- How To Find a File In Linux From the Command Line
- Locate Linux Files by Their Name or Extension
- Typical Linux Find Commands and Syntax
- Basic Examples
- Options and Optimization for Find Command for Linux
- Find Files by When They Were Modified
- Use Grep to Find Files Based on Content
- How to Locate and Process Files Using the Find Command in Linux
- How To Manage Files Using Plesk?
- How to Edit Files in File Manager
- How to Change Permissions with File Manager
- File Search in File Manager
- 5 Ways to Find a ‘Binary Command’ Description and Location on File System
- 1. whatis Command
- 2. apropos Command
- 3. type Command
- 4. which Command
- 5. whereis Command
How To Find a File In Linux From the Command Line
Need to know how to find a file in Linux? Well, surprise, surprise, you’re going to need the find command in Linux to scour your directory or file system. The Linux find command can filter objects recursively using a simple conditional mechanism, and if you use the -exec flag, you’ll also be able to find a file in Linux straightaway and process it without needing to use another command.
Locate Linux Files by Their Name or Extension
Type find into the command line to track down a particular file by its name or extension. If you want to look for *.err files in the /home/username/ directory and all sub-directories, try this: find /home/username/ -name «*.err»
Typical Linux Find Commands and Syntax
find command expressions look like this:
find command options starting/path expression
The options attribute controls the behavior and optimization method of the find process. The starting/path attribute defines the top-level directory where the find command in Linux begins the filtering process. The expression attribute controls the assessments that scour the directory tree to create output.
Let’s break down a Linux find command where we don’t just want Linux find file by name:
find -O3 -L /var/www/ -name «*.html»
It enables the top-level optimization (-O3) and permits find to follow symbolic links (-L). The find command in Linux searches through the whole directory hierarchy under /var/www/ for files that have .html on the end.
Basic Examples
If you need to know how to find a file in Linux called thisfile.txt, it will look for it in current and sub-directories.
Look for all .jpg files in the /home and directories below it.
Look for an empty file inside the current directory.
4. find /home -user randomperson-mtime 6 -iname «.db»
Look for all .db files (ignoring text case) that have been changed in the preceding 6 days by a user called randomperson.
Options and Optimization for Find Command for Linux
find is configured to ignore symbolic links (shortcut files) by default. If you’d like the find command to follow and show symbolic links, just add the -L option to the command, as we did in this example.
find can help Linux find file by name. The Linux find command enhances its approach to filtering so that performance is optimised. The user can find a file in Linux by selecting three stages of optimisation-O1, -O2, and -O3. -O1 is the standard setting and it causes find to filter according to filename before it runs any other tests.
-O2 filters by name and type of file before carrying on with more demanding filters to find a file in Linux. Level -O3 reorders all tests according to their relative expense and how likely they are to succeed.
- -O1 – (Default) filter based on file name first
- -O2 – File name first, then file-type
- -O3 – Allow find to automatically re-order the search based on efficient use of resources and likelihood of success
- -maxdepth X – Search this directory along with all sub-directories to a level of X
- -iname – Search while ignoring text case.
- -not – Only produce results that don’t match the test case
- -type f – Look for files
- -type d – Look for directories
Find Files by When They Were Modified
The Linux find command contains the ability to filter a directory hierarchy based on when the file was last modified:
find /home/randomuser/ -name «*jpg» -mtime 4
The initial Linux find command pulls up a list of files in the whole system that end with the characters jpg and have been modified in the preceding 5 days. The next one filters randomuser’s home directory for files with names that end with the characters “conf” and have been modified in the preceding 4 days.
Use Grep to Find Files Based on Content
The find command in Linux is great but it can only filter the directory tree according to filename and meta data. To search files based on what they contain you’ll need a tool like grep. Take a look:
find . -type f -exec grep «forinstance» ‘<>‘ \; -print
This goes through every object in the current directory tree (.) that’s a file (-type f) and then runs grep ” forinstance ” for every file that matches, then prints them on the screen (-print). The curly braces (<>) are a placeholder for those results matched by the Linux find command. The <> go inside single quotes (‘) so that grep isn’t given a misshapen file name. The -exec command is ended with a semicolon (;), which also needs an escape (\;) so that it doesn’t end up being interpreted by the shell.
Before -exec was implemented, xargs would have been used to create the same kind of output:
find . -type f -print | xargs grep «forinstance»
How to Locate and Process Files Using the Find Command in Linux
The -exec option runs commands against every object that matches the find expression. Let’s see how that looks:
This filters all objects in the current directory tree (.) for files named rc.conf and runs the chmod o+r command to alter file permissions of the results that find returns.
The root directory of the Linux is where the commands that -exec runs are executed. Use -execdir to execute the command you want in the directory where the match is sitting, because this might be more secure and improve performance under certain circumstances.
The -exec or -execdir options will continue to run on their own, but if you’d like to see prompts before they do anything, swap out -exec -ok or -execdir for -okdir.
How To Manage Files Using Plesk?
Let’s say you have a website that’s all ready to go on your laptop/desktop and you’d like to use File Manager to upload it to the Plesk on Linux server:
- On your machine, you’ll need to take the folder with all of your website’s files on it and add it to a compressed archive in one of the usual formats (ZIP, RAR, TAR, TGZ, or TAR.GZ).
- In Plesk, go to Files, click the httpdocs folder to open it, click Upload, choose the archive file, and then click Open.
- As soon as you’ve uploaded it, click in the checkbox you see alongside and then on Extract Files.
How to Edit Files in File Manager
File Manager lets you edit your website pages by default. To do this you can use:
- An HTML editor or a “what-you-see-is-what-you-get” style of editor, which is a nice option because it adds the HTML tags for you. If you aren’t all that confident with HTML then this can be a helpful option.
- Code editor. When you open HTML files with this one you’ll be presented with text where the HTML syntax is highlighted. If you’re comfortable with adding HTML tags yourself then code editor is for you.
- Text editor. HTML files are opened as ordinary text with this one.
Your Plesk administrator may have already et up the Rich Editor extension, in which case you can use it for HTML file editing. Rich Editor works in a what-you-see-is-what-you-get fashion, just like Code Editor, although it’s better specced with features like a spellchecker for instance.
Here’s how to use File Manager to edit a file:
- Put the cursor over the file and the line that corresponds with it will show a highlight.
- Open the context menu for the file by clicking on it.
- Click Edit in … Editor (this will vary depending on your chosen editor).
How to Change Permissions with File Manager
There are some web pages and files that you don’t necessarily want to share with the world, and that’s where altering their permissions settings can come in handy.
To achieve this, find the item you want to restrict Internet access for like this:
- Place your cursor over it and wait for the highlight to appear as in the previous example.
- Click on the file to open its context menu and do the same again on Change Permissions.
- Make your change and then hit OK. If you’d like to find out more about how to look at and alter permissions in Setting File and Directory Access Permissions.
File Manager’s default approach is to change permissions in a non-recursive manner, so consequently, sub-files and directories don’t aren’t affected by the changed permissions of the higher-level directories they belong to. With Plesk for Linux, you can make File Manager modify permissions in a recursive manner, assuming that your Plesk administrator set up the Permissions Recursive extension and that you understand the octal notation of file permissions.
To enable recursive editing of access permissions:
- Place the cursor over the directory and wait for the highlight.
- Click to open its context menu and then again on Set Permissions Recursive.
- Now you can edit them. “Folder Permissions” is talking about the higher-level directory and any of its associated sub-directories. “File Permissions” applies to sub-files in this instance.
- When you’ve completed your permission amendments, click OK.
File Search in File Manager
You’ve got a little bit of latitude with file searches. You can have File Manager hunt for a specific bit of text either in the file name, in the content, or in both. You can choose how you want it to search for files by clicking on the icon that appears adjacent to your chosen search field, and then clicking on whichever type you prefer.
5 Ways to Find a ‘Binary Command’ Description and Location on File System
With the thousands of commands/programs available in Linux systems, knowing the type and purpose of a given command as well as its location (absolute path) on the system can be a little challenge for newbies.
Knowing a few details of commands/programs not only helps a Linux user master the numerous commands, but it also enables a user understand what operations on the system to use them for, either from the command line or a script.
Therefore, in this article we will explain to you five useful commands for showing a short description and the location of a given command.
To discover new commands on your system look into all the directories in your PATH environmental variable. These directories store all the installed commands/programs on the system.
Once you find an interesting command name, before you proceed to read more about it probably in the man page, try to gather some shallow information about it as follows.
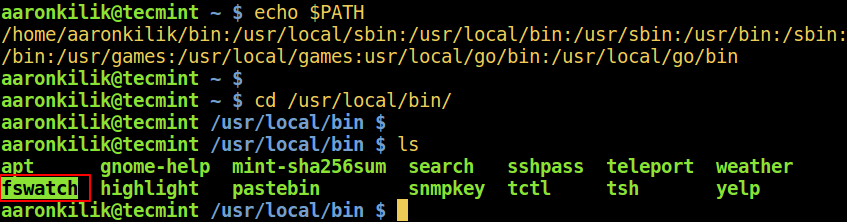
Assuming you have echoed the values of PATH and moved into the directory /usr/local/bin and noticed a new command called fswatch (monitors file modification changes):
$ echo $PATH $ cd /usr/local/bin
Now let’s find out the description and location of the fswatch command using following different ways in Linux.
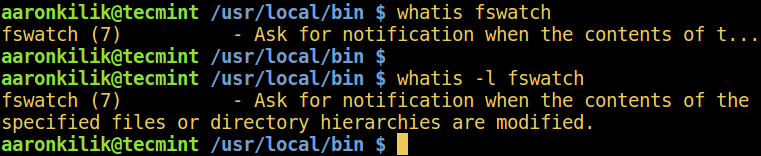
1. whatis Command
whatis is used to display one-line manual page descriptions of the command name (such as fswatch in the command below) you enter as an argument.
If the description is too long some parts are trimmed of by default, use the -l flag to show a complete description.
$ whatis fswatch $ whatis -l fswatch
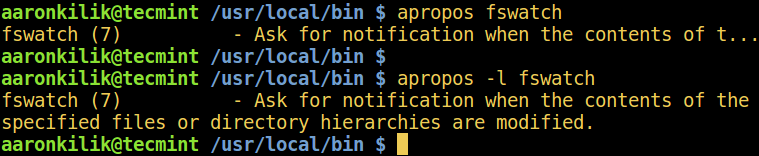
2. apropos Command
apropos searches for the manual page names and descriptions of the keyword (considered a regex, which is the command name) provided.
The -l option enables showing of the compete description.
$ apropos fswatch $ apropos -l fswatch
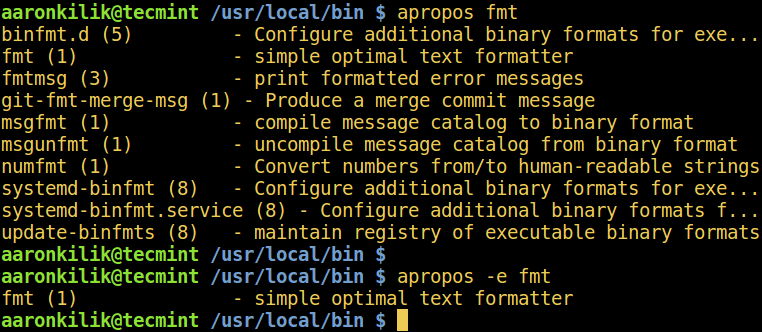
By default, apropos may show an output of all matched lines, as in the example below. You can only match the exact keyword using the -e switch:
$ apropos fmt $ apropos -e fmt
3. type Command
type tells you the full pathname of a given command, additionally, in case the command name entered is not a program that exists as a separate disk file, type also tells you the command classification:
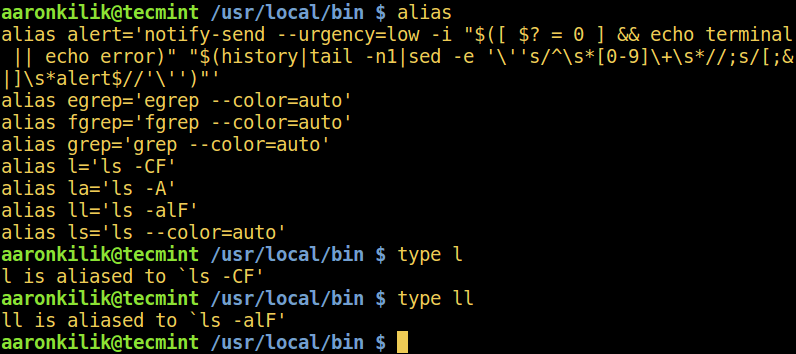
When the command is an alias for another command, type shows the command executed when the alias is run. Use the alias command to view all aliases created on your system:
4. which Command
which helps to locate a command, it prints the absolute command path as below:
Some binaries can be stored in more than one directory under the PATH, use the -a flag to show all matching pathnames.
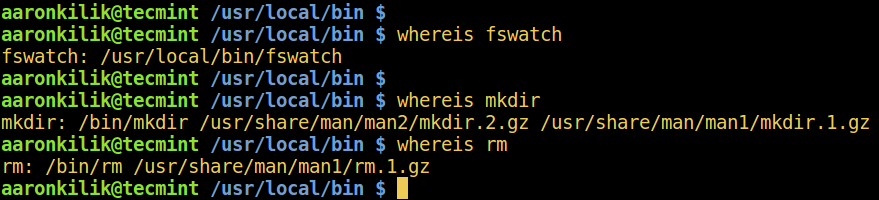
5. whereis Command
whereis command locates the binary, source, and manual page files for the command name provided as follows:
$ whereis fswatch $ whereis mkdir $ whereis rm
Although the commands above may be vital in finding some quick info about a command/program, opening and reading through its manual page always provides a full documentation, including a list of other related programs:
In this article, we reviewed five simple commands used to display short manual page descriptions and location of a command. You can make a contribution to this post or ask a question via the feedback section below.