- How to fix permission denied error in Linux? [Solutions]
- What is Linux Permission Denied Error?
- How To Fix Permission Denied Error in Linux?
- Representation of permissions
- Symbolic representation
- How to Solve Bash Permission Denied?
- Conclusion
- Ошибка bash permission denied
- Ошибка bash permission denied
- Выводы
- Linux Bash “Permission Denied” Error and Solutions
- Bash Permission Denied Error
- Set Execution Permission
- Set Execution Permission For File System
- Set Target/Directory Path Permission
How to fix permission denied error in Linux? [Solutions]
When you are working with the Linux Operating system then a common error occurs i.e. permission denied, In this article, you will get to know about how to ‘permission denied’ error in Linux?[linux permissions denied]
List of content you will read in this article:
In the Linux operating system, you cannot execute any command without proper permission. Every file and directory has some permission or privilege (read, write, or execute) associated with them. If you are not authorized to access the file or directory, executing any command on that will result as a “permission denied” error in Linux. This prevalent common can only be resolved by getting the proper access to that file and directory. In this article, we will help you with how to fix the permission denied errors in Linux and what type of error this is with the help of various Linux commands.
What is Linux Permission Denied Error?
This type of error will occur whenever you run a command for which you do not have the execute permission. Similarly, you cannot perform read or write actions if you do not have read or write permission for any file or directory. These Linux permissions are the primary reason behind the security of Linux, as they will help in protecting the data from unauthorized access.
Linux system has three types of permissions
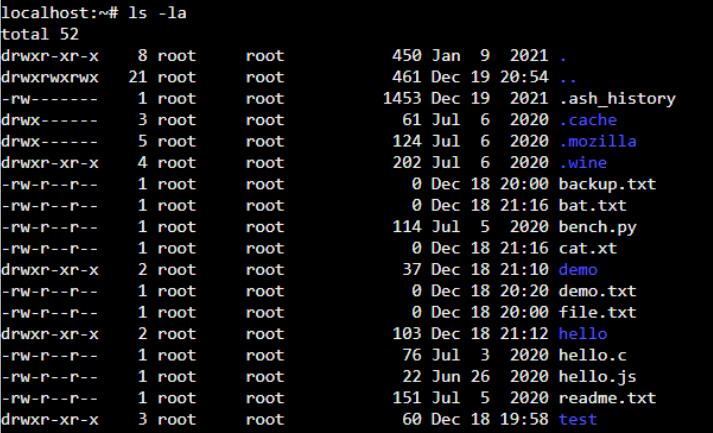
So, if you want to solve a Linux permission denied error, you can check your privileges for the specific file or folder using the following command.
This command will display the long listing of all files and folders along with the permission, as shown below.
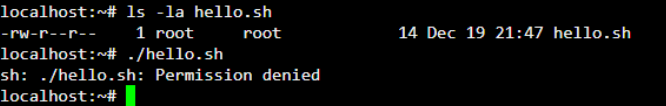
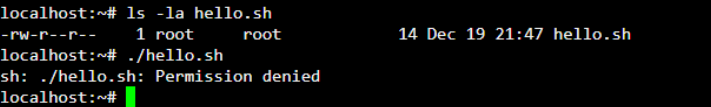
As shown below, we have created a shell script “hello.sh” without the execute permission. On executing “hello.sh”, you will get a “permission denied” error.
How To Fix Permission Denied Error in Linux?
For solving this error, you need to add the correct permissions to the file to execute. However, you need to be a “root” user or have sudo access for changing the permission. For changing the permission, Linux offers a chmod command. The chmod stands for change mod. This command has a simple syntax, as shown below.
chmod flags permissions filename
- Flags are the additional options that users can set.
- Permissions can either be read, write or execute in the file. You can represent them in symbolic form (r, w, and x) or octal numbers.
- The Filename specifies the file’s name for changing the permissions.
Representation of permissions
Below is the symbolic and octal representation of the user’s permissions while executing the “chmod” command. First, we will understand the representation before using it.
Symbolic representation
- r specifies the read permissions
- w specifies the write permissions
- x specifies the execute permissions
- Octal representation-
- 4 specifies the read permissions
- 2 specifies the write permissions
- 1 specifies the execute permissions
- 0 means no permissions issued.
How to Solve Bash Permission Denied?
Now, we are aware of the error, as shown below.
Giving the appropriate permission to the user will solve the problem. Thus, we are giving the execute permission to the user to run the “hello.sh” shell script. Execute the below command to provide execute permission.
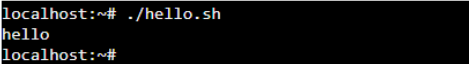
Now, we can see the change in the permission of the “hello.sh” script file. The above command provides the execute permission to the file. As you can see, the root user can make the required changes. If we execute the shell script, we should not get the error. Let’s try by running the below command.
After executing the “hello.sh”, we get the output that displays the “hello.” Changing permission has solved the problem of bash permission denied.
Conclusion
If you are a regular Linux user, you might have faced the “permission denied” error while executing various commands. This might be due to the incorrect privileges to run that command. Only a root user or user with sudo access can change the permissions for the file or directory you want to access or execute. If you are the correct user to make the required permission changes, you can run the “chmod” command and add the desired permission.
This is all about how you can solve/fix permission denied errors in Linux with the help of the above-listed commands/methods. If you think there are other alternatives to achieve the goal, you can put them down via the comment box. Also, you can buy a Linux VPS server to run and test the above-listed commands.
Ошибка bash permission denied
Многие новички пытаются выполнить запись определенных значений в системные файлы с помощью операторов перенаправления ввода и вывода и получают ошибку bash permission denied. Эта ошибка выводится, даже если вы использовали sudo.
Казалось бы, sudo есть, значит права суперпользователя получены и все должно работать но тут все не так просто. В этой статье мы рассмотрим почему возникает ошибка bash permission denied и как ее обойти.
Ошибка bash permission denied
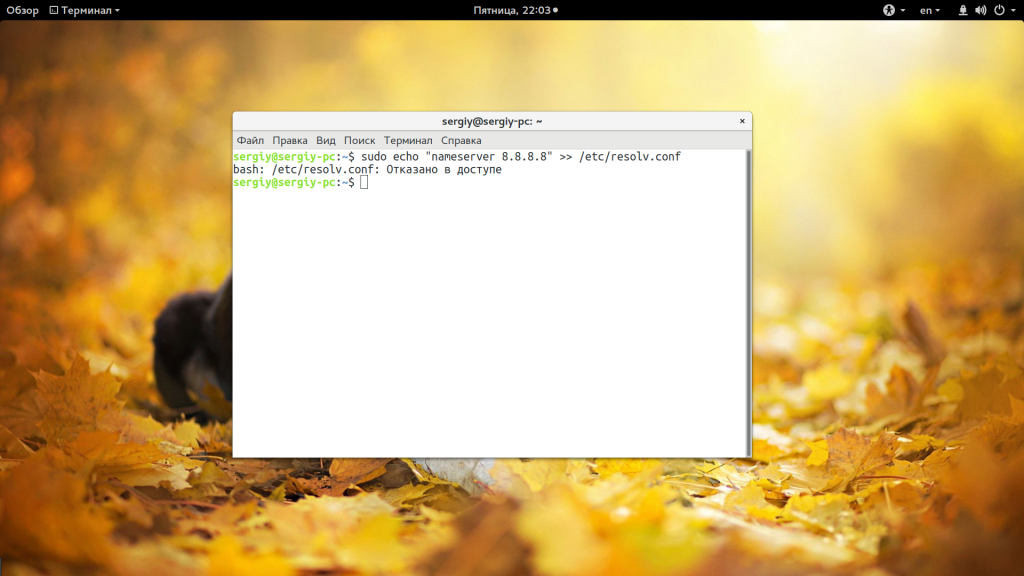
Допустим, вы выполняете команду:
sudo echo «nameserver 8.8.8.8» >> /etc/resolv.conf
А в результате вместо записи строчки в /etc/resolv.conf получаете ошибку:
bash: /etc/resolv.conf permission denied
В русской локализации это будет отказано в доступе bash linux. Так происходит потому что вы запускаете с правами суперпользователя утилиту echo и она честно выводит вашу строку в стандартный вывод bash с правами суперпользователя. Но bash запущен от обычного пользователя, и когда интерпретатор bash пытается записать полученную строчку в системный файл, естественно, что вы получите ошибку.
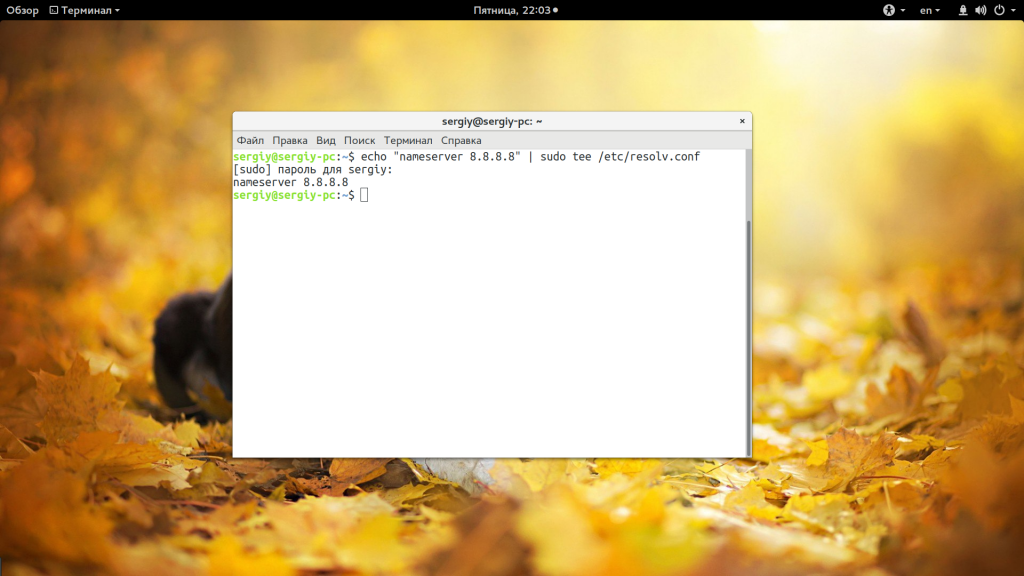
Но существует несколько способов обойти это ограничение, вы можете, например, использовать команду tee, которая записывает стандартный вывод в файл или запустить саму оболочку от имени суперпользователя. Рассмотрим сначала вариант с tee:
echo ‘текст’ | sudo tee -a /путь/к/файлу
echo ‘nameserver 8.8.8.8’ | sudo tee -a /etc/resolv.conf
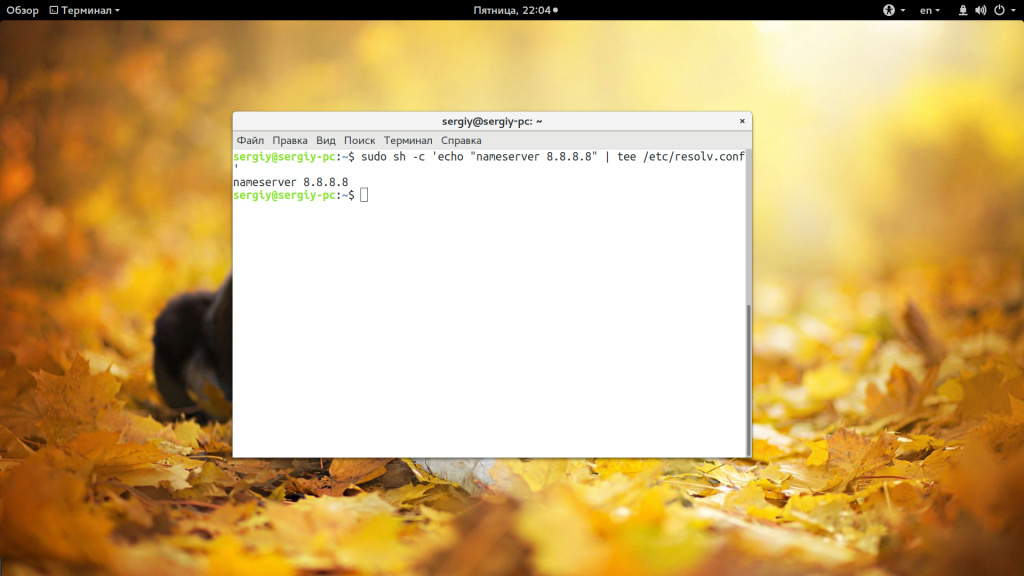
Это очень простое решение, но, кроме того, вы можете запустить оболочку bash с правами суперпользователя, чтобы дать ей доступ на запись:
sudo sh -c ‘echo текст >> /путь/к/файлу’
sudo bash -c ‘echo текст >> /путь/к/файлу’
sudo bash -c ‘echo nameserver 8.8.8.8 >> /etc/resolv.conf
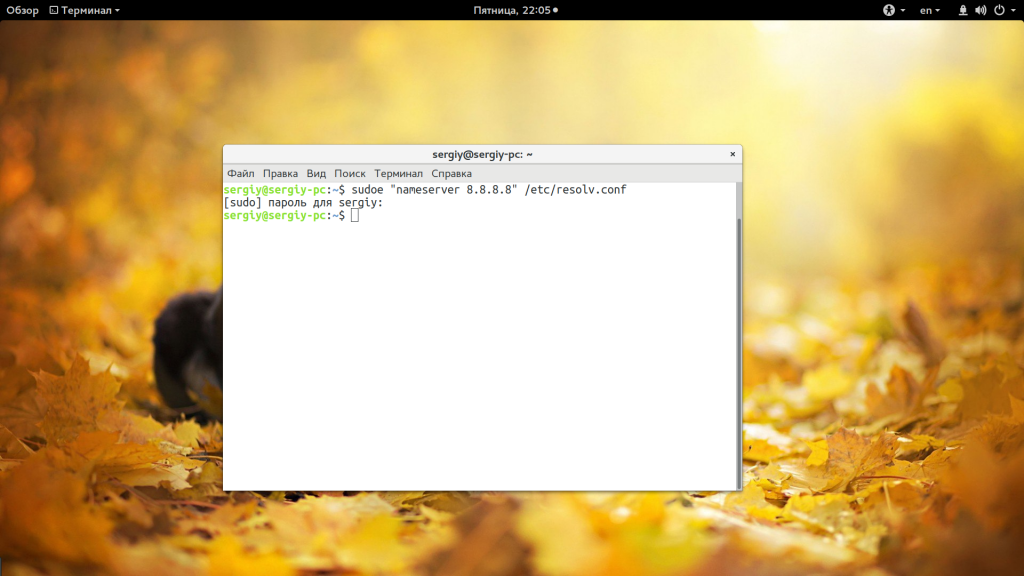
Еще одно решение, призванное, упростить эту команду, добавить такой код в ~/.bashrc:
sudoe() [[ «$#» -ne 2 ]] && echo «Usage: sudoe » && return 1
echo «$1» | sudo tee —append «$2» > /dev/null
>
Дальше для вывода строки в файл выполняйте:
sudoe ‘текст’ >> /путь/к/файлу
sudoe «nameserver 8.8.8.8» > /etc/resolv.conf
Теперь все будет работать, как и ожидалось, и ошибка bash отказано в доступе не появится. Еще можно поменять права на файл, а потом уже выводить в него строку. Но это очень неправильное решение. И даже не потому, что это небезопасно, а больше потому что там намного больше действий.
Выводы
В этой небольшой статье мы разобрали почему возникает ошибка bash permission denied при использовании команды echo для системных файлов, а также несколько путей ее решения. Как видите, все достаточно просто. Надеюсь, эта информация была полезной для вас.
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
Linux Bash “Permission Denied” Error and Solutions
Linux bash can be used to run and execute scripts, programs, applications, and commands in a fast and practical way. When a script, program, application, or command is tried to be executed there may be errors like “Permission Denied“. This error can be caused for different reasons. In this tutorial, we list some solutions to the permission denied error.
Bash Permission Denied Error
Linux requires different privileges and permissions in order to execute, read, write files, scripts, and commands, etc. If the required permissions are not set you may get the “Permission Denied” error.
Set Execution Permission
The first way to solve the permission denied error is settings proper permissions. In order to run an executable, program, application or script we should have the execution permission. The execution permission can be set with the chmod u+x command for the owner.
But this makes the file executable for the current owner of the executable, program, application, or script. Let’s list the owner information about the specified script.
-rwxrwxr-x 1 ismail ismail 16864 Nis 11 18:28 helloworld
We can see that the current owner of the helloworld command is the user “ismail”. We can see that the user ismail has the execution permission which is depicted in the rwxrwxr-x.
The current owner of the file can be changed with the chown command. But this operation requires the root privileges which can be provided with the sudo command. In the following example, we change the file owner user and owner group to the ahmet. The first ahmet is the owner user and the second ahmet is the owner group.
Set Execution Permission For File System
If setting execution permission and changing the owner user of the file is not solved the problem there are other things to do. The commands are stored in a disk where they are mounted to the Linux system with file systems. File systems may prevent the execution of the command, script, program, or application it mounted as with noexec option. Check the file system if it is mounted with the noexec option by using the mount command with the -l option.
After specifying the file system with the noexec option we should remount this file system with the exec option. In the following examle we remount the partition “/dev/sda3” to the “/” with the exec option.
sudo mount -o remount,exec /dev/sda3 /Set Target/Directory Path Permission
If the permission denied error is not solved yet the last step is setting the directory permission recursively where the binary, executable, script, application file resides. This can be a bit dangerous because it may lower the security barier and may give the owner users to execute other binaries. In the following example we made all files in the /mnt/d executable for their owners.
![How to fix permission denied error in Linux? [Solutions]](https://monovm.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/permission-denied-linux327-main.webp)