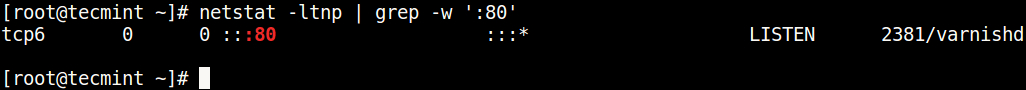3 Ways to Find Out Which Process Listening on a Particular Port
A port is a logical entity that represents an endpoint of communication and is associated with a given process or service in an operating system. In previous articles, we explained how to find out the list of all open ports in Linux and how to check if remote ports are reachable using the Netcat command.
In this short guide, we will show different ways of finding the process/service listening on a particular port in Linux.
1. Using netstat Command
netstat (network statistics) command is used to display information concerning network connections, routing tables, interface stats, and beyond. It is available on all Unix-like operating systems including Linux and also on Windows OS.
In case you do not have it installed by default, use the following command to install it.
$ sudo apt-get install net-tools [On Debian/Ubuntu & Mint] $ sudo dnf install net-tools [On CentOS/RHEL/Fedora and Rocky Linux/AlmaLinux] $ pacman -S netstat-nat [On Arch Linux] $ emerge sys-apps/net-tools [On Gentoo] $ sudo dnf install net-tools [On Fedora] $ sudo zypper install net-tools [On openSUSE]
Once installed, you can use it with the grep command to find the process or service listening on a particular port in Linux as follows (specify the port).
In the above command, the flags.
- l – tells netstat to only show listening sockets.
- t – tells it to display tcp connections.
- n – instructs it to show numerical addresses.
- p – enables showing of the process ID and the process name.
- grep -w – shows matching of exact string (:80).
Note: The netstat command is deprecated and replaced by the modern ss command in Linux.
2. Using lsof Command
lsof command (List Open Files) is used to list all open files on a Linux system.
To install it on your system, type the command below.
$ sudo apt-get install lsof [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] $ sudo yum install lsof [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky Linux/AlmaLinux] $ sudo emerge -a sys-apps/lsof [On Gentoo Linux] $ sudo pacman -S lsof [On Arch Linux] $ sudo zypper install lsof [On OpenSUSE]
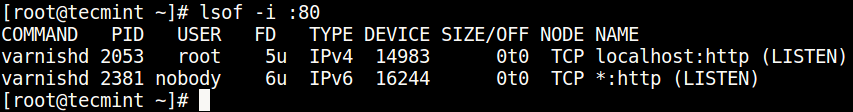
To find the process/service listening on a particular port, type (specify the port).
3. Using fuser Command
fuser command shows the PIDs of processes using the specified files or file systems in Linux.
You can install it as follows:
$ sudo apt-get install psmisc [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] $ sudo yum install psmisc [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky Linux/AlmaLinux] $ sudo emerge -a sys-apps/psmisc [On Gentoo Linux] $ sudo pacman -S psmisc [On Arch Linux] $ sudo zypper install psmisc [On OpenSUSE]
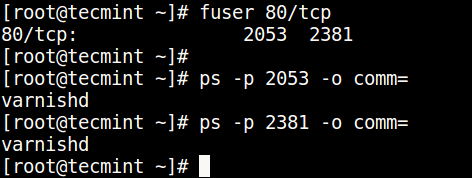
You can find the process/service listening on a particular port by running the command below (specify the port).
Then find the process name using PID number with the ps command like so.
$ ps -p 2053 -o comm= $ ps -p 2381 -o comm=
You can also check out these useful guides about processes in Linux.
You might also like:
That’s all! Do you know of any other ways of finding the process/service listening on a particular port in Linux, let us know via the comment form below.
How can I see what ports are open on my machine?
I would like to see what ports are open on my machine, e.g. what ports my machine is listening on. E.g. port 80 if I have installed a web server, and so on. Is there any command for this?
10 Answers 10
If the netstat command is not available, install it with:
sudo apt install net-tools -l already filters for listening. grep LISTEN won’t help beyond hiding 2 lines of header information.
-t : tcp, -l : listening socket, -p : show pid and program name, -n : print 127.0.0.1:80 instead of localhost:http . Reference: linux.die.net/man/8/netstat
The expanded command is sudo netstat —tcp —listening —programs —numeric . There’s no need to use grep unless you want to eliminate column headers.
nmap (install)
Nmap («Network Mapper») is a free and open source utility for network exploration or security auditing.
Use nmap 192.168.1.33 for internal PC or nmap external IP address .
More information man nmap .
Zenmap is the official GUI frontend.
Remember that there is a difference between nmap localhost and nmap 192.168.0.3 (or what ever you machine IP is)
I think netstat is a better answer to this. netstat will list what the system is listening on directly, and without using an additional application or doing unnecessary calls over localhost or thought the network.
This is stupid. If you have access to the computer, just use netstat -ln . You’ll instantly see all the open ports.
nmap localhost didn’t find services that were bound only to localhost. For example, I run influxd with bind-address:localhost:8086 . That didn’t show up in sudo nmap localhost , but did show up in sudo netstat -tulpn .
Other good ways to find out what ports are listenting and what your firewall rules are:
To list open ports use the netstat command.
$ sudo netstat -tulpn | grep LISTEN tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:53 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 5452/dnsmasq tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:631 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1037/cupsd tcp6 0 0 ::1:631 . * LISTEN 1037/cupsd In the above example three services are bound to the loopback address.
IPv4 services bound to the loopback address «127.0.0.1» are only available on the local machine. The equivalent loopback address for IPv6 is «::1». The IPv4 address «0.0.0.0» means «any IP address», which would mean that other machines could potentially connect to any of the locally configured network interfaces on the specific port.
Another method is to use the lsof command:
$ sudo lsof -nP -i | grep LISTEN cupsd 1037 root 9u IPv6 11276 0t0 TCP [::1]:631 (LISTEN) cupsd 1037 root 10u IPv4 11277 0t0 TCP 127.0.0.1:631 (LISTEN) dnsmasq 5452 nobody 5u IPv4 212707 0t0 TCP 127.0.0.1:53 (LISTEN) For more details see man netstat or man lsof .
How to find ports opened by process ID in Linux?
Hmm..I don’t seem to have the —all and —program options. I’m using OSX. Brew doesn’t seem to have a formula for it either.
-n will dramatically speed things up by not resolving hostnames. netsta -tupan is a good default command all and easy to remember.
You can use the command below:
As a side note, netstat -ao will read the /proc/PID/tcp etc to see the ports opened by the process. This means that its reading information supplied by the system (the linux KERNEL), and is in no way directly looking on the network interface or other means. Same goes for lsof.
If you are doing this as a security measure, you failed. You should never (NEVER EVER) trust the output of netstat, even if you are 100% sure you are in fact running a real netstat program (as opposed to a trojaned version) or any other program that reads the /proc filesystem. Some people seem to think that netstat, ls, ps or any other of the standard unix tools do some sort of magic and poll information from the sources, the truth is all of them rely on the /proc filesystem to get all of their data, which can be easily subverted by a rootkit or hypervisor.
If you’re dealing with a rootkitted system or a compromised hypervisor, you can’t trust anything, including something that purports to look directly at the network interface.
You can use the netstat command line tool with the -p command line argument:
-p (Linux):
Process: Show which processes are using which sockets (similar to -b under Windows). You must be root to do this.
To display all ports open by a process with id $PID :
In some embedded devices or with old version of Linux, the problem is netstat do not have —process or -p options available.
The following script shows process with its IP and port, you must be root.
#!/bin/bash for protocol in tcp udp ; do #echo "protocol $protocol" ; for ipportinode in `cat /proc/net/$ | awk '/.*:.*:.*/'` ; do #echo "#ipportinode=$ipportinode" inode=`echo "$ipportinode" | cut -d"|" -f3` ; if [ "#$inode" = "#" ] ; then continue ; fi lspid=`ls -l /proc/*/fd/* 2>/dev/null | grep "socket:\[$inode\]" 2>/dev/null` ; pid=`echo "lspid=$lspid" | awk 'BEGIN /socket/'` ; if [ "#$pid" = "#" ] ; then continue ; fi exefile=`ls -l /proc/$pid/exe | awk 'BEGIN ">/->/'` #echo "$protocol|$pid|$ipportinode" echo "$protocol|$pid|$ipportinode|$exefile" | awk ' BEGIN function iphex2dec(ipport) < ret=sprintf("%d.%d.%d.%d: %d","0x"substr(ipport,1,2),"0x"substr(ipport,3,2), "0x"substr(ipport,5,2),"0x"substr(ipport,7,2),"0x"substr(ipport,10,4)) ; if( ret == "0.0.0.0:0" ) #compatibility others awk versions < ret= strtonum("0x"substr(ipport,1,2)) ; ret=ret "." strtonum("0x"substr(ipport,3,2)) ; ret=ret "." strtonum("0x"substr(ipport,5,2)) ; ret=ret "." strtonum("0x"substr(ipport,7,2)) ; ret=ret ":" strtonum("0x"substr(ipport,10)) ; >return ret ; > < print $1" pid:"$2" local="iphex2dec($3)" remote="iphex2dec($4)" inode:"$5" exe=" $6 ; >' ; #ls -l /proc/$pid/exe ; done ; done tcp pid:1454 local=1.0.0.127:5939 remote=0.0.0.0:0 inode:13955 exe=/opt/teamviewer/tv_bin/teamviewerd tcp pid:1468 local=1.1.0.127:53 remote=0.0.0.0:0 inode:12757 exe=/usr/sbin/dnsmasq tcp pid:1292 local=0.0.0.0:22 remote=0.0.0.0:0 inode:12599 exe=/usr/sbin/sshd tcp pid:4361 local=1.0.0.127:631 remote=0.0.0.0:0 inode:30576 exe=/usr/sbin/cupsd tcp pid:1375 local=1.0.0.127:5432 remote=0.0.0.0:0 inode:12650 exe=/usr/lib/postgresql/9.3/bin/postgres With ls you can know the process route.
The fuser command says that the process is: 2054
I’ve added IPv6 support and made a few fixes. Additionally on my system the octets of the IP address are reversed. Dependencies are only to posix shell, awk and cut.
My Version can be found on Github
#!/bin/sh # prints all open ports from /proc/net/* # # for pretty output (if available) start with # ./linux-get-programm-to-port.sh | column -t -s $'\t' #set -x ip4hex2dec () < local ip4_1octet="0x$" local ip4_2octet="$" ip4_2octet="0x$" local ip4_3octet="$" ip4_3octet="0x$" local ip4_4octet="$" ip4_4octet="0x$" local ip4_port="0x$" # if not used inverse #printf "%d.%d.%d.%d:%d" "$ip4_1octet" "$ip4_2octet" "$ip4_3octet" "$ip4_4octet" "$ip4_port" printf "%d.%d.%d.%d:%d" "$ip4_4octet" "$ip4_3octet" "$ip4_2octet" "$ip4_1octet" "$ip4_port" > # reoder bytes, byte4 is byte1 byte2 is byte3 . reorderByte() < if [ $-ne 8 ]; then echo "missuse of function reorderByte"; exit; fi local byte1="$" local byte2="$" byte2="$" local byte3="$" byte3="$" local byte4="$" echo "$byte4$byte3:$byte2$byte1" > # on normal intel platform the byte order of the ipv6 address in /proc/net/*6 has to be reordered. ip6hex2dec()< local ip_str="$" local ip6_port="0x$" local ipv6="$(reorderByte $)" local shiftmask="$" ipv6="$ipv6:$(reorderByte $)" shiftmask="$" ipv6="$ipv6:$(reorderByte $)" ipv6="$ipv6:$(reorderByte $)" ipv6=$(echo $ipv6 | awk '< gsub(/(:0|^0)/, ":"); sub(/(:0)+:/, "::");print>') printf "%s:%d" "$ipv6" "$ip6_port" > for protocol in tcp tcp6 udp udp6 raw raw6; do #echo "protocol $protocol" ; for ipportinode in `cat /proc/net/$protocol | awk '/.*:.*:.*/'` ; do #echo "#ipportinode=$ipportinode" inode=$ if [ "#$inode" = "#" ] ; then continue ; fi lspid=`ls -l /proc/*/fd/* 2>/dev/null | grep "socket:\[$inode\]" 2>/dev/null` ; pids=`echo "$lspid" | awk 'BEGIN /socket/ END>'` ; # removes duplicats for this pid #echo "#lspid:$lspid #pids:$pids" for pid in $pids; do if [ "#$pid" = "#" ] ; then continue ; fi exefile=`ls -l /proc/$pid/exe | awk 'BEGIN ">/->/'`; cmdline=`cat /proc/$pid/cmdline` local_adr_hex=$ remote_adr_hex=$ remote_adr_hex=$ if [ "#$" = "#6" ]; then local_adr=$(ip6hex2dec $local_adr_hex) remote_adr=$(ip6hex2dec $remote_adr_hex) else local_adr=$(ip4hex2dec $local_adr_hex) remote_adr=$(ip4hex2dec $remote_adr_hex) fi echo "$protocol pid:$pid \t$local_adr \t$remote_adr \tinode:$inode \t$exefile $cmdline" done done done