- How to Fix Ubuntu/Debian apt-get 404 Not Found Repository Errors
- The Problem
- How to Fix The Problem
- Distribution Upgrade
- Update Packages Url
- Get Notified on New Future Studio Content and Platform Updates
- How to fix Ubuntu Failed to fetch http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main…
- Solution
- By Leendert de Borst
- “Failed to fetch” error in Linux
- Are there any pre-requisites?
- Reason 1: Issues with your internet connection
- Diagnosis: Run the ping tool
- Solution: Fixing the internet connection
- Reason 2: You might be connected to a proxy network
- Solution 1: Configuring the proxy settings for APT
- Reason 3: You are using a release that has reached its EoL (End of Life)
- Solution 1: Upgrading your system to the latest version
- References
- Conclusion
How to Fix Ubuntu/Debian apt-get 404 Not Found Repository Errors
When using the desktop version of Ubuntu you’ll eventually get or probably have the problem that apt-get update throws a lot «Failed to fetch 404 Not Found» errors. Additionally, you may have the same problem when running apt-get install . Don’t worry, it will be fixed in a minute.
The Problem
You may see messages like the ones below when executing apt-get update or apt-get install . That is because Ubuntu releases are only supported for 9 months. LTS (Long Term Support) releases have support for 5 years. Once support is cut for the version you’re using, you’ll see those error messages. Ubuntu moves the repositories to another server and the defined URL to reach the sources are no longer available on default location http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/dist/ .
$ sudo apt-get update Ign http://de.archive.ubuntu.com raring Release.gpg Ign http://de.archive.ubuntu.com raring-updates Release.gpg Ign http://de.archive.ubuntu.com raring-backports Release.gpg Ign http://security.ubuntu.com raring-security Release.gpg Ign http://de.archive.ubuntu.com raring Release Ign http://de.archive.ubuntu.com raring-updates Release Ign http://de.archive.ubuntu.com raring-backports Release … 404 Not Found [IP: 91.189.92.201 80] Err http://security.ubuntu.com raring-security/restricted Sources 404 Not Found [IP: 91.189.92.201 80] Err http://security.ubuntu.com raring-security/universe Sources 404 Not Found [IP: 91.189.92.201 80] Err http://security.ubuntu.com raring-security/multiverse Sources 404 Not Found [IP: 91.189.92.201 80] Ign http://de.archive.ubuntu.com raring-backports/main Translation-en Ign http://de.archive.ubuntu.com raring-backports/multiverse Translation-en Err http://security.ubuntu.com raring-security/main amd64 Packages … W: Failed to fetch http://de.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/dists/raring/restricted/source/Sources 404 Not Found [IP: 141.30.13.30 80] W: Failed to fetch http://de.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/dists/raring/universe/source/Sources 404 Not Found [IP: 141.30.13.30 80] W: Failed to fetch http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/dists/raring-security/main/source/Sources 404 Not Found [IP: 91.189.92.201 80] W: Failed to fetch http://de.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/dists/raring/multiverse/source/Sources 404 Not Found [IP: 141.30.13.30 80] … E: Some index files failed to download. They have been ignored, or old ones used instead. How to Fix The Problem
There are two solutions to get your apt commands working again. First: upgrade the Ubuntu release. Second: update the sources url to the old package repositories. Both solutions are described below in more detail.
Distribution Upgrade
The most simple solution is to upgrade your Ubuntu instance to the newest release:
If the distribution upgrade is not an option right now, you can update the sources url for the Ubuntu repositories to find the old packages.
Update Packages Url
You can use the sed command to update the sources in /etc/apt/sources.list file to the new location for old package repositories 2 .
Run the following command to update archive.ubuntu.com and security.ubuntu.com package repository 4 URLs with old-releases.ubuntu.com . Since the normal Ubuntu releases link to the archive.… and security.… URLs, the support will be removed after their live cycle of 9 months and respective repositories 3 moved to old-releases.… .
sudo sed -i -e 's/archive.ubuntu.com\|security.ubuntu.com/old-releases.ubuntu.com/g' /etc/apt/sources.list **Linux Mint additionally requires the execution of this command:** sudo sed -i -e 's/archive.ubuntu.com\|security.ubuntu.com/old-releases.ubuntu.com/g' /etc/apt/sources.list.d/official-package-repositories.list To check whether there are other files in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ which need to be updated, use the following grep command.
grep -E 'archive.ubuntu.com|security.ubuntu.com' /etc/apt/sources.list.d/* That’s it. Now you can update your sources again.
- 1 :Myles McNamara’s blog post saved me a lot of time to understand the problem and find a solution
- 2 :Ask Ubuntu: Install Software From Old Repositories (sed command)
- 3 :Ubuntu Old Releases
- 4 :Ubuntu Current Releases
Get Notified on New Future Studio
Content and Platform Updates
Get your weekly push notification about new and trending
Future Studio content and recent platform enhancements
How to fix Ubuntu Failed to fetch http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main…
Do you get an error like the following when you are trying to download a package via apt-get ?
E: Failed to fetch http://nl.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main/g/glibc/libc-dev-bin_2.31-0ubuntu9.2_amd64.deb 404 Not Found [IP: 213.136.12.213 80] E: Failed to fetch http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main/l/linux/linux-libc-dev_5.4.0-90.101_amd64.deb 404 Not Found [IP: 213.136.12.213 80] E: Failed to fetch http://nl.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main/g/glibc/libc6-dev_2.31-0ubuntu9.2_amd64.deb 404 Not Found [IP: 213.136.12.213 80] E: Failed to fetch http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main/g/gcc-9/libasan5_9.3.0-17ubuntu1~20.04_amd64.deb 404 Not Found [IP: 213.136.12.213 80] E: Failed to fetch http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main/g/gcc-9/libgcc-9-dev_9.3.0-17ubuntu1~20.04_amd64.deb 404 Not Found [IP: 213.136.12.213 80] E: Failed to fetch http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main/g/gcc-9/gcc-9_9.3.0-17ubuntu1~20.04_amd64.deb 404 Not Found [IP: 213.136.12.213 80] E: Failed to fetch http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main/g/gcc-9/libstdc++-9-dev_9.3.0-17ubuntu1~20.04_amd64.deb 404 Not Found [IP: 213.136.12.213 80] E: Failed to fetch http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main/g/gcc-9/g++-9_9.3.0-17ubuntu1~20.04_amd64.deb 404 Not Found [IP: 213.136.12.213 80] E: Failed to fetch http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main/p/python3.8/libpython3.8-dev_3.8.10-0ubuntu1~20.04.1_amd64.deb 404 Not Found [IP: 213.136.12.213 80] E: Failed to fetch http://nl.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main/z/zlib/zlib1g-dev_1.2.11.dfsg-2ubuntu1.2_amd64.deb 404 Not Found [IP: 213.136.12.213 80] E: Failed to fetch http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main/p/python3.8/python3.8-dev_3.8.10-0ubuntu1~20.04.1_amd64.deb 404 Not Found [IP: 213.136.12.213 80]
Solution
The issue most likely has to do with that the Ubuntu package repositories have become outdated. Try the following:
After this command has successfully executed, try the original apt-get command again. If it still doesn’t work, then check your internet connection to see if your Ubuntu machine can connect to the internet. You can do this by issueing the command ping google.com in a terminal.
By Leendert de Borst
Freelance software architect with 10+ years of experience. Expert in translating complex technical problems into creative & simple solutions.
“Failed to fetch” error in Linux
The apt command-line tool is one of the critical components of Debian and Ubuntu-based Linux distros. It facilitates retrieval and installation of packages reliably, thus, allowing users to enjoy the hassle-free installation of software and its dependencies. It is certainly one of the distinguishing features of Linux.
Sometimes, you may encounter the annoying Failed to fetch error while trying to use the apt tool which may look something like the following:
W: Failed to fetch http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/dists/precise/Release.gpg Temporary failure resolving 'in.archive.ubuntu.com'
In this tutorial, we will take a look at possible reasons one may encounter this error and its solutions.
Are there any pre-requisites?
There are no major pre-requisites for being able to fix this issue but keep in mind that you need to have the superuser privilege for your device. If you are not the admin or do not have access to the password of the device, you might not be able to fix this issue.
With the pre-requisites out of the way, now let us look at the possible reasons this error may occur.
Reason 1: Issues with your internet connection
As the apt command fetches packages from the web servers, there is no doubt that you must to have a proper internet connection.
If you are unsure why the terminal is unable to connect to the internet, go through the following steps to perform a diagnosis.
Diagnosis: Run the ping tool
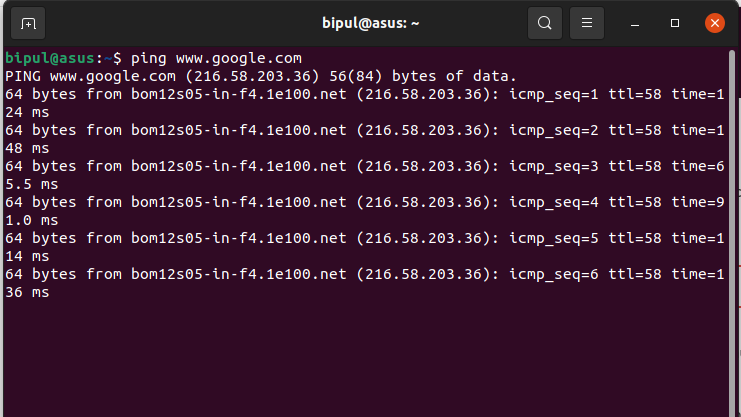
The best way to determine whether the terminal is connected to the internet is by trying to ping a host. Enter the following command:
If you are getting a continuous sequence of replies from the host as shown in the above image, it means that your internet is working fine. Press Ctrl+C to stop the ping tool.
Solution: Fixing the internet connection
One of the following things might get you back online:
- Look for disconnected ethernet cables.
- The WiFi/Network adapter might be switched off, try turning it on.
- Look for malfunctions in your network devices.
- Try contacting the ISP.
Reason 2: You might be connected to a proxy network
If your device is connected to a network belonging to an organization (like your office, university, library, etc.), chances are, you might be connected to the internet through a proxy server.
You will need to configure the proxy settings for APT to work. Follow the steps below:
Solution 1: Configuring the proxy settings for APT
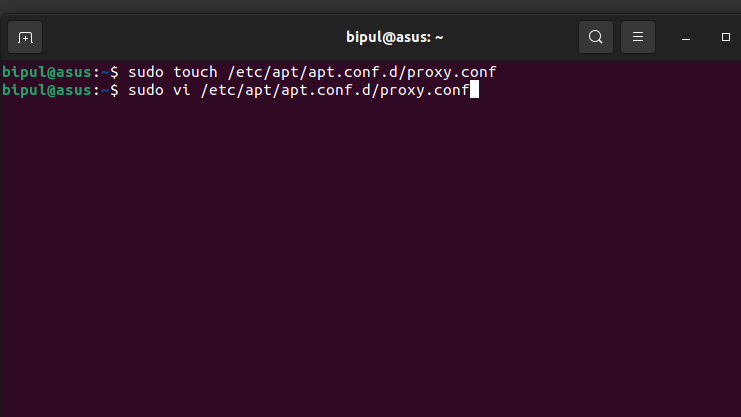
We have to manually create a separate configuration file called proxy.conf in the apt configuration folder.
sudo touch /etc/apt/apt.conf.d/proxy.conf
When prompted, enter the password. This code will create the desired proxy.conf file in the location /etc/apt/apt.conf.d/proxy.conf.
2. Using the Vi editor, now we will edit the text file. Enter the following code:
sudo vi /etc/apt/apt.conf.d/proxy.conf
3. You will enter the edit mode, now add the following piece of code:
Make sure that you replace the with your proxy server hostname and with the port. For example, if your proxy hostname is 10.32.0.1 and port is 8080, the code will look like this:
4. Exit the vi editor saving the changes by entering :wq!
5. Restart your device and check if your problem is resolved.
Reason 3: You are using a release that has reached its EoL (End of Life)
If you are using an old or interim release (like the Ubuntu 21.04), it might have reached its end of life and isn’t supported anymore. You will need to upgrade to a newer version for the proper function of APT.
Solution 1: Upgrading your system to the latest version
1. First, you need to retrieve the updated package list:
2. Now, run the below codes to download and install the required packages:
sudo apt-get upgrade sudo apt-get dist-upgrade
3. You will need to install the update manager:
sudo apt-get install update-manager-core
4. Reboot your device, then enter the following code to start downloading and upgrading your distribution:
Now the system will start downloading the latest version. It might take hours depending on the download size and your device specification.
References
Conclusion
Unless one fully understands the details behind the exceptions thrown by the terminal in Linux, solving issues like this can become somewhat tricky. Nevertheless, I hope that the above-mentioned guide was able to solve the problems.