- Команда echo в Linux
- Команда echo linux
- Примеры работы echo
- Выводы
- Команда Echo в Linux с примерами
- эхо-команда
- echo Примеры
- Выводы
- echo Command in Linux: 7 Practical Examples
- Examples of the echo command in Linux
- 1. Displaying the value of a variable
- 2. Don’t print the final newline character
- 3. Redirect the output to a file
- 4. Using escape characters with echo command
- 5. Display text with single or double quotes with echo command
- 6. Display files in directory
- 7. Use echo command to empty a file in Linux
- Bonus Tips
- Display echo command output in color
- See what a command will do without running it
- What else?
Команда echo в Linux
Команда echo — это очень простая и в то же время часто используемая встроенная команда оболочки Bash. Она имеет только одно назначение — выводить строку текста в терминал, но применяется очень часто в различных скриптах, программах, и даже для редактирования конфигурационных файлов.
В этой статье мы рассмотрим что представляет из себя команда echo linux, как ее можно использовать и в каких ситуациях. Но сначала рассмотрим синтаксис самой команды.
Команда echo linux
Команда echo — это не системная утилита, у нее нет исполняемого файла. Она существует только внутри интерпретатора Bash. Синтаксис команды echo linux очень прост:
$ echo опции строка
Опций всего несколько, давайте рассмотрим их, чтобы вы могли лучше ориентироваться в работе утилиты:
- -n — не выводить перевод строки;
- -e — включить поддержку вывода Escape последовательностей;
- -E — отключить интерпретацию Escape последовательностей.
Это все опции, если включена опция -e, то вы можете использовать такие Escape последовательности для вставки специальных символов:
- /c — удалить перевод строки;
- /t — горизонтальная табуляция;
- /v — вертикальная табуляция;
- /b — удалить предыдущий символ;
- /n — перевод строки;
- /r — символ возврата каретки в начало строки.
Пожалуй, это все, что нужно знать о команде echo, а теперь давайте рассмотрим как с ней работать.
Примеры работы echo
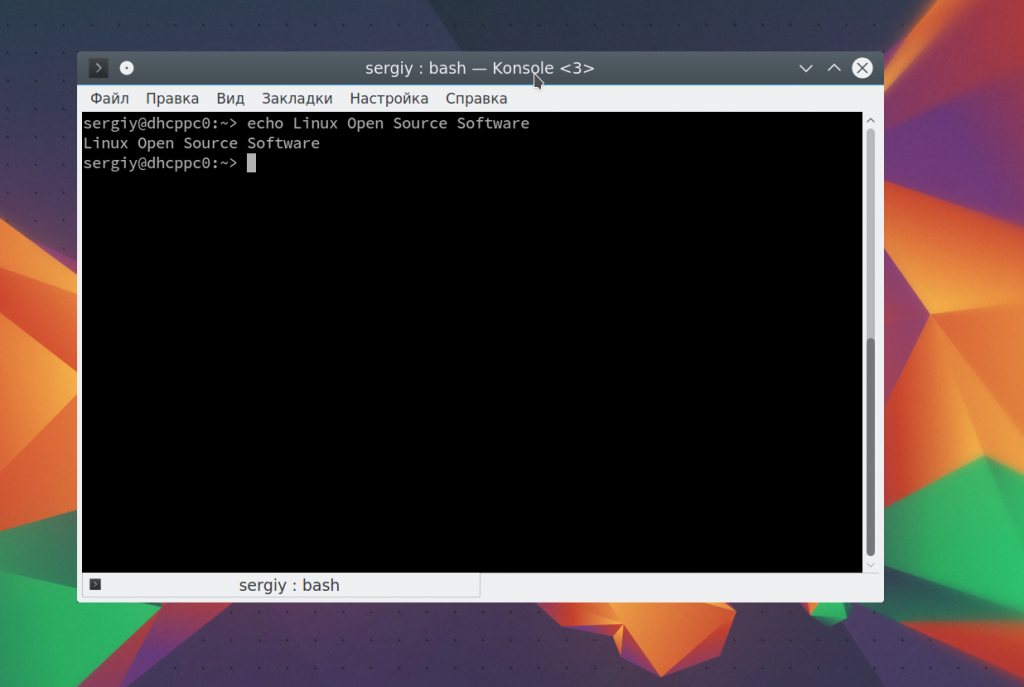
Давайте рассмотрим как пользоваться echo. Сначала просто выведем строку на экран:
echo Linux Open Source Software Technologies
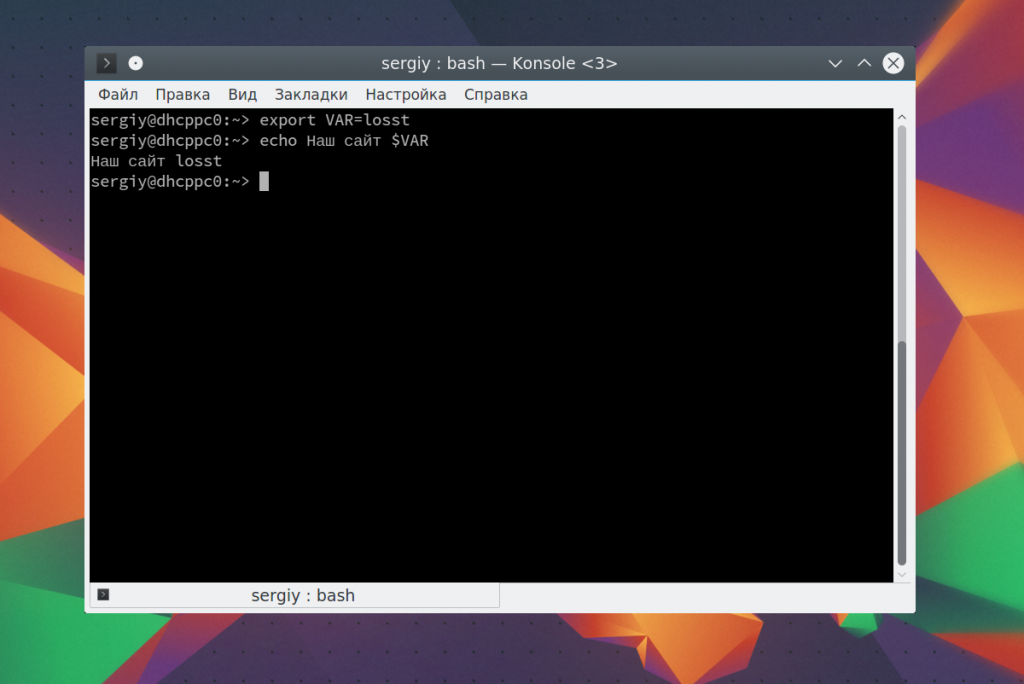
Также можно вывести значение переменной. Сначала объявим переменную:
Затем выведем ее значение:
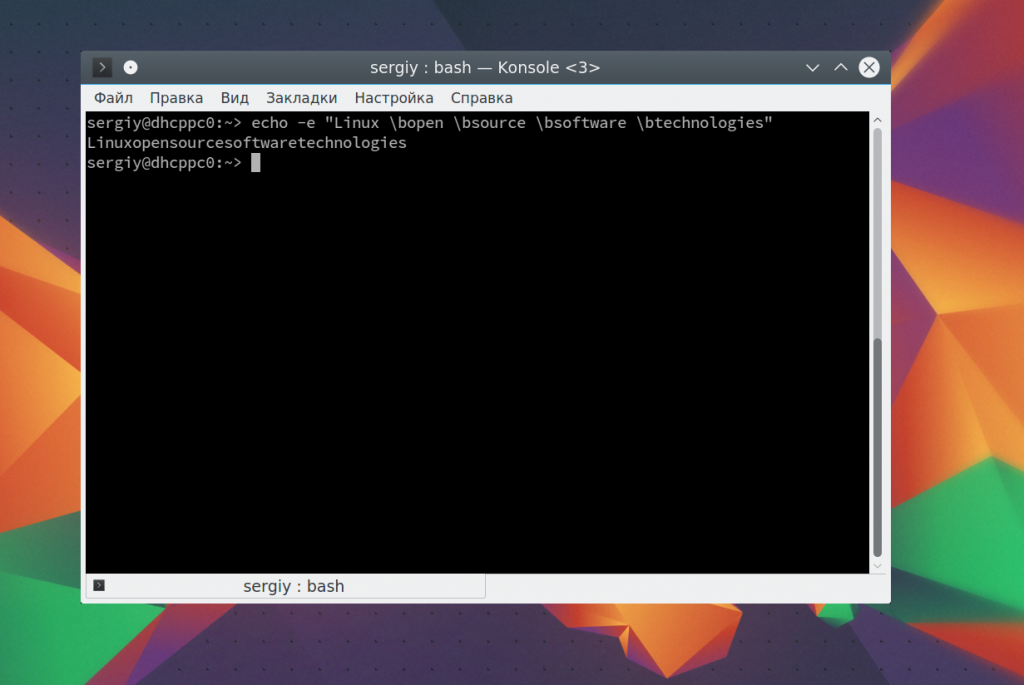
Как уже говорилось, с помощью опции -e можно включить интерпретацию специальных последовательностей. Последовательность \b позволяет удалить предыдущий символ. Например, удалим все пробелы из строки:
echo -e «Linux \bopen \bsource \bsoftware \btechnologies»
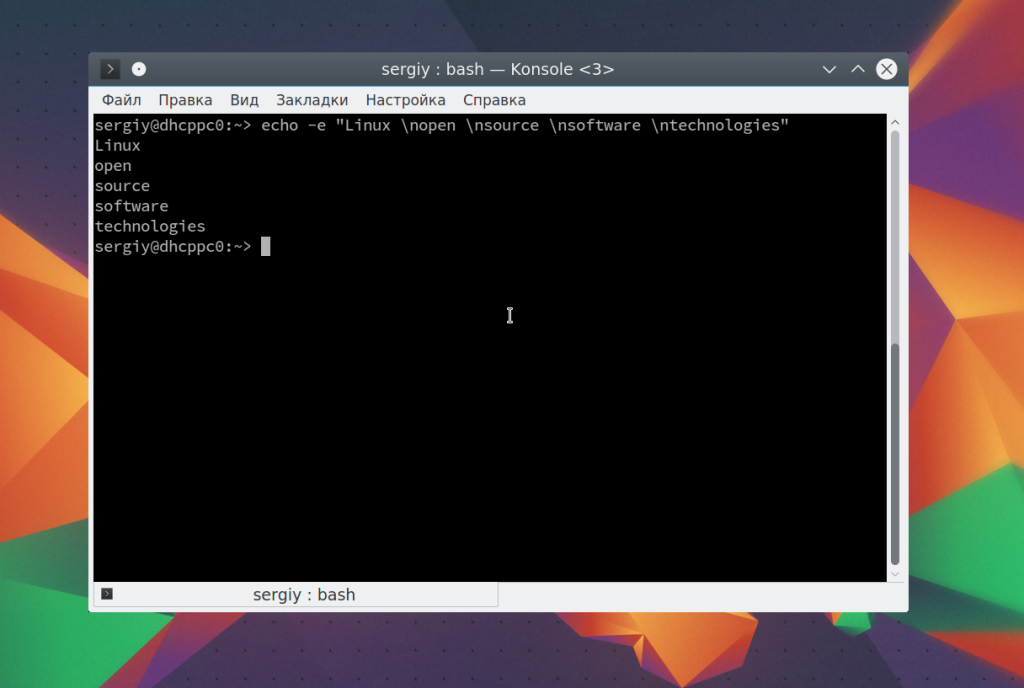
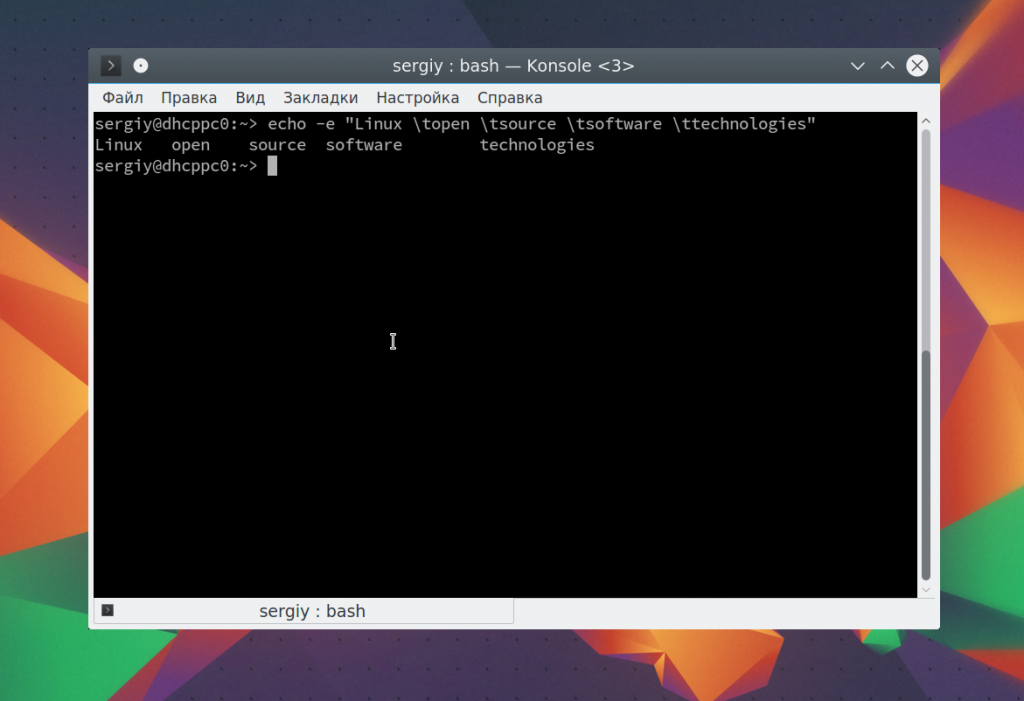
Последовательность \n переводит курсор на новую строку:
echo -e «Linux \nopen \nsource \nsoftware \ntechnologies»
С помощью \t вы можете добавить горизонтальные табуляции:
echo -e «Linux \topen \tsource \tsoftware \ttechnologies»
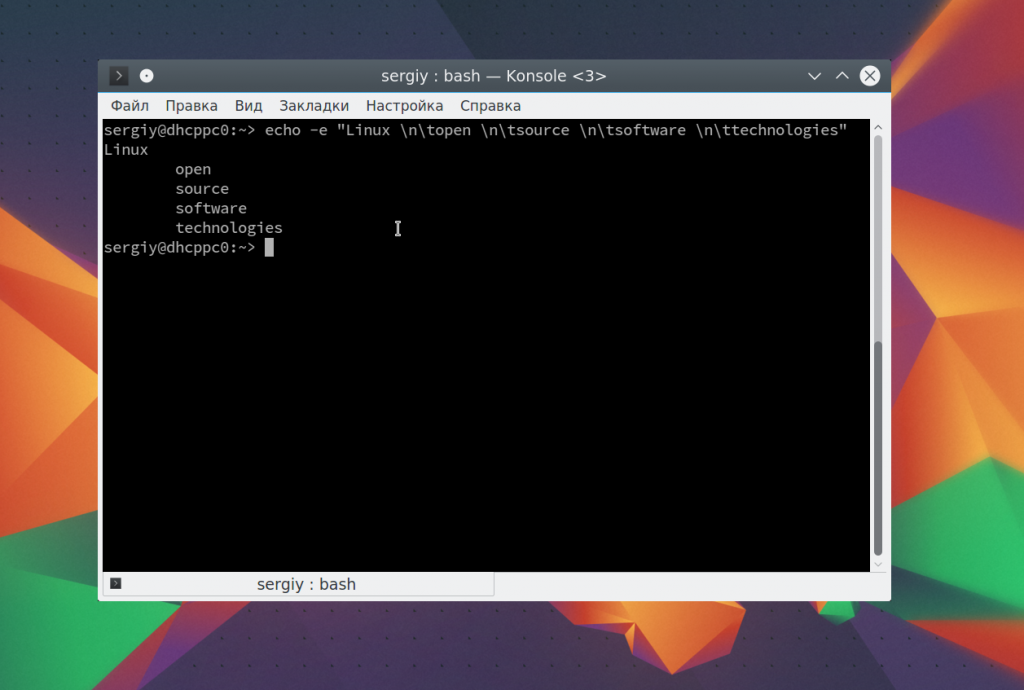
Можно совместить переводы строки и табуляции:
echo -e «Linux \tnopen \tnsource \tnsoftware \tntechnologies»
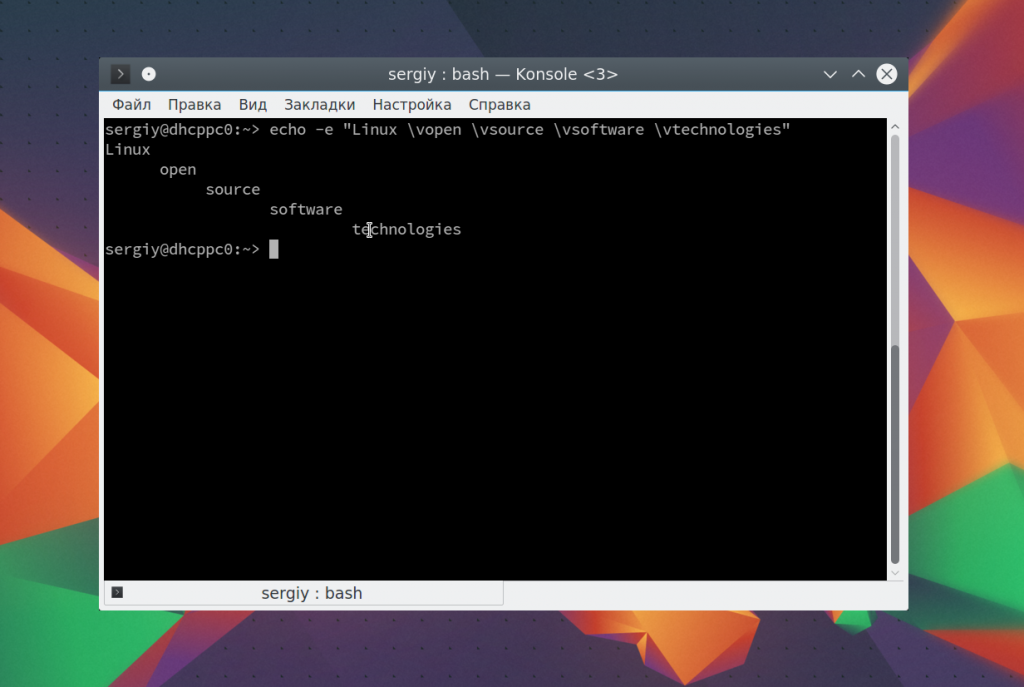
Точно так же можно применить вертикальную табуляцию:
echo -e «Linux \vopen \vsource \vsoftware \vtechnologies»
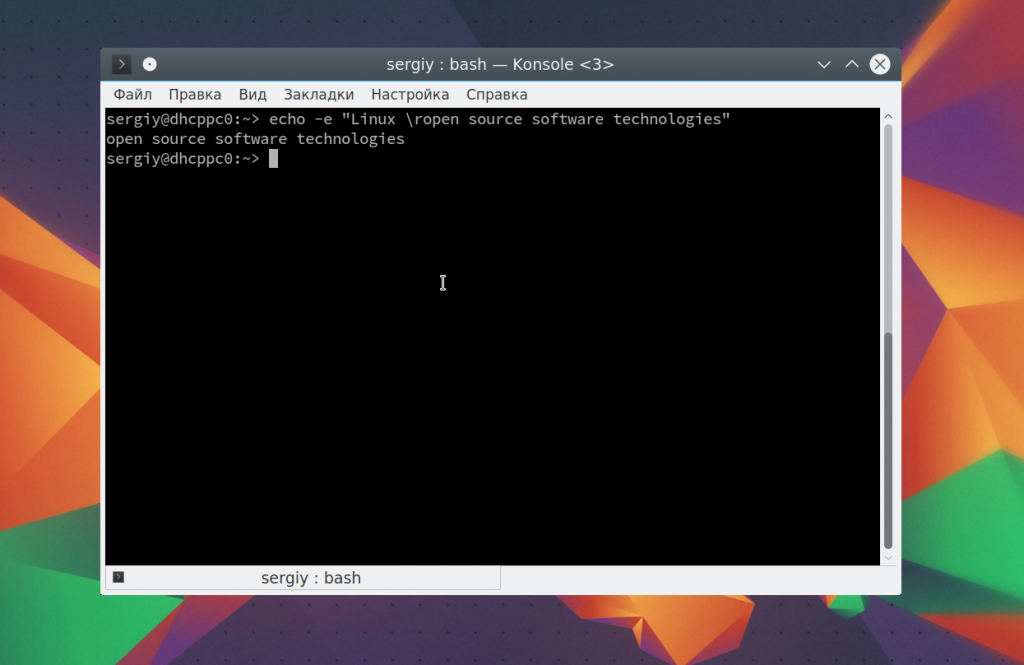
С помощью последовательности \r можно удалить все символы до начала строки:
echo -e «Linux \ropen source software technologies»
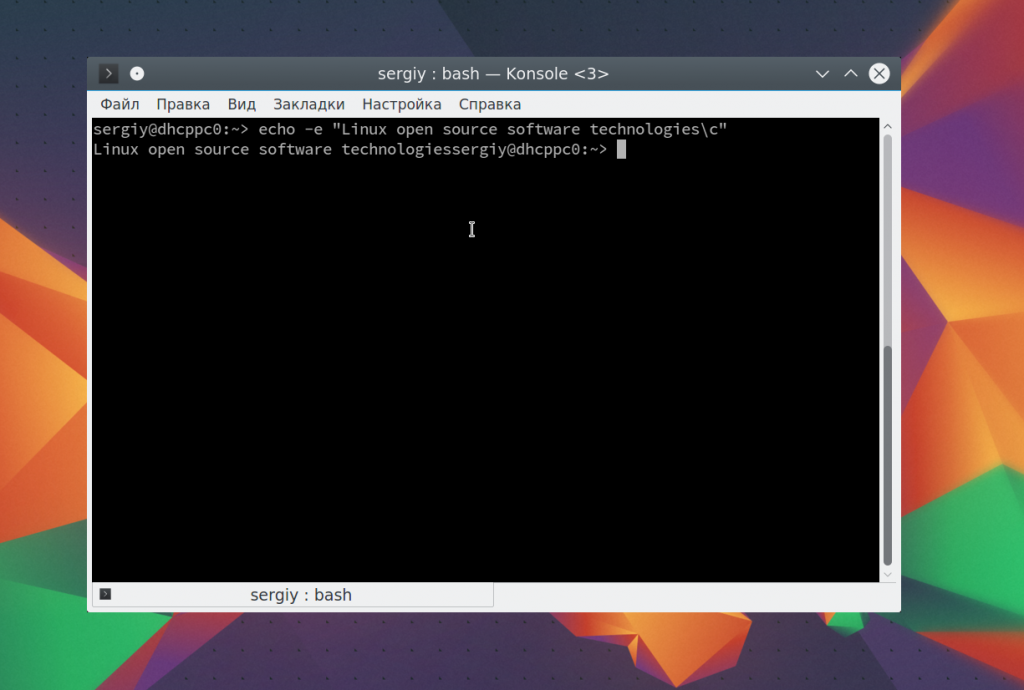
Последовательность -c позволяет убрать перевод на новую строку в конце сообщения:
echo -e «Linux open source software technologies\c»
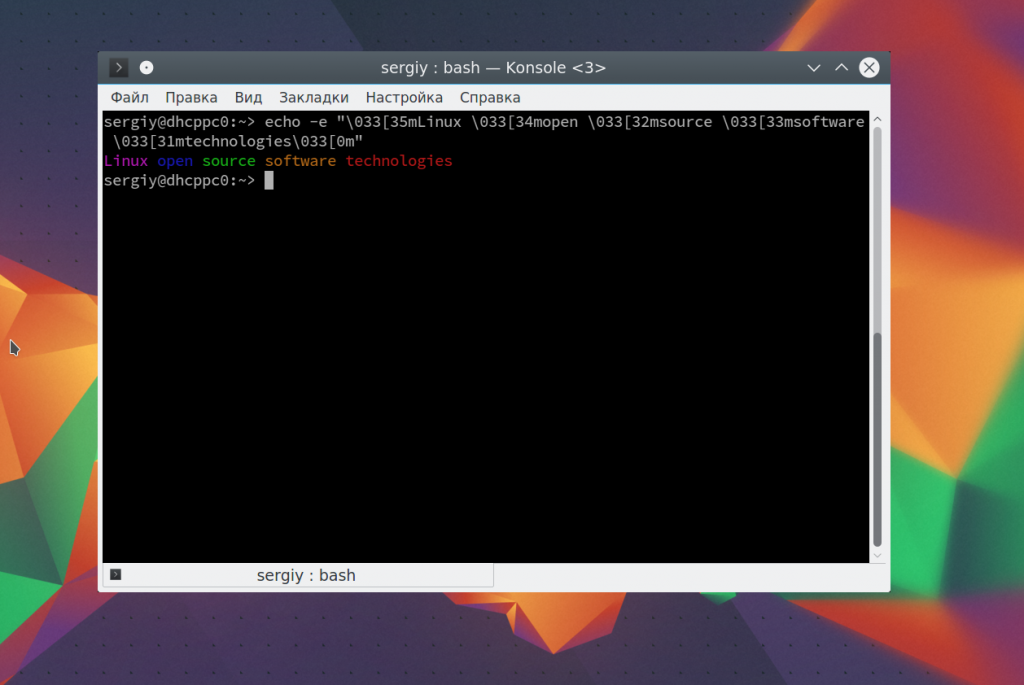
Дальше — больше. Вы можете разукрасить вывод echo с помощью последовательностей управления цветом Bash. Для доступны такие цвета текста:
Например. раскрасим нашу надпись в разные цвета:
echo -e «\033[35mLinux \033[34mopen \033[32msource \033[33msoftware \033[31mtechnologies\033[0m»
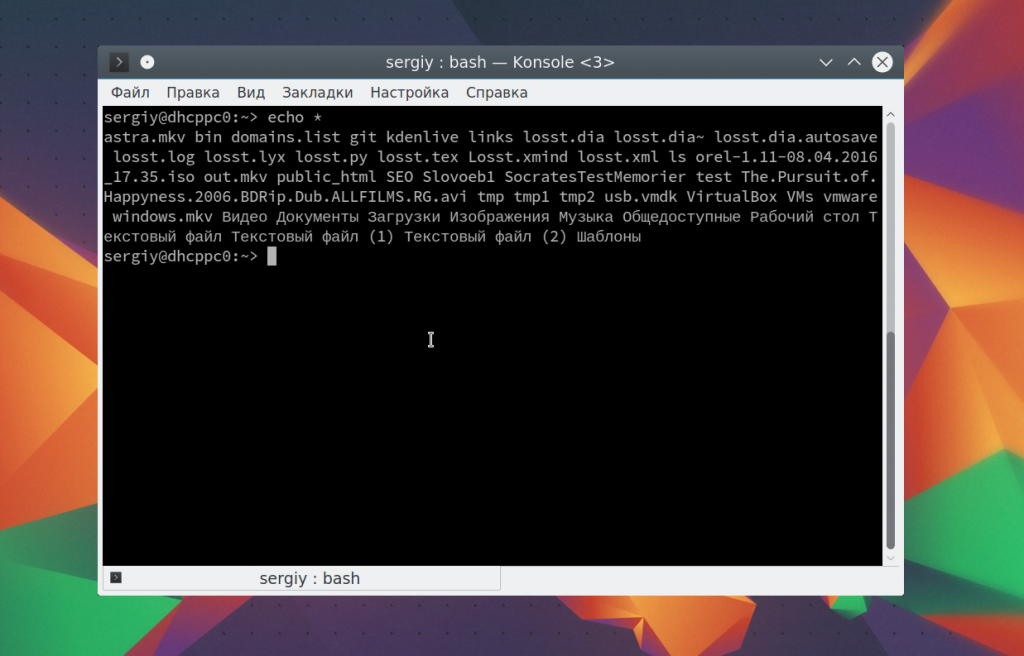
С основными параметрами команды echo разобрались, теперь рассмотрим еще некоторые специальные символы bash. Вы можете вывести содержимое текущей папки просто подставив символ *:
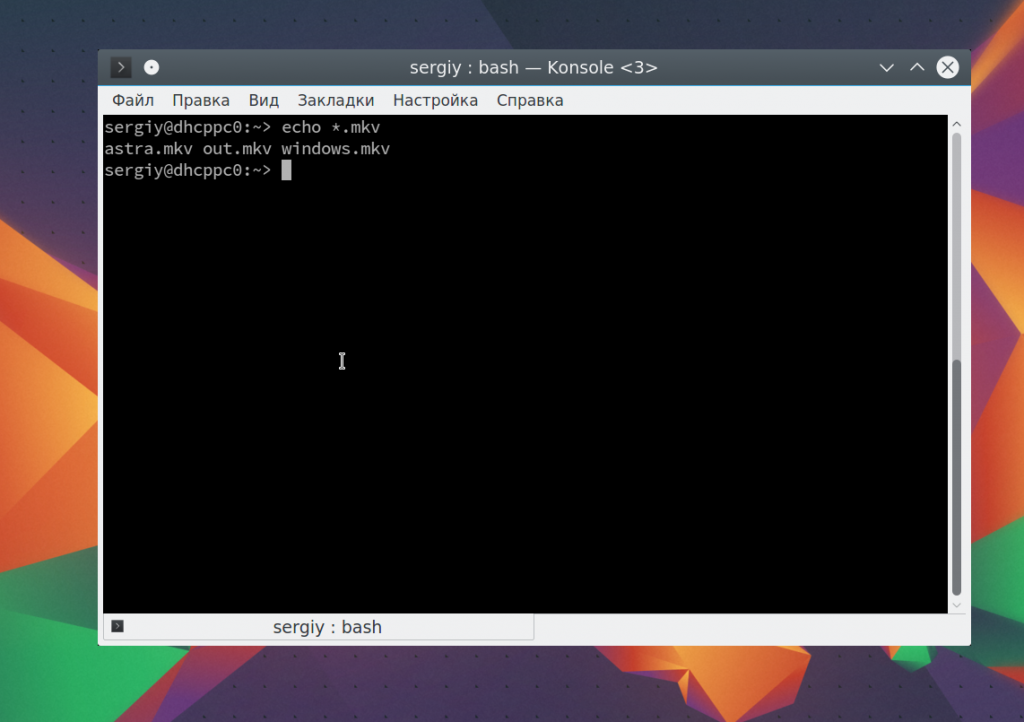
Также можно вывести файлы определенного расширения:
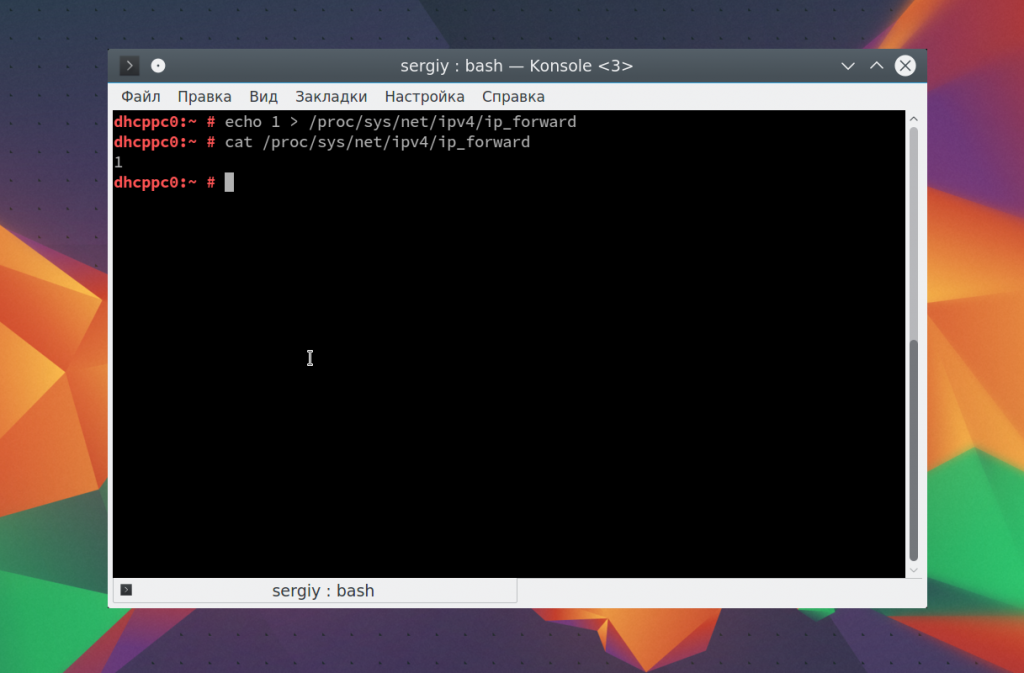
Я уже говорил, что echo можно использовать для редактирования конфигурационных файлов. Вы можете использовать запись echo в файл linux, если он пуст:
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
Если файл не пуст, и вам необходимо добавить свою строчку в конец файла используйте символ перенаправления вывода >>:
echo «UUID=09ec0871-2f55-4dd5-aeb2-cacc4a67907c /var/tmp btrfs subvol=@/var/tmp 0 0» >> /etc/fstab
Если строка содержит какие-либо специальные символы или может быть понята интерпретатором неоднозначно, следует заключить ее в кавычки.
Выводы
В этой статье была рассмотрена команда echo linux. Несмотря на свою простоту, она может применяться для решения различных задач и незаменима при написании простых скриптов. Надеюсь, эта информация была вам полезной.
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
Команда Echo в Linux с примерами
Команда echo — одна из самых основных и часто используемых команд в Linux. Аргументы, переданные в echo выводятся на стандартный вывод.
echo обычно используется в сценариях оболочки для отображения сообщения или вывода результатов других команд.
эхо-команда
echo — это оболочка, встроенная в Bash и большинство других популярных оболочек, таких как Zsh и Ksh. Его поведение немного отличается от оболочки к оболочке.
Существует также отдельная утилита /usr/bin/echo , но обычно встроенная версия оболочки имеет приоритет. Мы рассмотрим встроенную в Bash версию echo .
Синтаксис команды echo следующий:
- Когда используется опция -n , завершающий символ новой строки подавляется.
- Если задана опция -e будут интерпретироваться следующие символы, экранированные обратной косой чертой:
- \ — отображает обратную косую черту.
- a — Предупреждение (BEL)
- b — отображает символ возврата.
- c — подавить любой дальнейший вывод
- e — отображает escape-символ.
- f — отображает символ перевода страницы.
- n — отображает новую строку.
- r — отображает возврат каретки.
- t — отображает горизонтальную вкладку.
- v — отображает вертикальную вкладку.
При использовании команды echo следует учитывать несколько моментов.
- Оболочка заменит все переменные, сопоставление подстановочных знаков и специальные символы перед передачей аргументов команде echo .
- Хотя это и не обязательно, рекомендуется заключать аргументы, передаваемые в echo в двойные или одинарные кавычки.
- При использовании одинарных кавычек » буквальное значение каждого символа, заключенного в кавычки, будет сохранено. Переменные и команды расширяться не будут.
echo Примеры
В следующих примерах показано, как использовать команду echo:
- Вывести строку текста на стандартный вывод.
echo -e "You know nothing, Jon Snow.nt- Ygritte"You know nothing, Jon Snow. - Ygritteecho The PHP files are: *.phpThe PHP files are: index.php contact.php functions.phpecho -e 'The only true wisdom is in knowing you know nothing.nSocrates' >> /tmp/file.txtЕсли файл file.txt не существует, команда создаст его. При использовании > файл будет перезаписан, а символ >> добавит вывод в файл . Используйте команду cat для просмотра содержимого файла:
The only true wisdom is in knowing you know nothing. Socratesecho -e "33[1;37mWHITE"echo -e "33[0;30mBLACK"echo -e "33[0;34mBLUE"echo -e "33[0;32mGREEN"echo -e "33[0;36mCYAN"echo -e "33[0;31mRED"echo -e "33[0;35mPURPLE"echo -e "33[0;33mYELLOW"echo -e "33[1;30mGRAY"Выводы
К настоящему времени вы должны хорошо понимать, как работает команда echo .
Если у вас есть какие-либо вопросы или отзывы, не стесняйтесь оставлять комментарии.
echo Command in Linux: 7 Practical Examples
Learn to use the echo command in Linux with these simple but useful examples. The echo command is useful for displaying information in bash shell scripts.
The echo command is perhaps one of the first few commands you see when you start learning Linux commands or bash shell scripting.
Echo is a simple command that simply prints its arguments on display.
[email protected]:~$ echo Hello World Hello WorldYou can guess why this command is called ‘echo’. Like the sound echo, the command also simply prints what it receives in the input.
Examples of the echo command in Linux
Echo is often used in shell scripts to display information, such as asking for the user to provide input or displaying the error or warning for a certain action in the script.
The echo command has a simple syntax with a few options:
echo [options] [input string]Let’s see some examples of the echo command.
1. Displaying the value of a variable
Let’s say you declared a variable var = 100. You can display the value of this variable using the echo command:
echo The value of variable var is $varIts output would be displayed as this:
The value of variable var is 1002. Don’t print the final newline character
By default, the output of the echo command adds a new line to the output so that you have the output displayed in one entire line.
[email protected]:~$ echo Hello World Hello WorldYou can suppress this new line character using the option -n:
[email protected]:~$ echo -n Hello World Hello [email protected]:~$3. Redirect the output to a file
You can use echo command to create a new file in Linux or append new text to an existing file by redirecting the output to a file:
echo "This text goes to a file" >> file.txt4. Using escape characters with echo command
The option -e with echo allows you to interpret the escape characters. With escape characters, you can display your text on the screen in a different manner of your choice.
The following escape characters are available with escape:
- \a – alert (plays a beep sound)
- \b – backspace
- \c – don’t print the final newline (same as -n option)
- \f – from feed
- \n – newline
- \r – carriage return
- \t – horizontal tab
- \v – vertical tab
- \\ – backslash
- \’ – single quote
- \” – double quote
While -e option asks the echo command to interpret the escape characters, the -E option does the opposite and ignores the escape characters.
Now let’s see how to use some of these escape characters with echo command.
echo -e "An eye for an eye leaves the whole world blind\n\t- Gandhi"Can you guess what would be the output of the above command? Here it is:
An eye for an eye leaves the whole world blind – GandhiLet’s see some other examples of escape characters. The carriage return character prints only the text after that character.
If you use the backspace character, it will remove one character before it:
[email protected]:~$ echo -e “Hello \bWorld” HelloWorldYou can play with other escape characters in the similar way.
5. Display text with single or double quotes with echo command
Dealing with single quotes and double quotes is often a headache.
If you have a single quote in the text that you want to display, you should wrap the entire input within double quotes:
[email protected]:~$ echo “It’s My World” It’s My WorldIf you want to display the double quotes, you have to ‘escape’ it:
[email protected]:~$ echo “It’s \”My\” World” It’s “My” World6. Display files in directory
You probably use the ls command to display the files in a directory. You can also use echo command for this purpose.
To display the contents of the present directory, you can use this command:
You can also use echo command to display only a certain type of files:
If you want to list only the directories, use it like this:
You cannot view the file content with echo, unfortunately.
7. Use echo command to empty a file in Linux
I have already shown this tip for emptying log files in Linux. If you have a text file and you want to clear its content without deleting the file itself, you can use the echo command in the following fashion:
Bonus Tips
Here are a few bonus tip to use the echo command in unusual or colorful manner.
Display echo command output in color
You probably would have come across some bash script that displays the text output in different color. Have you ever wondered how it is done? Let me quickly show you how to change the color of echo output.
You can use the ANSI escape sequence and change the appearance of the output like background color, underscore, bold etc.
To change the color of the output text, you can use these:
echo -e “\033[30mThis is Black”
echo -e “\033[31mThis is Red”
echo -e “\033[32mThis is Green”
echo -e “\033[33mThis is Yellow”
echo -e “\033[34mThis is Blue”
echo -e “\033[35mThis is Magenta”
echo -e “\033[36mThis is Cyan”
echo -e “\033[37mThis is White”Sample colored output for your understanding:
\033[ represents ESC[ in the above commands.
See what a command will do without running it
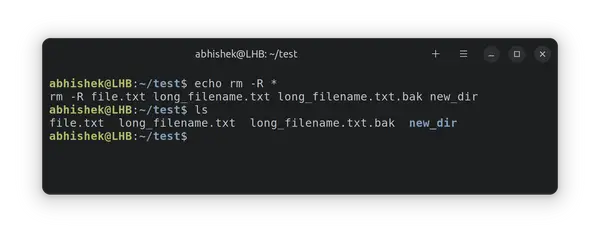
In many cases, the echo command saves you the trouble of accidentally doing something you didn’t expect.
It allows you to expand the wildcards to understand what will happen before you actually run the command.
This will output what will be passed to the rm command (and therefore what would be deleted), putting echo before a command renders it harmless (it just expands wildcards so you know what it will do).
What else?
The echo command is good for quickly printing desired output on the screen. If you want a more complicated formatted output, use the C-styled printf command in bash.
Well, that’s it. I think you have seen a good number of examples of the echo command in Linux. If you use echo for some specific purpose that could be useful to others, please share it with us in the comment section.