- How to find all failed ssh login attempts in Ubuntu
- Installation of SSH
- Enable SSH
- Start SSH
- Check Status of SSH
- List unsuccessful SSH logins
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Kalsoom Bibi
- How to view authentication logs on Ubuntu 20.04
- BitLaunch
- BitLaunch
- How to check system logins
- View the most recent logins
- See when users last logged in
- What to look for in authentication logs
- How to fix the ssh permission denied (publickey) error
- How to install and use PostgreSQL on Ubuntu 20.04
How to find all failed ssh login attempts in Ubuntu
One of the normal tasks of administrators is to keep track of successful and failed login attempts to ensure that the environment is free of unwanted and illegal intrusions. Administrators can also look through the logs to see if there have been any security problems on the servers. A log file is created whenever someone tries to log in to a server using SSH. You may see the requested login date, timestamp, user account, and IP address. SSH was created as a protocol for creating connections between two systems that rely on a client/server architecture, allowing administrators and users to access the server or computer remotely.
This protocol is most commonly used by the system and network administrators and anyone who wants to administer a computer remotely. One of the most prominent benefits is that it is in charge of encrypting the link session to improve security by prohibiting attackers from reading unencrypted passwords. The rsyslog daemon in Linux keeps track of every attempt to login to an SSH server and records it in a log file. Combining, showing, and filtering log files is the most basic approach for listing all failed SSH login attempts on Ubuntu. In this article, we will find all failed ssh login attempts in Ubuntu 20.04 Linux system.
Installation of SSH
To find all unsuccessful ssh login attempts in Ubuntu 20.04 Linux system, open the terminal. You may either type “terminal” into your search engine of the application area or press “CTRL + ALT + T” on your keyboard. Installing OpenSSH is a simple process. It needs a connection to the server’s terminal as well as the machine you are using to connect. You have to install it by typing the listed command in the terminal window of the Ubuntu 20.04 Linux system.
When prompted, enter your sudo user password. After the hard disk prompt, Enter Y to begin the installation. If you press “N”, the installation will be stopped, and you have to execute the same command again.
Enable SSH
Once installation is done, you can enable ssh by typing the listed command in the terminal window.
The execution of the above command will display an almost similar output as shown in the screenshot.
Start SSH
Now you are ready to start the ssh by executing the mentioned command in the terminal window of the Ubuntu 20.04 Linux system.
The above command will start the ssh.
Check Status of SSH
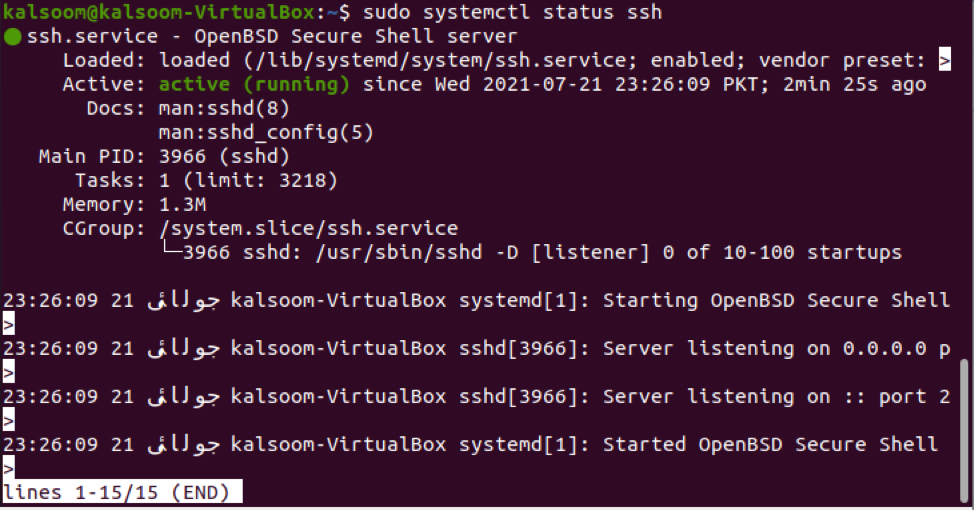
Type the following command to see if the SSH server is running on the Ubuntu 20.4 Linux system:
The output is displaying “Active”. This means all of our instructions are successfully executed.
List unsuccessful SSH logins
Execute some of the commands described in this tutorial to show a list of failed SSH logins in Ubuntu. Make sure you are running these instructions with root privileges.
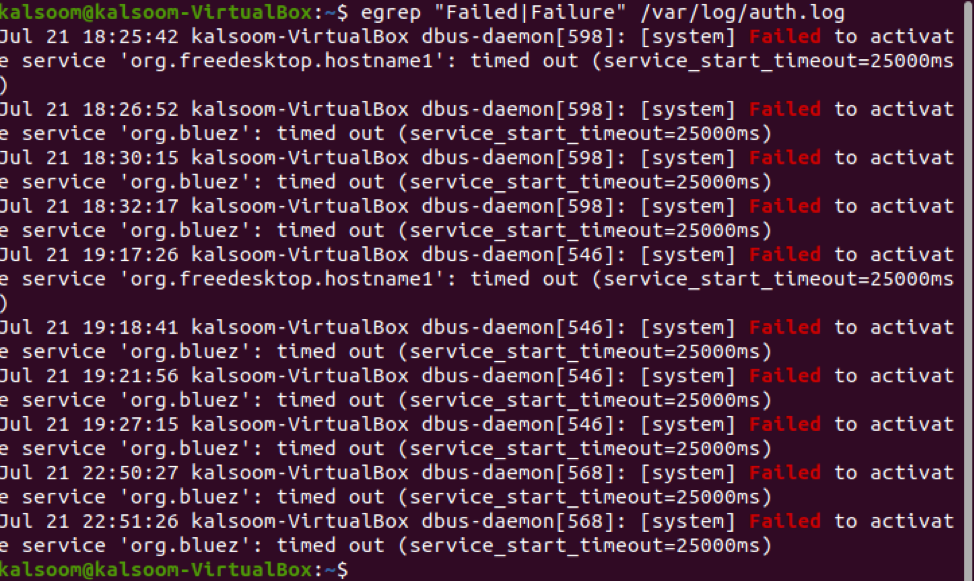
The command shown below is the simplest way to list all unsuccessful SSH logins.
Another same command can be utilized for this purpose with the keyword “cat”. Execute it in the terminal as:
If you want to get more information about unsuccessful SSH logins on Linux, run the command appended below.
The details are much more comprehensive, as you can view from the above-displayed screenshot.
Conclusion
In this guide, we have explained the importance of ssh in the Ubuntu 20.04 system. Along with that, we have listed a way to install ssh on Ubuntu 20.04 system by using the apt command. By checking and following this tutorial, you will be able to find all failed ssh login attempts in the Ubuntu 20.04 Linux system. I hope this guide will be supportive for you during your relevant work.
About the author
Kalsoom Bibi
Hello, I am a freelance writer and usually write for Linux and other technology related content
How to view authentication logs on Ubuntu 20.04
Authentication logs form a vital part of server security. If you suspect a breach, they can provide a full list of every remote login attempt on your server, alongside the account, date, and timestamp.
BitLaunch
BitLaunch
Authentication logs form a vital part of server security. If you suspect a breach, they can provide a full list of every remote login attempt on your server, alongside the account, date, and timestamp. They also list each prompt that asks for a user password, such as the sudo command, and whether or not the authentication was successful.
How to check system logins
The majority of Linux systems keep these logs at /var/log/auth.log or /var/log/secure . For Ubuntu, it’s the former. We can view these with nano or vim like we would any other text file, but the following command will give us faster load times and let us easily view the file page-by-page:
OUTPUT: Jan 8 15:07:22 5ff8750c7437d20001bb84c5 passwd[395]: password for 'root' changed by 'root' Jan 8 15:07:42 5ff8750c7437d20001bb84c5 sshd[546]: Received signal 15; terminating. Jan 8 15:07:42 5ff8750c7437d20001bb84c5 sshd[1321]: Server listening on 0.0.0.0 port 22. Jan 8 15:07:42 5ff8750c7437d20001bb84c5 sshd[1321]: Server listening on :: port 22. Jan 8 15:08:01 5ff8750c7437d20001bb84c5 sshd[1321]: Received signal 15; terminating. Jan 8 15:08:01 5ff8750c7437d20001bb84c5 sshd[1727]: Server listening on 0.0.0.0 port 22. Jan 8 15:08:01 5ff8750c7437d20001bb84c5 sshd[1727]: Server listening on :: port 22. Jan 8 15:09:41 5ff8750c7437d20001bb84c5 sshd[1738]: error: kex_exchange_identification: read: Connection reset by peer Jan 8 15:09:46 5ff8750c7437d20001bb84c5 sshd[1739]: pam_unix(sshd:auth): authentication failure; logname= uid=0 euid=0 tty=ssh ruser= rhost=81.161.63.100 user=root Jan 8 15:09:49 5ff8750c7437d20001bb84c5 sshd[1739]: Failed password for root from 81.161.63.100 port 54150 ssh2 Jan 8 15:14:36 5ff8750c7437d20001bb84c5 sshd[1896]: pam_unix(sshd:auth): authentication failure; logname= uid=0 euid=0 tty=ssh ruser= rhost=71.221.154.110 user=root Jan 8 15:14:37 5ff8750c7437d20001bb84c5 sudo: root : TTY=pts/0 ; PWD=/root ; USER=root ; COMMAND=/usr/bin/less /var/log/auth.log Jan 8 15:14:37 5ff8750c7437d20001bb84c5 sudo: pam_unix(sudo:session): session opened for user root by root(uid=0) (END) Above is a cut-down example from a server that was just created. You can see that it also lists the initial password change when the server was programmatically created.
Once you’re ready, press q to quit the document.
View the most recent logins
If you just want to check the most recent logins, it’s even simpler. Back in the command-line, type last and press Enter.
The output will look something like this:
root pts/0 12.34.567.89 Fri Jan 8 15:30 still logged in root pts/0 12.34.567.89 Fri Jan 8 15:13 - 15:29 (00:16) reboot system boot 5.4.0-1009-kvm Fri Jan 8 15:07 still running The last tool pulls its data from /var/log/wtmp , which is written to each time a user logs in. It’ll show username, tty, IP address, date and time, and session start/stop times.
If that’s too verbose, you can apply filters to the command with the following syntax:
Let’s look at an example. If we wanted to view all of the logins from the root user, we could run:
OUTPUT: root pts/0 12.345.678.90 Fri Jan 8 15:30 still logged in root pts/0 12.345.678.90 Fri Jan 8 15:13 - 15:29 (00:16)Or, if we want to restrict it to a specific user and TTY:
See when users last logged in
If you notice an unauthorized change to the system, it’s often useful to see when each user last logged in. This way, you can determine who made the adjustment. We can do this via the lastlog command, which pulls data from /etc/log/lastlog and sorts them by /etc/password entries:
Username Port From Latest root pts/0 12.345.678.90 Fri Jan 8 15:30:06 +0000 2021 daemon **Never logged in** bin **Never logged in** sys **Never logged in** sync **Never logged in** bitlaunch pts/1 83.253.230.46 Fri Jan 8 16:09:53 +0000 2021 hack0r pts/1 83.253.230.46 Fri Jan 8 16:10:20 +0000 2021 You’ll notice quite a few users with a **Never logged in** entry in the Latest column. This is normal on account of them being system users.
But what if you just found out about a historical incursion or are looking for more specific information? lastlog has several options that can be of use.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| -u, —user [LOGIN] | Print logs for a specific user with a specified login |
| -b, —before [DAYS] | Print records older than a specified number of days |
| -t, —time [DAYS] | Print records that are more recent than a specified number of days |
This is particularly useful if we want to get the last time a specific user logged in:
OUTPUT: root pts/0 12.345.678.90 Fri Jan 8 15:30:06 +0000 2021What to look for in authentication logs
Now you know how to view authentication logs, it’s important to develop a pro-active mindset. Don’t just run these commands if you notice something strange – make it a habit to check regularly.
When you do so, look out out for the following:
- Users who are requesting sudo privileges to perform tasks that are outside their scope of work
- Is one user attempting to access or modify the content of another? Was a password changed unexpectedly?
- Attackers often create a new account so that they can perform actions without as much oversight
Of course, there’s one issue with all this. If an attacker gains access to your root account, they will be able to modify or delete your authentication log. An absence of authentication logs can be very telling, but it also doesn’t leave you with much information about the incursion.
As a result, it’s vital that you keep your root account secure and make regular backups of your log files and full server. Though they can help in the case of a breach, authentication logs are far from a replacement for basic security.
How to fix the ssh permission denied (publickey) error
The SSH permission denied (publickey) error is a frustrating one. Here’s how to fix it in a few simple steps.
How to install and use PostgreSQL on Ubuntu 20.04
In today’s guide we’re going to focus on how to install PostgreSQL on Ubuntu 20.04 as quickly as possible. For those unfamiliar, PostgreSQL, or Postgres, is a free, open-source database management system with high extensibility and compliance.