- 26 Useful examples of find command in linux
- What is the use of find command?
- 1) Find all files and directories of present working directory
- 2) Lists all the files of particular directory
- 3) Find a file with name from a directory
- 4) Find files in multiple directories
- 5) Find a file with name ignoring case
- 6) Find all file types other than the mentioned type
- 7) Find files with multiple conditions
- 8) Find files with using OR condition
- 9) Find files based on their permissions
- 10) Find all the hidden files
- 11) Find all the files with SGID
- 12) Find all the files with SUID
- 13) Find all files which are readable but don’t have execute permissions
- 14) Search Several File types
- 15) Find all the files owned by a user
- 16) Find all the files owned by a group
- 17) Find files based on their size
- 18) Do not descend directories on other filesystems
- 19) Find files that are modified N days ago
- 20) Find files that have been accessed N days ago
- 21) Find all the empty files and directories
- 22) Search and delete files
- 23) Find largest and smallest files
- 24) Find all log files and redirect them to a file
- 25) Search Files and change their permissions
- 26) Search Text from files
- 4 thoughts on “26 Useful examples of find command in linux”
- Leave a Comment Cancel reply
- Recent Posts
- Pages
26 Useful examples of find command in linux
Hello Readers, in this post we will cover 26 useful examples of find command in linux.
What is the use of find command?
find command in Linux & UNIX systems used to find files and directories and can perform subsequent actions on them.
With the help of find command, system admin can look for the files that are needed based on a number of search criteria. we can use single or combine a number of criteria and then we can perform actions on the result obtained. Search criteria can be based on file name, directory name, creation date, modification date, owner and permissions.
Actions on find command result can be
- – delete : Delete files or directories
- -exec command <>\; : Run the command on the result obtained from find command
- -ok command : It will run command same as -exec but it will prompt before the actual execution.
Without any further delay let’s jump into find command examples,
1) Find all files and directories of present working directory
To find only directories from your present working directories, run
To search all the files only & not directories, run
2) Lists all the files of particular directory
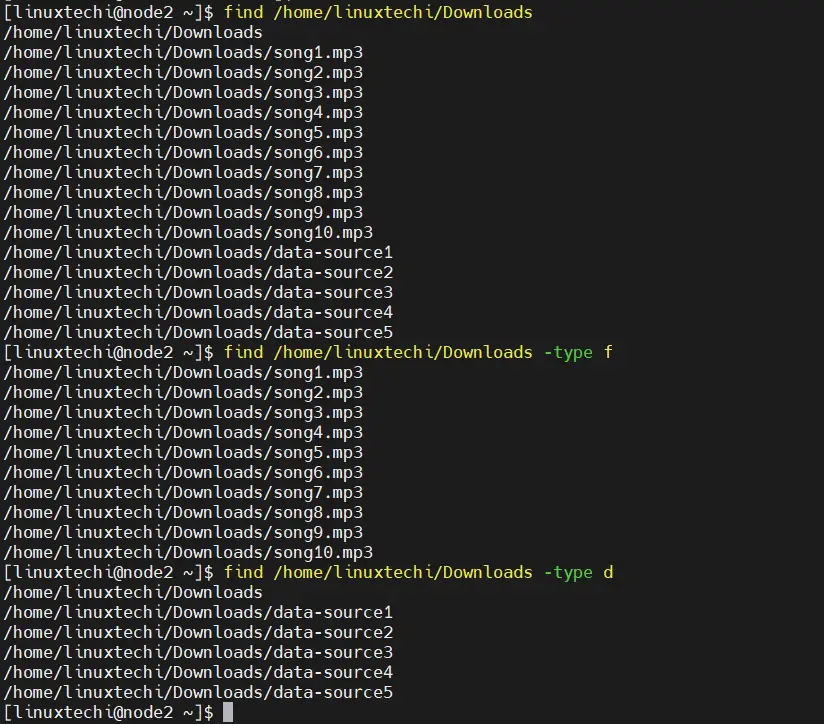
To find all the files of particular directory, let’s suppose we want to list all files and directories of /home/linuxtechi/Downloads folder, run
$ find /home/linuxtechi/Downloads
$ find /home/linuxtechi/Downloads -type f
Run following command to find only directories,
$ find /home/linuxtechi/Downloads -type d
3) Find a file with name from a directory
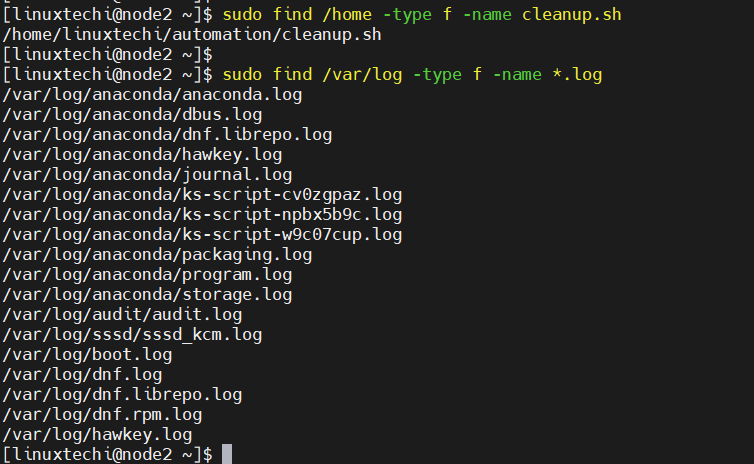
To look for a file by its name in a particular directory, run
$ sudo find /home -type f -name cleanup.sh
Above command will look for cleanup.sh file in /home folder. We can also look for all the files with .log extension in /var/log folder, run
$ sudo find /var/log -type f -name *.log
4) Find files in multiple directories
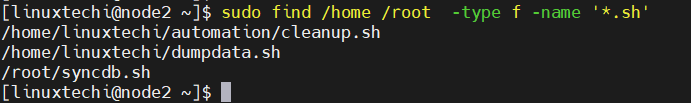
Let’s assume we want to find .sh extension files in /home and /root folder, run
$ sudo find /home /root -type f -name '*.sh'
5) Find a file with name ignoring case
To look for file with its name irrespective of the case i.e. whether its upper case or lower case, we can use ‘-iname’ option in find command.
$ sudo find /home -type f -iname CleanUP.SH /home/linuxtechi/automation/cleanup.sh $
The result of the command will find the file with name cleanup.sh, whether its in lower case or upper case or in mixed cases.
6) Find all file types other than the mentioned type
Let’s suppose we want to find all the files that are not the mentioned type, to achieve this we can use -not option in find command. Example is shown below,
$ sudo find /home -type f -not -name '*.mp3'
7) Find files with multiple conditions
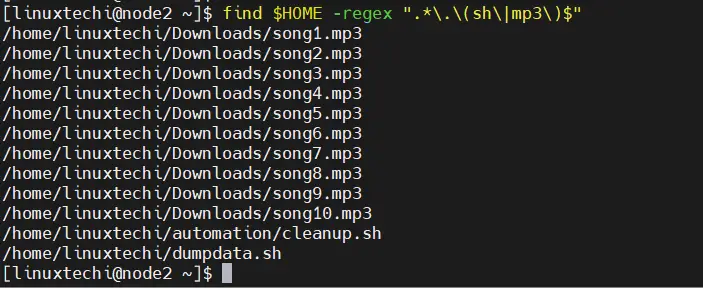
We can also combine more than one condition to search the files using regular expression , Let’s suppose we want to search files of ‘.sh’ and ‘.mp3’ extensions in our home directory, run
8) Find files with using OR condition
We can also combine multiple search criteria & then look for the files based on the fulfillment of any of the one condition using OR operator,
$ find $HOME -name "*.sh" -o -name "jumpscripts" /home/linuxtechi/automation/cleanup.sh /home/linuxtechi/dumpdata.sh $
9) Find files based on their permissions
To look for files based on the permissions, use -perm option in find command. Find all files in /home folder with permissions ‘0777’, run
$ sudo find /home -type f -perm 0777
Find all the executable scripts in user’s home directory
10) Find all the hidden files
To search for all the hidden files in user’s home directory, run the command
11) Find all the files with SGID
To locate all the files with SGID bits, we can use
12) Find all the files with SUID
To locate all the files with SUID bits, run
13) Find all files which are readable but don’t have execute permissions
To only look for the files that are readable by everybody but can not be executed by anybody, run
$ find $HOME -perm -a+r \! -perm /a+x
14) Search Several File types
In single find command, we can search multiple file types,
15) Find all the files owned by a user
To locate all the file that are owned by a particular user in /home directory, run following command,
$ sudo find $HOME -user linuxtechi
16) Find all the files owned by a group
To locate all the files that are owned by a particular group, below command will search all files which are owned by apache group.
17) Find files based on their size
Use ‘-size’ option in find command to search files based on the size. Run following command to find all files whose size is exactly 50MB.
$ find $HOME -size 50M /home/linuxtechi/dbstuff $
Find files whose is size greater than 50MB,
Search files whose size is less than 50MB
Find all files whose size is in range between 40MB to 500MB
$ find $HOME -size +40M -size -500M
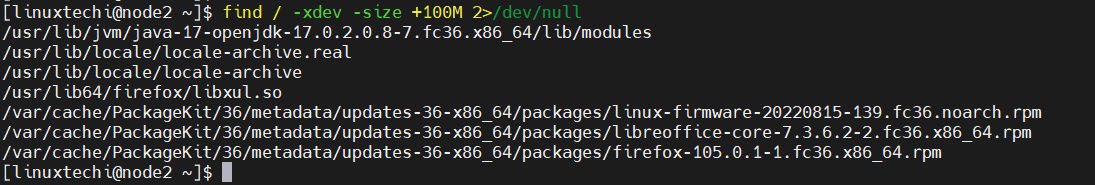
18) Do not descend directories on other filesystems
The option -xdev in find command to list mount points or partitions in another file system, but it doesn’t descend into them.
Beneath command will search all files whose size is more than 100MB in / file system and exclude other mounted file system moreover it will redirect error message to /dev/null
$ find / -xdev -size +100M 2>/dev/null
19) Find files that are modified N days ago
For example, we want to locate all the files that have been modified 10 days ago. We can accomplish that using ‘-mtime’ option in find command
$ sudo find / -mtime 10 2>/dev/null
20) Find files that have been accessed N days ago
Similarly like above example, we can also locate files that have been accessed 30 days ago using ‘-atime’ ,
$ sudo find / -atime 30 2>/dev/null
21) Find all the empty files and directories
To search all the empty files in user’s home directory, run
$ find $HOME -type f -empty or $ find $HOME -type f -size 0
Similarly, to locate all the empty directories
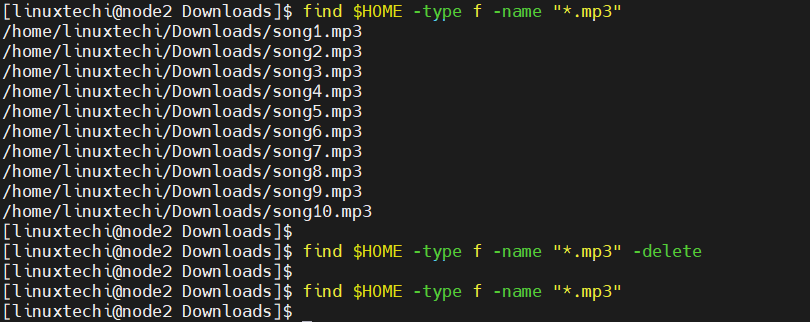
22) Search and delete files
Using find command, we search and delete the files in single command. ‘-delete’ option in find command can delete files.
In following example, we are searching and deleting mp3 files from user’s home directory
$ find $HOME -type f -name "*.mp3" -delete
Note : Above is destructive command, be careful while executing it.
23) Find largest and smallest files
To find largest and smallest file, we will combine sort command with find command & if we further want to list top three of those largest files, we will combine head command .
To list top three files in the user’s home directory, run
$ find $HOME -type f -exec ls -s <> \; | sort -n -r | head -3 51200 /home/linuxtechi/dbstuff 8276 /home/linuxtechi/.cache/gnome-software/appstream/components.xmlb 2764 /home/linuxtechi/.local/share/gnome-photos/tracker3/private/meta.db-wal $
We can similarly find the smallest files in the user’s home directory,
$ find $HOME -type f -exec ls -s <> \; | sort -n | head -3
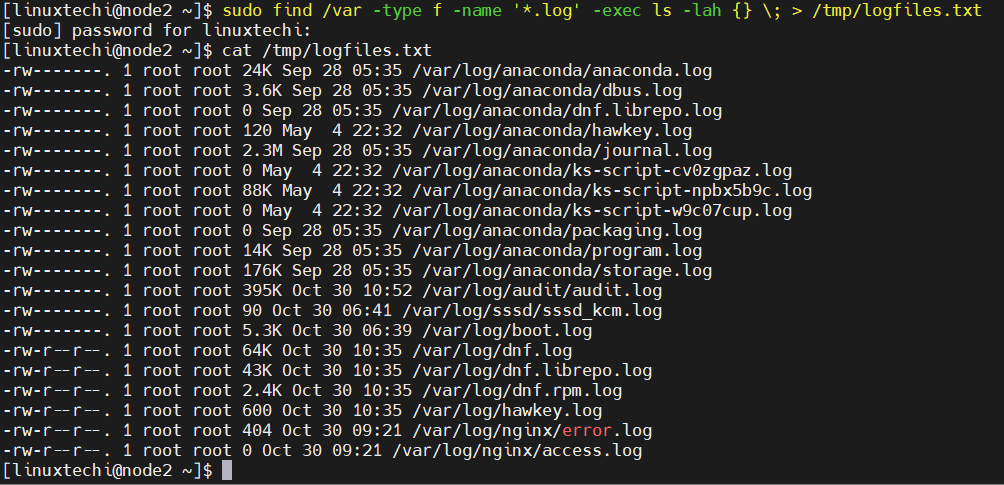
24) Find all log files and redirect them to a file
To run command on find command result use -exec option, it’s syntax given below,
Following command will locate all the files and redirect their names to a file /tmp/logsfiles.txt
$ sudo find /var -type f -name '*.log' -exec ls -lah <> \; > /tmp/logfiles.txt
25) Search Files and change their permissions
Let’s suppose we want to search all files whose permissions is 777 and change their permissions to 644
$ find $HOME -type f -perm 777 -exec chmod 644 <> \;
26) Search Text from files
Let’s assume we want to search error word in all log files, run following command
$ sudo find /var -type f -name '*.log' -exec grep -i 'error' <> \;
In above command we have combined find and grep command to accomplish the task.
That’s all from this post, These were some simple examples demonstrating the functionality of find command & it can be used to perform tedious, repetitive search/locate task more easy.
4 thoughts on “26 Useful examples of find command in linux”
Item 8
We can also combine more than one condition to search the files we need,
$ find ./root -name “*.txt” | -name “linuxtechi*”
That pipe looks like a mistake. Reply
Thank you for making an awesome list of commands. It’s very useful but I don’t find anything about grep command? It’s amazingly powerful and helpful command in Linux to access file contents. Reply
Sir, how to install Nero application in my laptop. I am using Linux ubuntu 16.4 OS at dell inspiron 15 5000 core i5 7th gen. I am confused. So clear and send practice video and pdf Reply
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Recent Posts
- How to Install PHP 8 on RHEL 8 / Rocky Linux 8 / CentOS 8
- How to Install and Use Wireshark in Ubuntu 22.04
- Top 10 Things to Do After Installing Debian 12 (Bookworm)
- How to Install Debian 12 (Bookworm) Step-by-Step
- How to Upgrade Debian 11 to Debian 12 (Bookworm) via CLI
- How to Setup Dynamic NFS Provisioning in Kubernetes Cluster
- How to Install Nagios on Rocky Linux 9 / Alma Linux 9
- How to Install Ansible AWX on Kubernetes Cluster
- How to Install Docker on Fedora 38/37 Step-by-Step
- How to Setup High Availability Apache (HTTP) Cluster on RHEL 9/8