- How to display Unix time in the timestamp format?
- You must log in to answer this question.
- Related
- Hot Network Questions
- Subscribe to RSS
- How to get the current Unix timestamp or epoch time from a Linux command line
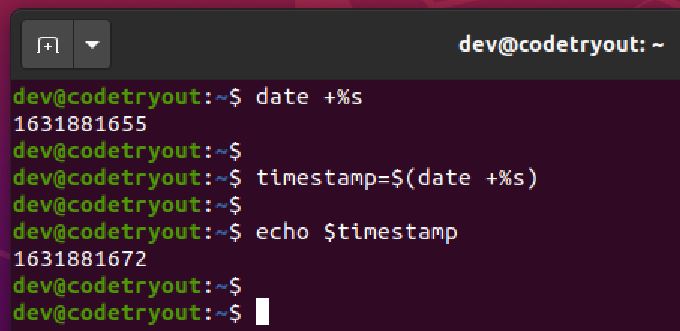
- Echo Unix timestamp using the date command
- For example in an Ubuntu terminal/command line
- Storing timestamp in a bash script variable, and echo it
- What is epoch time (Unix timestamp)?
- The latest
- Bash-Basics
- How Can I Generate UNIX Timestamps in Linux
- What is a Unix Timestamp
- How to Convert Unix Timestamp to Date
- Method 1: Using the date Command
- Example 1: Convert a Unix Timestamp to a Date and Time in a Specific Time Zone
- Example 2: Convert a Unix Timestamp to a Date Only
- Method 2: Using the Perl Programming Language
- Method 3: Using the Python Programming Language
- Method 4: Using a Bash Script
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Kashif
- Dates and Timestamps in UNIX/Linux
- Get the Current Date and Time in Linux
- UNIX Time
- Related Article — Linux Date
- Get Timestamp in Bash
- Get Timestamp Using the date Command in Bash
- Get UNIX Timestamp
- Get Date/Time in a Bash Script
How to display Unix time in the timestamp format?
srand without a value uses the current timestamp with these Awk implementations:
The following will convert Date Time to Unix time on Unix-like environment.
# Current UNIXTIME unixtime() < datetime2unixtime "$(date -u +'%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')" ># From DateTime(%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S)to UNIXTIME datetime2unixtime() < set -- "$" "$" set -- "$" "$" "$" "$" set -- "$1" "$" "$" "$3" "$" "$" set -- "$1" "$" "$" "$" "$" "$" [ "$2" -lt 3 ] && set -- $(( $1-1 )) $(( $2+12 )) "$3" "$4" "$5" "$6" set -- $(( (365*$1)+($1/4)-($1/100)+($1/400) )) "$2" "$3" "$4" "$5" "$6" set -- "$1" $(( (306*($2+1)/10)-428 )) "$3" "$4" "$5" "$6" set -- $(( ($1+$2+$3-719163)*86400+$4*3600+$5*60+$6 )) echo "$1" > # From UNIXTIME to DateTime format(%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S) unixtime2datetime() < set -- $(( $1%86400 )) $(( $1/86400+719468 )) 146097 36524 1461 set -- "$1" "$2" $(( $2-(($2+2+3*$2/$3)/$5)+($2-$2/$3)/$4-(($2+1)/$3) )) set -- "$1" "$2" $(( $3/365 )) set -- "$@" $(( $2-( (365*$3)+($3/4)-($3/100)+($3/400) ) )) set -- "$@" $(( ($4-($4+20)/50)/30 )) set -- "$@" $(( 12*$3+$5+2 )) set -- "$1" $(( $6/12 )) $(( $6%12+1 )) $(( $4-(30*$5+3*($5+4)/5-2)+1 )) set -- "$2" "$3" "$4" $(( $1/3600 )) $(( $1%3600 )) set -- "$1" "$2" "$3" "$4" $(( $5/60 )) $(( $5%60 )) printf "%04d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d\n" "$@" ># Examples unixtime # => Current UNIXTIME date +%s # Linux command datetime2unixtime "2020-07-01 09:03:13" # => 1593594193 date -u +%s --date "2020-07-01 09:03:13" # Linux command unixtime2datetime "1593594193" # => 2020-07-01 09:03:13 date -u --date @1593594193 +"%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S" # Linux command You must log in to answer this question.
Related
Hot Network Questions
Subscribe to RSS
To subscribe to this RSS feed, copy and paste this URL into your RSS reader.
Site design / logo © 2023 Stack Exchange Inc; user contributions licensed under CC BY-SA . rev 2023.7.14.43533
By clicking “Accept all cookies”, you agree Stack Exchange can store cookies on your device and disclose information in accordance with our Cookie Policy.
How to get the current Unix timestamp or epoch time from a Linux command line
Unix timestamp or epoch time is one of the most popular and easily generatable timestamp formats, quickly in a bash shell. Linux date command is a very powerful utility to get or set system time in various ways. Let us check, how to get Unix timestamp from a Docker container, Linux / Ubuntu terminal.
Echo Unix timestamp using the date command
By default, the Unix timestamp (epoch) is calculated in UTC, so there will be no difference in it regardless of the timezone.
For example in an Ubuntu terminal/command line
Storing timestamp in a bash script variable, and echo it
$ timestamp=$(date +%s) $ echo $timestamp 1262322992What is epoch time (Unix timestamp)?
The Unix epoch is the time 00:00:00 UTC on 1 January 1970. The current epoch time is the number of seconds counted from there. Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Unix_time
The latest
Bash-Basics
- 40+ BASH commands for everyday use
- bash alias with arguments
- bash change case lower to upper
- bash check remote file exists
- bash date change from commandline
- bash date day before yesterday
- bash date day x days after
- bash date day x days ago
- bash date full date
- bash date iso 8601 format
- bash default value for variable
- bash delete tilde named directory
- bash env check
- bash if then else examples
- bash print date and time
- bash redirect stdout stderr separate files
- bash return code
- bash sed uncomment lines
- bash string remove spaces
- bash test command
- bash test symlink
- bash timestamp epoch time
- bash tr delete character(s)
- bash tree command not found
- bash until loop
- bash while loop
- bashrc alias
How Can I Generate UNIX Timestamps in Linux
In Unix timestamp we represent any date and time together in a single long number. This single number describes the total seconds passed since January 1st,1970 at 00:00:00 UTC. In this guide, we’ll cover everything about converting Unix timestamps to dates, including what Unix timestamps are, how to convert them to a date, and some practical examples to help you get started.
Content for this article is:
What is a Unix Timestamp
A Unix timestamp shows a single number which corresponds to date and time. This single number shows the total seconds that have passed since January 1st,1970 at 00:00:00 UTC. We also called this single number time the Unix epoch. Unix timestamps are used in many different programming languages to represent dates and times in any time zone.
How to Convert Unix Timestamp to Date
In Linux there are different methods to convert a Unix Timestamp to a date or vice versa. In this article we will start from the basic method which is using the date command in the terminal window.
- Using date Command
- Using the Perl Programming Language
- Using the Python Programming Language
- Using a Bash Script
Method 1: Using the date Command
To convert a Unix timestamp to a human-readable date and time, we can use the date command in the terminal. The syntax for the date command is as follows:
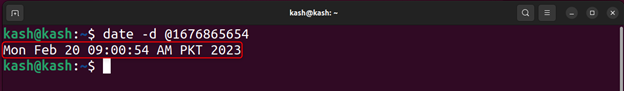
For example, to convert a Unix timestamp of 1676865654 to a human-readable date and time run the following command:
As you can see, the output includes complete details of current date and time including time zone, and the year.
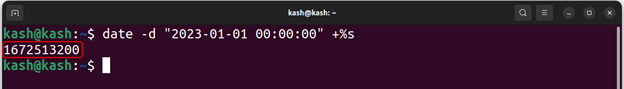
Similarly, we can also generate timestamp value for a specific date. For example, timestamp value for January 1, 2023, at 12:00:00 AM can be get using the following command:
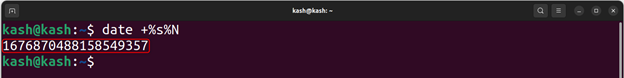
Following command will return UNIX timestamps for current date in nanoseconds format:
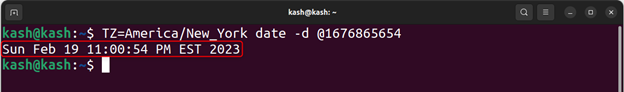
Example 1: Convert a Unix Timestamp to a Date and Time in a Specific Time Zone
To convert a Unix timestamp to a date and time in a specific time zone, following command syntax will be followed:
For example, to convert a Unix timestamp of 1613475901 to a human-readable date and time in the Eastern Time zone, run below command:
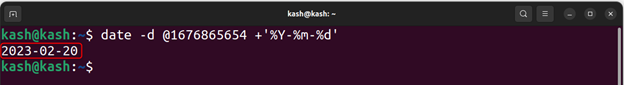
Example 2: Convert a Unix Timestamp to a Date Only
To convert a Unix timestamp to a date only, you can use the following command:
For example, if we have a Unix timestamp of 1613475901 and to convert it in the format of year-month-day (e.g. 2023-02-20) we can use following command:
This will output the date corresponding to the Unix timestamp of 1613475901:
Method 2: Using the Perl Programming Language
Perl is a popular programming language that can be used to generate UNIX timestamps in Linux.
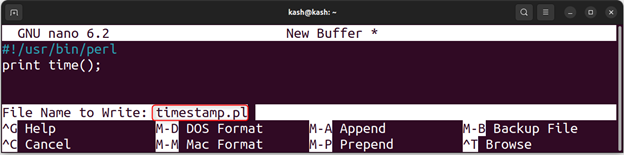
Now create a simple Perl script that generates a UNIX timestamp for the current date and time:
Press Ctrl + O, then save this script as “timestamp.pl” and hit Enter, then press Ctrl + X to save and exit:
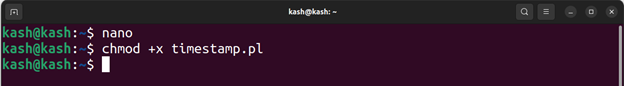
Now make this executable by running:
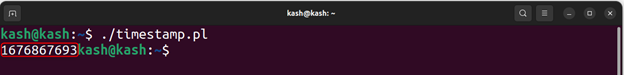
Run the script with the command “./timestamp.pl” to generate a UNIX timestamp:
Method 3: Using the Python Programming Language
Python is another popular programming language that can be used to generate UNIX timestamps in Linux.
First, we have to install Python3 on Linux, to do that run command:
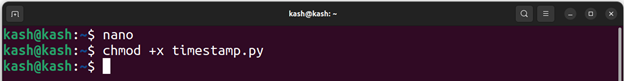
Now open nano editor using:
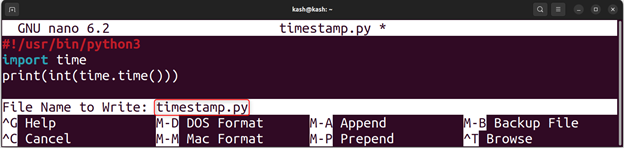
Create a simple Python script that generates a UNIX timestamp for the current date and time:
Press Ctrl + O, then save this script as “timestamp.py” and hit Enter, then press Ctrl + X to save and exit.
The above script can be made executable by below command:
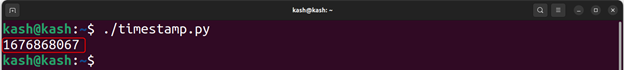
Run the script with the command “./timestamp.py” to generate a UNIX timestamp.
Method 4: Using a Bash Script
If you need to generate UNIX timestamps in a more complex or automated way, you can use a Bash script.
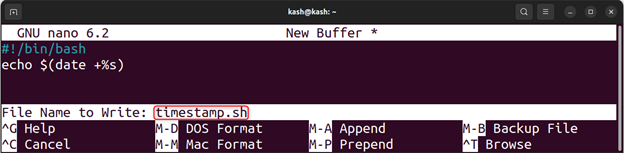
Open the nano editor using:
Write following script in editor that generates a UNIX timestamp for the current date and time:
Press Ctrl + O, then save this script as “timestamp.sh” and hit Enter, then press Ctrl + X to save and exit:
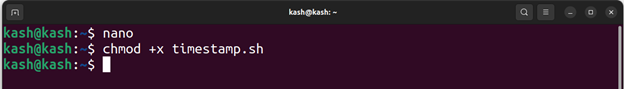
Now make this script executable by running the command:
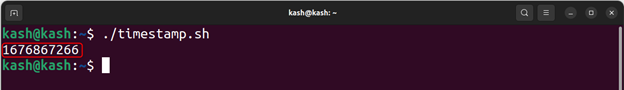
Run the script with the command “./timestamp.sh” to generate a UNIX timestamp:
Conclusion
UNIX timestamps show total seconds passed since January 1, 1970. To generate UNIX timestamps in Linux, the date command can be used in the command line by passing the +%s argument. Alternatively, we can also create a bash script or use the pearl and python language script to give us timestamps for exact date and time zone.
About the author
Kashif
I am an Electrical Engineer. I love to write about electronics. I am passionate about writing and sharing new ideas related to emerging technologies in the field of electronics.
Dates and Timestamps in UNIX/Linux
- Get the Current Date and Time in Linux
- UNIX Time
Date and time information isn’t quite as visible on the command line as it would be with a graphical version of Linux, but we can certainly get that information with the date command.
This tutorial will explain how to use the date command to get, parse, convert dates and times, and print them in different formats on Linux, assuming a Bash shell command line.
Get the Current Date and Time in Linux
As shown, running date gives us the current date and time, with the time zone.
user@linux:~$ date Tue 01 Jan 2022 12:00:00 AM +04 The default date-time format will be in the time zone you are located in — in this case, the output of date is for a user whose time zone is Gulf Standard Time, or GMT+04 . To print out the date and time in a different format, such as UTC or GMT, or yyyy/mm/dd or dd/mm/yyyy , you can specify that format using special modifiers as follows.
# to print the current date in dd/mm/yyyy format date +%d-%m-%Y # to print the current date and time in UTC date -u # to print the date and/or time as per IETF RFC3349 date --rfc-3339=seconds # to print the date and time within a custom string date +"Today is %D and the time is %I:%M:%S" UNIX Time
In most UNIX systems, the current time is stored as the time elapsed since a particular moment to simplify, keeping the time as a long integer, called the UNIX epoch. The universally accepted moment for all UNIX systems is January 1st 1970, 12:00:00 AM . This is called a UNIX timestamp and is recognized by all modern UNIX/Linux systems.
For example, if we wish to find the UNIX timestamp for 1st January 2022, we can use the date command.
user@linux:~$ date -d"1 January 2022 12:00 AM" +%s 1640980800 date attempts to parse the string for a formatted date and time (or, if a timestamp is not specified, assumes the time as 12:00 AM) and then prints out the UNIX timestamp form of the given date and/or time. 1640980800 is the exact number of seconds that have elapsed since January 1 1970, 12:00:00 AM.
The converse is also possible, whereby we take a UNIX timestamp and convert it to a date representation. To get back our original date, we can pass the UNIX timestamp as shown to convert it.
user@linux:~$ date -d @1640980800 Sat 01 Jan 2022 12:00:00 AM +04 If we wish, we can also include other parameters to format the date in a specific way, such as UTC or GMT, as explained above.
Related Article — Linux Date
Get Timestamp in Bash
- Get Timestamp Using the date Command in Bash
- Store UNIX Timestamp in a Variable
This article discusses the date Bash command to get system date/time and UNIX timestamp.
Get Timestamp Using the date Command in Bash
The Linux terminal uses the date command to print the current date and time. The date command’s simplest version can be executed without any argument.
Following is a sample output for the date command showing the current date and time of the system:
Thu Aug 25 08:43:54 UTC 2022 We can use a different argument with the date command to set the specific format for printing. For example, the command date +»%m-%d-%y» outputs the date in the following format:
In the above command, %m is used to show the month, %d is used to indicate the day, and %y is used to show the year. Similarly, we can use the date command in many different formats.
We can print the current time only using the date +»%T» command. %T is used to print time only.
The output of date +»%T» is as follows:
Get UNIX Timestamp
We can use the date command to show the UNIX timestamp using the date +%s command. The output of date +%s is as follows:
The above output is a UNIX timestamp.
Get Date/Time in a Bash Script
We can also use the date command in the Bash script. Consider the following Bash script myscript.sh to display the current date on the terminal: