- Как настроить простой DNS-сервер для локальной сети
- Шаг 1. Установка необходимых пакетов
- Шаг 2. Настройка пакетов
- Шаг 3. Настройка используемых DNS-серверов
- Шаг 4. Локальное тестирование DNS-сервера
- Шаг 5. Тестирование DNS-сервера с других хостов
- Дополнительная информация
- Заключение
- How to use the Linux BIND command to install and configure DNS
- How DNS works
- Great Linux resources
- Where does DNS get IP addresses?
- Forward and reverse lookups
- Install and configure DNS
- Configure the /etc/named.conf file
- Define the forward and reverse zones
- Create forward and reverse zone files
- Add the nameserver IP to /etc/resolv.conf
- Start/restart and enable the named service
- Verify the DNS name resolution
- Query with nslookup
- Query with dig
- Wrap up
Как настроить простой DNS-сервер для локальной сети
Если вы впервые столкнулись с необходимостью поднять DNS-сервер для локальной сети под Linux, то эта статья – для вас. Преимущество предлагаемого способа – простота: сервер можно настроить буквально за несколько минут. Но этот способ, скорее всего, не подойдёт для продакшн серверов.
Автор статьи провёл несколько часов в борьбе с ошибками, багами и непонятным поведением системы прежде чем получил стабильный результат.
Далее будем считать, что имеется локальная сеть, состоящая из нескольких хостов. Локальная сеть настроена, сетевой доступ между хостами имеется. На хостах установлен Ubuntu 18.04.4 LTS (для других версий не проверялось).
Шаг 1. Установка необходимых пакетов
Следующие шаги выполняются на хосте, на котором будет устанавливаться DNS-сервер.
- Установите Dnsmasq: sudo apt-get install dnsmasq При установке выведутся следующие ошибки:
failed to create listening socket for port 53: Address already in use
FAILED to start up
Failed to start dnsmasq — A lightweight DHCP and caching DNS server.
При рестарте системы файл /etc/resolv.conf автоматически пересоздаётся. Поэтому если прописать в него нужный адрес вручную, то изменения окажутся стёртыми после перезапуска. По умолчанию после перезапуска в этот файл прописывается адрес 127.0.0.53 , который используется сервисом systemd-resolve . Этот сервис осуществляет определение IP-адресов доменов для приложений, работающих на том же хосте, на котором запущен сервис. Но мы планируем перестать использовать этот сервис и начать использовать dnsmasq .
Шаг 2. Настройка пакетов
- Отредактируйте файл /etc/dnsmasq.conf :
- no-resolv Эта настройка выключает загрузку настроек из /etc/resolv.conf . Все настройки будут браться из редактируемого файла /etc/dnsmasq.conf . Это сильно упрощает конфигурацию Dnsmasq’а, поскольку файл /etc/resolv.conf автоматически пересоздаётся при рестарте системы.
- server=8.8.8.8 8.8.8.8 — это адрес DNS-сервера Гугл. Этот адрес можно заменить на любой другой адрес публичного DNS-сервера. Например, на адрес DNS-сервера вашего провайдера или ранее используемого DNS-сервера. Запросы, которые не сможет обработать Dnsmasq будут направлены на этот сервер.
- listen-address=0.0.0.0 Эта настройка позволит осуществлять запросы к Dnsmasq’у с других хостов.
- bind-interfaces Задаёт режим, при котором Dnsmasq не осуществляет привязку к интерфейсам, по которым не должна осуществляться обработка запросов. Без этой настройки в предлагаемом варианте конфигурации сервер не работает.
Шаг 3. Настройка используемых DNS-серверов
Данная настройка выполняется на всех хостах-клиентах, с которых будут отправляться запросы на хост с сервисом Dnsmasq.
Проще всего настроить используемые DNS-сервера в графическом интерфейсе. Укажите адрес хоста, на котором установлен Dnsmasq, первым в списке:
Шаг 4. Локальное тестирование DNS-сервера
Проверку настроек можно и не делать. Но если вам интересно узнать, всё ли работает правильно, то выполните следующие команды на хосте с сервисом Dnsmasq.
- Проверьте, что в файле /etc/resolve.conf прописан адрес 127.0.0.1 : cat /etc/resolve.conf
- Выполните команду: sudo netstat -tulpen Вы должны увидеть, что адрес 0.0.0.0:53 занят Dnsmasq’ом, а адрес 127.0.0.53:53 не фигурирует в списке.
- Выполните команду: dig ya.ru Вы должны получить вывод, в котором присутствует примерно такая строчка. В начале строки не должно быть символов ; . ya.ru. 220 IN A 87.250.250.242
- Выполните команду: dig myserver.tst Вы должны получить вывод, в котором присутствует примерно такая строчка: myserver.tst. 0 IN A 1.2.3.4
Шаг 5. Тестирование DNS-сервера с других хостов
Теперь можно проверить работу DNS-сервера с других хостов.
Выполните пункты 3 и 4 из предыдущего раздела. Вывод в консоль должен быть аналогичен результатам, указанным в предыдущем разделе.
Дополнительная информация
- Следующая команда в режиме реального времени выводит в консоль все запросы, выполняемые на порт 53. Это помогает определить факт выполнения запросов. sudo tcpdump -l port 53 Данную команду логично выполнять в другом терминале – не в том, в который вводятся команды, подлежащие проверке.
- Обратите внимание, что DNS-запросы кэшируются и сервисом systemd-resolved, и сервисом dnsmasq. Для сброса кэша проще всего перезапустить используемый сервис: sudo systemctl restart dnsmasq (на серверном хосте) sudo systemctl restart systemd-resolved (на клиентских хостах)
Заключение
В этой статье мы рассмотрели, как можно сравнительно быстро настроить DNS-сервер для локальной сети под Linux. Если вы знаете какие-то другие фишки по настройке DNS-сервера, напишите об этом в комментариях.
How to use the Linux BIND command to install and configure DNS
The Domain Name System helps you get where you want to be on the internet. Make sure you know what it is and how to set up, configure, and test it.
The Domain Name System (DNS) is used to resolve (translate) hostnames to internet protocol (IP) addresses and vice versa. A DNS server, also known as a nameserver, maps IP addresses to hostnames or domain names.
In this article, you will learn the basics of DNS, from how DNS gets the IP address and hostname, to the concepts of forward and reverse lookup zones. It will also show you how to install and configure DNS, define and edit zone files, and verify whether the DNS can resolve to the correct address with the help of commands. If you are new to DNS, this article will help you play with it on your system using basic configurations.
How DNS works
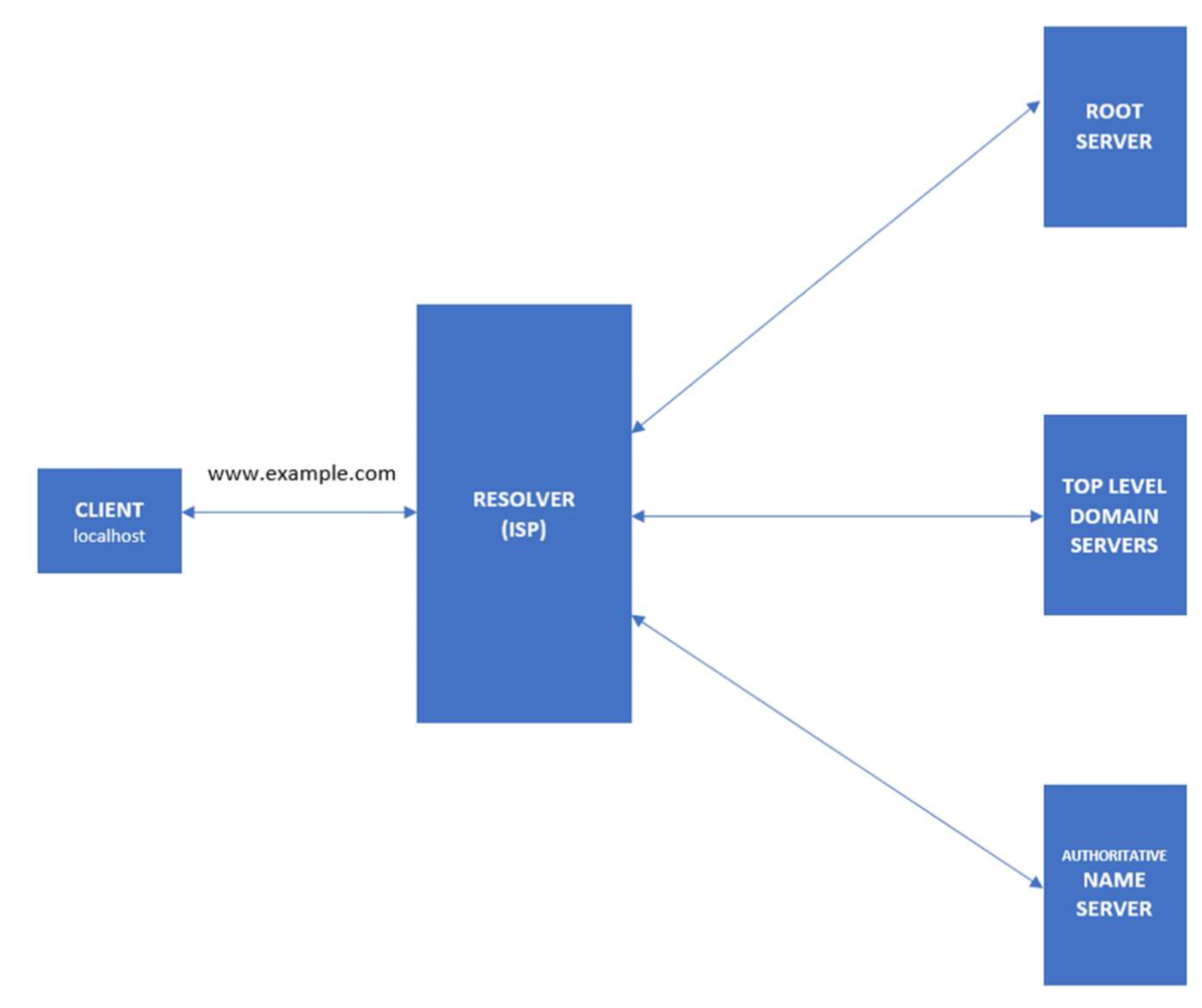
When a client requests information from a nameserver, it usually connects to port 53, and then the nameserver resolves the name requested.
Great Linux resources
Where does DNS get IP addresses?
You might wonder how DNS gets the IP of the corresponding hostname or domain name. How does DNS search among different IP addresses and associate your domain name correctly? Who stores those mappings between domain names and IP addresses?
The DNS workflow illustrates how communication happens within DNS and how it resolves the addresses.
- When the client searches for the domain www.example.com , the request will initially go to the internet service provider’s (ISP) resolver. It will respond to the user’s request to resolve a domain name.
- If the IP address is not found on the resolver, the request is forwarded to a root DNS server and later to the top-level domain (TLD) servers.
- TLD servers store information for top-level domains, such as .com or .net.
- Requests are forwarded to the nameservers, which know detailed information about domains and IP addresses.
- Nameservers respond to the ISP’s resolver, and then the resolver responds to the client with the requested IP.
- When the resolver doesn’t know the IP, it stores the IP and its domain in a cache to service future queries.
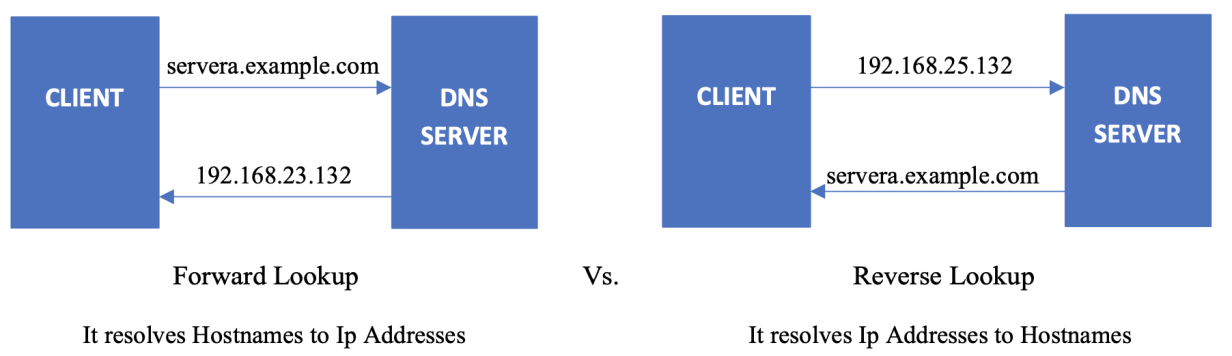
Forward and reverse lookups
The forward lookup zone uses the domain name to search for IP addresses, whereas the reverse lookup zone uses IP addresses to search for the domain name.
Install and configure DNS
BIND is a nameserver service responsible for performing domain-name-to-IP conversion on Linux-based DNS servers.
[root@servera ~] # yum install bindThe BIND package provides the named service. It reads the configuration from the /etc/named and /etc/named.conf files. Once this package is installed, you can start configuring DNS.
Configure the /etc/named.conf file
First, add or edit the two values in the options field. One is the DNS server address, and the other is the allow-query to any.
[root@servera ~] # vim /etc/named.conf listen-on port 53 < 127.0.0.1; 192.168.25.132; >; allow-query < localhost; any; >;Here are the values from the above file:
- 192.168.25.132 – DNS server address
- any – matches every IP address
Define the forward and reverse zones
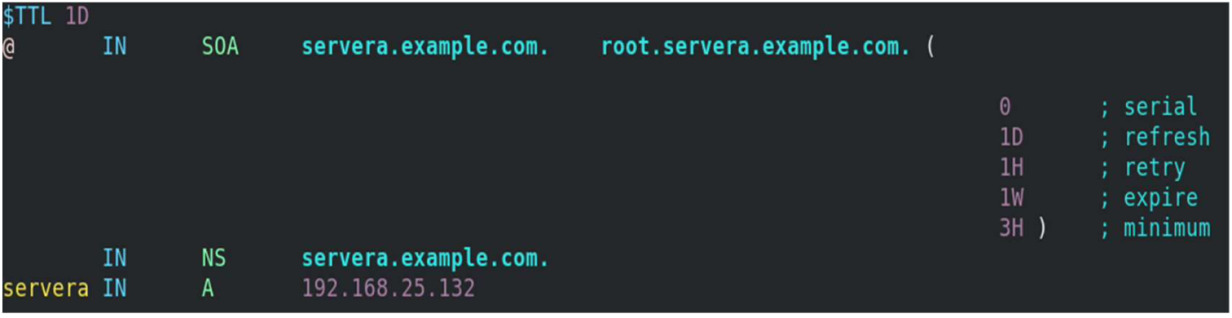
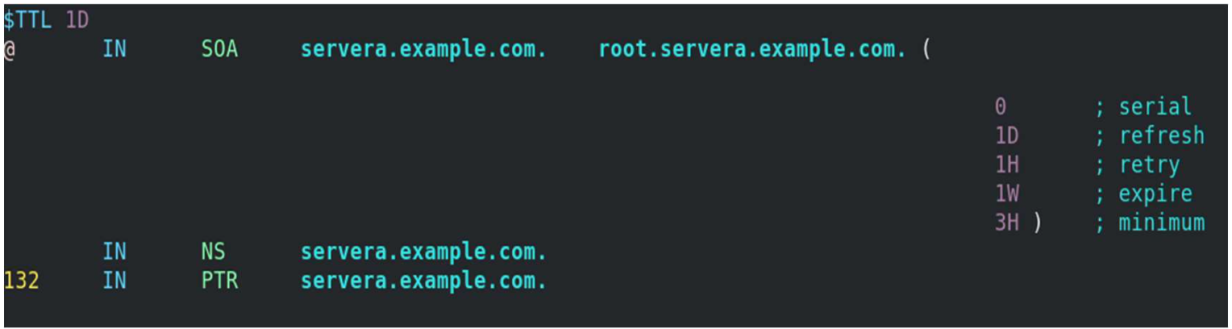
Define the forward and reverse zones in the /etc/named.conf or /etc/named.rfc1912.zones (you can define zones in either of those files). In this example, I am appending zone definition details to the /etc/named.rfc1912.zones file.
[root@servera ~] # vim /etc/named.rfc1912.zones zone "example.com" IN < type master; file "example.forward.zone"; allow-update < none; >; >; zone "25.168.192.in-addr.arpa" IN < type master; file "example.reverse.zone"; allow-update < none; >; >; Create forward and reverse zone files
You also need to create forward and reverse zone files in the /var/named directory.
Note: By default, the named.conf file includes the /var/named directory for checking zone files. Sample zone files named.localhost and named.loopback are created during the installation of the BIND package.
[root@servera ~] # vim /var/named/example.forward.zone[root@servera ~] # vim /var/named/example.reverse.zoneAdd the nameserver IP to /etc/resolv.conf
First, you must disable DNS processing by NetworkManager because it dynamically updates the /etc/resolv.conf file with DNS settings from its active connection profiles. To disable this and allow manual editing of /etc/resolv.conf , you must create a file (For example, 90-dns-none.conf ), as root in the /etc/NetworkManager/conf.d/ directory that contains the following:
Save the file and reload (restart) NetworkManager.
# systemctl reload NetworkManagerAfter you reload NetworkManager, it won’t update /etc/resolv.conf . Now, you can manually add the nameserver’s IP address to the /etc/resolv.conf file.
[root@servera ~] # vim /etc/resolv.conf # Generated by NetworkManager search localdomain example.com nameserver 192.168.25.132[ Be prepared in case something goes wrong. Read An introduction to DNS troubleshooting. ]
Start/restart and enable the named service
If the named service is not running or is disabled, then start and enable it. If it is already active (running) and you made all these configurations, you need to restart the service to make changes.
[root@servera ~] # systemctl status named.service [root@servera ~] # systemctl start named.service [root@servera ~] # systemctl enable named.service [root@servera ~] # systemctl restart named.service Verify the DNS name resolution
You have installed the BIND package, configured named files, created lookup zones, and restarted the service to make configurations take effect. Now use the nslookup and dig commands to check whether DNS is working properly and verify whether you are getting the intended results.
- nslookup is a program to query internet domain name servers.
- dig is a tool for interrogating DNS servers. It performs DNS lookups and displays the answers that are returned from the nameserver.
Query with nslookup
[root@servera ~] # nslookup servera.example.com Server: 192.168.25.132 Address: 192.168.25.132#53 Name: servera.example.com Address: 192.168.25.132 [root@servera ~] # nslookup 192.168.25.132 132.25.168.192.in-addr.arpa name = servera.example.com.Query with dig
Here is a forward lookup, where DNS responds with 192.168.11.132 as an IP for servera.example.com:
[root@servera ~] # dig servera.example.com . output truncated. ;; ANSWER SECTION: servera.example.com. 86400 IN A 192.168.25.132 ;; AUTHORITY SECTION: example.com. 86400 IN NS servera.example.com. . output truncated. This example displays a reverse lookup, where the DNS server responds with servera.example.com as the domain name for 192.168.25.132:
[root@servera ~] # dig -x 192.168.25.132 . output truncated. ;; ANSWER SECTION: 132.25.168.192.in-addr.arpa. 86400 IN PTR servera.example.com. ;; AUTHORITY SECTION: 25.168.192.in-addr.arpa. 86400 IN NS servera.example.com. ;; ADDITIONAL SECTION: servera.example.com. 86400 IN A 192.168.25.132 . output truncated. [ Network getting out of control? Check out Network automation for everyone, a free book from Red Hat. ]
Wrap up
In this article, you learned what DNS is and how it works. Also, you now know what forward and reverse lookup zones are and how they work. You also learned how to install the BIND package, which is responsible for setting up DNS on the system and configuring the named files and lookup zones. Finally, you learned two commands, nslookup and dig , to interrogate DNS resolutions.