- Linux Home Directory
- What Is the Linux Home Directory?
- Advantages of the Linux Home Directory or Partition:
- Enter Your Home Directory With Just a Command:
- The Home Directory Permissions:
- Conclusion:
- About the author
- David Adams
- Linux домашняя директория пользователя root
- Learn Latest Tutorials
- Preparation
- Trending Technologies
- B.Tech / MCA
- Javatpoint Services
- Training For College Campus
- Linux домашняя директория пользователя root
- Типичная структура ФС системы Linux
- / – корневая директория (root)
- /bin – главные бинарные файлы (исполняемые программы)
- /boot – файлы для загрузки ОС
- /dev – файлы устройств
- /etc – конфигурационные файлы
- /home – домашние директории пользователей
- /lib – основные библиотеки
- /lib64 – 64-битные основные библиотеки
- /lost+found – восстановленные файлы
- /media – точка для автоматического монтирования
- /mnt – точка для ручного монтирования
- /opt – вспомогательные пакеты программ
- /proc – файлы ядра и процессов
- /root – Домашняя директория пользователя root
- /run – файлы состояния приложений
- /sbin – бинарные файлы (программы) для администрирования системы
- /selinux – виртуальная файловая система SELinux
- /srv – данные сервисных служб
- /sys – виртуальная файловая система sysfs
- /tmp – временные файлы
- /usr – пользовательские бинарные файлы, используемые только для чтения
- /var – директория для часто меняющихся данных
Linux Home Directory
In this article, you will learn both theoretical and practical information on the Linux Home directory, which stores all information related to the users.
After reading this tutorial, you will know what a Home Directory is, the permissions structure, and application scenarios. This is useful for Linux distributions and other Unix-based operating systems like BSD.
Practical instructions in this tutorial include screenshots, making it easy for any Linux user to follow them.
What Is the Linux Home Directory?
Contrary to Microsoft Windows, Linux was designed to be a multiuser and multitasking operating system. This means that Linux is optimized to be used by different users. This is also useful to interact within networks securely.
Linux systems include a universal directory named Home, whose parent directory is the root (/) directory as a multiuser operating system.
In other words, the Linux Home Directory or partition stores personal directories of each user, which is restricted only to the homeowner and root user.
Let’s say you have a user named linuxhint in your system and another user named systemuser, then the path for each user’s personal directory will be:
Where “/” is the root directory, home is the general directory or partition storing all personal account directories (e.g. linuxhint or systemuser).
The exception to this rule is the root personal directory, which is not located under the /home/ partition/directory but under the root system location (/root/).
Home Directories are followed by a tilde slash (~), as shown below:
Advantages of the Linux Home Directory or Partition:
As said previously, the Home of a user isolates or restricts access to user files. This includes customization settings. Here, you can store configuration files that will affect only the Homeowner.
As you can imagine, this includes executable files stored only under a user’s Home Directory, which can be executed only within the user environment specifically. This also prevents malicious code from infecting the entire system.
This is one of the main reasons Linux is a more secure operating system than Windows. Linux was natively created under the premise, while Windows, developed for personal use, patched its operating system to implement a similar feature. In contrast, Linux was developed to grant privacy and security to different users.
Like other operating systems, this directory is created automatically when installing your system. During the Linux installation process, you can assign the Home directory an exclusive partition. This will ease your backup and restoration tasks and just save them.
Enter Your Home Directory With Just a Command:
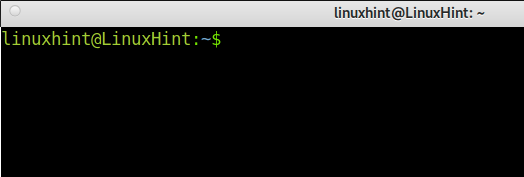
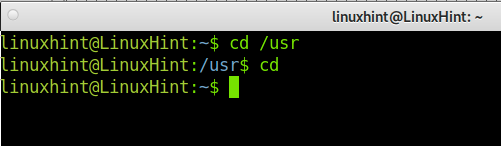
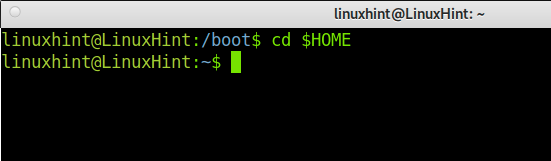
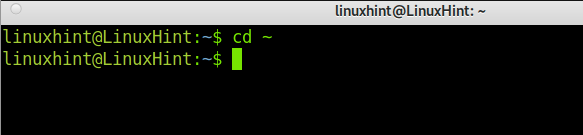
There are different commands to access your Home Directory immediately: cd, tile slash (~), and cd $Home.
A cd command example, where the user changes the current directory from the /usr to /home/username directory.
A cd $HOME command example, where the user changes the current directory from /boot to /home/username directory.
A cd ~ command example, where the user changes the current directory from /boot to /home/username directory.
You can use the pwd command example to show the current directory to learn if you are in your /home.
Note: you can move to other directories by typing cd /, such as cd /user and cd /boot. To access files and directories when the current path isn’t the /home directory, always add the /home/ path as the parent directory in the path.
The Home Directory Permissions:
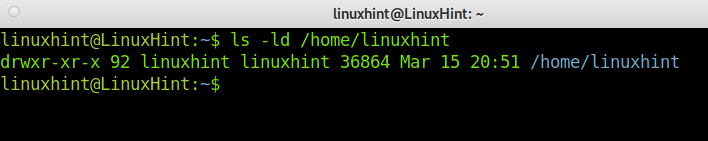
Default permissions of the /home directory are drwxr-xr-x (755), allowing the user group to execute and read files and others to execute files within the Home Directory.
You can check your Home Directory permission as shown in the following image:
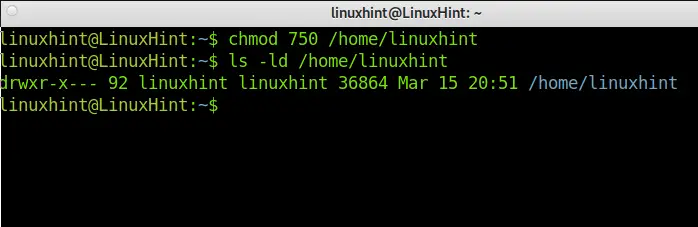
If you are looking for better security and privacy, you can change the default permissions to 750.
Below you can see the command execution and result:
As you can see, others can’t read or execute files now. The owner keeps full rights, and the group read and execution permissions.
The /home directory is a formidable way to manage the users’ files. This allows users to manage users’ privacy, to move an entire user dedicated directory storing one’s files, for example, for backup purposes.
The root user is the only one allowed to access all users’ Home Directories with full permissions. Use the privileged user (root) to change permissions globally in your system. Yet, other users have global rights when reading files. You can change specific directory permissions by running the last command explained in this tutorial. It is recommended to increase your privacy, changing permissions to a more private policy.
Learning Linux permissions will allow you to customize your file access, as shown previously. You can get additional information on changing Linux permissions here. Understanding the home directory theoretic is useful to deal with other operating systems aside from Linux, like the BSD-based systems. In Macintosh, users, the equivalent to the /home directory is /users/, where users directories are /users/username.
Conclusion:
The Home Directory, as a separate component of your system filesystem, shows Linux as the superior structure of this operating system over others; even over other systems, which didn’t include the multiuser feature natively, patching it later. Learning Linux permissions will allow you to customize your file access, as shown previously.
Thank you for reading this Linux tutorial about the /home directory. I hope it was helpful for you to understand more about Linux. Keep following Linux Hint for more Linux professional articles.
About the author
David Adams
David Adams is a System Admin and writer that is focused on open source technologies, security software, and computer systems.
Linux домашняя директория пользователя root
Learn Latest Tutorials
Preparation
Trending Technologies
B.Tech / MCA
Javatpoint Services
JavaTpoint offers too many high quality services. Mail us on h[email protected], to get more information about given services.
- Website Designing
- Website Development
- Java Development
- PHP Development
- WordPress
- Graphic Designing
- Logo
- Digital Marketing
- On Page and Off Page SEO
- PPC
- Content Development
- Corporate Training
- Classroom and Online Training
- Data Entry
Training For College Campus
JavaTpoint offers college campus training on Core Java, Advance Java, .Net, Android, Hadoop, PHP, Web Technology and Python. Please mail your requirement at [email protected].
Duration: 1 week to 2 week
Like/Subscribe us for latest updates or newsletter 




Linux домашняя директория пользователя root
Файловая концепция Linux – это четкая структура каталогов и файлов. В этом посте рассмотрим предназначения всех директорий. Файловые системы Линукс содержат большое множество каталогов, большинство из них подходят под спецификацию FHS (Filesystem Hierarchy Standard). Почему существуют термины “каталог”, “директория” и “папка”? В чем их отличие? Давайте узнаем.
Каталог, он же директория, (от англисйкого Directory) – это объект в ФС (файловой системе), необходимый для того, чтобы упросить работу с файлами. Папка (от английского Folder) – это определение применяется для отображения директорий в графическом пользовательском интерфейсе (GUI). Отсюда вытекает, что все эти определения значат, в принципе, то же самое. Чтобы было удобно, будем применять в этом посте определение “директори”, по мнению большинства пользователей Линукс, это более правильный термин.
Типичная структура ФС системы Linux
Наличие тех или иных директорий может быт в зависимости от того, какой дистрибутив Вы используете. Ниже список наиболее важных и часто встречающихся:
/
/bin
/boot
/dev
/etc
/home
/lib
/lib64
/lost+found
/media
/mnt
/opt
/proc
/root
/run
/sbin
/selinux
/srv
/sys
/tmp
/usr
/var
Итак, рассмотрим все по-порядку.
/ – корневая директория (root)
Родительская директория, в ней находится все, что есть в нашей ОС. В ней хранятся другие каталоги.
/bin – главные бинарные файлы (исполняемые программы)
Содержит основные модули, утилиты и командные оболочки, которые могут обеспечить необходимый минимально уровень работоспособности ОС. Размещение этих файлов в директории /bin гарантирует, что в системе эти важные утилиты будут даже в случае, если другие файловые системы не смонтированы.
/boot – файлы для загрузки ОС
Хранятся образы ядер Linux и файлы менеджеров загрузки (grub, lilo и т.д.).
/dev – файлы устройств
В Linux все устройства предоставлены в виде специфических файлов, расположеных в этой директории. К примеру, файл /dev/sda представляет диск SATA. Также в этой директории хранятся файлы псевдо-устройств (виртуальных), для этих файлов нет соответствующего реального устройства. Например, файл /dev/random генерирует случайные числа, а файл /dev/null является специальным устройством для удаления всех входных данных.
/etc – конфигурационные файлы
Содержит основные конфигурационные файлы операционной системы и различных программ.
/home – домашние директории пользователей
По идеологии UNIX для обеспечения безопасности ОС рекомендуется хранить пользовательские данные именно в этой директории. Например, если ваше имя пользователя user, то у вас есть домашняя дирекотория, которая находится в /home/user и содержит пользовательские конфигурационные файлы и личную информацию. Каждый пользователь имеет доступ на запись только в свою домашнюю директорию.
/lib – основные библиотеки
Эта директория предназначена для хранения системных библиотек и компонентов компилятора языка С, необходимых для работы программ из директорий /bin и /sbin и операционной системы в целом.
/lib64 – 64-битные основные библиотеки
Эта директория присуствует в основном на 64-битных системах, содержит набор библиотек и компонентов компилятора языка С для 64-битных программ.
/lost+found – восстановленные файлы
Присуствует во всех ОС Linux. При сбое в работе файловой системы и дальнейшей проверке файловой системы (при загрузке ОС), все найденные поврежденные файлы будут помещены в директорию lost+found, их можно попытаться восстановить.
/media – точка для автоматического монтирования
Используемая для автоматического монтирования различных устройств CD-ROM, USB-накопителей и т.д.
/mnt – точка для ручного монтирования
Используется для временного ручного монтирования (с помощю команды mount) различных устройств, таких как CD-ROM, USB-накопителей и т.д.
/opt – вспомогательные пакеты программ
Находятся субдиректории для дополнительных пакетов программного обеспечения. Каталог широко используется проприетарным программным обеспечением, которое не подчиняется стандартной иерархии файловых систем.
/proc – файлы ядра и процессов
В эту директорию примонтирована виртуальная файловая система procfs. В ней находятся специальные файлы, в которых представлена информация о системе и о выполняющихся процессах. Например, в файле /proc/cpuinfo собержиться информация о процессоре.
/root – Домашняя директория пользователя root
Вместо того, чтобы находиться в /home/root, он помещается в /root для большей надёжности системы.
/run – файлы состояния приложений
Является достаточно новой директорией, в которой приложениям предоставляется возможность стандартным образом хранить вспомогательные файлы, которые им требуются, например, сокеты и идентификаторы процессов. Эти файлы нельзя хранить в каталоге /tmp, поскольку эти файлы могут быть там удалены.
/sbin – бинарные файлы (программы) для администрирования системы
Директория /sbin похожа на /bin. В ней находятся важные двоичные файлы, которые, как правило, предназначены для их запуска пользователем при администрировании системы.
/selinux – виртуальная файловая система SELinux
В некоторых дистрибутивах (Red Hat, Fedora и т.п) для обеспечения безопасности используется пакет SELinux (Security-Enhanced Linux), при этом создается директория с файлами /selinux.
/srv – данные сервисных служб
Эта директория присуствует не во всех дистрибутивах, содержит “данные для сервисов, предоставляемых системой” (например сервер Apache может хранить файлы вашего сайта в этой директории). В большинстве случаев директория пуста.
/sys – виртуальная файловая система sysfs
Эта директория появилась с выходом ядра версии 2.6 и в нее примонтирована виртуальная файловая система sysfs с информацией об устройствах, драйверах, ядре ОС и т.п.
/tmp – временные файлы
Временные файлы, обычно удаляются при перезагрузке системы. Все пользователи имеют права чтения и записи в эту директорию.
/usr – пользовательские бинарные файлы, используемые только для чтения
В этой директории находятся приложения и файлы, используемые только пользователями, а не самой системой.
/var – директория для часто меняющихся данных
Здесь находятся журналы операционной системы, системные log-файлы, cache-файлы и т.д.