- Read filename without extension in Bash
- How can I find the file name without extension?
- How do I read a filename in bash?
- How do I remove a filename extension in bash?
- What is filename without extension called?
- How do I get filenames without an extension in Unix?
- How do I save a file name without an extension?
- What is bash file extension?
- How do I read in bash?
- How do I list files in bash?
- How do you remove a filename extension in Unix?
- How do I remove a file extension in Linux?
- How do I see file extensions in bash?
- Read filename without extension in Bash
- Using `basename` command to read filename
- Example-1: Using NAME and SUFFIX
- Example-2: Using ‘-a’ option and NAME
- Example-3: Using ‘-z’ option and NAME
- Example-4: Using ‘-s’ option and NAME
- Example-5: Remove file extension without SUFFIX
- Example-6: Convert file extension from txt to docx
- Example-7: Read filename without extension using Shell parameter expansion
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Fahmida Yesmin
Read filename without extension in Bash
If you want to retrieve the filename without extension, then you have to provide the file extension as SUFFIX with `basename` command. Here, the extension is “. txt”.
- How can I find the file name without extension?
- How do I read a filename in bash?
- How do I remove a filename extension in bash?
- What is filename without extension called?
- How do I get filenames without an extension in Unix?
- How do I save a file name without an extension?
- What is bash file extension?
- How do I read in bash?
- How do I list files in bash?
- How do you remove a filename extension in Unix?
- How do I remove a file extension in Linux?
- How do I see file extensions in bash?
How can I find the file name without extension?
Returns the file name without the extension of a file path that is represented by a read-only character span.
How do I read a filename in bash?
- #!/bin/bash.
- file=$1.
- while read line; do.
- #Readind each line in sequence.
- echo $line.
- done
How do I remove a filename extension in bash?
- basename /path/to/file. tar. gz . gz – Strip directory and suffix from filenames.
- $VAR%pattern – Remove file extension.
- $VAR#pattern – Delete from shortest front pattern.
What is filename without extension called?
It is just called a «file» if referring to its base name according to wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Filename. https://stackoverflow.com/questions/39007908/filename-without-extension-terminology/39007966#39007966. Share.
How do I get filenames without an extension in Unix?
If you want to retrieve the filename without extension, then you have to provide the file extension as SUFFIX with `basename` command.
How do I save a file name without an extension?
- This task will loop through files in a folder, strip the file extensions from the filenames using the ExtractFileName(), Left() and InStr() functions and display them one at a time using a message dialog. ExtractFileName() extracts the name and extension parts of a file name. .
- Task Category: Looping.
- DOWNLOAD FILE.
What is bash file extension?
The «bash» type is associated with files that have an extension of «. sh». Since many Bash scripts do not have a file extension, any «plaintext» file that contains the text «#!/bin/bash» within the first line of the file (upon opening the file) will also be interpreted as a bash script!
How do I read in bash?
The general syntax of the read built-in takes the following form: read [options] [name. ] To illustrate how the command works, open your terminal, type read var1 var2 , and hit “Enter”. The command will wait for the user to enter the input.
How do I list files in bash?
To see a list of all subdirectories and files within your current working directory, use the command ls .
How do you remove a filename extension in Unix?
13 Answers. You should be using the command substitution syntax $(command) when you want to execute a command in script/command. name=$(echo «$filename» | cut -f 1 -d ‘. ‘)
How do I remove a file extension in Linux?
Change the directory to the location of where the file is located. In our example below, we rename the file «myfile. txt» to «myfile» to delete the file extension. Unless the file already exists, you’ll get no message or an «OK» message indicating that the file was renamed and the file extension was removed.
How do I see file extensions in bash?
#!/bin/bash for file in «$PATH_TO_SOMEWHERE»; do if [ -d $file ] then # do something directory-ish else if [ «$file» == «*. txt» ] # this is the snag then # do something txt-ish fi fi done; My problem is determining the file extension and then acting accordingly.
Command
16 Commands to Check Hardware Information on Linuxlscpu. The lscpu command reports information about the cpu and processing units. . lshw — List Har.
Command
What does the free command do in Linux?What are the basic command in Linux?What is the fastest way to learn Linux commands?What is free command in Ubu.
Install
How to Install OCS Inventory Asset Management Software CentOS 8Prerequisites.Getting Started.Install Apache, MariaDB, and PHP.Configure MariaDB Databa.
Latest news, practical advice, detailed reviews and guides. We have everything about the Linux operating system
Read filename without extension in Bash
Linux users need to work with files regularly for many purposes. Sometimes the users need to read the basename of the file only by removing the file extension. Filename and extension can be separated and stored on different variables in Linux by multiple ways. Bash built-in command and shell parameter expansion can be used to remove the extension of the file. How the filename without extension can be read by using the ways mentioned above are explained in this tutorial.
Using `basename` command to read filename
`basename` command is used to read the file name without extension from a directory or file path.
Here, NAME can contain the filename or filename with full path. SUFFIX is optional and it contains the file extension part that the user wants to remove. `basename` command has some options which are described below.
| Name | Description |
| -a | It is used to pass multiple filenames with path or without path as command arguments. |
| -s | It is used to pass the extension as suffix that needs to remove. |
| -z | It is used to display the multiple filenames by separating each file with null. |
| –help | It is used to display the information of using `basename` command. |
| –version | It is used to display the version information. |
Example-1: Using NAME and SUFFIX
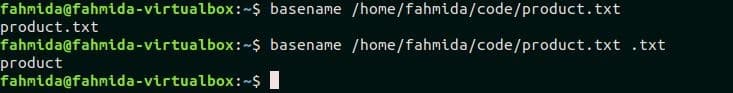
The following `basename` command will retrieve the filename with extension. SUFFIX is omitted from this command. Here, the output is ‘product.txt’.
If you want to retrieve the filename without extension, then you have to provide the file extension as SUFFIX with `basename` command. Here, the extension is “.txt”. Run the following command to remove the extension from the file.
Example-2: Using ‘-a’ option and NAME
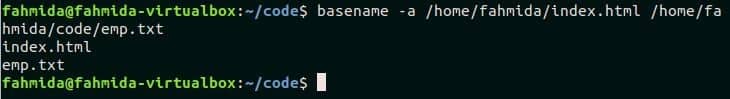
The use of ‘-a’ option of `basename` command is shown in this example. Here, two file paths are passed as arguments with `basename` command. Each filename with extension will retrieve from the path and print by newline.
Example-3: Using ‘-z’ option and NAME
‘-z’ option is used with `basename` command to print the multiple filenames with null value instead of newline. The following command uses two options together, ‘-a’ and ‘-z’. Here, two filenames, index.html and emp.txt will print without any space or newline.
Example-4: Using ‘-s’ option and NAME
The following command can be used as an alternative of SUFFIX with `basename`. File extension needs to pass with ‘-sh’ option to remove the file extension from the file. The following example will remove the extension, ‘-sh’ from the file, ‘addition.sh’.
Example-5: Remove file extension without SUFFIX
If you don’t know the extension of the file that you want to remove from the filename, then this example will help you to solve the problem. Create a file named read_file.sh with the following code to retrieve filename of any extension. `sed` command is used in this example to remove any type of extension from the filename. If you run the script, the output will be ‘average’ after removing the extension ‘py’.
read_file.sh
#!/bin/bash
# Set the filename with path
filename = «/home/fahmida/code/average.py»
# Read the filename without extension by using ‘basname’ and `sed` command
echo » $(basename «$filename» | sed ‘s/\(.*\) \..*/\1/’)»
Example-6: Convert file extension from txt to docx
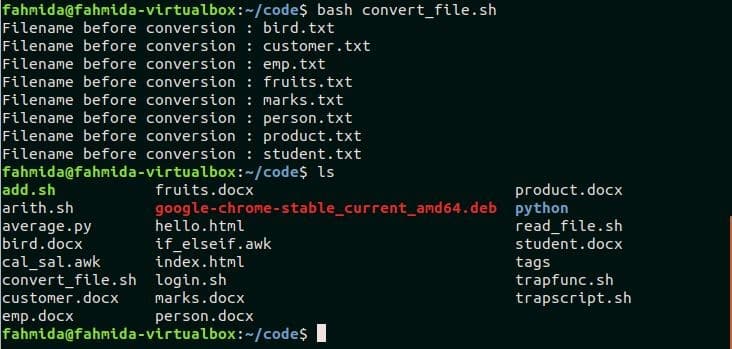
Filename without extension needs to convert the file from one extension to another. This example shows that how you can change the extension of all text files (.txt) into the word files (.docx) by using `basename` command in the bash script. Create a file named, convert_file.sh with the following code. Here, a for-in loop is used to read all the text files with “.txt” extension from the current directory. The filename without extension is read by `basename` command and renamed by adding “.docx” extension in each iteration of the loop.
convert_file.sh
#!/bin/bash
# the loop will read each text file from the current directory
for filename in ` ls * .txt `
do
# Print the text filename before conversion
echo «Filename before conversion : $filename »
# Change the extension of the file txt to docx
mv — » $filename » » $(basename — «$filename» .txt) .docx»
done
Check the text files are converted or not by using `ls` command.
Example-7: Read filename without extension using Shell parameter expansion
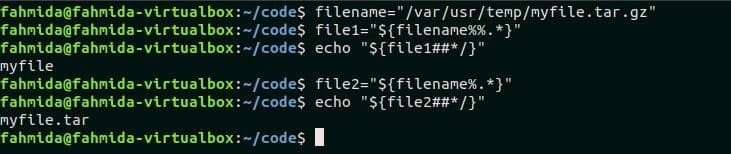
Shell parameter expansion is another way to read the filename without extension in bash. This example shows the uses of shell parameter expansion. The following command will store the file pathname in the variable, $filename.
The following command will remove all types of extension from the path and store the file path without extension in the variable, $file1.
The following command will print the filename only from the path. Here, the output will ‘myfile’.
If the filename contains two extensions with two dot(.) and you want to read the filename by removing the last extension of the file then you have to use the following command. Run the following command that store the file path into the variable, $file2 by removing the last extension of the file.
Now, run the following command to print the filename with one dot (.) extension. Here, the output will be “myfile.tar”.
Conclusion
Filename without extension is required for various purposes. Some uses of filename without extension are explained in this tutorial by using some examples such as file conversion. This tutorial will help those users who are interested to learn the ways to separate the file name and extension from the file path. Two ways are explained here. The user can follow any of these ways to extract the filename only from the file path.
About the author
Fahmida Yesmin
I am a trainer of web programming courses. I like to write article or tutorial on various IT topics. I have a YouTube channel where many types of tutorials based on Ubuntu, Windows, Word, Excel, WordPress, Magento, Laravel etc. are published: Tutorials4u Help.