- Shell linux read only file system to write
- Script to check for read only filesystem
- Can’t edit a read-only file for which I have the write access and also can not change its permission; how to remount its parent folder?
- Unable to open /dev/sdb read-write (Read-only file system)
- Systemd: Failed to disable unit: Read-only file system
- Исправление Read-Only File System в Linux
- Ошибки файловой системы и опция remount-ro
- Read-only файловая система в виртуальных машинах
Shell linux read only file system to write
In some instances you may want to skip any remote mounts which may be RO by design You also may want to skip things that are mounted via automount Solution 3: If you intent is to find filesystems with problems (i.e. the mounting status has been changed to READ-ONLY due to a filesystem error), then I’d do the following (assumming ext* filesystems): EX: What this does is panic the system, thus rebooting the server, possibly invoking a fsck on the problem filesystem to fix it. To check the permission of the mount you can use: If it’s permission issue, to solve it could change the permissions with or just change the ownership recursively, and this is what I’ve shown below: Now if you need, you may also set the permissions with chmod: (which gives owner, group and the world RW permissions for all the files in the target.) (which gives owner, group and the world RWX permissions for all the directories in the target.) (use if the owner is root) Solution: Sometimes on embedded systems the filesystem is mounted readonly, usually because it’s on a storage type that degrades with many writes, and longevity is a priority.
Script to check for read only filesystem
I’ve used the following in the past
In some instances you may want to skip any remote mounts which may be RO by design
grep ' ro ' /proc/mounts | grep -v ':' You also may want to skip things that are mounted via automount
grep ' ro ' /proc/mounts | egrep -v 'automount|autofs' If you intent is to find filesystems with problems (i.e. the mounting status has been changed to READ-ONLY due to a filesystem error), then I’d do the following (assumming ext* filesystems):
tune2fs -e panic [raw-disk-partition-name] What this does is panic the system, thus rebooting the server, possibly invoking a fsck on the problem filesystem to fix it. Thus a serious filesystem problem is handled by having the system fix it automatically, instead of dumping it into Read-ONLY mode which I have not found very helpful. Besides I’d rather panic a problem filesystem, fixing it than attempting to run with it damaged which as time goes on might cause more damage.
Unable to mount filesystem as read-write in recovery, Here the filesystem is mounted but in read-only mode so you can’t edit to rename the directory back for correction. To mount the filesystem in read-write mode, use following command. Command: mount -o rw,remount / It would mount the filesystem in read-write mode. Now you can correct the name of the directory …
Can’t edit a read-only file for which I have the write access and also can not change its permission; how to remount its parent folder?
Problem is solved, I remounted folder by using «mount -o remount,rw /» and then edited the file, without changing any permissions, it worked.
Linux — Can’t edit a read-only file for which I have the, But the file is appearing to be read only, I am unable to edit it. So I tried to change the permission using command chomd [admin@appliance targetfolder]# chmod 666 file.sh chmod: changing permissions of `file.sh’: Read-only file system But still it is just read-only. Someone suggested to remount the …
Unable to open /dev/sdb read-write (Read-only file system)
First try the command sudo hdparm -r0 /dev/sdb (method taken from another askubuntu answer). Then try remounting rw the partition. If these steps don’t work then you are most likely out of luck with that pendrive.
Since the kernel says that the whole drive is write protected you have to deal with the protection at the drive level.
hdparm does this. If it can’t solve this it is likely that your pendrive is write protected by design or it is failed.
Maybe it has a hardware switch under its casing if you take it apart. If it was writable before maybe this switch got flipped, if it was never writable maybe it was always on.
Also googling for your device gives out a lot of hits with the same problem even on windows. This is from the Sandisk forums:
For the SanDisk USB stick the answer has been posted many times. If new return it to where you bought it. If under warrantee return it to SanDisk. BOTH options will get you a new USB stick. There are no other consistent options.
Also from the Sandisk forum:
This is an offical answer if you contact customer service:
«I understand that you are getting write protection error while accessing your Cruzer flash drive. The flash drive has detected a potential fault and has become write protected to prevent data loss. There is no method to fix this. You will need to backup your data and replace the flash drive. Our team of developers is in combination with the OS developers looking into a solution to resolve this issue. Please note that only a minor percentage of users are experiencing the write protection issue and these are the customers posting on the internet to find a solution.»
So likely there is no way to solve it.
My problem is always that the little lock switch on the side of the SD card is moved to «lock». Yes, I mean the physical switch on the side of the SD card.
If you’ve not tried this, first unmount the partition which you want to format and then continue the further jobs.
To check the permission of the mount you can use:
If it’s permission issue, to solve it could change the permissions with chmod or just change the ownership recursively, and this is what I’ve shown below:
sudo chown : -R /path/to/target Now if you need, you may also set the permissions with chmod:
find /path/to/target -type f -execdir chmod 666 -Rv <> + (which gives owner, group and the world RW permissions for all the files in the target.)
find /path/to/target -type d -execdir chmod 777 -Rv <> + (which gives owner, group and the world RWX permissions for all the directories in the target.)
(use sudo chmod if the owner is root)
How To Read and Set Environmental and Shell Variables, This is actually a more complex problem than it initially seems, due to the numerous configuration files that the bash shell reads depending on how it is started. The Difference between Login, Non-Login, Interactive, and Non-Interactive Shell Sessions. The bash shell reads different configuration files depending on …
Systemd: Failed to disable unit: Read-only file system
Sometimes on embedded systems the / filesystem is mounted readonly, usually because it’s on a storage type that degrades with many writes, and longevity is a priority.
A temporary solution to this particular issue is to remount the filesystem as rw , make the necessary change, and then remount again to `ro. This will likely only be temporary because the change probably hasn’t been made to the persistent storage.
Sometimes, the image will come with a way to make the changes persistent, e.g., by writing to a configuration file in the persistent storage that gets read during boot (in your case, the first place I would look would be in /persist , but also in the documentation of the image, if there is some).
If this is truly an incompatible set of services, the proper solution is probably to fix the underlying image by only enabling the services that are needed, and then reflashing your device.
Unable to open /dev/sdb read-write (Read-only file system), If you’ve not tried this, first unmount the partition which you want to format and then continue the further jobs. To check the permission of the mount you can use: ls -ld /path/to/target. If it’s permission issue, to solve it could change the permissions with chmod or just change the ownership recursively, and this is …
Исправление Read-Only File System в Linux
21.10.2022
itpro
CentOS, Linux, Ubuntu
Один комментарий
В некоторый случаях файловая система в Linux может перейти в состояние read-only, при котором вы можете только читать данные с диска, а при попытке записи любых изменение или создании нового файла появдляется ошибка Read-only file system.
Ошибки файловой системы и опция remount-ro
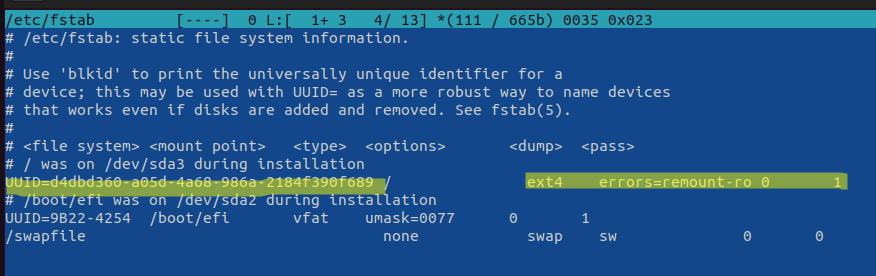
Проверьте параметры монтирования дисков при загрузке Linux. Настройки монтирования файловых систем при загрузке задаются в файле /etc/fstab.
Обратите что в fstab есть строка монтирования корневой директории вида:
UUID=aaaaaaaaa-aaaa-aaaa-aaaa-aaaaaaaaa / ext4 errors=remount-ro 0 1
Параметр errors=remount-ro означает, что данная директория будет смонтирована в режиме чтения, если на файловой системе устройства обнаружены проблемы. В этом случае нужно выполнить проверку диска с помощью FSCK.
Обычные файловые системы такие как EXT4/BTRFS/XFS можно монтировать как в режиме записи, так и только для чтения (в отличии от файловых систем ISO или SquashFS, которые доступны только для чтения).
В случае обнаружения ошибок на диске вы можете использовать одну из трех опций errors=[continue|remount-ro|panic]
- continue – игнорировать ошибки,
- remount-ro – перемонтировать диск в режиме только для чтения
- panic – остановить загрузку системы
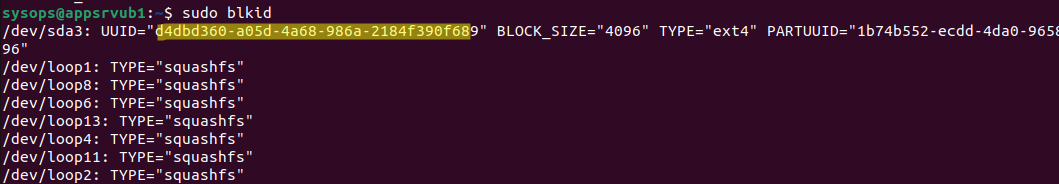
Вы можете вывести соответствие между UUID диска и именем устройства:
В данном примере вы получили, что вашему UUID соответствует устройство /dev/sda3.
Также можно имена устройства и точки монтирования с помощью команды:
Т.к. в данном примере ошибки обнаружены в корневой директории которая является точкой монтирования, вы сможете выполнить ее проверку только загрузившись с LiveCD. Для исправления ошибок файловой системы используется команда:
$ sudo fsck –y UUID=aaaaaaaaa-aaaa-aaaa-aaaa-aaaaaaaaa
Если вы не можете прямо сейчас выполнить проверку диска, и вы хотите немедленно вывести файловую систему из режима read-only, нужно выполниться команду:
Read-only файловая система в виртуальных машинах
Файловая система раздела Linux на виртуальной машине можете перейти в read-only в случае недоступность системы хранения данных (СХД). Самый простой способ восстановить работу ОС – выполнить сброс виртуальной машины (фактически перезапуск с параметрами по умолчанию).
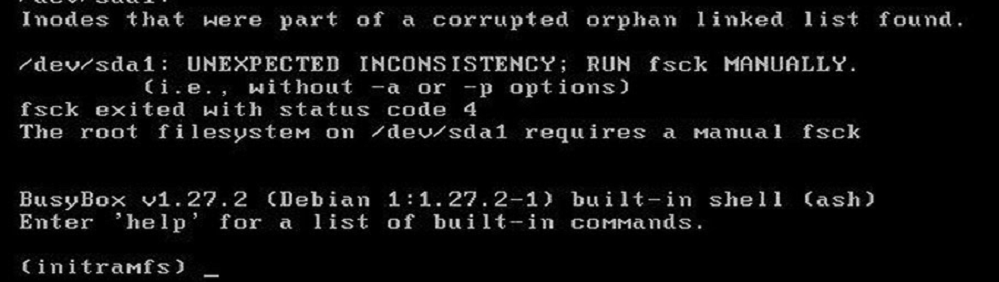
Может оказаться, что ВМ с Linux вообще не загружается и вам доступна только командная строка initramfs с предупреждениями:
UNEXPECTED INCONSISTENCY: RUN fsck MANUALLY. Fsck exitrd with code 4. The root file system of /dev/sdx requires a manual fsck.
Initramfs это начальная файловая система в оперативной памяти, которая основана на tmpfs, которая содержит утилиты и скрипты, необходимые для работы с дисками, файловыми системами и тд. После запуска initramfs отобразится проблемная ситуация.
Если же ошибок нет – просто вводим exit. Иначе выполняем проверку диска:
Здесь указан том (в данной случае /dev/sda1), для которого требуется выполнить ручную проверку. С помощью следующей команды можно проверить все подключенные файловые системы:
После этого перезагрузите ВМ.