- How to Generate, Encrypt and Decrypt Random Passwords in Linux
- PWgen – Generate a Random Password on Linux
- Makepasswd – Generate Unique Passwords on Linux
- mkpasswd – Encrypt a Password in Linux
- Encrypt a String with Password in Linux
- Decrypt a String in Linux
- 10 ways to generate a random password on Linux
- How do I generate a random password in Shell?
- How do I generate a random password using openssl?
- How do you get a random number from Dev random?
- What is Linux password?
- Is password generator safe?
- How do I generate a random number in bash?
- What is Dev random in Linux?
- What command may be used to generate strong user passwords?
- How random is Shuf?
- How use Urandom Linux?
- How random is $random?
- Password Generator in Linux – Generate Random Passwords in Command Line
- How to achieve (pseudo)randomness
- Creating random passwords with only alphanumeric characters
- Setting the length of the password
- Deleting the new-line characters
- Conclusion
How to Generate, Encrypt and Decrypt Random Passwords in Linux
In this article, we will share some interesting command-line tools to generate random passwords and also how to encrypt and decrypt passwords with or without the slat (a security measure used in password hashing) method.
Security is one of the major concerns of the digital age. We set passwords to computers, email, cloud, phones, documents, and whatnot. We all know the basic to choose a password that is easy to remember and hard to guess.
What about some sort of machine-based password generation automatically using pwgen or makepasswd – a command-line password generator used to generate random passwords based on length, complexity, and character.
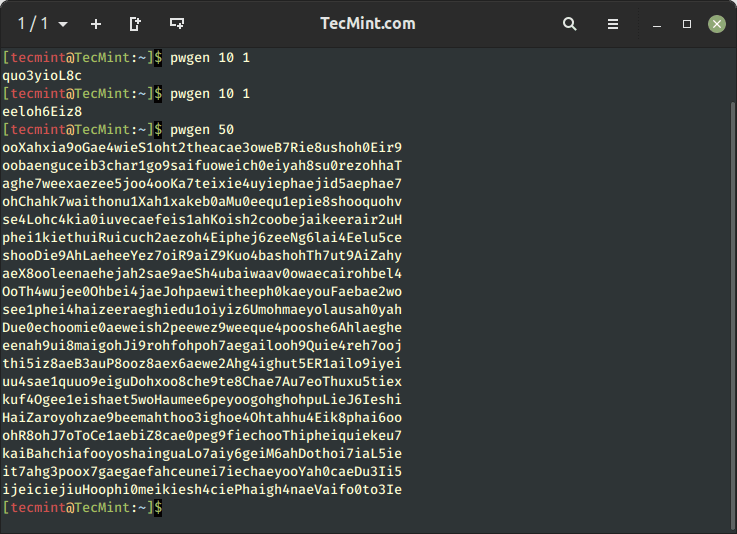
PWgen – Generate a Random Password on Linux
To generate a random unique password of length equal to 10 characters use the ‘pwgen‘ command. If you have not installed pwgen, you can install it using your respective package managers as shown.
$ sudo apt install pwgen [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] $ sudo yum install pwgen [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky/AlmaLinux] $ sudo emerge -a sys-apps/pwgen [On Gentoo Linux] $ sudo apk add pwgen [On Alpine Linux] $ sudo pacman -S pwgen [On Arch Linux] $ sudo zypper install pwgen [On OpenSUSE]
Once ‘pwgen‘ is installed, you can use it to generate a single password as shown.
To generate several random unique passwords of character length 50 in one go, use:
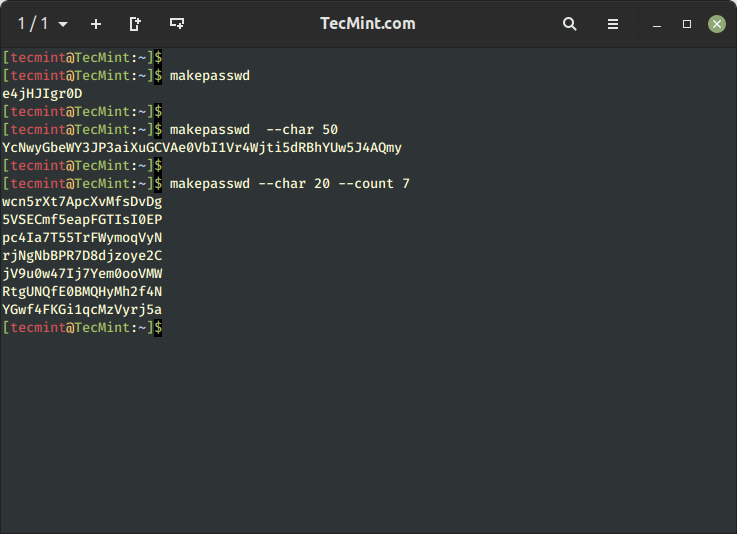
Makepasswd – Generate Unique Passwords on Linux
The makepasswd command is another password generator that is used to generate unique random passwords based on a given length.
Before you can use the makepasswd command, make sure you have installed it. If not, you may install it using your distribution’s package manager as shown.
$ sudo apt install makepasswd [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] $ sudo yum install makepasswd [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky/AlmaLinux] $ sudo emerge -a sys-apps/makepasswd [On Gentoo Linux] $ sudo apk add makepasswd [On Alpine Linux] $ sudo pacman -S makepasswd [On Arch Linux] $ sudo zypper install makepasswd [On OpenSUSE]
To generate a random password of character length 10 (default value is 10).
To generate a random password of character length 50.
To generate 7 random passwords of 20 characters.
$ makepasswd --char 20 --count 7
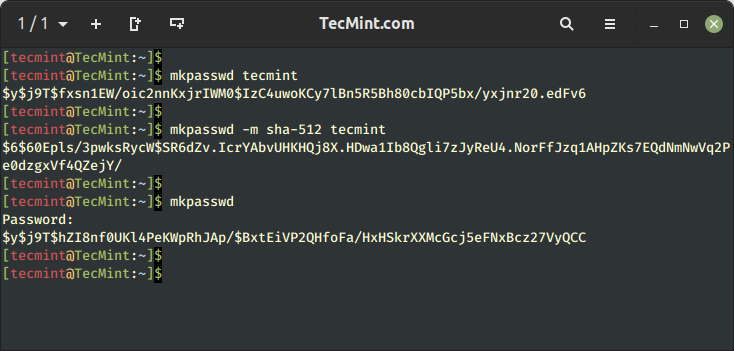
mkpasswd – Encrypt a Password in Linux
To encrypt a password using crypt (a Python standard library) along with the salt method.
For those who may not be aware of salt, which is random data that serves as an additional input to a one-way function in order to protect passwords against dictionary attacks.
The mkpasswd command is a part of the whois package, and it is not installed on most modern Linux distributions, you need to install it using your distribution’s package manager.
$ sudo apt install whois [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] $ sudo yum install whois [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky/AlmaLinux] $ sudo emerge -a sys-apps/whois [On Gentoo Linux] $ sudo apk add whois [On Alpine Linux] $ sudo pacman -S whois [On Arch Linux] $ sudo zypper install whois [On OpenSUSE]
Now run the makepasswd command, which will encrypt the password with salt. The salt value is taken randomly and automatically. Hence every time you run the below command it will generate different outputs because it is accepting a random value for salt every time.
Running the above command will generate a random salt value and use it to create the password hash for the password “tecmint.” The output will include the generated password hash.
To generate an SHA-512 password hash with the password “tecmint”, you can use the following command:
$ mkpasswd -m sha-512 tecmint
The output will be the generated password hash, which you can use for password storage or authentication purposes.
Moreover, mkpasswd is interactive and if you don’t provide a password along with the command, it will ask password interactively.
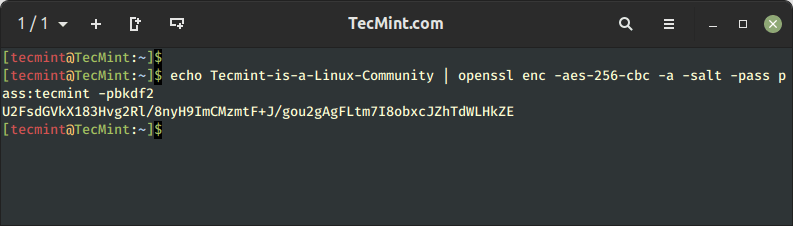
Encrypt a String with Password in Linux
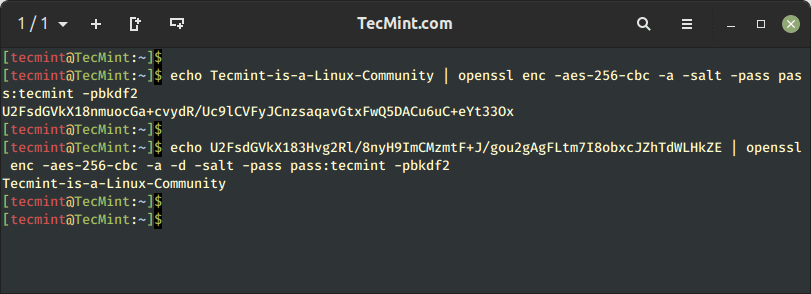
To encrypt a string say “Tecmint-is-a-Linux-Community” using aes-256-cbc encryption using a password say “tecmint” and salt.
$ echo Tecmint-is-a-Linux-Community | openssl enc -aes-256-cbc -a -salt -pass pass:tecmint -pbkdf2
Here in the above example, the output of the echo command is pipelined with the openssl command that passes the input to be encrypted using Encoding with Cipher (enc) that uses aes-256-cbc encryption algorithm with salt it is encrypted using the password (tecmint) and -pbkdf2 algorithm.
Decrypt a String in Linux
To decrypt the above string use the openssl command using the -aes-256-cbc decryption.
# echo U2FsdGVkX18Zgoc+dfAdpIK58JbcEYFdJBPMINU91DKPeVVrU2k9oXWsgpvpdO/Z | openssl enc -aes-256-cbc -a -d -salt -pass pass:tecmint
That’s all for now. If you know any such tips and tricks you may share in the comment section, your tip will be published under your name and also we will include it in our future article.
10 ways to generate a random password on Linux
To generate a random password you can use pwgen : pwgen generates random, meaningless but pronounceable passwords. These passwords contain either only lowercase letters, or upper and lower case mixed, or digits thrown in.
How do I generate a random password in Shell?
In order to generate entire random passwords, we can run apg -a 1, which will give us the passwords with 8-10 random characters. The command we used for this purpose is apg –a 1. We will run and see various passwords generated in the output. The output has many random passwords.
How do I generate a random password using openssl?
The OpenSSL rand command can be used to create random passwords for system accounts, services or online accounts. The rand command outputs num pseudo-random bytes after seeding the random number generator once. You only have to decide the byte-length of your password or string, and OpenSSL does all the calculations.
How do you get a random number from Dev random?
Generating random numbers
You can use /dev/urandom to generate pseudo-random numbers on the command line like this. Commands like this that pull data from /dev/urandom and use od to process it can generate nearly random numbers. Run the same command numerous times and you’ll see that you get a range of numbers.
What is Linux password?
The /etc/passwd is the password file that stores each user account. The /etc/shadow file stores contain the password information for the user account and optional aging information. The /etc/group file is a text file that defines the groups on the system.
Is password generator safe?
Overall, it is generally safe to use a password generator for your online accounts. If your password generator’s settings are configured to create lengthy passwords containing letters, numbers, and special characters, rest assured it’s is generally safe for most purposes.
How do I generate a random number in bash?
- $ echo $RANDOM 720 $ echo $RANDOM 29582. .
- #!/bin/bash echo -n «Let’s play a game: Pick a number between 0 and 32767: » read a if (( RANDOM == a )); then echo AMAZING, your answer is correct else echo Sorry, that was wrong fi. .
- $ unset RANDOM $ RANDOM=42 $ echo $RANDOM 42 $ echo $RANDOM 42.
What is Dev random in Linux?
In Linux, the device files /dev/random and /dev/urandom are the userland interfaces to the crypto PRNG which can reliably generate random bits. The kernel maintains an entropy pool which is used to store random data generated from events like inter-keypress timings, inter-interrupt timings, etc.
What command may be used to generate strong user passwords?
pwgen is simple, yet useful command line utility to generate a random and strong password in seconds. It designs secure passwords that can be easily memorized by humans. It is available in the most Unix-like operating systems. There are also some useful options available to use with pwgen command.
How random is Shuf?
The shuf utility shuffles its input by outputting a random permutation of its input lines. According to it’s manpage, «Each output permutation is equally likely». . Because shuf performs a random permutation of it’s input. If the input lines contain no duplicates, the output from shuf will contain no duplicates.
How use Urandom Linux?
Configuration If your system does not have /dev/random and /dev/urandom created already, they can be created with the following commands: mknod -m 666 /dev/random c 1 8 mknod -m 666 /dev/urandom c 1 9 chown root:root /dev/random /dev/urandom When a Linux system starts up without much operator interaction, the entropy .
How random is $random?
Computers can generate truly random numbers by observing some outside data, like mouse movements or fan noise, which is not predictable, and creating data from it. This is known as entropy. Other times, they generate “pseudorandom” numbers by using an algorithm so the results appear random, even though they aren’t.
Group
How do I use Groupby in pandas?How do you group by mean in Python?How do I get DataFrame from Groupby?How do I group multiple columns in pandas?What i.
Wine
How do I get wine on Arch Linux?Is wine safe for Linux?Is my wine 32 or 64 bit?How do I install Wine on Linux?Where is wine installed in Linux?How do .
Apt-get
Just launch the command terminal and type in the following command:$sudo apt-get update. $ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:menulibre-dev/daily.$ sudo apt-.
Latest news, practical advice, detailed reviews and guides. We have everything about the Linux operating system
Password Generator in Linux – Generate Random Passwords in Command Line
There are many times when we face the problem of creating a strong password. Unfortunately, humans are not good at fortuitousness, and creating a random password is one of the most important factors in keeping in mind the security and privacy of data nowadays.
In this article, we’ll cover how to create a script that generates a truly random password. The character length can be customized to meet all expectations.
How to achieve (pseudo)randomness
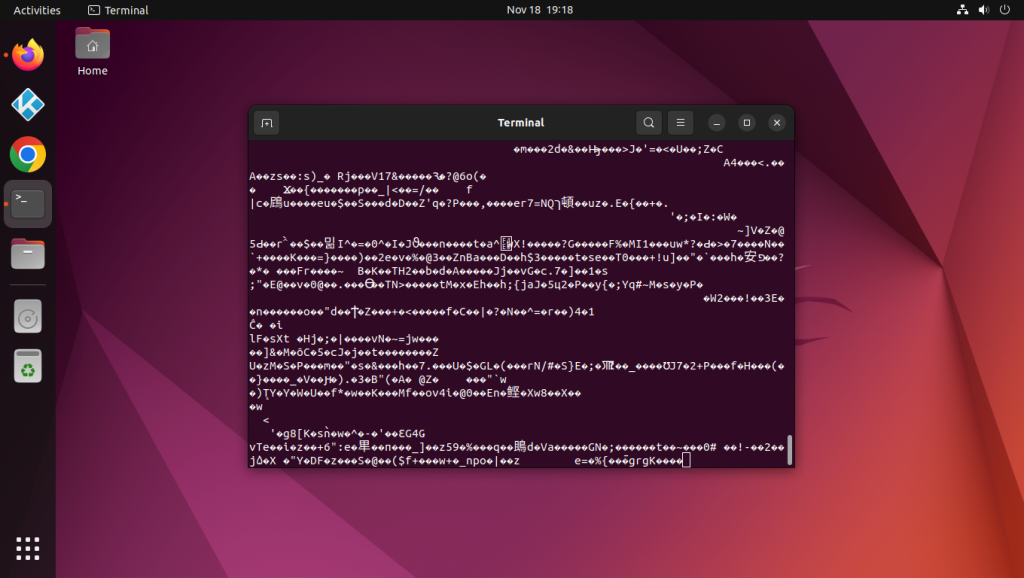
In every Unix device, there are a number of files that are used as Pseudorandom Number Generators. One of the files in Linux is /dev/urandom. You can go ahead and run the cat command on the file and see some binary output created on the terminal.
Creating random passwords with only alphanumeric characters
You might be seeing some random characters in your terminal window. We have to first filter this noise and allow only alphanumeric characters. We do that by using the strings command. We will also use the grep command in conjunction so that we can allow only certain characters in the password. Here we should mention one important distinction, we cannot use the standard command, we have to use the -a flag so that it grabs the text input.
cat /dev/urandom | strings |grep -Eoa "[a-zA-Z0-9]*"
If you run the above command you will see that only alphanumeric characters make it through to the terminal screen. So our filtering is working as expected.
If you also want special characters such as @, $, %, & etc to appear in your password, then simply add in those characters in the regex like so:
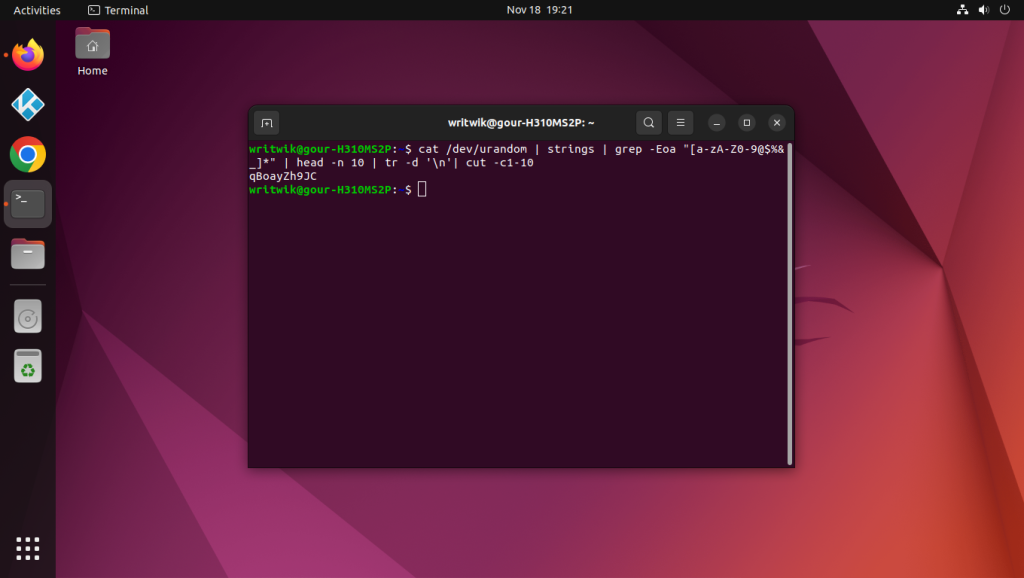
cat /dev/urandom | strings | grep -Eoa "[a-zA-Z0-9@$%&_]*"
Setting the length of the password
Now we will set the length of the password, using the head command, which will stop the output once the required number has been reached. So the command now looks like this:
cat /dev/urandom | strings | grep -Eoa "[a-zA-Z0-9@$%&_]*" | head -n 10
This only cuts the text to 10 lines rather than 10 characters, however, it is still of use, as we know with certainty that one line will contain at least one character(most often they contain more than one), so by running this command we are assuring that no matter what the password will be at least 10 characters long.
Deleting the new-line characters
Now we need to delete the new-line characters so that our password is in one line, we do that using the tr command:
cat /dev/urandom | strings | grep -Eoa "[a-zA-Z0-9@$%&_]*" | head -n 10 | tr -d '\n'
At this point we will also run the cut command to cut the password to the final length of 10 characters:
cat /dev/urandom | strings | grep -Eoa "[a-zA-Z0-9@$%&_]*" | head -n 10 | tr -d '\n'| cut -c1-10
Conclusion
Congratulations you have your own one-liner for a password generator that is completely customizable. You can use whatever set of characters you want in your password and do not have to depend upon human guesswork to create a safe and secure password. Hope you guys liked this article and thanks for reading it!