protocol which is used for connecting with remote servers. Let’s configure the server by changing the default port first and disabling root SSH login.
Type the following command in your terminal which will open the following file in nano editor:
$ sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_confiqOnce opened type the following in your editor:
port 2284 PermitRootLogin noWhen you are done typing the above lines, press CTRL+S to save the file and CTRL+X to exit.
Once done, type the following command in your terminal:
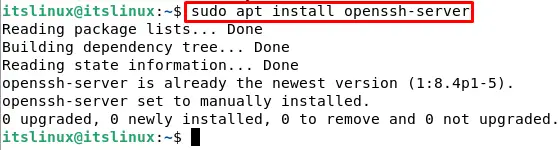
$ sudo systemctl restart sshIf somehow the file didn’t open then it means you are missing ssh server in the system. Install SSH server in your system by typing the following commands:
$ sudo apt install openssh-serverStep6: Configuring Firewall(UFW) on Debian 11
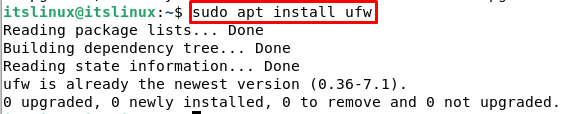
By default, Debian doesn’t have a firewall installed. In order to install firewall type the following command in your terminal:
I had ufw already installed that’s why it showed that “ufw is already the newest version”.
Once installed let’s enable our firewall. For this purpose type the following:
The next step is to allow the port set in step 5. For this type the following command in your terminal:
However, it is on anyone’s preference whether he/she wants to deny or allow the incoming or outgoing traffic. To deny the incoming traffic type the following command:
$ sudo ufw default deny incomingTo allow outgoing traffic type the following command:
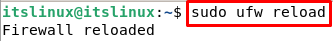
$ sudo ufw default allow outgoingThe next step is to reload the firewall UFW. For this purpose, type the following command:
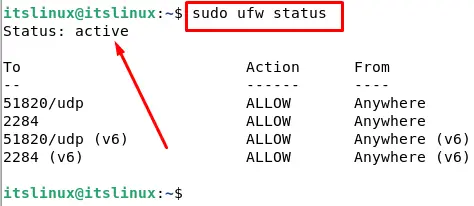
If you want to see whether UFW is active or not, check the status by the following command:
If it is active that means it is enabled.
Step7: System Reboot
The final step involves rebooting your system. For this purpose type the following command:
This command will reboot your system.
Conclusion
When you first install Debian 11 you need to set up a server. One must follow these steps to set up the server. These steps include updating and upgrading, adding a new sudo user, set up a firewall, and securing SSH.
In this article, we have learned today how to set up a server on Debian 11 Bullseye initially. These are some necessary steps when you start working in Debian 11.
TUTORIALS ON LINUX, PROGRAMMING & TECHNOLOGY
How to Install Debian 11 (Bullseye) Server Using Net Install
In this guide, we will walk you through the installation of a Debian 11 (Bullseye) Minimal Server, using the netinstall CD ISO image. This installation you will carry out is appropriate for building a future customizable server platform, without a GUI (Graphical User Interface).
You can use it to install only the necessary software packages that you need to work with, which we will show you in future guides. However, before you move further, read the system requirements, download the netinstall CD ISO image and then proceed to the Debian 11 installation instructions.
Requirements
- Minimum RAM: 512MB.
- Recommended RAM: 2GB.
- Hard Drive Space: 10 GB.
- Minimum 1GHz Pentium processor.
Important: These are only values for a test scenario, in a production environment, you probably want to use suitable RAM and Hard disk size to meet your local environment needs.
Download Debian 11
Debian 11 server system network installation minimal CD image:
Installation of Debian 11 Minimal Server
1. After downloading the Debian 11 minimal CD image from the above links, burn it to a CD or create a bootable USB stick using LiveUSB Creator called Unetbootin or Rufus.
2. Once you have created the installer bootable media, place your CD/USB into your system appropriate drive.
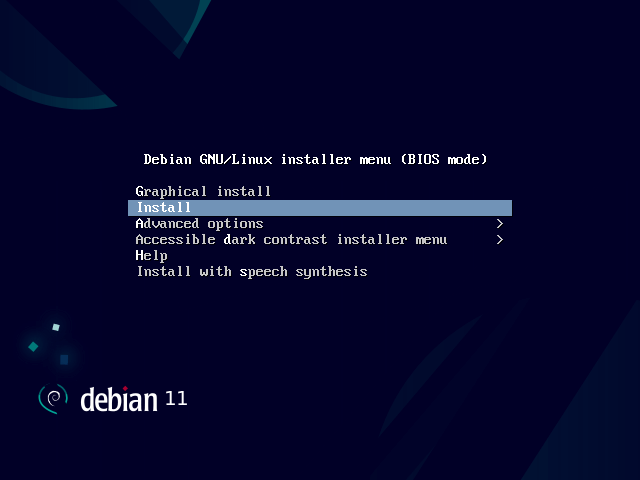
Then start the computer, select your bootable device, and the first Debian 9 installer boot menu should appear as shown below. Choose Install and press the [Enter] key.
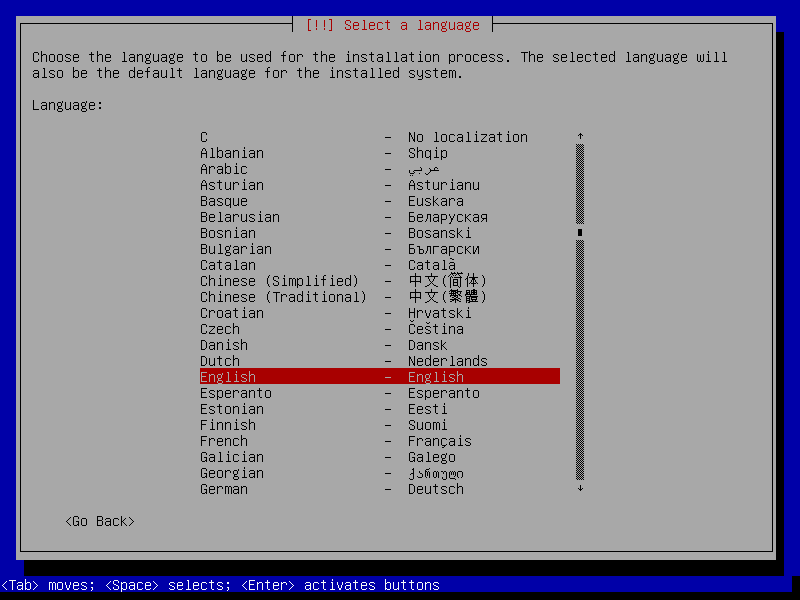
3. The system will start loading the media installer and a page to select the installation language should appear as shown below. Select your installation process language and click on Continue.
Configuring Location and Keyboard Settings
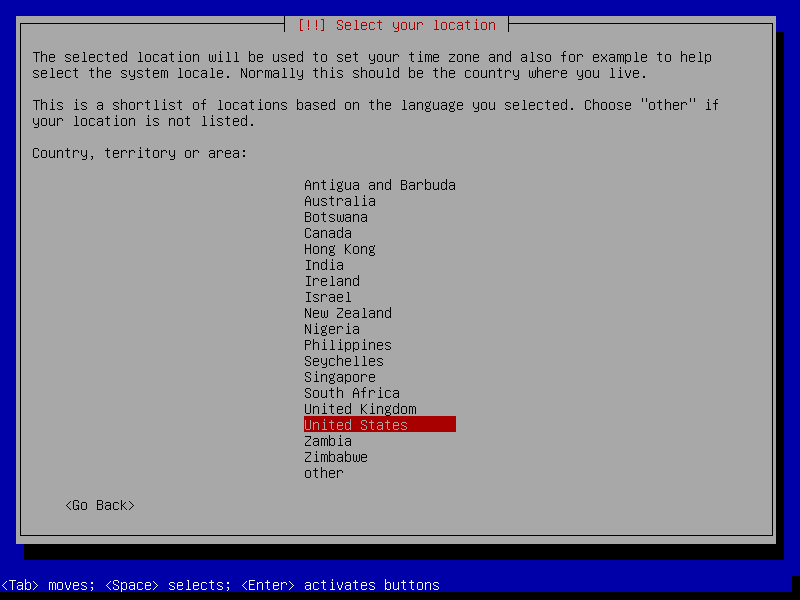
4. Now select your location used for setting the system timezone and locales, if not on the list go to Other and click on Continue. Find the region and the country. Once you are done click Continue as shown below.
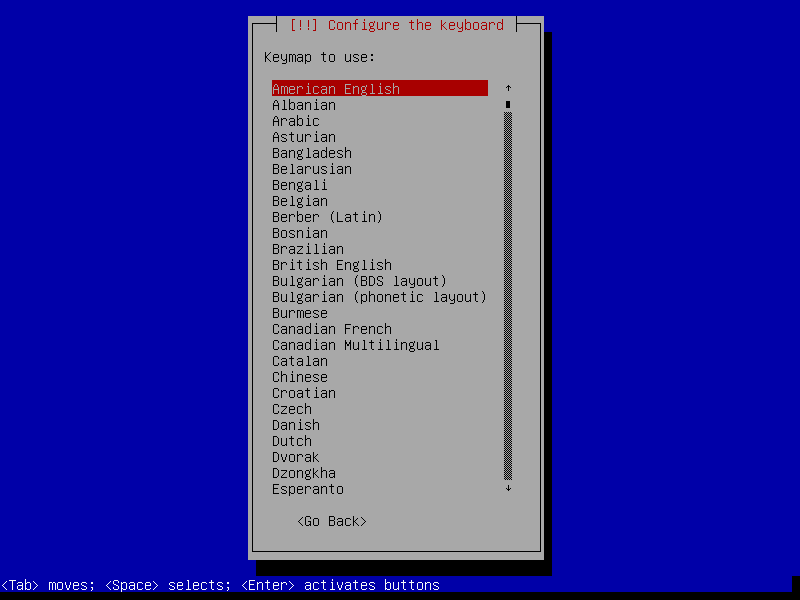
5. Next, choose your Keyboard Layout to use and click Continue.
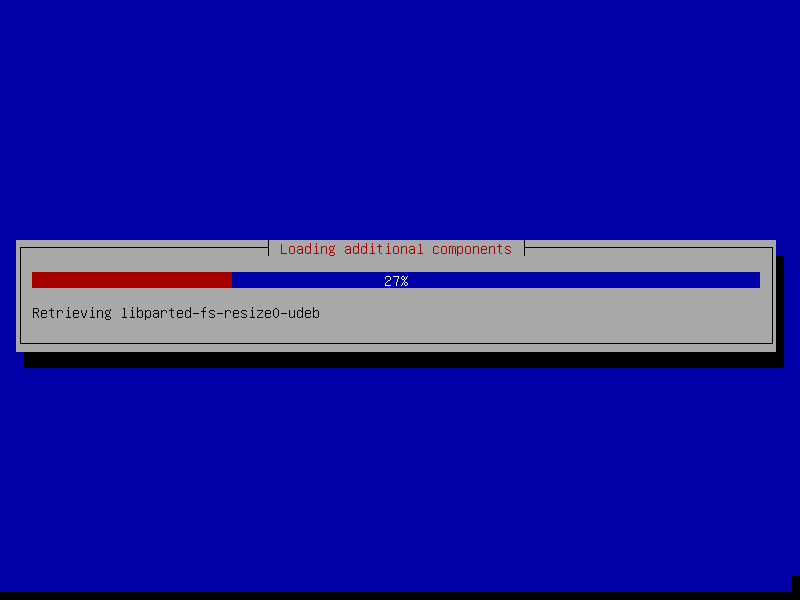
6. The installer will now load components from the CD shown below.
Configure Hostname and Domain Name
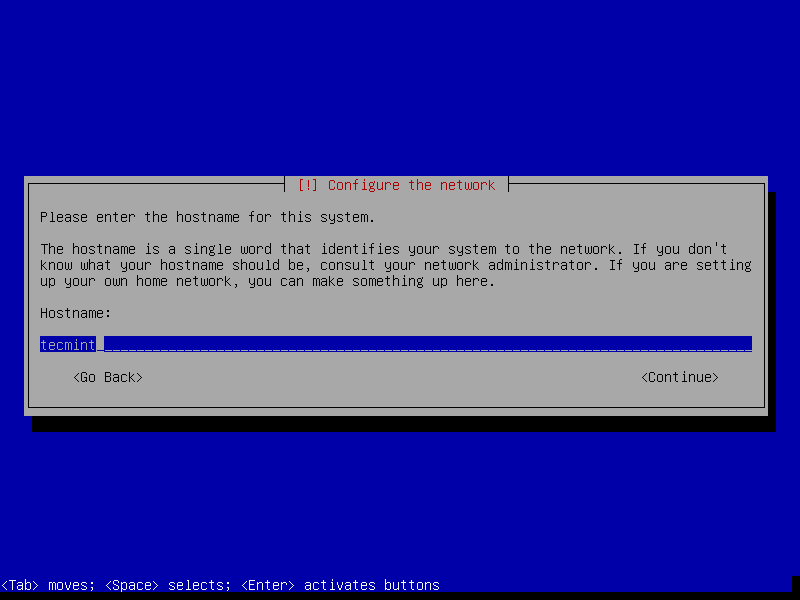
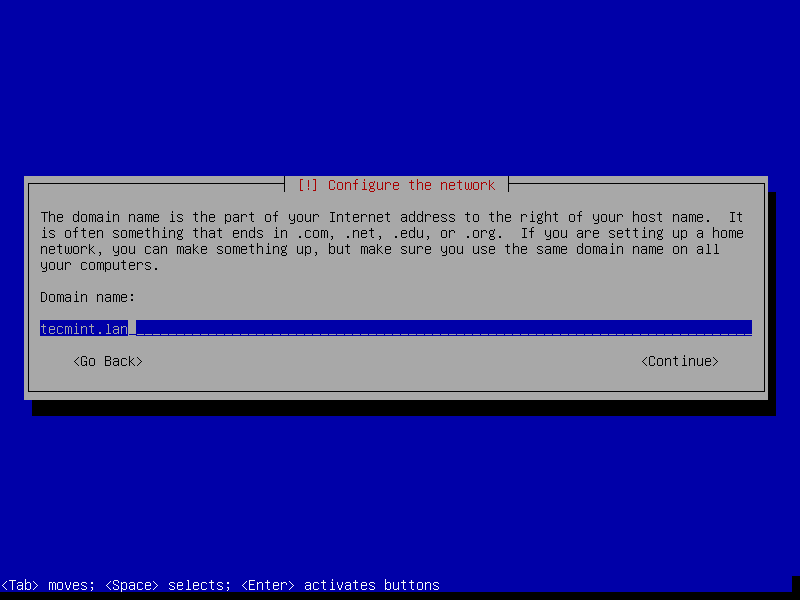
7. The next step is to set your system hostname and domain name and click Continue.
Configure Users and Password
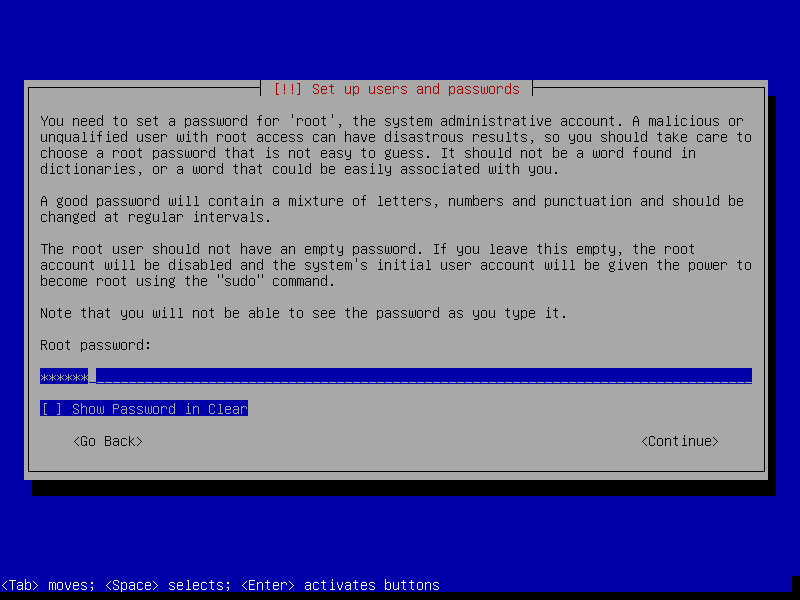
8. Here, you will configure system users and their passwords. Start by setting the root user password as shown below and click Continue when you are done.
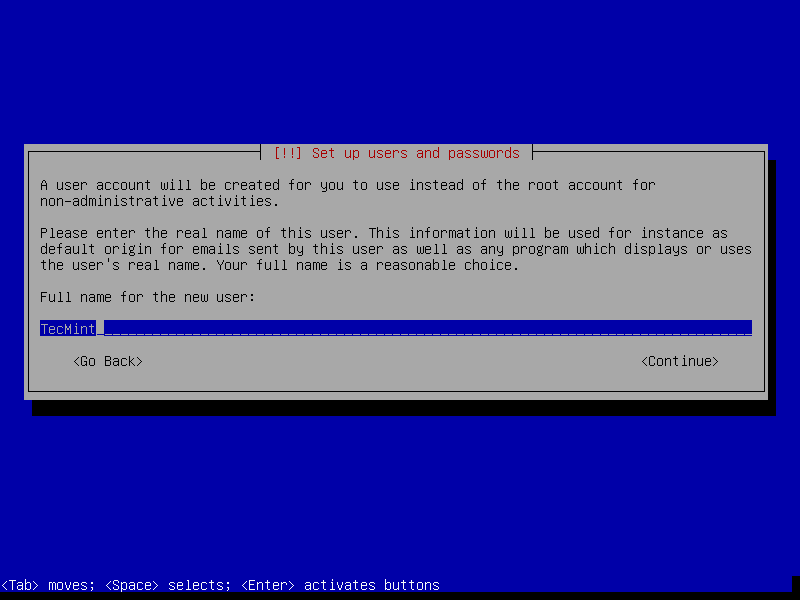
9. Then create a user account for the system administrator. First set the user’s full name as shown below and click Continue when you are done.
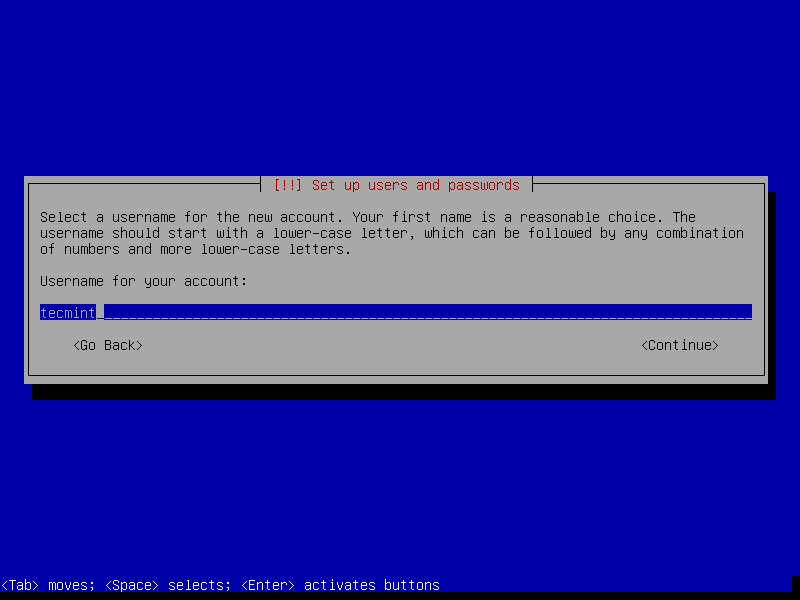
10. In this step, set the user’s system name and click Continue.
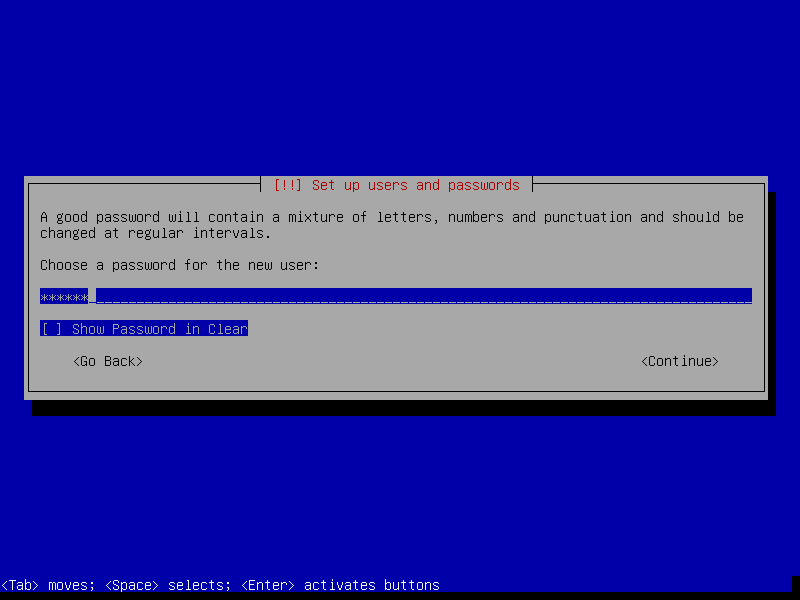
11. Now set the above user’s password and click Continue.
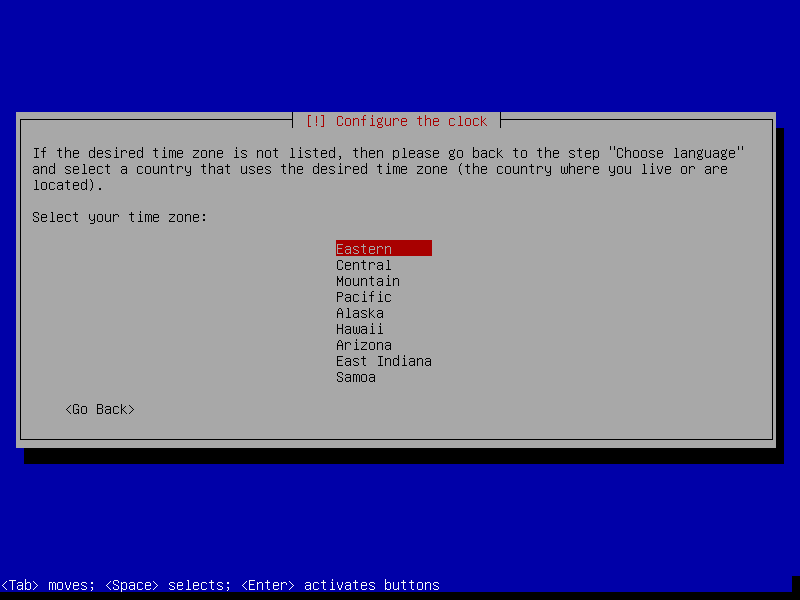
12. Configure your system clock.
Partitioning Disk
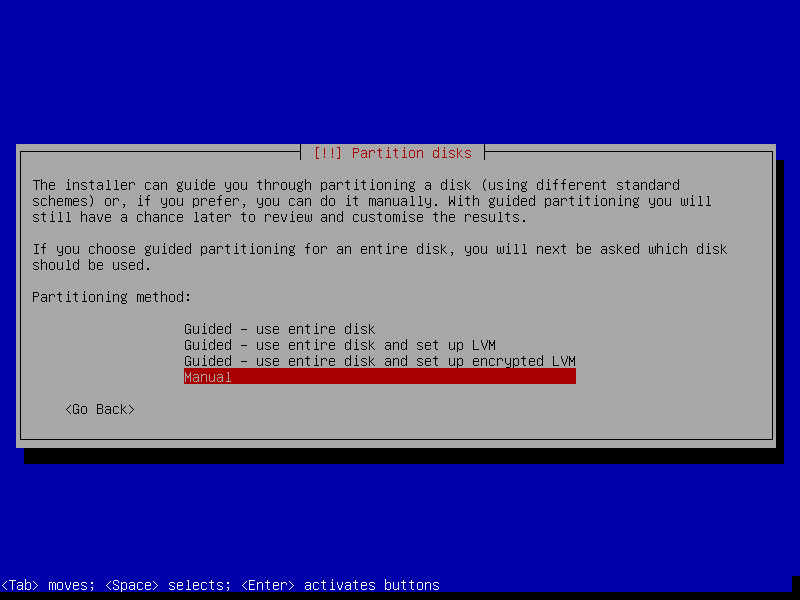
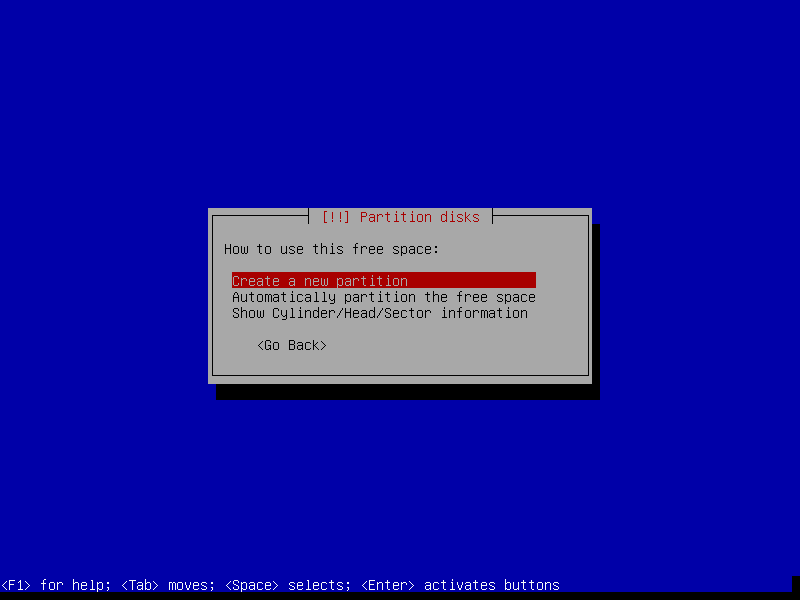
13. On the next screen, choose Manuel to perform disk partitioning.
Note: You can select Guided – use the entire disk and set up LVM (Logical Volume Manager) as partition layout for efficient disk space management and follow the instructions.
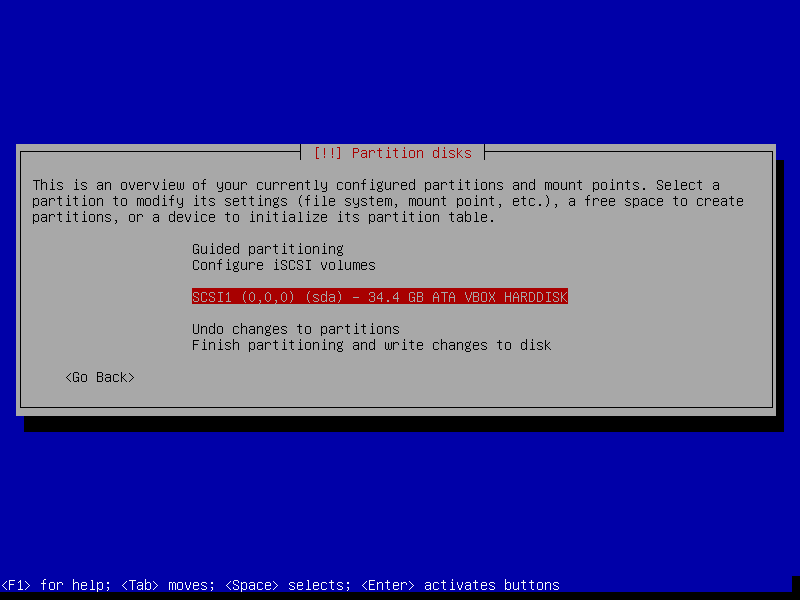
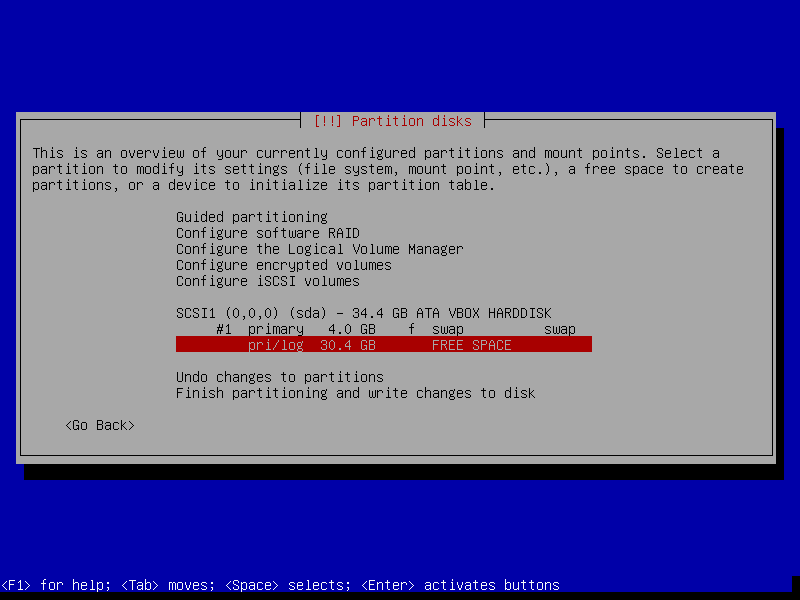
14. You will see an overview of your current system disks and mount points. Select the disk to be partitioned and click Continue.
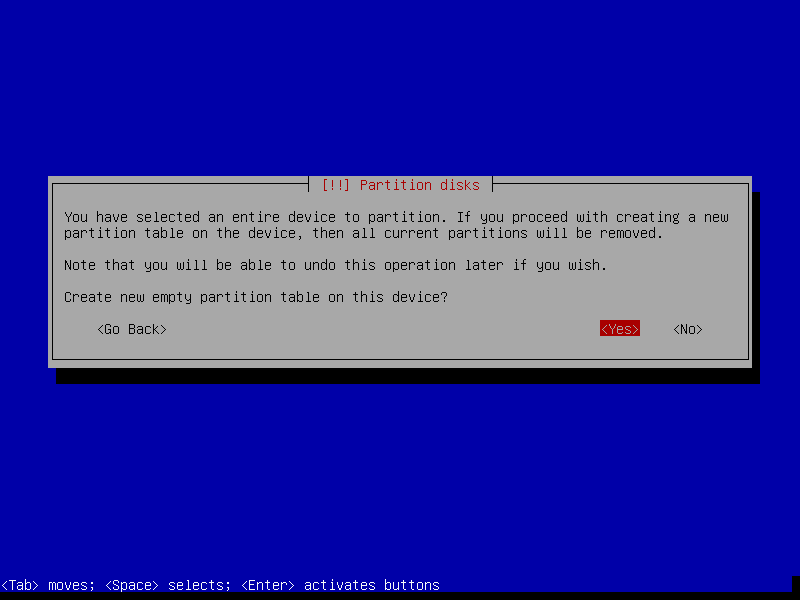
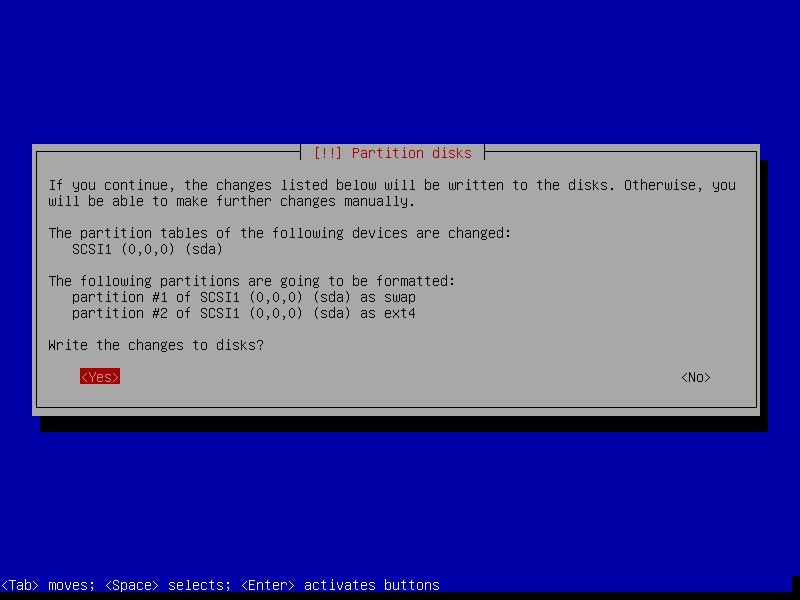
After that, select Yes to create a new empty partition table on the disk.
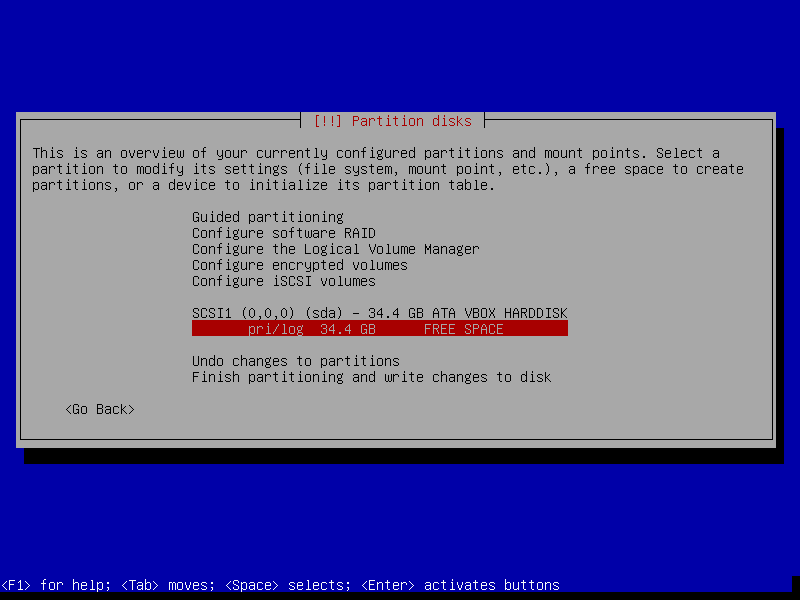
15. Next, select the free space on the disk to partition it and click Continue.
Creating Swap Partition
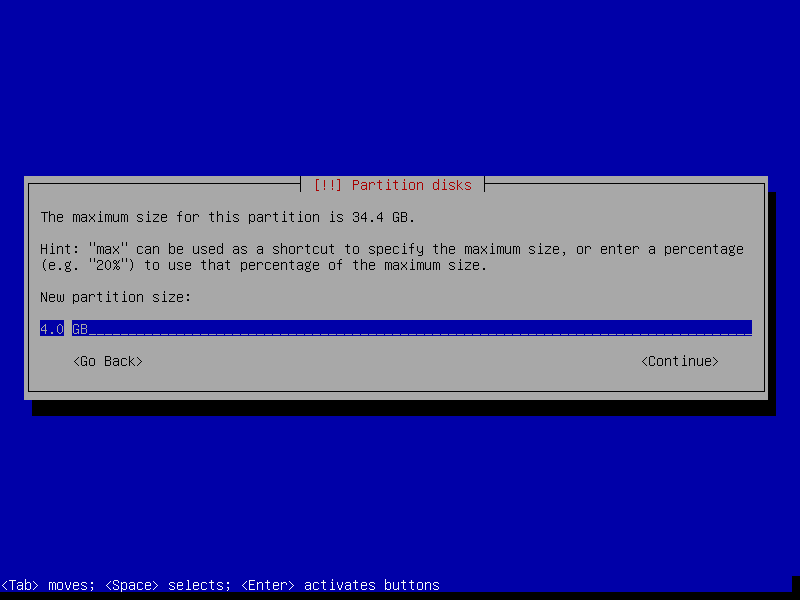
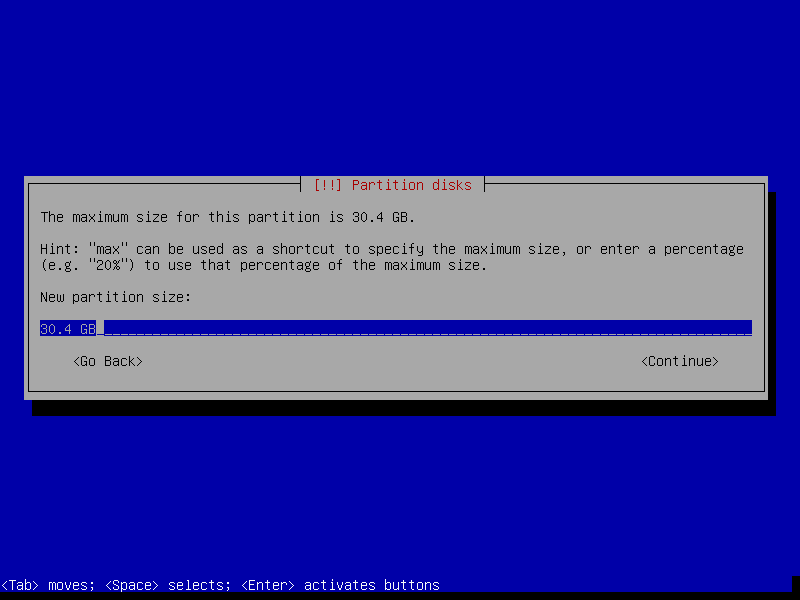
16. Now create the Swap area by selecting Create a new partition and set appropriate size as shown in the screenshots below. Then click Continue.
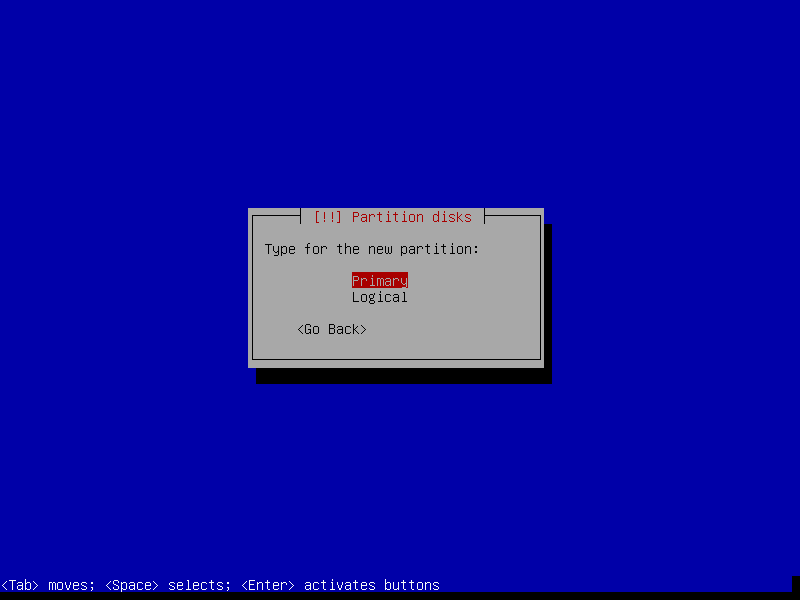
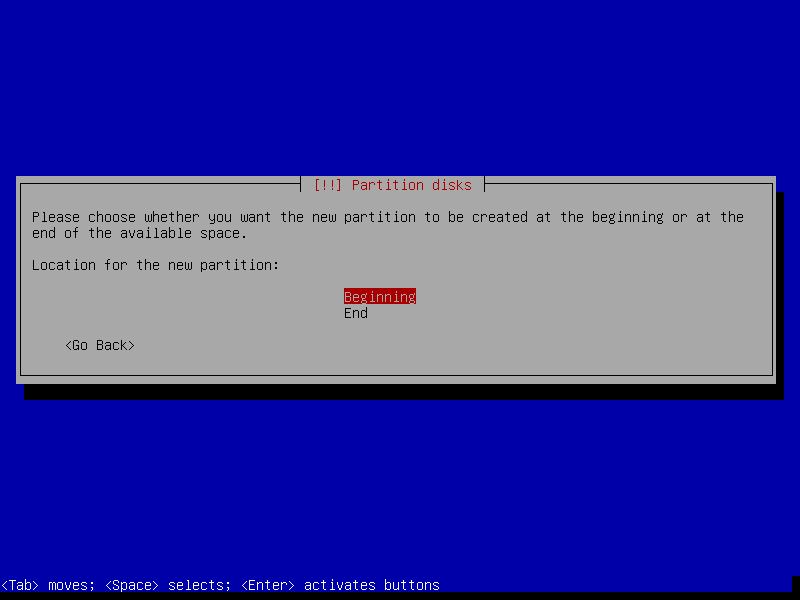
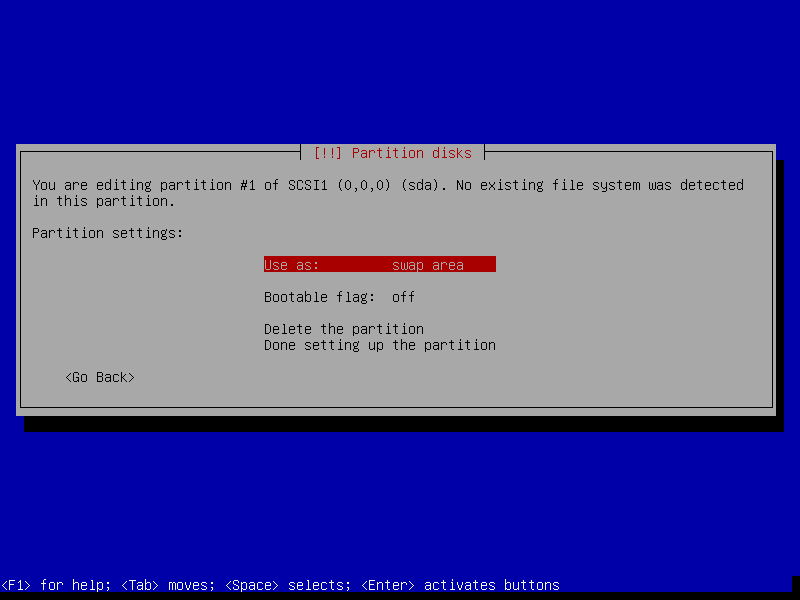
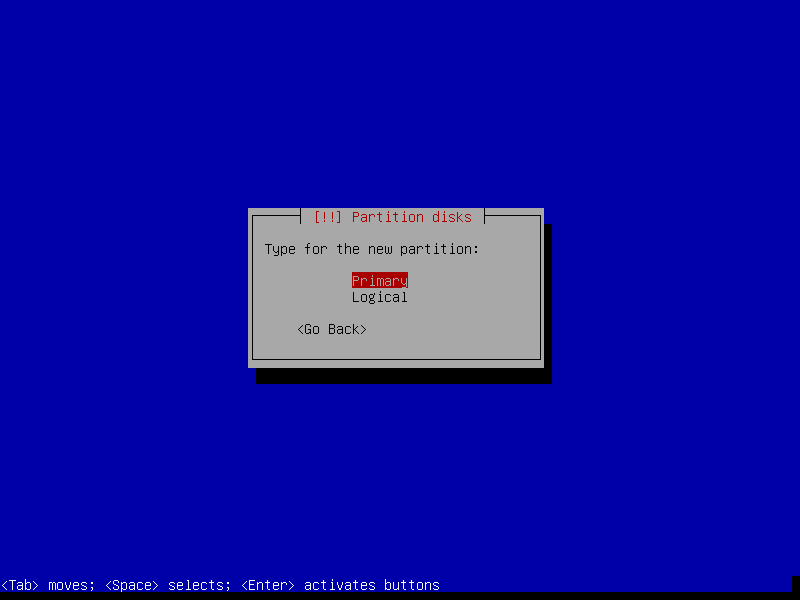
17. Set swap partition as Primary and choose the Beginning of the free space on disk and click Continue.
18. Now set partition as Swap area as shown in the following screenshot.
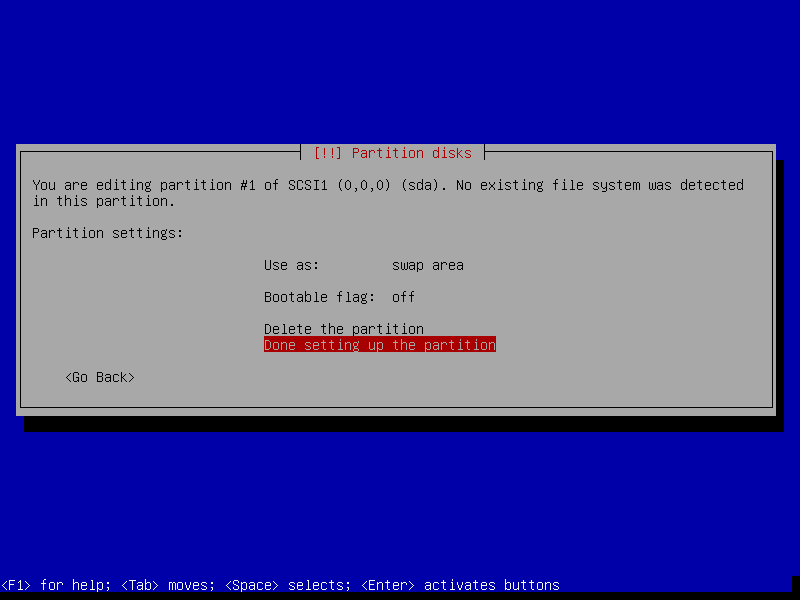
19. Now select Done setting up the partition and click Continue.
Create Root Partition
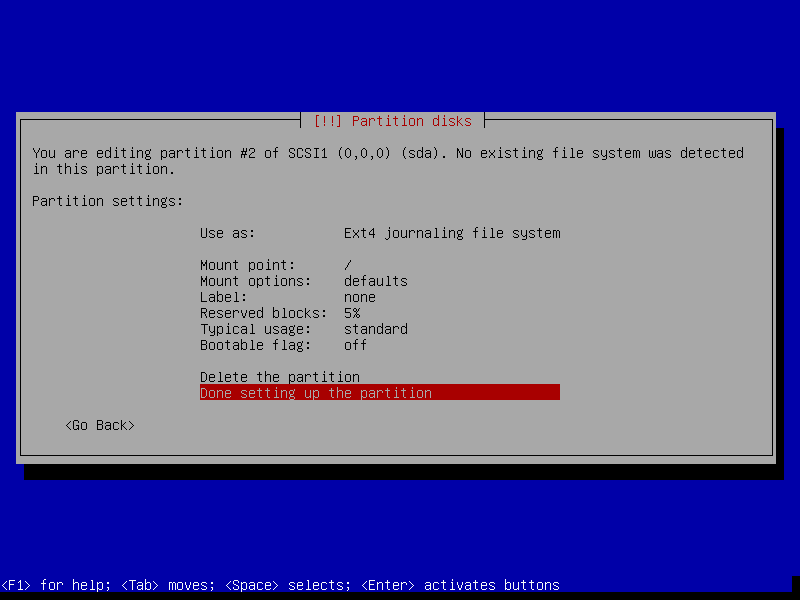
20. In this step, you can now create the root partition by selecting the free space, then select Create a new partition. Afterward set the root partition size, make it Primary and set it at the beginning of the free space.
Then use the Ext4 file system on it and finally select Done setting up partition and click Continue as shown in the following screenshots.
Create Home Partition
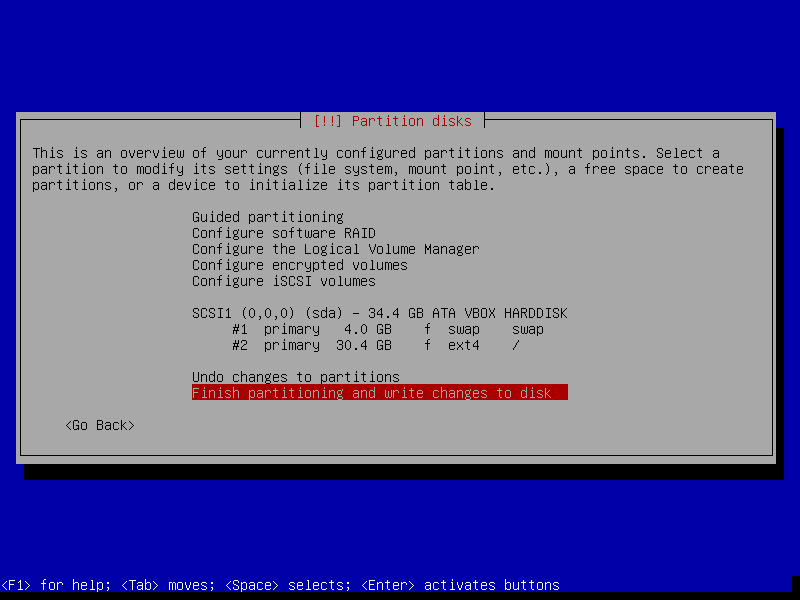
21. Similarly to create a /home partition follow the same instruction as explained above using the remaining free space if you have.
22. Once you have created all the necessary partitions, click on Finish partitioning and write changes to disk.
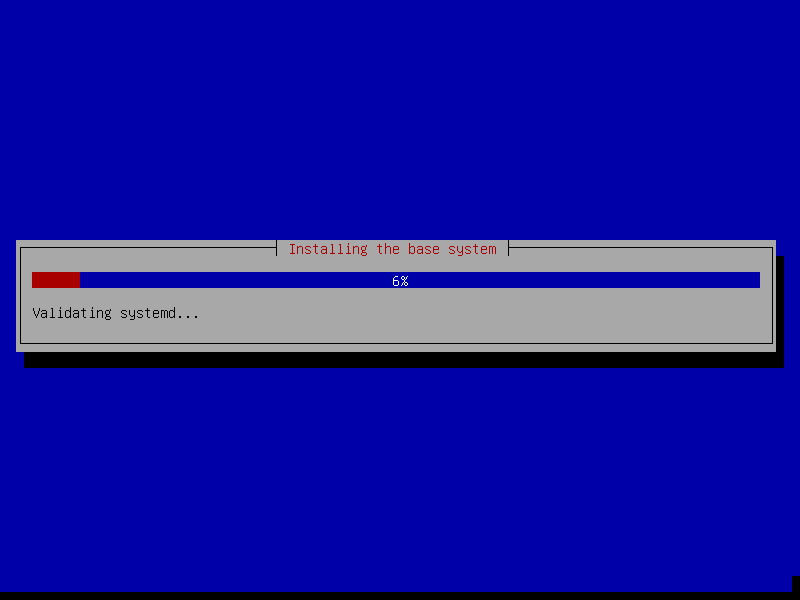
Finalizing Debian 11 Installation Process
23. At this point, installation of the base system should begin as shown below.
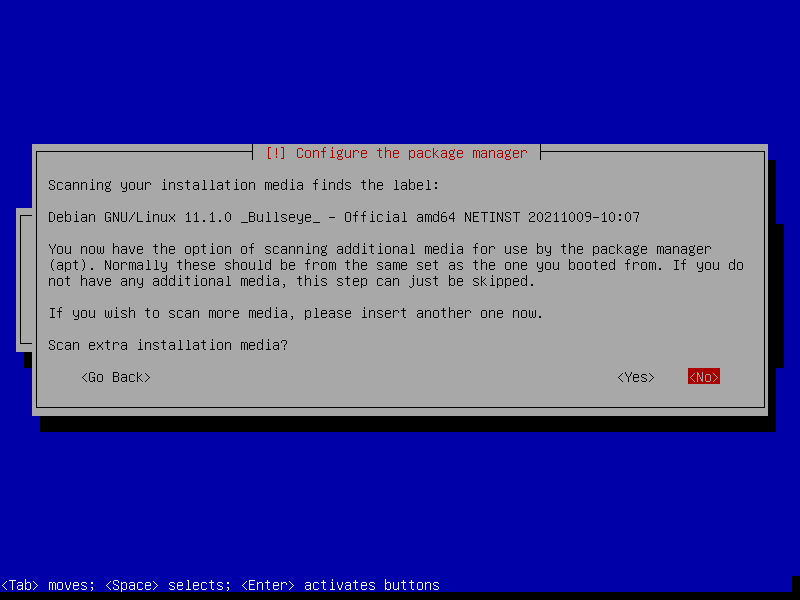
24. Now configure the package manager as shown in the screenshot below. Select No and click Continue.
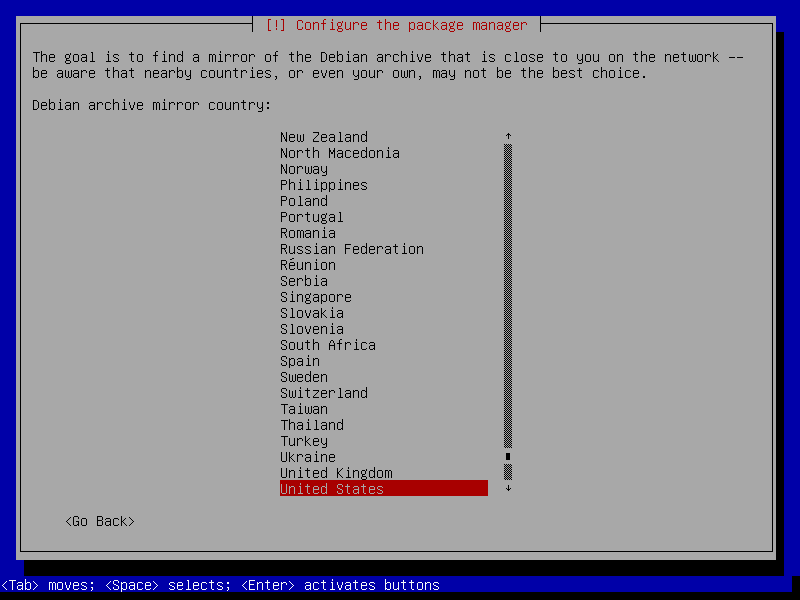
25. Afterwards, configure a network mirror by selecting the nearest country and then click Continue.
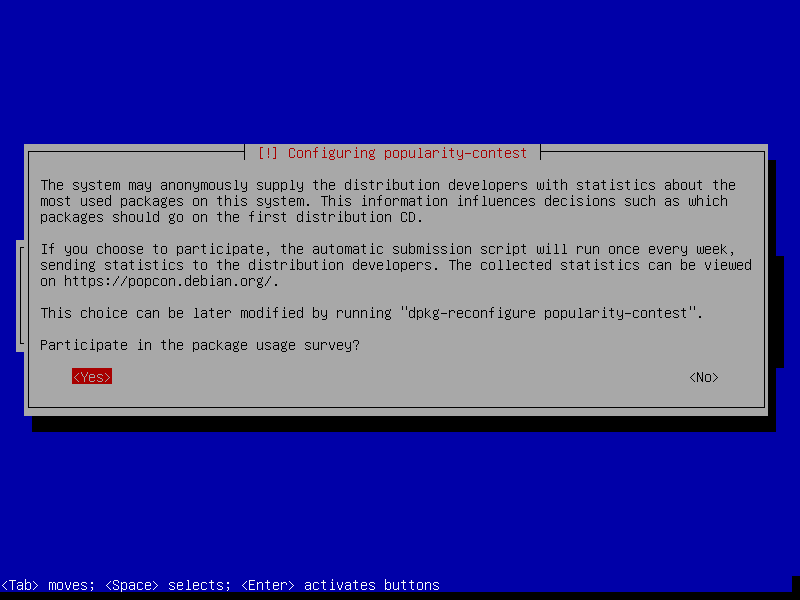
26. Next, choose whether to participate in the package usage survey or not. Then click Continue.
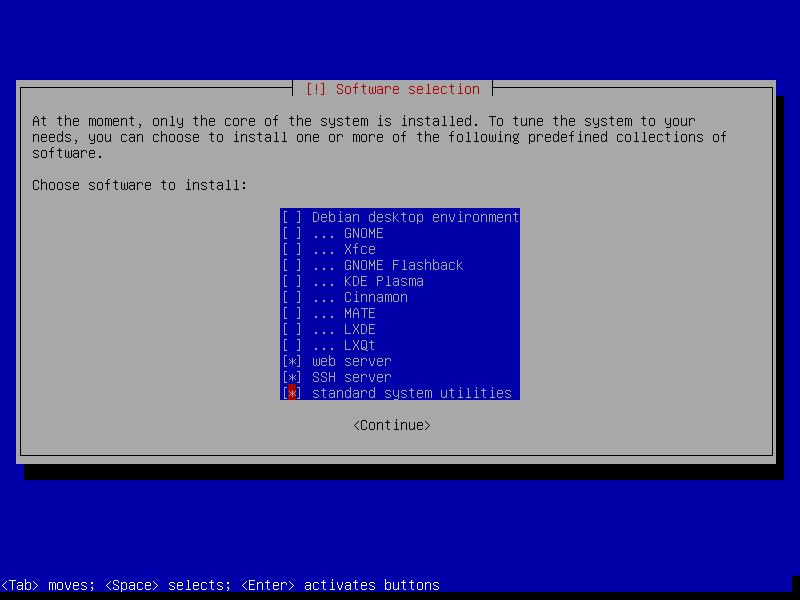
27. Now install standard system utilities and click Continue.
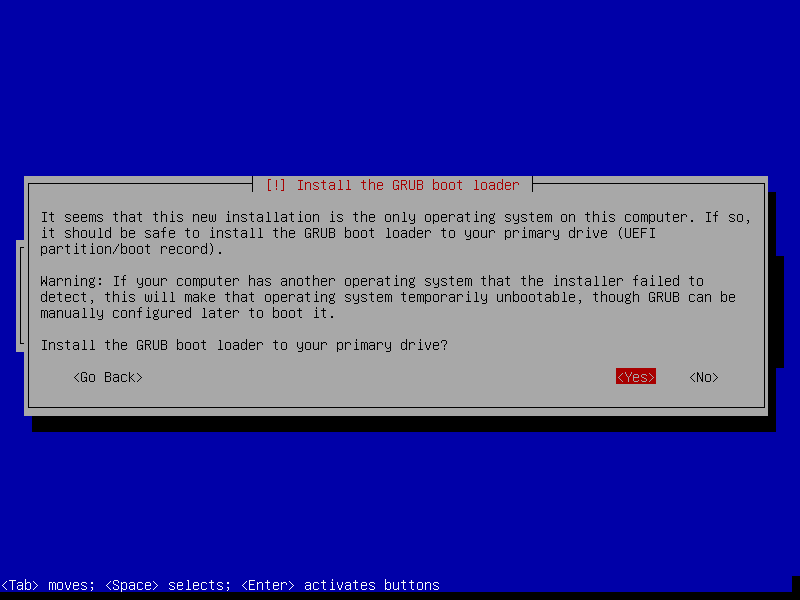
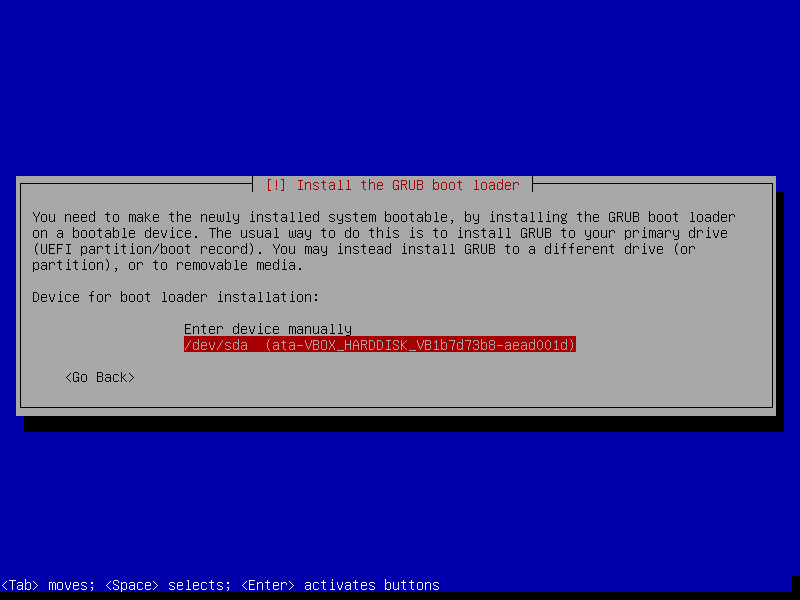
28. In this step, you will install the Grub boot loader by choosing Yes. After which you should choose the disk to install it.
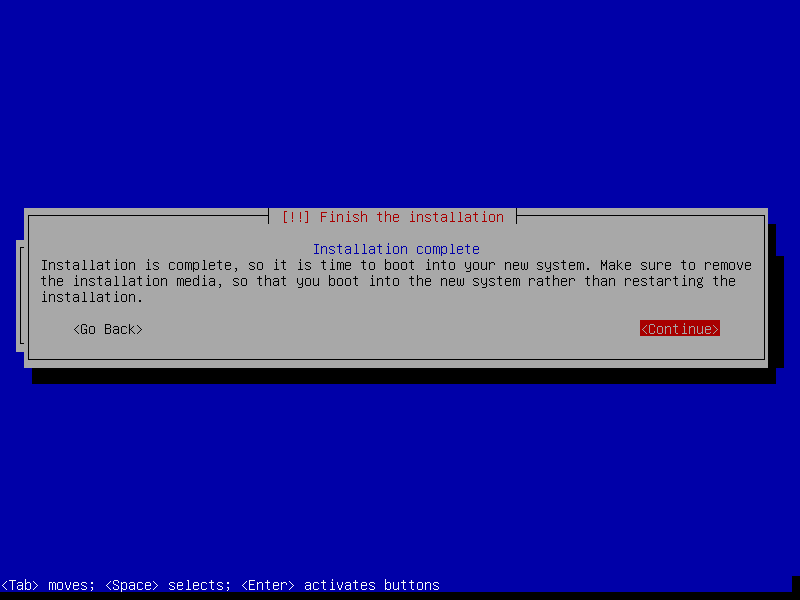
29. Finally, the installation is done, click Continue to reboot the machine and remove the bootable media, then boot in your system and login.
That’s all. You now have a working Debian 11 (Bullseye) Minimal Server for developing a future customizable server platform. If you are looking to deploy a web server such as Apache or Nginx, go through the following articles.
To send us any queries or thoughts, use the comment section below.