- How to see users currently logged in to Linux
- Method-1: Checking logged-in users with ‘w’ command
- Method-2: Identifying who is Logged-in using ‘who’ command
- Method-3: How to see Logged in users with ‘whoami’ command
- Method-4: Using users command
- Method-5: Show currently logged-in users with ‘finger’ command
- Bonus Tips
- Bonus Tips-1: How to show current logged-in users with ‘last’ command
- Bonus Tips-2: Manual Way to check who’s logged-in
- Over to You
- How to see Logged in Users in Linux
- 4 Commands to see logged users on Linux
- 1. Use w command to see logged in users in Linux
- 2. Check who is logged in with who command
- 3. Just get logged in users with users command
- 4. Using finger command to see logged in users
- Bonus Tip: see who logged on your system since last reboot
- How to List Current Logged-In Users on Linux
- 1. The users Command
- 2. Using the who Command
- 3. Using the w Command
- 4. Using the last Command
- 5. The finger Command
How to see users currently logged in to Linux
Linux is a multi-user operating system that allows multiple users to access the system at the same time.
As a Linux system administrator, you have to check who are logged into the system before starting to work on any issues, especially when you have a team members spread across multiple locations. Because, if multiple users are making the changes in the same configuration file, it may create additional problems.
So, make sure nobody is currently working on the issue before you take it up. To avoid these things, we need to check who all are logged into the system and what are they doing.
In this tutorial, we will show you how to check the current logged-in users with several commands in Linux.
Knowing more than one command to find the same information will not hurt you, and do not hesitate to check the alternate options.
Method-1: Checking logged-in users with ‘w’ command
‘w command’ shows who are logged-in and what are they doing. It displays information about current users on the machine by reading the file /var/run/utmp , and their processes /proc .
w command output comes with header information, which displays system activity such as current time, system up time, how many users are currently logged-in, and the system load (which averages for the past 1, 5, and 15 minutes)
w command contains the following values:
login user name, tty number, remote host, user’s login time, idle time, JCPU (time used by all processes attached to the tty), PCPU (time used by the current process), and which commands are currently being executed by the users. Please see below:
# w 17:13:34 up 1:52, 1 user, load average: 0.11, 0.18, 0.15 USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT root pts/0 203.99.204.108 15:22 6.00s 0.18s 0.00s w
Method-2: Identifying who is Logged-in using ‘who’ command
‘who command’ shows information about users who are currently logged in. It uses ‘/var/run/utmp’ & ‘/var/log/wtmp’ files to get those details.
- /var/run/utmp: It contains information about the users who are currently logged onto the system. Who command is used to fetch the information from the file.
- /var/log/wtmp: It contains historical utmp. It keeps the users login and logout history. The last command uses this file to display the information.
who command output contains the following values such as login user name, tty number, date & time, and remote host.
# who root pts/0 2017-05-31 15:22 (203.99.204.108)
Method-3: How to see Logged in users with ‘whoami’ command
whoami is basically the concatenation of the strings “who”,”am”,”i” as whoami. It displays the username of the current user. It’s similar to running the id command with the options -un as shown below:
Also, when you use whoami with space (who am i) that will give you a different output. It will display more details compared to whoami command as shown below:
$ who am i daygeek pts/1 2019-06-17 22:01 (192.168.1.6)
“id” command prints user and group information for a specified username, but we can add -un option with the “id” command to display all the currently logged-in users as shown below:
Method-4: Using users command
‘users command’ prints the usernames of users currently logged in to the current host. It uses /var/run/utmp & /var/log/wtmp files to get the details as shown below:
Method-5: Show currently logged-in users with ‘finger’ command
‘finger’ is a utility, which allows users to see the information about system users (login name, home directory, name, how long they’ve been logged in to the system, etc.).
Finger utility is available in all major Linux distributions, but it doesn’t come installed by default. Use distribution package manager to install “finger” on your system.
$ finger Login Name Tty Idle Login Time Office Office Phone magi daygeek tty7 7 Jun 1 16:05 (203.99.204.108)
Bonus Tips
Additionally, you can use the following methods to identify who all are logged-in on your system:
Bonus Tips-1: How to show current logged-in users with ‘last’ command
‘last command’ shows a list of last logged in users by searching the data from /var/log/wtmp file. Also, it shows the system reboot information.
“last” command output contains login user name, tty number, remote host, date, login time, logout time, and the total duration (working time).
Run the following command to show who all logged-in today. Also, you can check who’s currently logged in by filtering with the “still logged in” string.
# last -p today linuxgee tty2 tty2 Thu Mar 4 14:27 gone - no logout linuxgee : : Thu Mar 4 14:27 gone - no logout
Bonus Tips-2: Manual Way to check who’s logged-in
Last but not the least, we can get a list of logged in users on Linux machine manually by using less commands or more commands or head command or tail command, followed by the log file location.
User authentication logs are located @ /var/log/secure for RHEL based systems & /var/log/auth.log for Debian based systems.
$ head -5 /var/log/auth.log Jun 1 16:05:01 daygeek CRON[1944]: pam_unix(cron:session): session opened for user root by (uid=0) Jun 1 16:05:01 daygeek CRON[1944]: pam_unix(cron:session): session closed for user root Jun 1 16:05:44 daygeek lightdm: pam_unix(lightdm-greeter:session): session closed for user lightdm Jun 1 16:05:44 daygeek lightdm: pam_unix(lightdm:session): session opened for user magi by (uid=0) Jun 1 16:05:44 daygeek systemd: pam_unix(systemd-user:session): session opened for user magi by (uid=0)
Over to You
In this guide, you learnt how to find out who all are currently logged-in on your Linux system employing different commands.
If you found this article helpful, please do share with your friends and spread the knowledge. Please feel free to comment below if you have any queries/concerns. We will get back to you as soon as we can. Happy learning!
How to see Logged in Users in Linux
Check who is logged in your Linux system with these simple commands. You can also get additional information about logged in users such as their log in time.
Have you ever been curious about who is logged in to your Linux system? You can always list all the users on your Linux system but not all of them would be logged in all the time.
If you are on a multi-user Linux environment like a Linux server, checking logged in users could be useful and fun at the same time.
In this tutorial, I’ll show you various ways you list logged in users in Linux.
4 Commands to see logged users on Linux
Almost all these commands rely on the data stored in the /var or /proc directory. If you know a little about the directory structure in Linux, you know that these two directories contains data about the running processes on your system.
1. Use w command to see logged in users in Linux
Can it get any simpler than this? Just type a single letter command in the terminal and it will show the currently logged users in Linux.
And here is the output for the w command:
[email protected]:~$ w 09:54:54 up 26 min, 3 users, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00 USER TTY FROM [email protected] IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT root pts/0 202.91.87.114 09:37 21.00s 0.00s 0.00s -bash abhi pts/1 202.91.87.114 09:47 0.00s 0.00s 0.00s w rohini pts/2 157.43.53.142 09:48 6:13 0.00s 0.00s -bashLet me explain a few terms in the output of the w command. The same terms would be used in other commands as well.
TTY gives you information about the terminal used to log on. pts means pseudo terminal slave which indicates that the user logged in via SSH connection.
It shows the IP address of the user’s computer and login time. You can also see for how long a user has been idle (slacking at work? :D).
JCPU is the time used by all processes attached to the TTY and PCPU is the time used by the current process running by the user. You can see this current process under the WHAT column.
2. Check who is logged in with who command
Who command is another simple one. Just type who and it will show who is logged on to your Linux system currently.
You can also see the login time and the IP address of the logged on user.
[email protected]:~$ who root pts/0 Aug 6 09:37 (202.91.87.114) abhi pts/1 Aug 6 09:47 (202.91.87.114) rohini pts/2 Aug 6 09:48 (157.43.53.142)3. Just get logged in users with users command
All the commands you saw so far give you a lot of information about the logged in users. If you are working on a script and want to know just the name of the logged in users, parsing the output of those commands would be an additional and somewhat complicated task.
This is where the users command can help you. This command only outputs the logged in users, nothing else.
4. Using finger command to see logged in users
You may need to install finger command first because not all Linux distributions have it installed by default.
It is available in the universe repository of Ubuntu and you can install it with this command:
Once installed, just type finger in terminal:
And you’ll see who is logged in on your Linux system.
[email protected]:~$ finger Login Name Tty Idle Login Time Office Office Phone abhi Abhishek pts/1 Aug 6 09:47 (202.91.87.114) rohini Rohini Rachita pts/2 13 Aug 6 09:48 (157.43.53.142) root root *pts/0 Aug 6 09:37 (202.91.87.114)Bonus Tip: see who logged on your system since last reboot
What you saw so far was about the currently logged in users. How would you know if a user logged out?
The last command in Linux gives you information about all the users who logged in to the system since the last reboot. It will also show the log in and log out time of the logged out users.
Here’s the output of the last command which is self-explanatory I believe.
[email protected]:~$ last rohini pts/3 157.43.53.142 Tue Aug 6 10:05 - 10:05 (00:00) rohini pts/2 157.43.53.142 Tue Aug 6 09:48 still logged in abhi pts/1 202.91.87.114 Tue Aug 6 09:47 still logged in root pts/0 202.91.87.114 Tue Aug 6 09:37 still logged in reboot system boot 4.15.0-52-generi Tue Aug 6 09:28 still running wtmp begins Tue Aug 6 09:28:43 2019I hope this quick tutorial helped you in finding the users currently logged on to your Linux system. If you know some other way to do it, please share your trick with us in the comment section.
How to List Current Logged-In Users on Linux
You can get a list of all the users who are currently logged in on your Linux system, provided you have the necessary permissions.
Readers like you help support MUO. When you make a purchase using links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Read More.
Linux being a multi-user system allows multiple users to log in and run various programs at the same time. As a normal Linux user or system admin, you may sometimes need to check which users are currently logged into your system.
This information can be useful for various reasons such as for troubleshooting performance issues, monitoring user activity, or for simply checking who else is using the system.
There are several methods to list current logged-in users on Linux and see what they are doing.
1. The users Command
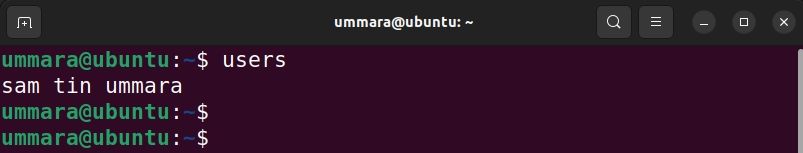
The users command in Linux lists all users who are currently logged in in alphabetic order.
Note that if a user has two login sessions, it will appear twice in the output.
The output below tells that there are three users logged into the system currently.
2. Using the who Command
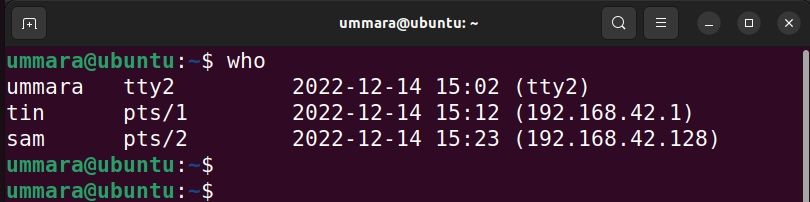
The who command prints the list of users currently logged into the system along with other information such as the terminal they’re using, login date and time, and IP address or hostname of the system if a user is on a remote machine.
To list current logged-in users on Linux, use the who command as follows:
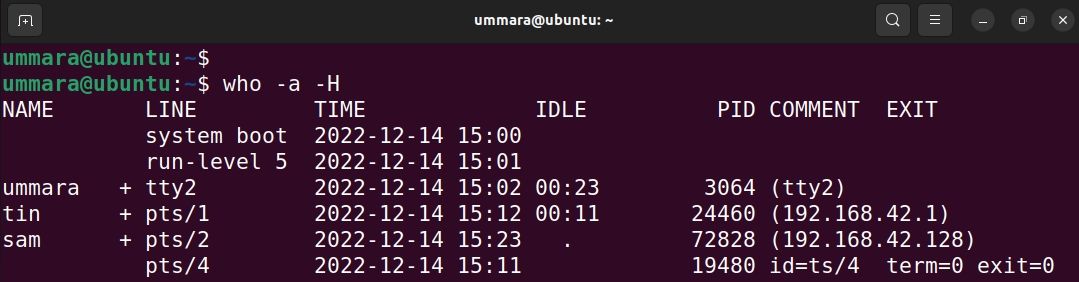
You can also use the who command with -a and -H flags to display idle time and PID of the user’s login shell:
3. Using the w Command
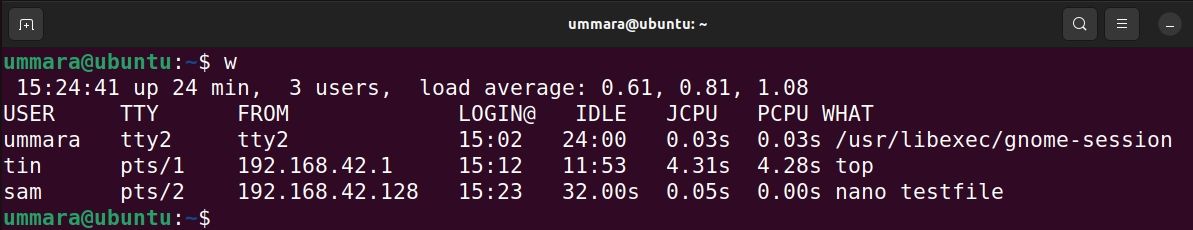
The w command in Linux shows logged-in users and their activities. It prints the list of users and their current processes in the command line.
The header in the output summarizes the status of the system which includes the current time, system uptime, number of logged-in users, and load average. Then for each logged-in user, it displays the user name, tty name, time of login, idle time, time used by all the processes (JCPU), time used by the current process (PCPU), and the current process the user is running.
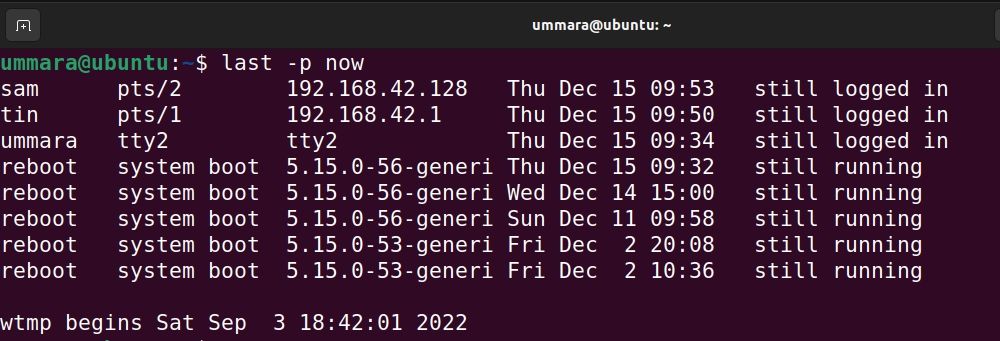
4. Using the last Command
The last command lists current as well as past logged-in and logged-out users. The information it provides includes the name of users and terminals, the IP address of the system they are logged in from, and the date and time of login.
To find the list of users logged in currently, use the last command with the -p now option as follows:
5. The finger Command
The finger command shows information about all the logged-in users on Linux including their username, tty, login date and time, and IP address. You can easily install finger on your Linux distribution using the default package managers.
On Debian-based distributions:
sudo apt-get install finger On RHEL-based distributions:
To display information on current logged-in users, run the finger command without any command-line options: