- linux — write commands from one terminal to another
- 7 Answers 7
- 16 echo command examples in Linux
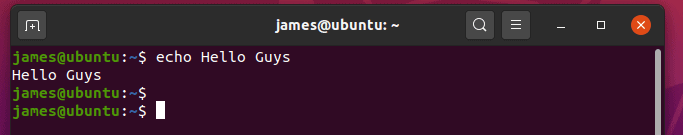
- 1) Display a simple message on the terminal
- 2) Print out the value of a variable with echo command
- 3) Print a line of text comprising of double quotes
- 4) Display a line of text consisting of a single quote
- 5) Redirect echo command output to a file
- 6) Use echo command to match identical files
- 7) List all files and folders in the current directory
- 8) Create new lines using the echo command
- 9) Create tab spaces between words in a sentence
- 10) Combine new line and tab spacing options in echo command
- 11) Create vertical tab spaces in echo command output
- 12) Combine new line and vertical tab spaces in echo command
- 13) Use the carriage return option
- 14) Truncate echo command output of text
- 15) Remove all spaces from the text string with echo command
- 16) echo command usage in bash shell script
- How to Send a Message to Logged Users in Linux Terminal
- Linux message to all terminals
- 1 Answer 1
linux — write commands from one terminal to another
What are you really trying to do? It may be your logic for trying this is in the first place is flawed; there might be an easier solution to get the same result. Also, terminals run in separate processes so you’d need some form of interprocess communication to get them to talk to one another.
7 Answers 7
#!/usr/bin/python import sys,os,fcntl,termios if len(sys.argv) != 3: sys.stderr.write("usage: ttyexec.py tty command\n") sys.exit(1) fd = os.open("/dev/" + sys.argv[1], os.O_RDWR) cmd=sys.argv[2] for i in range(len(cmd)): fcntl.ioctl(fd, termios.TIOCSTI, cmd[i]) fcntl.ioctl(fd, termios.TIOCSTI, '\n') os.close(fd) Is posible to show the output of a command on multiple terminals simultaneously with the following script., and it works with all console programs, including the editors. For example doing:
execmon.bash 'nano hello.txt' 5 Open an editor and both the output and the text that we introduce will be redirected to the virtual terminal number 5. You can see your terminals:
Each virtual terminal has an associated number.
Is work with the normal terminal, konsole and xterm, just create the file execmon.bash and put this:
#! / bin / bash # execmon.bash # Script to run a command in a terminal and display the output # in the terminal used and an additional one. param = $ # if [$ param-eq 2]; Then echo $ 1 | tee a.out a.out && cat> / dev / pts / $ 2 && exec `cat` a.out | tee / dev / pts / $ 2 && rm a.out else echo "Usage:" echo "execmon 'command' num ' echo "-command is the command to run (you have to enter ')" echo "-num is the number of virtual console to output to the" fi execmon.bash 'ls-l' 5 execmon.bash 'nano Hello.txt' 5 16 echo command examples in Linux
In this guide, we will explain Linux echo command with 16 practical examples.
Echo command in Linux is one of the widely used command in day-to-day operations task. The echo command is a built-in command-line tool that prints the text or string to the standard output or redirect output to a file. The command is usually used in a bash shell or other shells to print the output from a command. Echo command is also used frequently in bash shell scripts.
Syntax of echo command

1) Display a simple message on the terminal
To print a simple text message on the terminal with echo command , run the command:
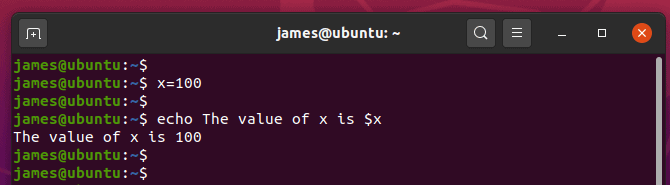
2) Print out the value of a variable with echo command
Let’s assume that you have initialized a variable x and assigned it a value of 100 as shown
You can echo its value by prefixing the variable name with a dollar sign as shown
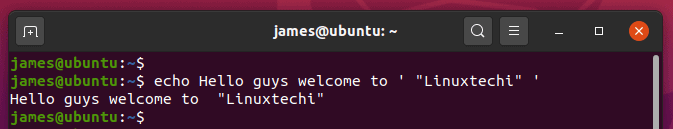
3) Print a line of text comprising of double quotes
To print a line of text with double quotes with echo command, simply enclose the phrase in double-quotes between single quotes.
$ echo Hello guys welcome to ' "Linuxtechi" '
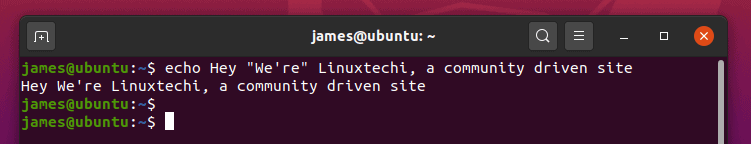
4) Display a line of text consisting of a single quote
If you wish to print a line with a word containing a single quote, enclose the word inside double quotation marks as shown:
$ echo Hey, "We're" Linuxtechi, a community driven site.
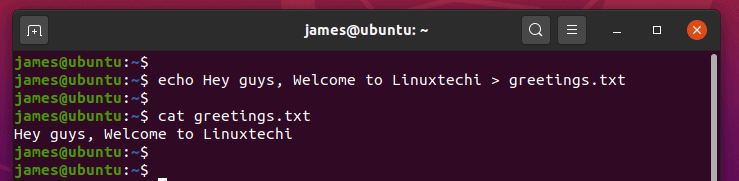
5) Redirect echo command output to a file
To redirect echo command output to a file instead of printing it on the screen use the greater than( > ) and double greater than ( >> ) operators.
When you use the greater than( > ) operator, the file will be overwritten. If the file does not exist, it will be created.
$ echo Hey guys, Welcome to Linuxtechi > greetings.txt
The double greater than operator ( >> ) appends text to a file. For example, to add an entry to the /etc/hosts files use the syntax shown
$ echo 192.168.2.100 web-server-01 >> /etc/hosts
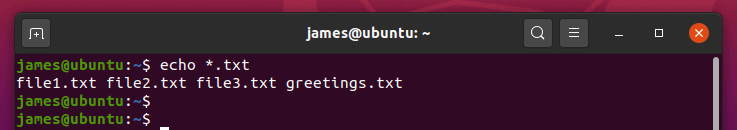
6) Use echo command to match identical files
You can use echo command with a wildcard character to return identical files i.e files that bear the same file extension. For example, to print out all text files with the .txt extension , run the command.
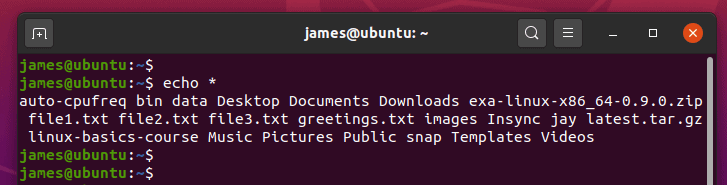
7) List all files and folders in the current directory
The echo command can act as the ls command and list all the files and folders in your current directory using the wildcard as shown:
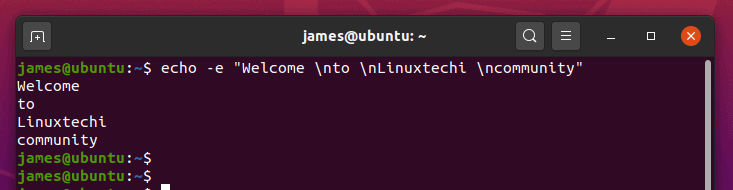
8) Create new lines using the echo command
Using the backslash interpreter -e , you can manipulate how the line appears on the output. For example, to print a new line, use the ‘ \n ‘ escape character option as shown below:
$ echo -e "Welcome \nto \nLinuxtechi \ncommunity"
9) Create tab spaces between words in a sentence
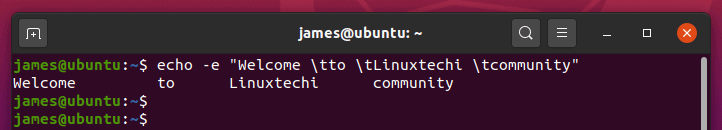
Apart from creating a new line, you can increase the spacing between words in a sentence using the ‘\t ‘ or TAB option as shown.
$ echo -e "Welcome \tto \tLinuxtechi \tcommunity"
10) Combine new line and tab spacing options in echo command
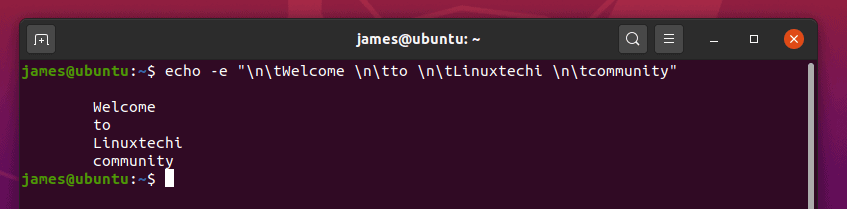
You can combine the ‘\n’ and ‘\t’ options at the same time as shown:
$ echo -e "\n\tWelcome \n\tto \n\tLinuxtechi \n\tcommunity"
11) Create vertical tab spaces in echo command output
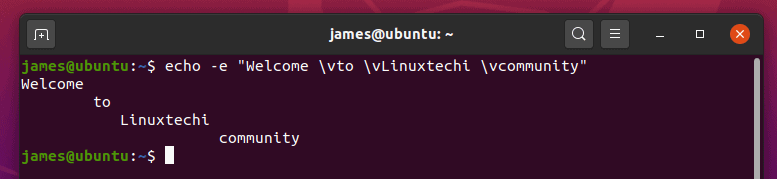
The \v option enables you to create vertical tab spaces as shown:
$ echo -e "Welcome \vto \vLinuxtechi \vtcommunity"
12) Combine new line and vertical tab spaces in echo command
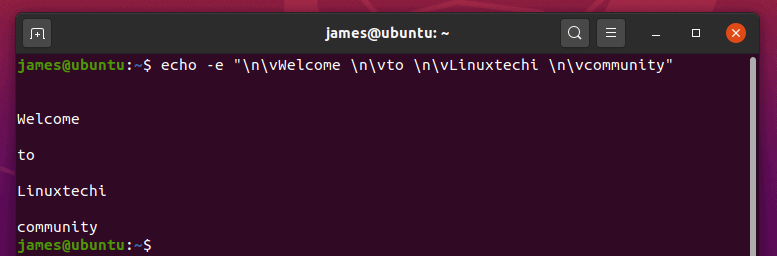
Additionally, you can experiment and combine the ‘\n’ and ‘\v ‘ options as shown.
$ echo -e "Welcome \n\vto \n\vLinuxtechi \n\vtcommunity"
13) Use the carriage return option
The \r option omits the preceding text. For example, the output of the command below omits the first 2 words.
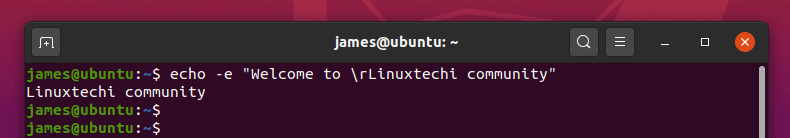
$ echo -e "Welcome to \rLinuxtechi community"
14) Truncate echo command output of text
To suppress any further output and proceed without going to the next line use the ‘\c’ option as shown:
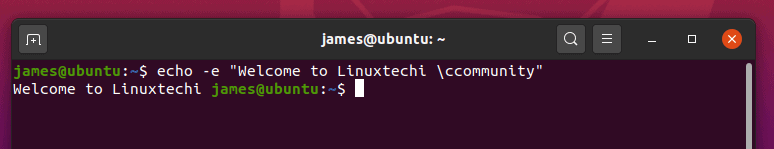
$ echo -e Welcome to Linuxtechi \ccommunity
15) Remove all spaces from the text string with echo command
Use ‘ \b’ option along with -e option in echo command to remove all the spaces from the text string, example is shown below:
$ echo -e "Welcome \bto \bLinux \bCommunity" WelcometoLinuxCommunity $
16) echo command usage in bash shell script
As we have already stated that echo command is frequently used in bash shell scripts. Example of echo command usage in shell script are listed below:
$ cat echo-bash.sh #!/bin/bash # Echo Command Usage in Script os_version=$(grep -i "PRETTY_NAME" /etc/os-release | awk -F'=' '' | sed 's/"//g') no_cpus=$(lscpu | grep '^CPU(s):' | awk -F":" '' | sed "s/^[ \t]*//") total_mem=$(grep MemTotal /proc/meminfo | awk -F":" '' | sed "s/^[ \t]*//") echo 'OS Version :' $os_version echo 'Number of CPUs :' $no_cpus echo 'Total Memory :' $total_mem $
Output of above script when it is executed:
$ bash echo-bash.sh OS Version : CentOS Linux 7 (Core) Number of CPUs : 4 Total Memory : 8008968 kB $
And that’s it. Thank you for taking your time in this guide. Hopefully, you are now better informed.
How to Send a Message to Logged Users in Linux Terminal
How can I send a messages to logged on users in a Linux server? If you are asking this question, then this guide will help you learn how to do that. We will demonstrate how to send a message to all or a specific logged on user, on the terminal in Linux.
Linux offers a variety of means for sending messages to users logged on to a server as explained in the two methods below.
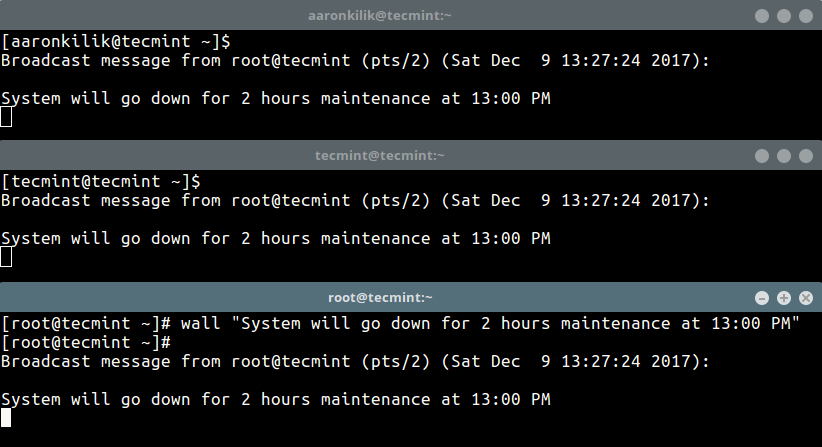
In the first method, we will use wall command – write a message to all currently logged in users on the terminal as shown.
# wall "System will go down for 2 hours maintenance at 13:00 PM"
To disable the normal banner printed by wall, for example:
Broadcast message from [email protected] (pts/2) (Sat Dec 9 13:27:24 2017):
Add the -n (Suppress the banner) flag, this however, can only be used by the root user.
# wall -n "System will go down for 2 hours maintenance at 13:00 PM"
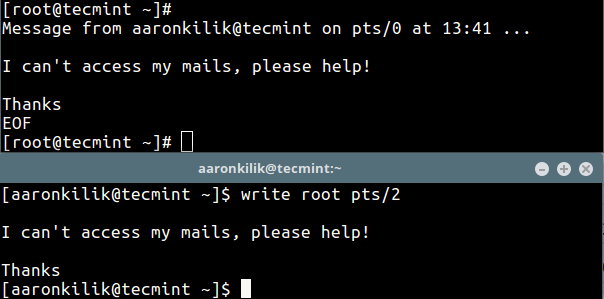
In the second method, we will use write command, which comes pre-installed on all if not most Linux distributions. It allows you to send a message to another user in the terminal using tty.
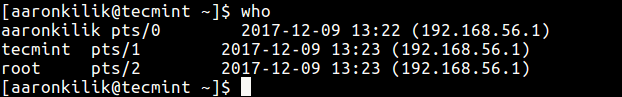
First check the all logged on users with the who command as shown.
There are currently two users are active on the system (tecmint and root), now the user aaronkilik is sending a message to the root user.
$ write root pts/2 #press Ctrl+D after typing the message.
That’s all! Do share with us other methods or commands for sending messages to all logged on users through the terminal in Linux. If you have any queries, please use the feedback form below.
Linux message to all terminals
When I’m trying to send some message to all terminals through echo «some message» > /dev/pts/* it works good. But when I do the same thing through bash script then error occurrs: myscript.sh: line 2: /dev/pts/*: Permission denied . Even when I set highest privileges to myscript.sh . What can I do to make it work?
read msg echo $msg > /dev/pts/* Do you interpret the file with bash or sh? Whichever shell it is, it doesn’t expand the glob, it seems. Use the same shell for running the script that you use in your interactive session.
1 Answer 1
Did you have a look at the wall command?
You need privileges to do this, but here is described a workaround
Ok, for your particular question, you can also try: source
Nothing appears in any terminal when I type wall -n
For the wall side, as root you can enable by setting mesg y in /etc/profile, so it becomes the default for all users. For the script, I am not sure why it behaves in a different way, please share the results when running like source myscript.sh , both with and without the shell line (#!/bin/sh or #!/bin/bash)
When I’m trying add #!/bin/bash or #!/bin/sh to myscript.sh then other error occurrs: myscript.sh: line 3: /dev/pts/*: ambiguous redirect . With source myscript.sh is error: myscript.sh:3: permission denied: /dev/pts/ptmx