- Change folder permissions and ownership
- 9 Answers 9
- How to Change File/Group Owner with chown Command in Linux
- How to view file permissions
- How to change file owner with chown command
- How to change the group owner with chown command
- How to change both file owner and group owner of a file
- How to recursively change file ownership
- How to change ownership using a reference file
Change folder permissions and ownership
I would like the user to have full rights on this folder (as well as all sub-directories and files in it):
currently owned by root. I have found numerous posts (in this forum and elsewhere) on how to do this for files but I can’t find a way to do it for whole folders.
9 Answers 9
Use chown to change ownership and chmod to change rights.
As Paweł Karpiński said, use the -R option to apply the rights for all files inside of a directory too.
Note that both these commands just work for directories too. The -R option makes them also change the permissions for all files and directories inside of the directory.
sudo chown -R username:group directory will change ownership (both user and group) of all files and directories inside of directory and directory itself.
sudo chown username:group directory will only change the permission of the folder directory but will leave the files and folders inside the directory alone.
As enzotib mentioned, you need to use sudo to change the ownership from root to yourself.
Note that if you use chown : (Note the left-out group), it will use the default group for that user.
If you want to change only the group, you can use:
BEWARE of recursively taking ownership of ANY directory. Think before you leap. Don’t be chown copypastin’ from the internet, kids. Just because you want to install a node package and it won’t let you, don’t sudo chown -R just because the fist hit from googling the error message says to. Reckless sudo chown -R -ing can kill your OS.
It needs to be said that using the -R option only applies to files and folders that exist in the directory already. It does NOT apply to future creations. For example, if you create another folder or file as root within the folder you’ve already changed permissions on, you will have the same experiences you’re having now until you chmod\chown them again.
Make the current user own everything inside the folder (and the folder itself):
very helpful for newbies (like me) when don’t know what to type in ‘usergroup’ for sudo chown
If you prefer, this can be done with a GUI as well. You will need to open Nautilus as root to do so. Press Alt + F2 to access the «Run Applications» dialog and enter gksu nautilus
Next, browse to and right click on the folder you would like to modify. Then, select «Properties» from the context menu. You can now select the user or group that you would like to be the «Owner» of the folder as well as the permissions you would like to grant them. Finally, press «Apply Permissions to Enclosed Files» to apply the changes recursively.
Though it seems this does not always work for some operations in a deep folder tree. If it does not work use the appropriate terminal command.
How to Change File/Group Owner with chown Command in Linux
Short for change ownership, Chown command is a command-line utility that is used to change the user or group ownership of a file or directory and even links. The Linux philosophy is such that every file or directory is owned by a specific user or group with certain access rights.
Using different examples, we will try and see the various use cases of the chown command . Chown command employs quite a simple and straight forward syntax.
$ chown OPTIONS USER: GROUP file(s)
Let’s briefly flesh out the parameters:
The attribute USER refers to the username of the user that will own the file. You can specify either the username or the UID ( User ID). Meanwhile, the GROUP option indicates the name of the new group that the file will acquire after running the command. The file option represents a regular file or a directory or even a symbolic link. These are the three entities whose permissions can be altered.
A few points to note:
1) When the USER option is specified alone, ownership of the file/directory changes to that of the specified user while the group ownership remains unchanged. Here’s an example:
In the above command, user ownership of the file file1.txt changes from the current user to the user john.
2) If the USER option is proceeded by a full colon i.e. USER: and the group name is not provided, then the user takes ownership of the file but the file’s group ownership switches to the user’s login group. For example:
In this example, the user john takes ownership of the file file1.txt, but the group ownership of the file changes to john’s login group.
3) When both the user and group options are specified separated by a colon i.e USER:GROUP – without any spaces therein – the file takes ownership of the new user and the group as specified
In the above example, the file takes the user and group ownership of user john.
4) When the USER option is left out and instead the group option is preceded by the full colon :GROUP then, only the group ownership of the file changes.
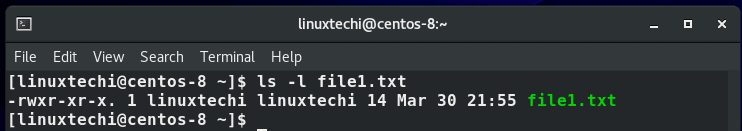
How to view file permissions
To view file permissions, simply use the ls -l command followed by the file name
From the output, we can see that the file is owned by user linuxtechi which and belongs to the group linuxtechi in the 3rd and 4th columns respectively.
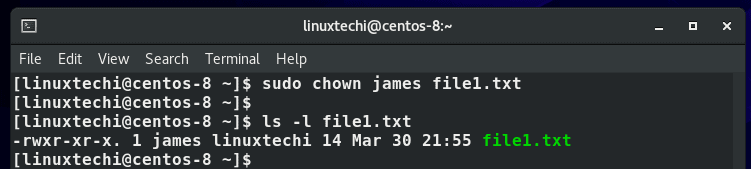
How to change file owner with chown command
Before changing permissions, always invoke sudo if you are not working as the root user. This gives you elevated privileges to change user and group ownership of a file.
To change file ownership, use the syntax:
$ sudo chown james file1.txt
From the output, you can clearly see that the ownership of the file has changed from linuxtechi to user james .
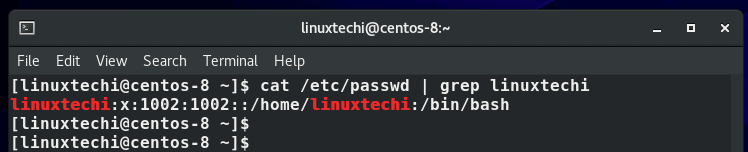
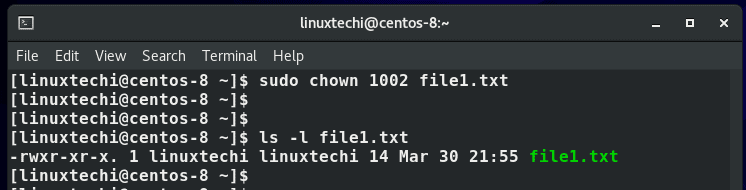
Alternatively, instead of using the username, you can pass the UID of the user instead. To get the UID, view the /etc/passwd file.
$ cat /etc/passwd | grep username
From the example below, we can see that the UID of user linuxtechi is 1002
To change the file ownership back to linuxtechi user, we shall execute the command:
How to change the group owner with chown command
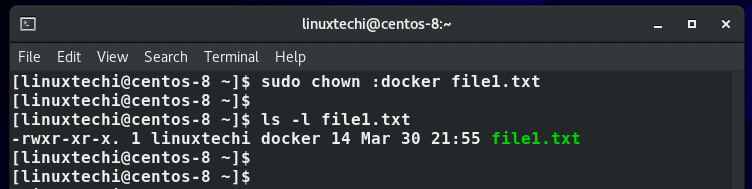
As earlier discussed, to change the group owner of a file, omit the user and simply prefix the group name with a full colon.
For example, to change the group owner of file1.txt from linuxtechi to docker , we executed the command:
$ sudo chown :docker file1.txt
How to change both file owner and group owner of a file
If you want to change both the owner and group that a file belongs to, specify both the user and group options separated by a full colon as shown in the syntax below. Be sure that there are no spaces between the options and the colon.
$ sudo chown user:group filename
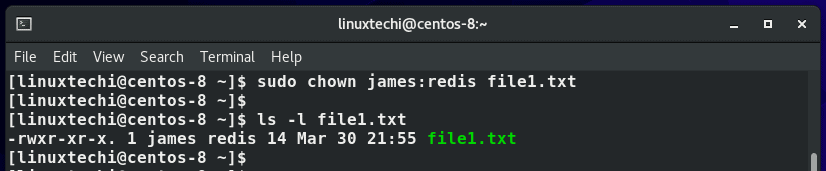
For example, the following command changes the ownership of the file file1.txt to user james and group redis as verified using the ls command.
$ sudo chown james:redis file1.txt
How to recursively change file ownership
When applying permissions to directories, you might want to apply changes recursively i.e make the ownership changes to descend and apply to files and sub-directories. To achieve this, user the recursive option -R or –recursive directive.
$ sudo chown -R user:group directory
For example, the command below assigns all files and folders in the /var/www directory ownership to the www-data group.
$ sudo chown -R :www-data /var/www
The example below assigns ownership of the directory reports alongside all the files and folders in the directory to the user linuxtechi.
$ sudo chown -R linuxtechi reports
How to change ownership using a reference file
Lastly, there’s a nifty way that you can use to change ownership of a file, and that is by using a reference file. Using the chown command, you can change the user and group ownership of a file using another file as the point of reference.
The syntax is shown below:
$ chown –reference=ref_file file
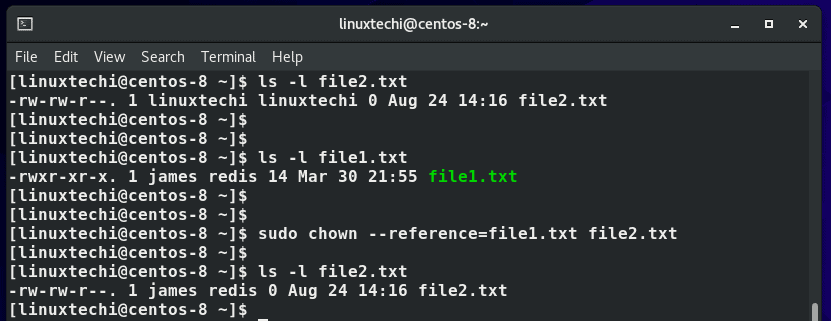
Suppose you want to assign user and group ownership of file1.txt to another file file2.txt. How would you go about it? This is illustrated in the command below.
$ chown --reference=file1.txt file2.txt
The output above confirms that file2.txt inherits the user and group ownership of file1.txt .In the command, file1.txt is the reference file.
Chown command is a powerful tool that is used for managing file and directory ownership. For additional information, check out the chown man pages.