- How can I get the current date and time in the terminal and set a custom command in the terminal for it? [closed]
- Как работать с датой и временем в Bash с помощью команды date
- Изменить системную дату и время Linux
- Параметры форматирования
- Дата обработки в Linux
- Время обработки в Linux
- С флагом —date или -d
- Общие операции
- How to Work with Date and Time in Bash Using date Command
- Change Linux System Date and Time
- Formatting Options
- Handling Date in Linux
- Handling Time in Linux
- With –date or -d Flag
- Common Operations
How can I get the current date and time in the terminal and set a custom command in the terminal for it? [closed]
Closed. This question does not meet Stack Overflow guidelines. It is not currently accepting answers.
This question does not appear to be about a specific programming problem, a software algorithm, or software tools primarily used by programmers. If you believe the question would be on-topic on another Stack Exchange site, you can leave a comment to explain where the question may be able to be answered.
I have to check the time in a Linux terminal. What is the command for getting date and time in a Linux terminal? Is there a way in which we can set a custom function?
This question seems on topic as it relates to a specific computing task on a specific operating system (which is just a software layer itself). As, @drstevens said, this is the first result in Google and it was informative for me needs. If it were off-topic, it would read something like «Do operating systems tell time?» or «What do you guys think about operating systems that tell time.» Stack Overflow is a great resource for beginners and it seems like this was closed as for being too beginner of a question. It should instead just be listed as a beginner question.
StackExchange is the place for answers. This is a good question. Perhaps the question should be migrated, but it should not be closed, in my opinion. This question appeared first in my Google results when I searched for «linux check time».
Как работать с датой и временем в Bash с помощью команды date
Команда Date — это внешняя программа bash, которая позволяет устанавливать или отображать системную дату и время. Он также предоставляет несколько вариантов форматирования. Команда Date установлена во всех дистрибутивах Linux по умолчанию.
Введите команду даты в терминал, которая отобразит текущую дату и время.
Изменить системную дату и время Linux
С помощью команды date можно изменить системную дату, время и часовой пояс, и это изменение должно быть синхронизировано с аппаратными часами.
$ date --set="Thu Nov 12 13:06:59 IST 2020" $ hwclock --systohc
Параметры форматирования
Хорошим местом для получения списка параметров форматирования будет справочная страница.
Давайте рассмотрим некоторые из наиболее распространенных параметров форматирования, которые мы будем использовать.
- Чтобы применить форматирование, используйте «+, а затем «formatter».
- Чтобы получить список параметров форматирования для GNU\LINUX, взгляните на связанную справочную страницу.
- Чтобы получить список параметров форматирования для BSD, взгляните на связанную справочную страницу.
Две важные части команды date — это использование формата +% и параметр –date.
Теперь давайте применим форматирование к команде даты. Чтобы применить форматирование, добавьте знак плюса (+) , а затем %formatter , как показано в примерах.
Дата обработки в Linux
Давайте посмотрим, как использовать средства форматирования, связанные с датой, в простом сценарии оболочки под названием «date.sh».
# PRINT YEAR,MONTH,DAY AND DATE. echo "We are in the year = $(date +%Y)" echo "We are in the year = $(date +%y)" # Difference between %Y and %y is %Y will print 4 digits while %y will print the last 2 digits of the year. echo "We are in the month = $(date +%m)" echo "We are in the month = $(date +%b)" echo "We are in the month = $(date +%B)" # Difference between %B and %b is, %B will print full month name while %b will print abbreviated month name. echo "Current Day of the month = $(date +%d)" echo "Current Day of the week = $(date +%A)" echo "Current Day of the week = $(date +%a)" # Difference between %A and %a is, %A will print full Weekday name while %a will print abbreviated weekday name. # Instead of formatting to get the date, we can use %D which will print the date as %m/%d/%y or %F which prints in %Y-%M-%d format. echo "Date using %D = $(date +%D)" echo "Date using %F = $(date +%F)"
Время обработки в Linux
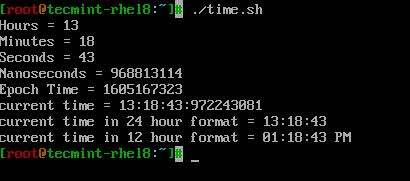
Давайте посмотрим, как использовать средства форматирования, связанные с временем, в простом сценарии оболочки под названием «time.sh».
# PRINT HOURS, MINS, SECONDS, NANO SECONDS echo Hours = $(date +%H) echo Minutes = $(date +%M) echo Seconds = $(date +%S) echo Nanoseconds = $(date +%N) echo Epoch Time = $(date +%s) echo "current time = $(date +%H:%M:%S:%N)" # can also use %T which displays Time in HH:MM:SS format. echo "current time in 24 hour format = $(date +%T)" # can also use %r to display time in 12 hour format. echo "current time in 12 hour format = $(date +%r)"
С флагом —date или -d
С помощью флага —date или -d ввод может быть передан как строка, и команда date знает, как с этим справиться.
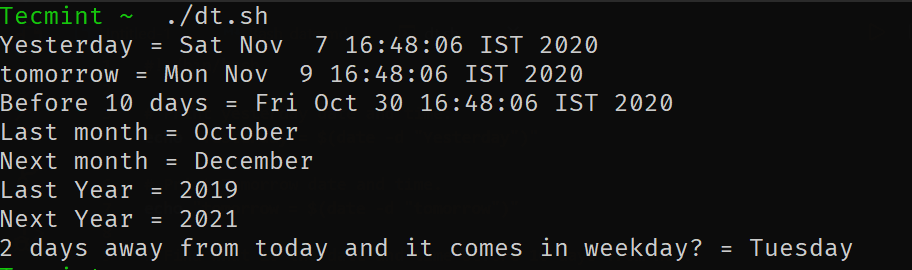
Давайте посмотрим на несколько примеров, чтобы понять, как это работает.
# Print yesterday's date and time. echo "Yesterday = $(date -d "Yesterday")" # Print Tomorrow date and time. echo "tomorrow = $(date -d "tomorrow")" # Find what is the date and time before 10 days from now. echo "Before 10 days = $(date -d "tomorrow -10 days")" # Find last month and next month echo "Last month = $(date -d "last month" "%B")" echo "Next month = $(date -d "next month" "%B")" # Find last year and next year echo "Last Year = $(date -d "last year" "+%Y")" echo "Next Year = $(date -d "next year" "+%Y")" # Forecast the weekday echo "2 days away from today and it comes on weekdays? = $(date -d "Today +2 days" "+%A")
Общие операции
вычислить количество дней между двумя заданными датами.
$ echo $(( ( $(date -d "2020-11-10" "+%s") - $(date -d "2020-11-01" "+%s") ) / 86400))
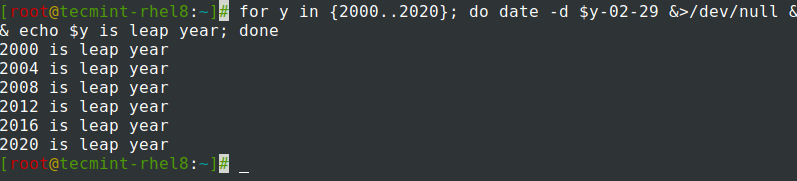
Найдите данный год високосным или нет.
$ for y in ; do date -d $y-02-29 &>/dev/null && echo $y is leap year; done
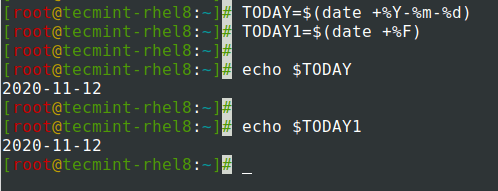
Присвоение вывода команды даты переменной.
$ TODAY=$(date +%Y-%m-%d) OR $ TODAY1=$(date +%F) $ echo $TODAY $ echo $TODAY1
Создайте файлы журнала с датой, добавленной к имени файла.
Добавление даты и времени при создании файлов журналов, резервных копий или текстовых файлов — это обычная операция, с которой мы сталкиваемся чаще всего. Возьмем пример, чтобы сделать резервную копию, мы создали сценарий оболочки.
Этот скрипт будет делать резервную копию с 00:00 до 23:59 и запускаться ежедневно в 00:00 следующего дня. Мы хотим создать файлы журналов со вчерашним форматом даты.
CUSTOM_FORMAT=$(date —date «Yesterday» «+%d-%y-%H:%M») LOG_FILE=/var/log/custom_application/application_$.log echo «Script started» >> $ . CODE BLOCKS . echo «Script completed» >> $
Это все для этой статьи. В этой статье мы увидели, как использовать дату и время bash в Linux. Дайте нам знать ваши отзывы.
How to Work with Date and Time in Bash Using date Command
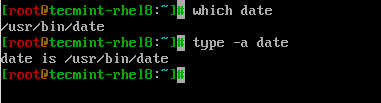
Date command is an external bash program that allows to set or display system date and time. It also provides several formatting options. Date command is installed in all Linux distros by default.
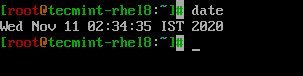
Type date command in terminal which will display current date and time.
Change Linux System Date and Time
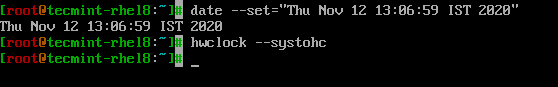
Using date command, system date, time and timezone can be modified and the change has to be synced with the hardware clock.
$ date --set="Thu Nov 12 13:06:59 IST 2020" $ hwclock --systohc
Formatting Options
A good place to get the list of formatting options will be the man page.
Let’s see some of the most common formatting options that we will use.
- To apply formatting use “+ followed by “formatter“.
- To get a list of formatting options for GNU\LINUX take a look at the linked man page.
- To get a list of formatting options for BSD take a look at the linked man page.
The two important parts of the date command is using Format +% and –date option.
Now let’s apply some formatting on the date command. To apply formatting, add plus sign (+) followed by %formatter as shown in examples.
Handling Date in Linux
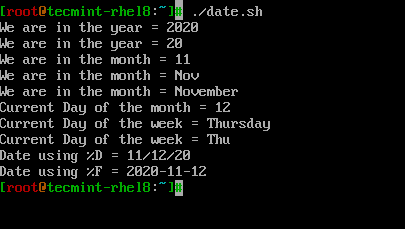
Let’s take a look at how to use date related formatters in a simple shell script called ‘date.sh‘.
# PRINT YEAR,MONTH,DAY AND DATE. echo "We are in the year = $(date +%Y)" echo "We are in the year = $(date +%y)" # Difference between %Y and %y is %Y will print 4 digits while %y will print the last 2 digits of the year. echo "We are in the month = $(date +%m)" echo "We are in the month = $(date +%b)" echo "We are in the month = $(date +%B)" # Difference between %B and %b is, %B will print full month name while %b will print abbreviated month name. echo "Current Day of the month = $(date +%d)" echo "Current Day of the week = $(date +%A)" echo "Current Day of the week = $(date +%a)" # Difference between %A and %a is, %A will print full Weekday name while %a will print abbreviated weekday name. # Instead of formatting to get the date, we can use %D which will print the date as %m/%d/%y or %F which prints in %Y-%M-%d format. echo "Date using %D = $(date +%D)" echo "Date using %F = $(date +%F)"
Handling Time in Linux
Let’s take a look at how to use time related formatters in a simple shell script called ‘time.sh‘.
# PRINT HOURS, MINS, SECONDS, NANO SECONDS echo Hours = $(date +%H) echo Minutes = $(date +%M) echo Seconds = $(date +%S) echo Nanoseconds = $(date +%N) echo Epoch Time = $(date +%s) echo "current time = $(date +%H:%M:%S:%N)" # can also use %T which displays Time in HH:MM:SS format. echo "current time in 24 hour format = $(date +%T)" # can also use %r to display time in 12 hour format. echo "current time in 12 hour format = $(date +%r)"
With –date or -d Flag
With —date or -d flag input can be passed as string and date command knows to handle it smartly.
Let’s see some examples to understand how it works.
# Print yesterday's date and time. echo "Yesterday = $(date -d "Yesterday")" # Print Tomorrow date and time. echo "tomorrow = $(date -d "tomorrow")" # Find what is the date and time before 10 days from now. echo "Before 10 days = $(date -d "tomorrow -10 days")" # Find last month and next month echo "Last month = $(date -d "last month" "%B")" echo "Next month = $(date -d "next month" "%B")" # Find last year and next year echo "Last Year = $(date -d "last year" "+%Y")" echo "Next Year = $(date -d "next year" "+%Y")" # Forecast the weekday echo "2 days away from today and it comes on weekdays? = $(date -d "Today +2 days" "+%A")
Common Operations
calculate the number of days between 2 given dates.
$ echo $(( ( $(date -d "2020-11-10" "+%s") - $(date -d "2020-11-01" "+%s") ) / 86400))
Find the given year is leap year or not.
$ for y in ; do date -d $y-02-29 &>/dev/null && echo $y is leap year; done
Assigning output of date command to a variable.
$ TODAY=$(date +%Y-%m-%d) OR $ TODAY1=$(date +%F) $ echo $TODAY $ echo $TODAY1
Create log files with the date added to the filename.
Adding date and time while creating log files, backup, or text files is a common operation that we will encounter most often. Let’s take an example, to take a backup, we have created a shell script.
This script will take a backup from 00:00 to 23:59 and scheduled to run daily at 00:00 of the next day. We want to create log files with yesterday’s date format.
CUSTOM_FORMAT=$(date —date «Yesterday» «+%d-%y-%H:%M») LOG_FILE=/var/log/custom_application/application_$.log echo «Script started» >> $ . CODE BLOCKS . echo «Script completed» >> $
That’s it for this article. In this article, we have seen how to use bash date and time in Linux. Let us know your feedback.