- How To Recover Deleted Files In Linux [Beginner’s Guide]
- How to recover deleted files in Linux using TestDisk
- Step 4
- Step 5
- Step 6
- Step 7
- Step 8
- Step 9
- Step 10
- A few tips on recovering deleted files in Linux using TestDisk
- Dave Merritt
- How To Recover Deleted Files by RM Command on Linux (Ubuntu)
- In this article
- Part 1: What Is the RM Command?
- How To Use the RM Command?
- Where Do Files Go When Running the RM Command
- Does RM Permanently Delete Files on Linux?
- Part 2: Recover RM Files in Linux Using Wondershare Recoverit (GUI Tool)
How To Recover Deleted Files In Linux [Beginner’s Guide]
Brief: This article shows you how to recover deleted files in Linux using command line tool Test Disk. It’s an easy to use tool that almost anyone can use to recover lost files in Ubuntu or other Linux distributions.
Have you ever gotten that horrible feeling? The one you get when you realize that you accidentally deleted files and it’s not even in the trash? Often it is immediately preceded by denial: I know I have another copy of it somewhere.
But rather than going through all the stages of grief, don’t worry. And remember you’re not alone; sooner or later everyone does this.
“Don’t worry?” you counter, “I just erased the only copy of my resume!”
No really, don’t worry. All that’s happened is that it’s been bumped off a list. So long as you don’t write onto the drive, it absolutely still exists. In fact, depending on the size of the file and the free space on your drive deleted files can persist indefinitely—even if you do write on the drive.
“Yes, fine” you say, “I’ll rest easy knowing my resume ‘exists’ in some abstract sense. But so far as I’m concerned if I can’t open, edit or print from it, it doesn’t exist in any practical sense. What would really help would be a way to ‘un-delete’ files. And one that doesn’t require an IT forensics lab.”
Really, don’t worry—you don’t need a lab to recover the deleted files. Furthermore, if you can get past using a primitive GUI, it’s actually easy to do! I’ll show you how to use TestDisk to recover deleted files.
How to recover deleted files in Linux using TestDisk
Let me present a simplified example: I took a clean thumb drive added some files, then deleted one. Now, my system has a feature which will directly delete files from removable media, by-passing the “trash” altogether; that is if I choose to “right” click on a file and then choose “delete”. It still presents a warning, but one click on the “yes” button and the file is gone forever. Or appears to be.
But this time I didn’t get that horrible feeling. And no, not because this is a cooked up scenario. I knew that all I had to do was open the terminal type “testdisk” and hit “enter”. When I did this for the first time I had one of my “Linux moments”. Because if you don’t have it—and I didn’t—it tells you how to get it! Just type “sudo apt install testdisk” and enter and you’ll have it in about 10 seconds.
If you prefer videos, you can watch this video of the same tutorial on It’s FOSS YouTube channel:
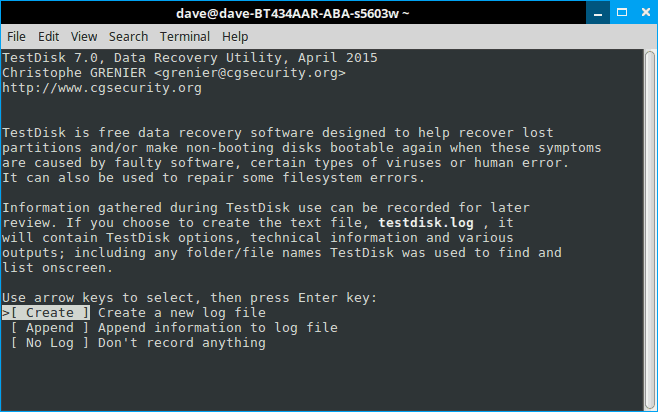
Screens that have extra commands will tell you so. Also note that TestDisk 7.0 tends to highlight the next reasonable step. It’s almost always right but do read the screen, since it can’t read your mind. In any case, when it wants you to let it create a log file, indulge it. It’s about to pull you out of a hole.
Step 4
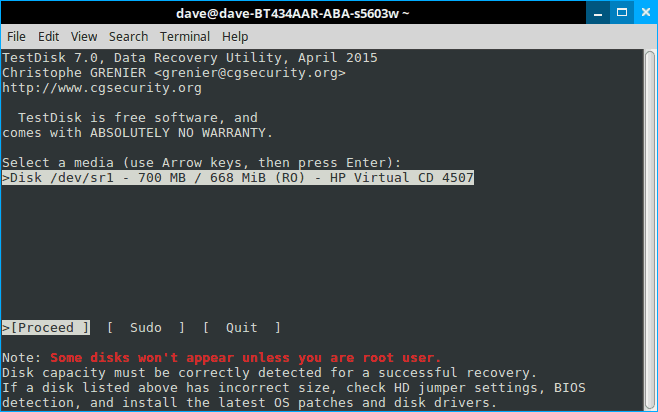
Now, at this point, if you’re lucky, you should see your drive. And you can proceed to the last steps. But let’s assume you’re not, that you have, say, a multi-boot machine. In this case, ownerships can get blurry, and Testdisk needs your permission to open them. You’ll see something like this:
Select “sudo” and enter your password. Hit “enter” and “enter” again on the next screen to create another log file.
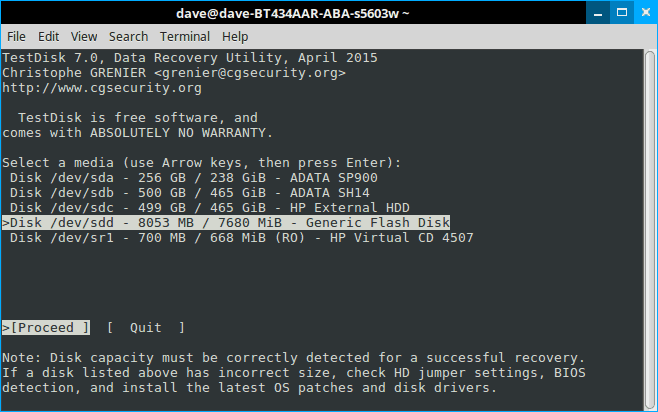
Step 5
This time Testdisk displays all your drives. Arrow key to the drive in question and hit enter.
Step 6
Testdisk has again selected the correct setting. This makes sense since a simple storage device is seldom partitioned. Again hit enter:
Step 7
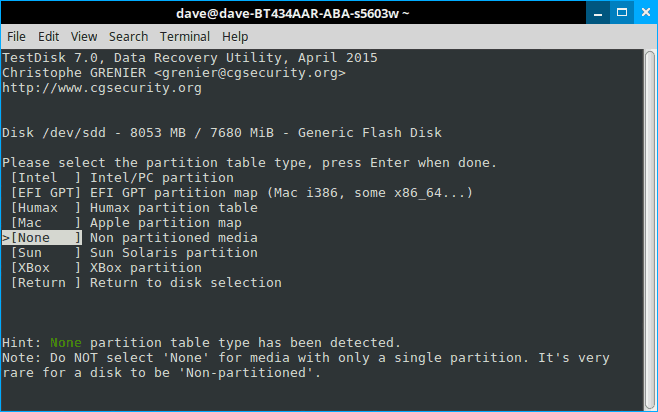
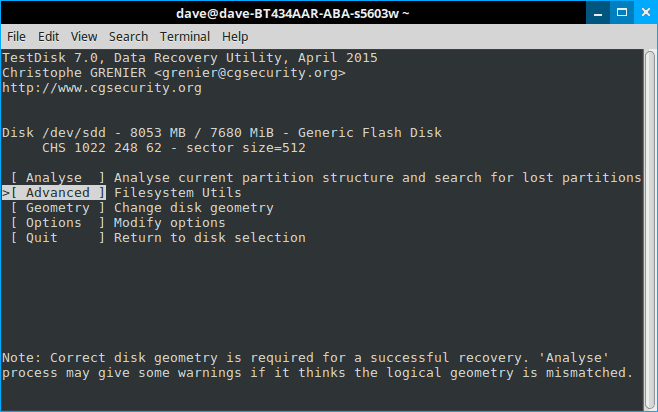
And finally we have to do a little thinking to do. If you read the first screen—and I’ll bet you didn’t—this program isn’t just for recovering deleted files. It’s a powerful disk utility. But if we remember what we’re trying to do the choice is fairly obvious: we’re not trying to fix a disk, we’re trying to recover a file. Select “Advanced” and hit “enter”.
Step 8
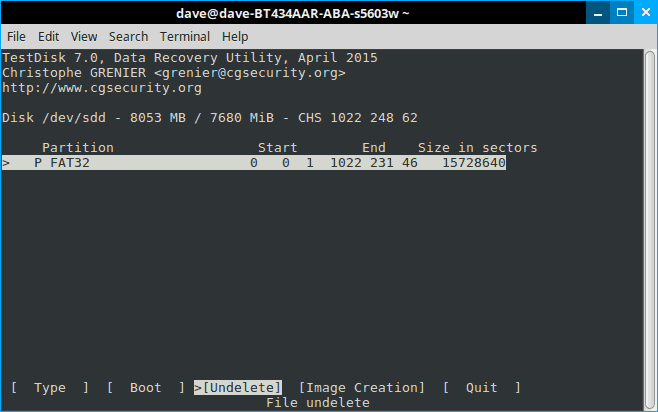
At the bottom of the page choose “Undelete” and get ready to see a ghost!
Step 9
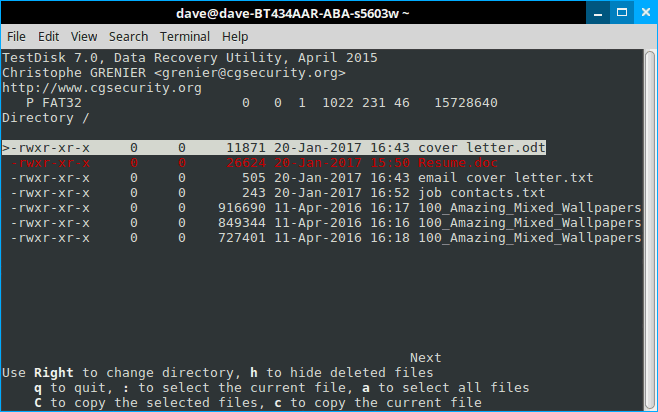
Testdisk will scan for files and produce a list of deleted files highlighted in red. Arrow down to it and carefully read the choices at the bottom.
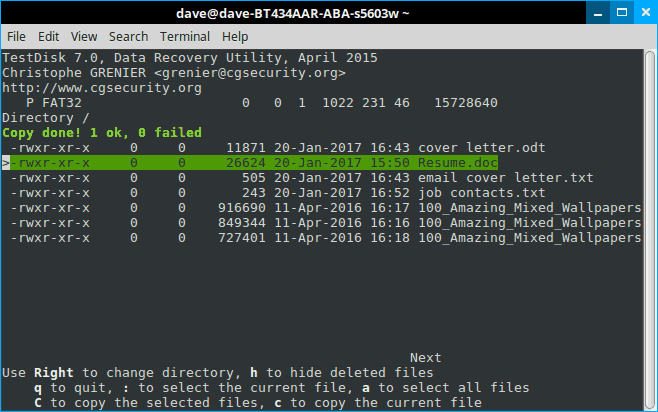
Step 10
Again, bear in mind that Testdisk is a multi-function tool. Most of these options deal with groups of files; we only want our damn resume back! So hit “c”.
As you can see from the scoreboard, we’ve won 1-0. After hitting “c” there are options about where you might want to recover the file to, but it defaults to your home folder. And again this is generally the best thing to do. Navigating in Testdisk is a little tricky, whereas dragging and dropping after the fact is a breeze.
A few tips on recovering deleted files in Linux using TestDisk
First, if you find yourself somewhere you don’t want to be, hit “q” for quit. This won’t close the program, instead, it will act like the “back” button on a program with a full blown GUI, and put you back a page. And just like a “back” button repeating will eventually lead you back to the beginning.
Second, as with anything, the fewer the distractions, the easier it is to find what you’re looking for. In other words, physically detach all other storage drives. In graphically simple environments simplicity is your friend.
Finally, Testdisk can also help you retrieve files that have become inaccessible for other reasons. In fact, this is why I started using the program in the first place. I was trying to save files from a corrupted drive that could not be made to boot. Normally it’s simply a matter of removing said drive any hooking it up to a USB adapter. You can then mount it on another PC and copy the files where ever you want.
But what if the drive is formatted to LVM? This was my problem because a mounted LVM drive looks nothing like a normal Linux OS. None of the usual files appear, and hunting around simply doesn’t help. This, among other reasons, is because most Linux file managers can no longer read ext.2 file systems.
Nevertheless, after a few false starts, I was able to find and save the missing files. Note, however, that the sequence of steps here will be a little different, you may need to use the “analyze” option for Testdisk to make sense of the drive and you may have to poke around a little to find the “home” folder once you do. Furthermore, the files you’re looking for will not appear in red since they were never deleted in the first place. But once you do find them, the copying procedure is basically the same.
With Testdisk and a little luck, you may never lose your resume again as you can always recover deleted files in Linux.
Disclaimer: This tutorial is a reader submission.
Dave Merritt
I’m a 59 years old, fulltime landscaper and parttime PCmedic. I’ve been an avid Linux user for over ten years. In that time, I do not claim to have made every possible mistake, only most of them. I’m a big fan of prog rock, avant jazz and J S Bach, and enjoy reading Neal Stevenson and anything to do with the foundational problems in modern physics.
How To Recover Deleted Files by RM Command on Linux (Ubuntu)
Here are the 3 methods to recover deleted files by RM command in Linux.
David Darlington
“Can files/directories deleted with rm be restored?” – askUbuntu
The » rm » command is a utility in Linux systems that allows you to delete files. However, sometimes you may accidentally delete important files using the rm command. There are even cases when this happens due to malware attacks, software-level corruption, or hard drive failure.
When it comes to Ubuntu, running the wrong command adds on. In such cases, it is possible to recover these deleted files using specific tools. This article will discuss how to recover deleted files in Linux using rm . We will explain the general concept of the rm command and the steps to recover files deleted by the rm command in Ubuntu using the GUI tool, command line tool, and extundelete.
In this article
Part 1: What Is the RM Command?
The » rm » command is a Linux utility used to delete files. It stands for «remove.» When you use the rm command to delete a file, it is permanently removed from the file system and cannot be recovered easily. Therefore, it is essential to be careful when using the rm command, especially if you delete important files.
Note: The rm command deletes files without asking for approval. As a result, it’s essential to use caution when using it to prevent unintentionally destroying important files.
How To Use the RM Command?
It would be best if you opened a Terminal on your Linux system to use the rm command. You can delete a file using the rm command by typing the command and the file’s name in the Terminal. As an example, you remove a file. The path to the file must be specified if it is in a separate directory. By separating the names of the files with a space, you can also remove multiple files at once.
The basic syntax for using the rm command is:
rm [options] file
Here, » file » is the name of the file that you want to delete. You can specify multiple files to be deleted by separating them with a space.
Deleting single file: If you want to delete a single file, you have to use the “rm” command followed by the file’s name as an argument.
rm filename
Deleting multiple files: You just need to pass the filenames as arguments separated by space if you want to delete multiple files.
rm filename1 filename2 filename3 filename 4
Removing directories: If you want to remove one or more than one directory, you have to use » -d «.
rm -d dirname
You can use several options with the rm command to modify its behavior. For example,
- The » -i » option forces the rm command to prompt for confirmation before deleting each file. It will display a message asking if you want to delete each file, and you can choose to delete or skip the file by typing » y » or » n ,» respectively.
- The » -f » option forces the rm command to ignore non-existent files and not prompt confirmation. It is helpful if you want to delete multiple files and wonder if some might not exist. The rm command will ignore the non-existent files and delete the rest.
- The » -r » option allows you to delete directories and their contents recursively. It will delete the directory and all its files and subdirectories. Be careful when using the » -r » option, as it can delete many files at once and is not reversible.
It is worth noting that the rm command does not send the deleted files to the trash bin or recycle bin. Instead, it permanently removes them from the file system, so it is important to be careful when using them.
For Windows XP/Vista/7/8/10/11
For macOS X 10.10 — macOS 13
Where Do Files Go When Running the RM Command
Let’s quickly review the Linux filesystem’s operation before moving to where the files are stored. The system establishes a link to the file when we create it. The system then uses these links to locate files on the disk.
The system only removes the link to the file when we use the rm command. It means that the file’s actual data is still present on the disk. Because of this, when we use the rm command, the filesystem deletes the references to the files and informs the operating system that the storage blocks have been released.
The rm command often instructs the system to mark the file’s inode and data blocks as unused. Data recovery was once possible in earlier Linux versions, but nothing can be recovered these days because the metadata has been erased.
There is no recycle bin or trash can with the rm command. Use the GUI, where files are typically relocated to the trash directory when removed if we need a recycle bin.
Does RM Permanently Delete Files on Linux?
Yes, when you use the rm command to delete a file in Linux, it is permanently removed from the file system and cannot be easily recovered. The rm command does not send the deleted files to the trash or recycle bin, as with some desktop environments. Instead, it permanently removes the files from the file system, so it is important to be careful when using it.
Even though the rm command permanently removes the files from the file system, it is still possible to recover the deleted files in some cases. It is because when a file is deleted, the system only marks the space occupied by the file as available for reuse, but the actual data is not immediately overwritten. Therefore, retrieving deleted files using specific tools is possible if new data has not been overwritten.
Part 2: Recover RM Files in Linux Using Wondershare Recoverit (GUI Tool)
We’ve all experienced the frustration of seeking a file to have it vanish, even in the trash. Well, that case will not be a problem anymore. Consider employing a third-party tool to recover your deleted files by RM command. One highly recommended tool is the Wondershare Recoverit Linux Recovery. Recoverit is a one-stop Linux data recovery solution that proudly offers its professional grade features like: