- List of Recently Modified Files
- 4 Answers 4
- How to Find Last Modified Files in Linux?
- Finding last day modified files in Linux:
- Find Last Modified Specific File Type in Linux:
- Finding Last Hour Modified Files in Linux:
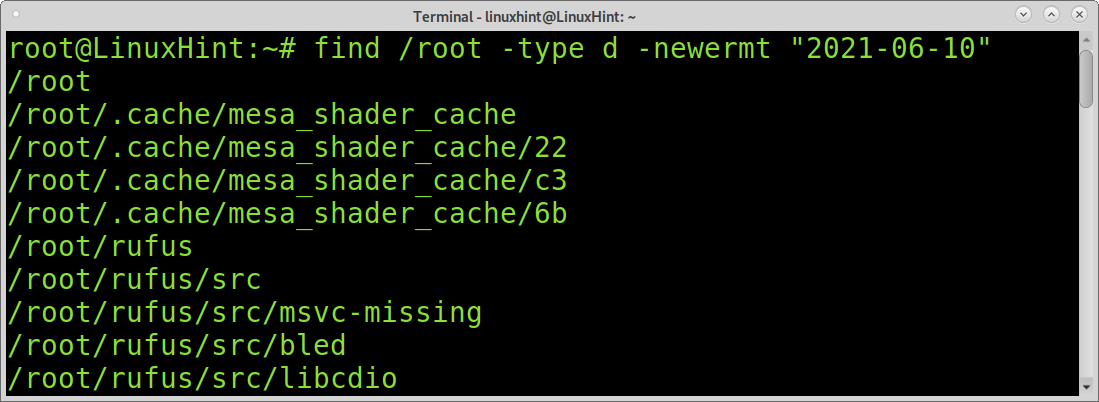
- Finding Files Modified on a Specific Date in Linux:
- Find Last Modified Files Recursively:
- Search File by Date Omitting Files or Directories:
- Find Files by Access Date:
- Conclusion:
- About the author
- David Adams
- List all recently changed files (recursive)
- 6 Answers 6
- Find the files that have been changed in last 24 hours
- 7 Answers 7
List of Recently Modified Files
How can I Get a list of all files modified , say 3 months ago. I checked this question but I was not able to apply it to my scenario. I am trying this now , it seems to be working , but I know there should be a better way using find.
ls -ltR | grep -v '2011-05' | grep -v '2011-06' | grep -v '2011-07' | grep -v '2011-08 4 Answers 4
One solution is: find . -type f -mtime 90
That finds files that was last modified 90 days ago (in those 24 hours that started 91 x 24 hours ago and ended 90 x 24 hours ago).
find . -type f -mtime -90 finds files that were modified in the last 90 days (or in the future).
find . -type f -mtime +90 finds files that were modified at least 91 days ago (at least in POSIX compliant find implementations).
As @hknik says, the -mtime operation on find is likely your best bet, but if you want to get all files around three months ago, then you need a bigger net:
find . -type f -mtime -105 -mtime +76 This will find the regular files in the month surrounding three months ago, between 11 and 15 weeks ago.
(note the 76 instead of 7 x 11 = 77, as you want files whose age rounded down to an integer number of days is strictly greater than 76 to get files that are at least 77 days (11 weeks) old).
will list files modified 90 days ago (in those 24 hours that started 91 x 24 hours ago and ended 90 x 24 hours ago like with POSIX find -mtime 90 ).
will list files modified in the last 90 days (or in the future),
will list files modified between 91 and 100 days ago.
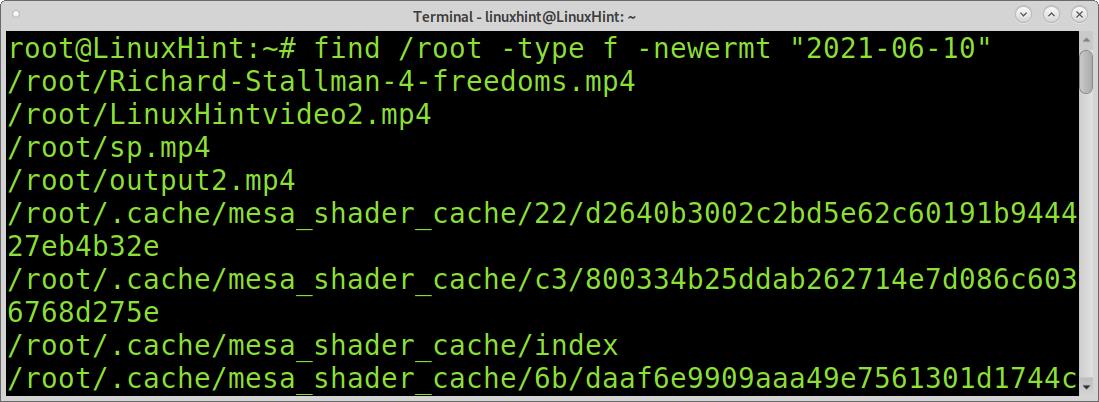
You can use «3 months ago» directly with the «newerXY» syntax:
find . -maxdepth 2 -xdev -type f -newermt '3 months ago' (I added maxdepth and xdev to limit the search)
With these relative dates minutes, hours, days, weeks and months can be used.
«m» stands for modification time, «t» means direct time (and not the date of a reference file).
Or by combining two absolute dates to choose a time span; here from Jan 1 to Jan 15:
#] find . -maxdepth 2 -newermt 'Jan 1' ! -newermt 'Jan 15' -ls 415640 4 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2190 Jan 8 15:14 ./df.man 412465 4 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 98 Jan 1 2020 ./ranfunc 412282 4 -rw------- 1 root root 23 Jan 13 16:53 ./.python_history 406542 0 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 56 Jan 8 19:46 ./.fvwm/.BGdefault -> /usr/share/fvwm/default-config/images/background/bg3.png 417900 28 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 25990 Jan 3 09:48 ./xterm.2020.01.03.09.48.03.xhtml How to Find Last Modified Files in Linux?
This tutorial explains how to find last modified files in Linux using different commands and according to custom needs.
After reading this tutorial you’ll know how to execute the following tasks:
- How to find files modified in a specific day range
- How to find last modified specific file type (e.g mp4, png)
- Finding files modified before / after X minutes
- How to find files modified in a specific date
- Finding modified files recursively
- Search omitting files or directories
- Find files by access date
Finding last day modified files in Linux:
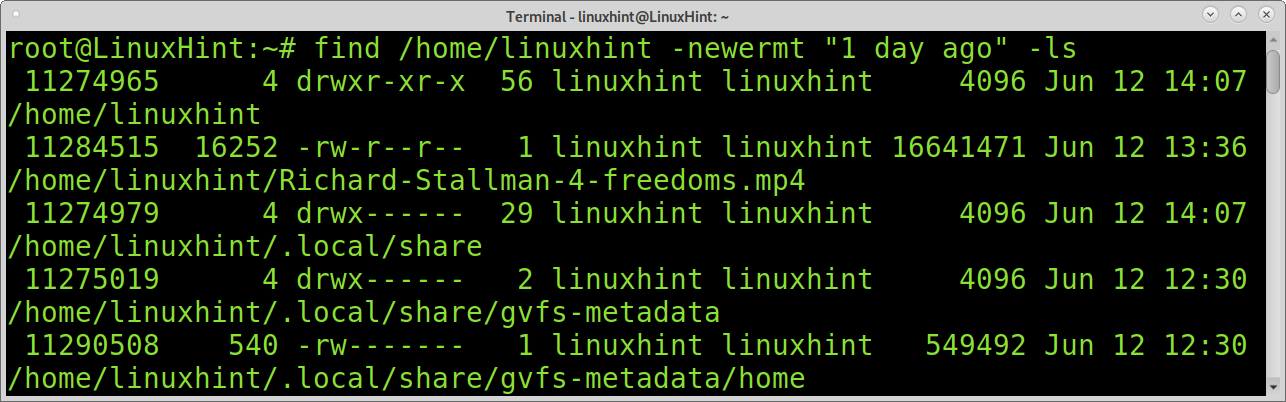
To start, let’s search files modified less than a day ago. To find files modified a day ago you can use the commands find and newermt used in the following example.
The find command is used to search files. The newermt command compares files timestamp with the argument passed, in this case “1 day ago”. Then, the ls command is passed to list the files.
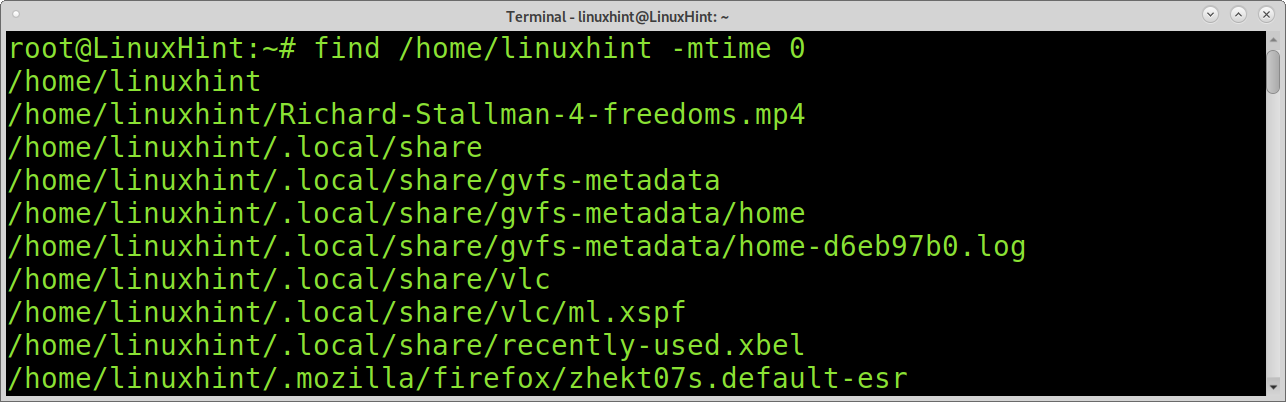
To find last day modified files, you can also use the mtime command together with find. By specifying the option 0 as in the example below, mtime will return all files modified in the last 24 hours.
Find Last Modified Specific File Type in Linux:
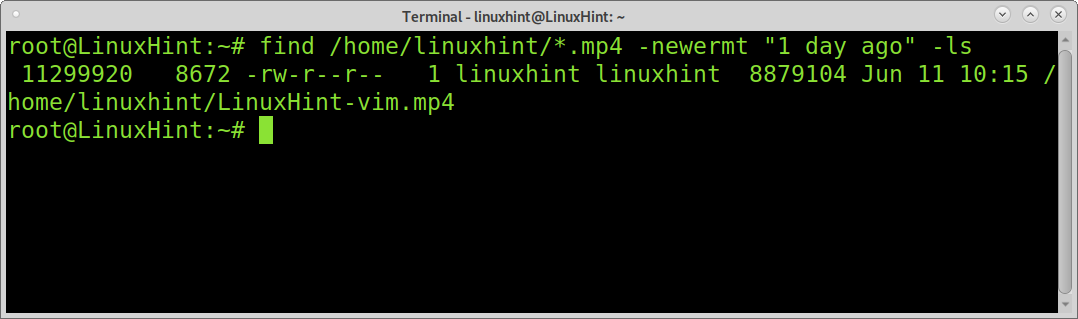
You can use a wildcard to limit your search to a specific file type. In the following example, find and newermt are instructed to list all mp4 files modified a day ago.
cc lang=”bash” width=”100%” height=”100%” escaped=”true” theme=”blackboard”]$ find /home/linuxhint/*.mp4 -newermt “1 day ago” -ls[/cc
In the following example, find and newermt are used to find all .png images less than 15 days old.
Finding Last Hour Modified Files in Linux:
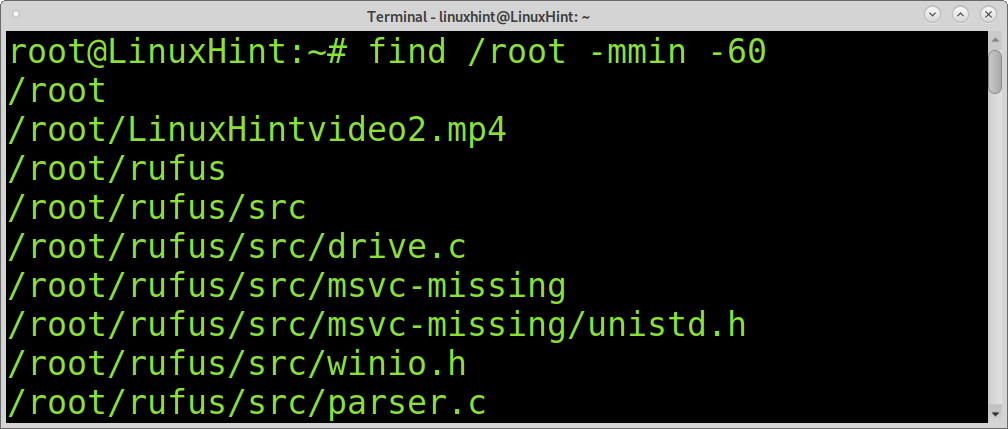
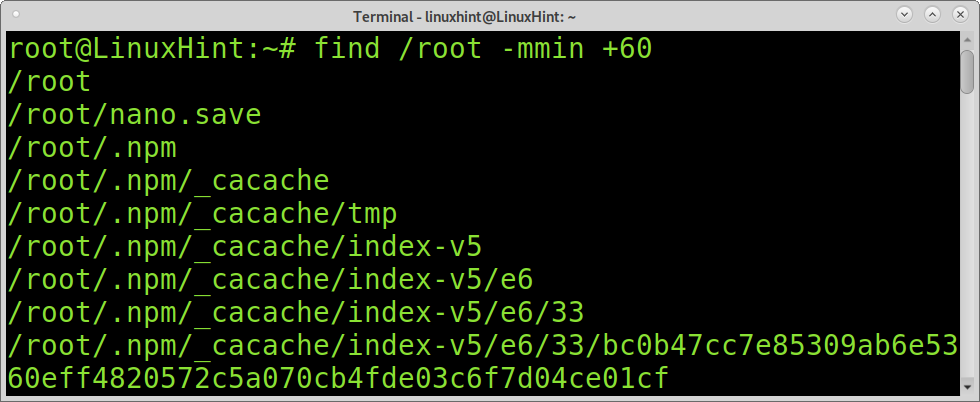
The following example combines the find command with the mmin command. We can use the mmin command to specify minutes. In the example below, the find and mmin commands will print all files under the /root directory, whose modifications are less than 60 minutes old.
Contrary to the previous example in which files modified in the past 60 minutes were found. You can also use +mmin to search files modified after X minutes. For example, the following command will show files modified 60 minutes ago or more.
Finding Files Modified on a Specific Date in Linux:
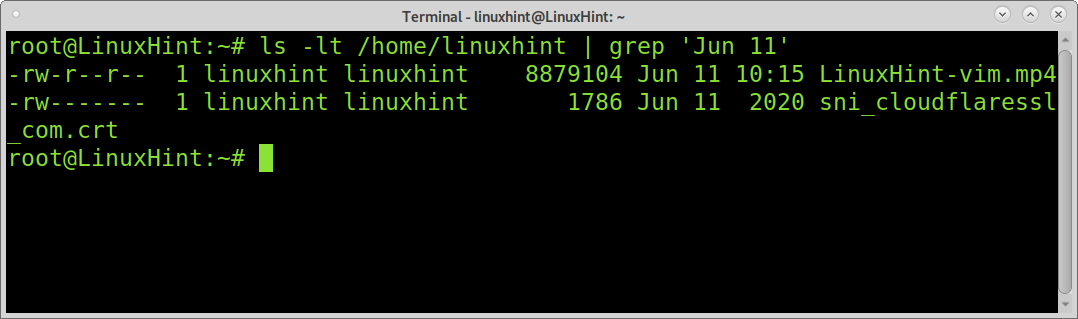
You can use the ls command to list files including their modification date by adding the -lt flag as shown in the example below. The flag -l is used to format the output as a log. The flag -t is used to list last modified files, newer first.
Then you can combine ls -lt with grep to print all files which were modified on a specific date.
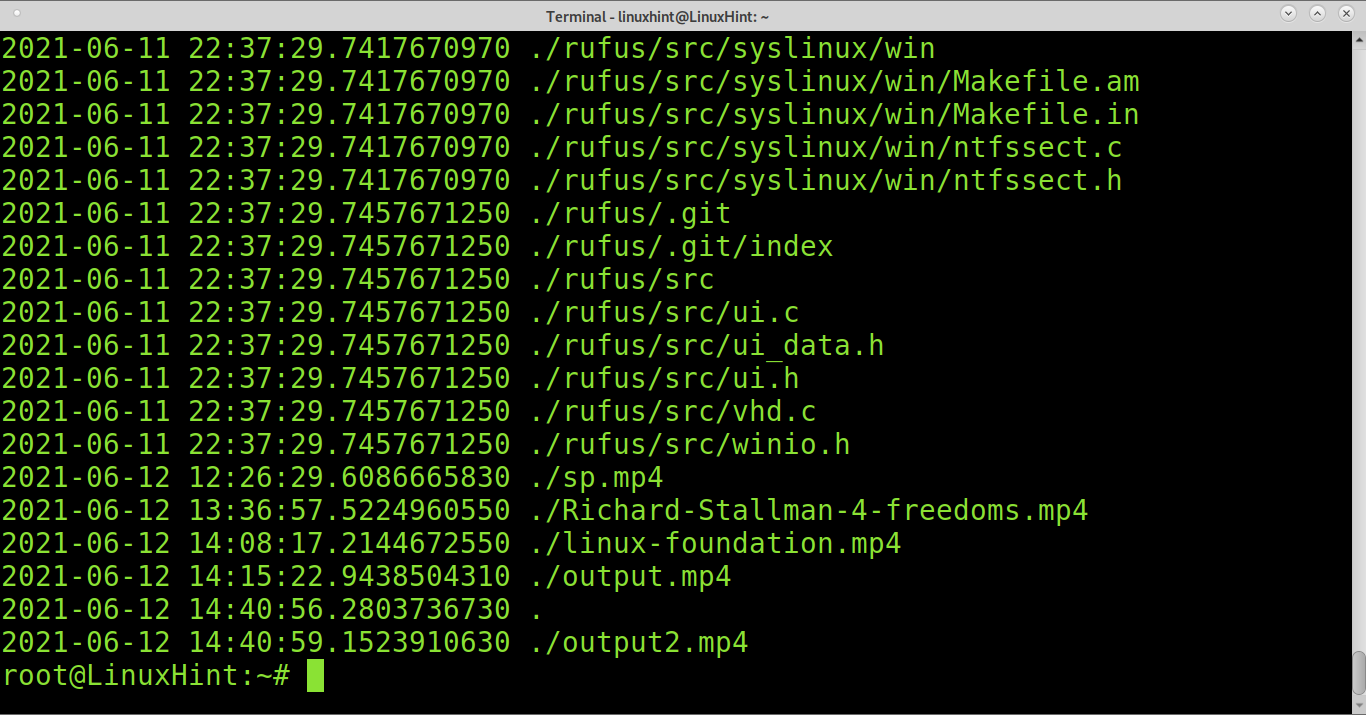
Find Last Modified Files Recursively:
Previous examples are useful to find last modified files
The command below can be used to print last modified files recursively.
Search File by Date Omitting Files or Directories:
Contrary to the previous example, you can search files omitting directories. For this purpose, you need to implement the -type flag with the option f (file) as shown in the following example. As a result, you’ll see only final files and no directories.
You can also search directories only and the output will omit files. For this, just replace the f with a d after the -type flag.
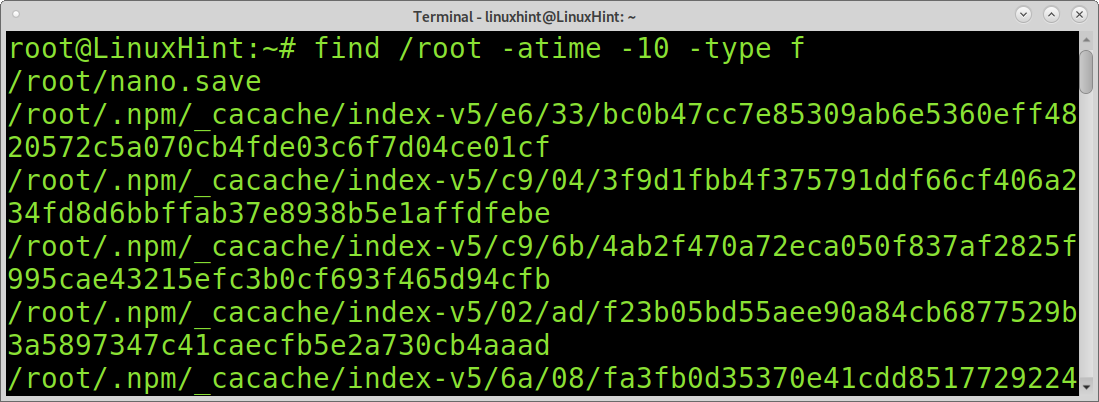
Find Files by Access Date:
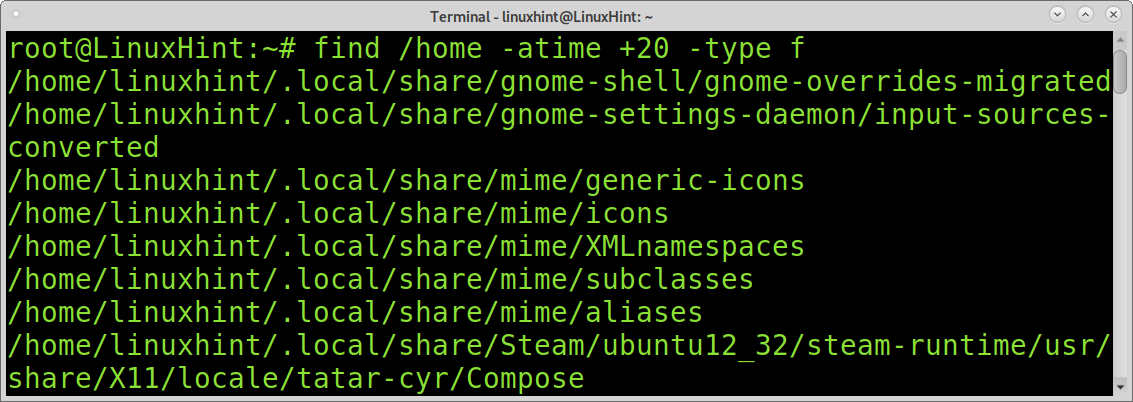
You also may want to find unmodified files by access date. For this purpose, you can use the atime command. It is similar to the mtime command explained before, but instead of identifying files by modification, it can display files by access. With this command you can learn the last accessed files and directories in the system.
The following command shows all files accessed in the past 10 days.
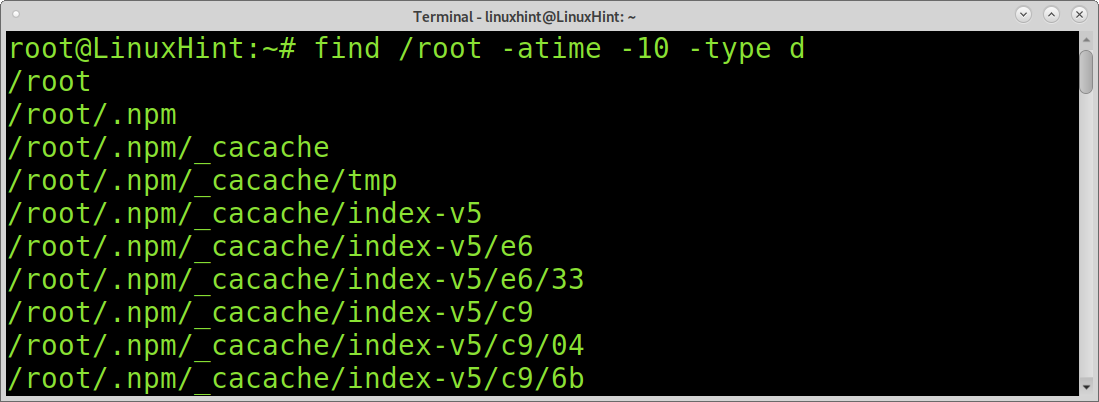
Like the previous command, you can also use the d option to show only directories:
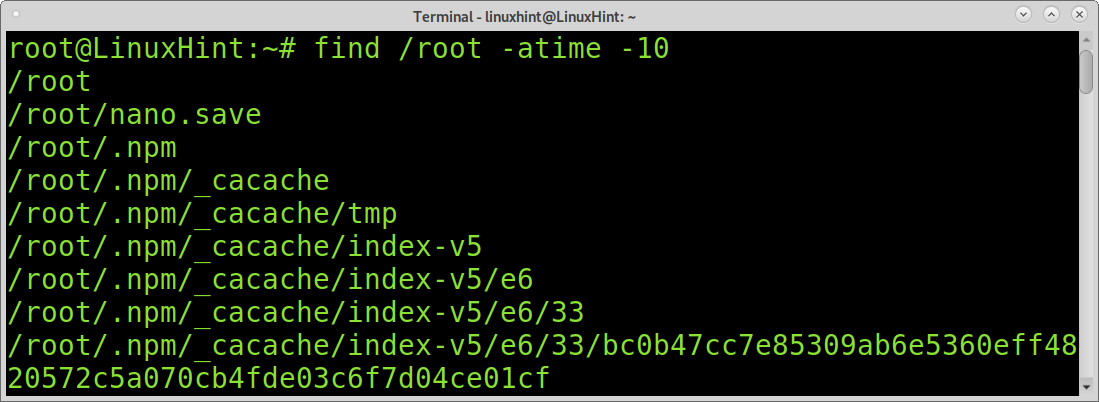
If you don’t specify a type, atime will show all files and directories:
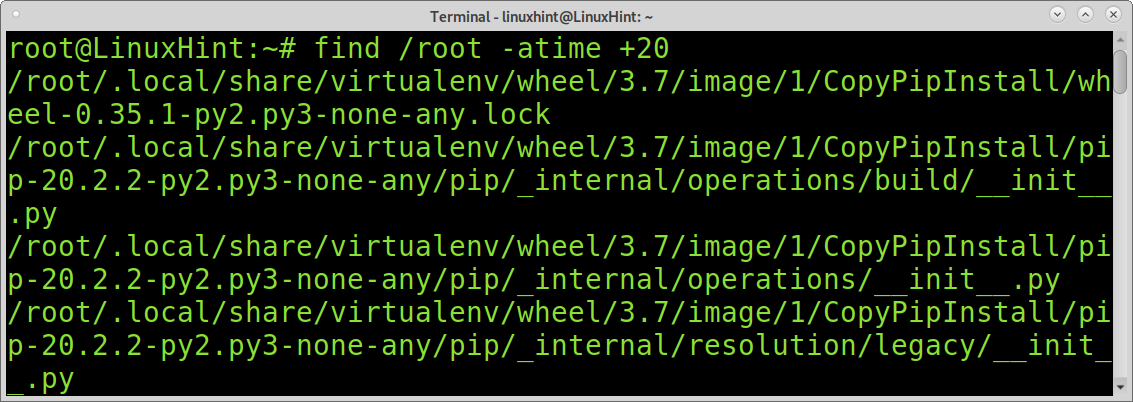
In the following example, find and atime are used to find files and directories with modification older than 20 days.
As with previous examples, you can also limit the listing to files or directories with the -type flag.
Conclusion:
As you can see, Linux offers different methods to find files according to modification time. Any Linux user level can easily learn those methods to search files with a single command. Finding files by modification or access within a system is part of the basic knowledge a Linux user needs.
I hope this tutorial was useful. Keep following Linux Hint for more Linux tips and tutorials.
About the author
David Adams
David Adams is a System Admin and writer that is focused on open source technologies, security software, and computer systems.
List all recently changed files (recursive)
So, I want to display (via ls for example) all files, which were changed in the last seven days. If I’m in my docroot-folder, it should be able to look «deeper». For example:
File Last changed docroot |- myfile1 30.11.2015 |- myfile2 10.11.2015 |- MySub |-sub1 30.11.2015 |-sub2 10.11.2015 So, the ls (or whatever fits) should output myfile1 and (if possible) MySub/sub1 . Is this doable with one command?
6 Answers 6
Of course. From the directory you are in do:
find . -type f -mtime -7 -exec ls -l <> \; Add a redirection to it (aka > results.txt to store them into that file).
- type f does only files and not directories
- mtime -7 does 7 days ago up to now (+7 would be ‘older than 7 days’)
- and it then feeds it to ls to show a long list
You can play with the ls -l part too:
find . -type f -mtime -7 -exec ls -Rl --time-style=long-iso <> \; find . -type f -mtime -7 -exec ls -R --time-style=long-iso <> \; will show a tree like method with directories in between the files in long list (1) or short list (2).
Sure but this makes it a bit more generic (I use this method to find files I need to -remove- and can change that command to do it 🙂 )
Also it is more appropriate to use find . -exec ls -l <> + which executes ls -l much more efficiently — fewer times with multiple parameters. This is a standard option of find specified by POSIX.
- **/* will look for files recursively starting from current directory
- (.m-7) is glob qualifier where . indicates regular file, m-7 indicates files that were modified within last 7 days
The following command works a dream on Mac OSX — maybe also on ubuntu …
find . -type f -mtime -7 -exec stat -lt "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S" <> \; | cut -d\ -f6- | sort -r This finds files in the current directory tree which have been modified in the last 7 days, outputs the modification date + time and path, sorted newest first.
2018-02-21 22:06:30 ./fmxmlsnippet.xml 2018-02-19 12:56:01 ./diff.html 2018-02-19 12:44:37 ./temp/iDDR/XMSC_fmxmlsnippet.xml 2018-02-18 22:04:05 ./temp/iDDR/XMFD_fmxmlsnippet.xml 2018-02-15 10:18:27 ./xml/iDDR/XML2_fmxmlsnippet.xml 2018-02-15 10:13:29 ./xsl/fmxmlsnippet/XML2_fmCM_AnalyseLayout.xsl 2018-02-15 10:11:36 ./xsl/.DS_Store 2018-02-15 10:10:51 ./xsl/_inc/inc.XML2_fmCM_ReportReferencesToExternalFiles.xsl 2018-02-15 10:10:09 ./xsl/_inc/.DS_Store 2018-02-15 10:07:35 ./xsl/fmxmlsnippet/XML2_fmCM_AnalyseLayout-NoAnchors.xsl 2018-02-15 10:07:35 ./xsl/_inc/inc.XML2_fmCM_AnalyseLayout.xsl I’d be grateful of any feedback from ubuntu users.
Find the files that have been changed in last 24 hours
E.g., a MySQL server is running on my Ubuntu machine. Some data has been changed during the last 24 hours. What (Linux) scripts can find the files that have been changed during the last 24 hours? Please list the file names, file sizes, and modified time.
7 Answers 7
To find all files modified in the last 24 hours (last full day) in a particular specific directory and its sub-directories:
find /directory_path -mtime -1 -ls The — before 1 is important — it means anything changed one day or less ago. A + before 1 would instead mean anything changed at least one day ago, while having nothing before the 1 would have meant it was changed exacted one day ago, no more, no less.
The argument to -mtime is interpreted as the number of whole days in the age of the file. -mtime +n means strictly greater than, -mtime -n means strictly less than.
Another, more humanist way, is to use -newermt option which understands human-readable time units (see man find and search for -newerXY ).
Unlike -mtime option which requires the user to read find documentation to figure our what time units -mtime expects and then having the user to convert its time units into those, which is error-prone and plain user-unfriendly. -mtime was barely acceptable in 1980s, but in the 21st century -mtime has the convenience and safety of stone age tools.
Example uses of -newermt option with the same duration expressed in different human-friendly units:
find / -newermt "-24 hours" -ls find / -newermt "1 day ago" -ls find / -newermt "yesterday" -ls