- How to list SAMBA share users
- 2 Answers 2
- Где Samba хранит пароли. Как извлечь имена пользователей и паролей Samba (РЕШЕНО)
- В каком файле Samba хранит пароли?
- В каком формате файл паролей Samba passdb.tdb?
- Можно ли просмотреть или извлечь пароли из базы данных Samba?
- Как просмотреть имена пользователей Samba?
- Как удалить одного пользователя из базы данных Samba?
- Как стереть базу данных с паролями Samba?
- Как управлять аккаунтами Samba?
- Связанные статьи:
- List samba shares and current users
- 9 Answers 9
How to list SAMBA share users
I have a linux server and a Windows server. On Linux was installed and configured Samba to share 2 directories to the windows server. In /etc/samba/smb.conf we have:
[Myapp PDF Reports] comment = Reports browseable = yes path = /var/www/myapp/reports_pdf printable = no guest ok = no read only = no create mask = 0700 [Myapp PDF Vault] comment = PDF Vault browseable = yes path = /var/www/myapp/PDFvault printable = no guest ok = no read only = no create mask = 0700 In windows I see the 2 shares under the linux server, but I don’t know which user I have to use to connect to them (unfortunatly I can’t ask to the person implemented them some years ago). How can I see in Linux r Windows which is the user with the right permission to access these 2 shares and then get the relative password? Kind regards, Matteo
2 Answers 2
Do not give the user ‘nobody’ a Samba password. The user ‘nobody’ is used with ‘map to guest = bad user’ in the global section of smb.conf and with ‘guest ok = yes’ in a share. If these are set, then Samba will map any unknown users to the guest user and all files created on the share will belong to nobody:nogroup.
If you need to create a new user, you must first create a Linux user and then make that user a Samba user with ‘smbpasswd -a username’ run as root, where ‘username’ is the name of the Linux user you just created.
Good point — I shouldn’t share my slackness in my home network to people who may be in corporate/professional environments. Thank you.
If you login to the Samba server, you can run the following command to list valid Samba users:
The above command will list users known to Samba — this is not the same as the users and passwords known the Linux server it is running on. Read that last sentence again.
If you don’t know the passwords for the old users, you have a couple of choices:
- change the password of an old, existing user to something new, or
- add a new user with a new password that you can use.
I think the first option is less desirable because it means if there are clients that know the old password and you change it, they will suddenly stop working.
So, I would add a new Samba user. This new user must have a login name on the Samba server, so either choose an existing Linux username you want to use, or add a new one. Here’s a way to add a user called samba :
- add samba as a regular user with a regular Linux login
- add samba as a Samba user
- set the Samba password for samba
- use those credentials when mounting a Samba share
sudo adduser samba # add a regular Linux user sudo smbpasswd -a samba # add Samba user called `samba` sudo smbpasswd -e samba # enable - may not be needed Now you should be able to mount the shares with username=samba and the password you just set.
Где Samba хранит пароли. Как извлечь имена пользователей и паролей Samba (РЕШЕНО)
Данная заметка посвящена базе данных паролей Samba. В ней даны ответы на популярные вопросы о том, где хранятся пароли Samba и как выполнить популярные действия с базой данных паролей Samba.
Для установки пароля Samba используется команда:
sudo smbpasswd -a ПОЛЬЗОВАТЕЛЬ
Если вы хотите, чтобы у пользователя не было пароля, то укажите опцию -n.
В каком файле Samba хранит пароли?
Пароли Samba хранятся в файле /var/lib/samba/private/passdb.tdb.
В зависимости от дистрибутива и версии Samba, путь до файла passdb.tdb может быть другим.
В каком формате файл паролей Samba passdb.tdb?
Файл passdb.tdb это бинарный, а не простой текстовый файл.
Файл passdb.tdb можно открыть с помощью утилиты tdbtool, но этот файл не предназначен для редактирования пользователем напрямую, в том числе с помощью утилиты tdbtool. Также с помощью утилиты pdbedit можно экспортировать и импортировать содержимое этого файла.
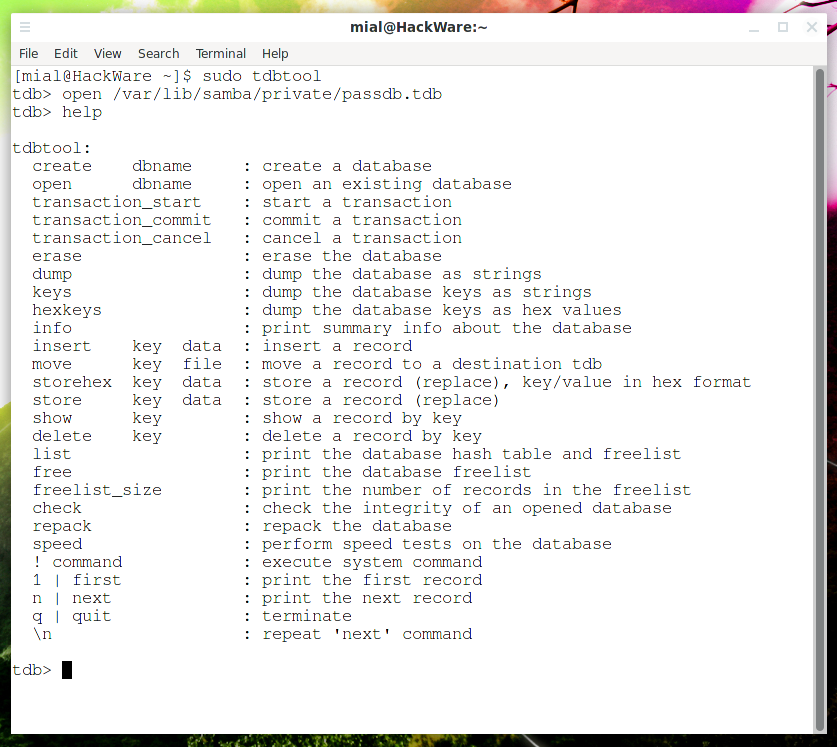
tdbtool — это инструмент для отображения и изменения содержимого файлов Samba TDB (Trivial DataBase). Каждая из перечисленных ниже команд может быть введена в интерактивном режиме или предоставлена в командной строке.
Чтобы открыть файл passdb.tdb необходимо запустить утилиту tdbtool с правами root, иначе у неё не хватит прав даже для просмотра этого файла:
Затем выполните команду open указав путь до файла, который вы хотите открыть:
open /var/lib/samba/private/passdb.tdb
Если во время открытия не произошло ошибок (например из-за того, что указан неправильный путь), то ничего не будет выведено.
Для вывода справки введите
Популярные команды, которые могут вам пригодиться:
распечатать хеш-таблицу базы данных и список свободных мест
показать содержимое базы данных в качестве строк
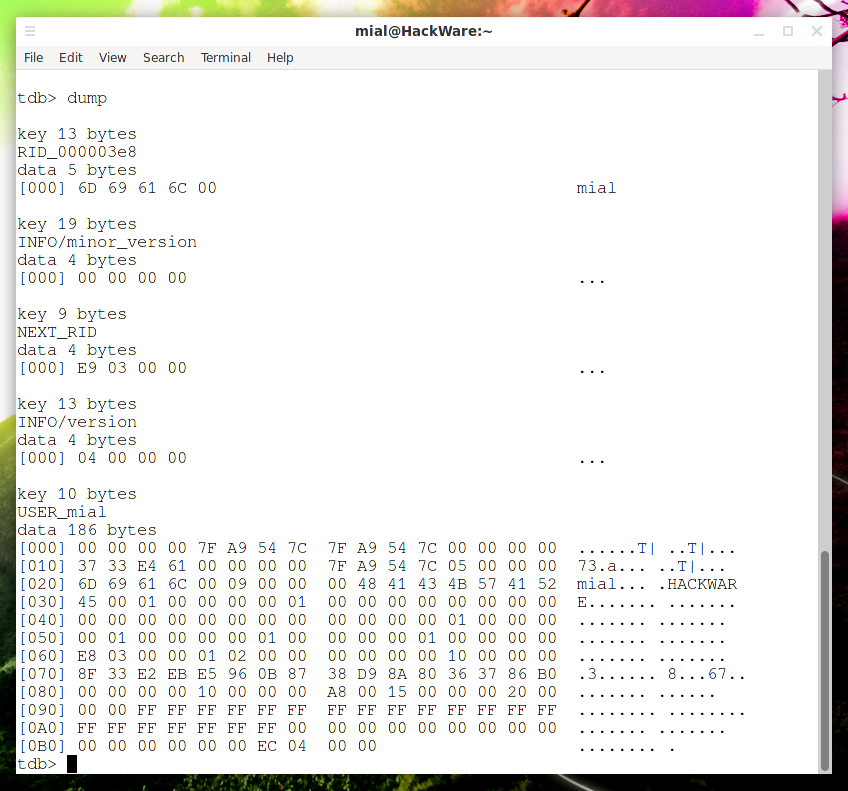
вывести список ключей базы данных в качестве строк
вывести сводную информацию о базе данных
Можно ли просмотреть или извлечь пароли из базы данных Samba?
Нет, невозможно посмотреть или извлечь пароли из файла passdb.tdb. Более того, в файле passdb.tdb не хранятся пароли в виде простого текста, база данных Samba содержит только хеши паролей.
Алгоритм используемого хеша — NTLM. Онлайн генератор хешей: LM/NTLM: https://suip.biz/ru/?act=ntlm-hash-generator
Вы можете экспортировать хеши в виде шестнадцатеричной строки следующей командой:
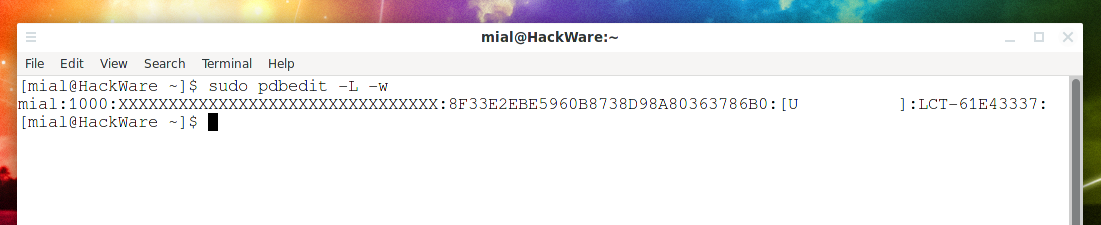
Следующая команда экспортирует все данные, включая хеши:
sudo pdbedit -e smbpasswd:/root/samba-users.backup
Как просмотреть имена пользователей Samba?
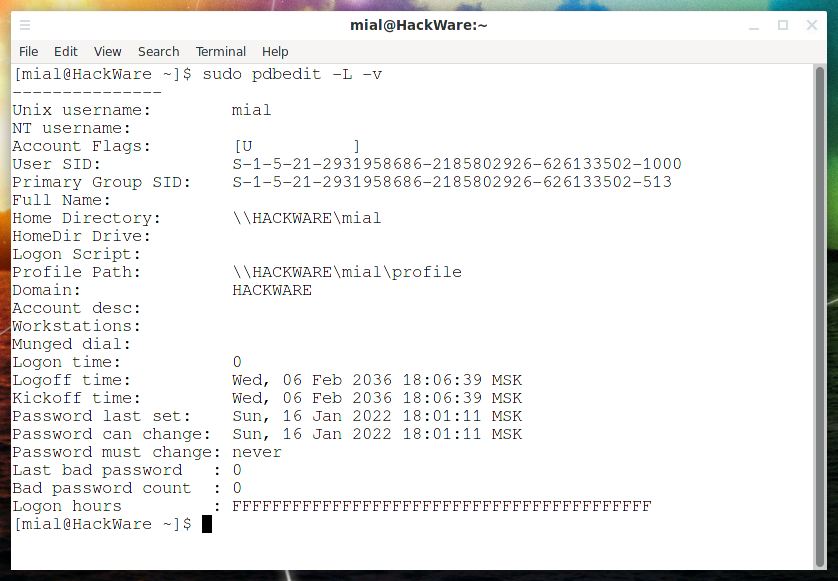
Имена пользователей вы можете посмотреть следующими командами:
sudo pdbedit -L sudo pdbedit -L -v
Как удалить одного пользователя из базы данных Samba?
Для удаления используйте опцию -x (—delete). Также необходимо указать имя пользователя с опцией -u, например:
Как стереть базу данных с паролями Samba?
Следующая команда сотрёт всю базу данных с паролями Samba:
sudo tdbtool /var/lib/samba/private/passdb.tdb erase
Как управлять аккаунтами Samba?
Опцию -c|—account-control ФЛАГ можно использовать с командой pdbedit при добавлении или изменении учётной записи пользователя. Он укажет свойство управления учётными записями пользователей. Возможные флаги перечислены ниже:
- N: No password required
- D: Account disabled
- H: Home directory required
- T: Temporary duplicate of other account
- U: Regular user account
- M: MNS logon user account
- W: Workstation Trust Account
- S: Server Trust Account
- L: Automatic Locking
- X: Password does not expire
- I: Domain Trust Account
Пример: -c «[X ]»
Связанные статьи:
List samba shares and current users
Looking for a simple way to do this from the command line. List samba shares and the users who can access each of them. List samba shares and the users currently connected to them. List samba shares and every connection (log, including user) that has been established to each of them. Any ideas? Anything you use that’s currently available that will give me the bits I need to put this together? Cheers!
We can list shares from command line using smbtree. We can parse: /etc/samba/smb.conf /var/lib/samba/usershares/*.conf
9 Answers 9
Try smbclient -L ip_of_net_interface -U your_user_name . This option allows you to look at what services are available on a server. You use it as smbclient -L host and a list should appear.
Try to use smbstatus , it seems to be what you need.
smbstatus only lists the current connections. What about listing all shares and users who can access them (even if not connected at the time)?
Will retrieve what’s being shared and which machine (if any) is connected to what.
Perfect! But it only shows if im browsing the share, but not if I just have it mapped to Windows. Where NFS shows constantly, but I guess thats because NFS is constantly «mounted», Windows is just mapped, and not mounted till accessed.
Try net usershare info —long .
/usr/bin/net -> /etc/alternatives/net /etc/alternatives/net -> /usr/bin/net.samba3 $ man net net - Tool for administration of Samba and remote CIFS servers. Best answer — it’s been a very long time since I worked with samba and didn’t know about the net command
Also, on most systems, typing testparm will give you info about the samba shares of the machine you’re currently using. After you press enter at the prompt it’ll also show you every uncommented line of smb.conf which can be useful.
No, testparm only checks for correctness of the configuration file, it shows nothing about what you are currently using.
Where -L is to list users & -v is to be verbose.
Getting the users
Getting the shares per user
Less verbose than smbclient -L is net rpc share list -U $USERNAME
You’ll need both because the list of visible shares differs per user.
While smbstatus —shares list active connections in your computer, you may want to know which folders are selected as samba shared, even when no current connection is active.
Go into this directory and you will get the name of such folders:
I am sharing the list of command that everyone need if you are using smb, I hope this will help you all. if need any help for the same, please comment, I will try to help you to have solution for your problems.
you can write sudo smbstatus command to see the logs shared folder and status of that as well
Samba version 4.7.6-Ubuntu PID Username Group Machine Protocol Version Encryption Signing ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- you can write the command sudo smbtree to get the tree of root folder and subfolders
WORKGROUP \\SSHEEL-HP ssheel-HP server (Samba, Ubuntu) \\SSHEEL-HP\Screenshots \\SSHEEL-HP\Movie \\SSHEEL-HP\IPC$ IPC Service (ssheel-HP server (Samba, Ubuntu)) \\SSHEEL-HP\sambashare Network Shared Folder by Samba Server on Ubuntu \\SSHEEL-HP\print$ Printer Drivers you can also type sudo smbcontrol command to get all list of controls that you can use with suffix of that command
if you are getting problem to login so you can also set password for smb to get access of shared folders sudo smbpasswd -a ssheel
ssheel@ssheel-HP:~/Videos$ sudo smbpasswd -a ssheel New SMB password: Retype new SMB password: Added user ssheel.