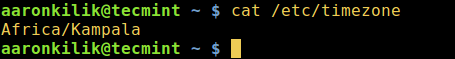Get current timezone as `Region/City`
Unfortunately timedatectl set-timezone doesn’t update /etc/timezone . How do I get the current timezone as Region/City , eg, given:
% timedatectl | grep zone Time zone: Asia/Kuala_Lumpur (+08, +0800) How do I get the Asia/Kuala_Lumpur part without getting all awk -ward? I’m on Linux, but is there also a POSIX way?
Don’t you have /etc/localtime as symbolic link to zoneinfo file? ( e.g. /etc/localtime -> ../usr/share/zoneinfo/Europe/Madrid ) In such case, you could get is by readlink /etc/localtime | sed «s[.*zoneinfo/[[«
2 Answers 2
timedatectl is a systemd thing that queries timedated over dbus and timedated derives the name of the timezone (like Europe/London ) by doing a readlink() on /etc/localtime . If /etc/localtime is not a symlink, then that name cannot be derived as those timezone definition files don’t contain that information.
Based on this and tonioc’s comment, I put together the following:
#!/bin/bash set -euo pipefail if filename=$(readlink /etc/localtime); then # /etc/localtime is a symlink as expected timezone=$ if [[ $timezone = "$filename" || ! $timezone =~ ^[^/]+/[^/]+$ ]]; then # not pointing to expected location or not Region/City >&2 echo "$filename points to an unexpected location" exit 1 fi echo "$timezone" else # compare files by contents # https://stackoverflow.com/questions/12521114/getting-the-canonical-time-zone-name-in-shell-script#comment88637393_12523283 find /usr/share/zoneinfo -type f ! -regex ".*/Etc/.*" -exec \ cmp -s <> /etc/localtime \; -print | sed -e 's@.*/zoneinfo/@@' | head -n1 fi How to Check Timezone in Linux
In this short article, we will walk newbies through the various simple ways of checking system timezone in Linux. Time management on a Linux machine especially a production server is always an important aspect of system administration.
There are a number of time management utilities available on Linux such as date and timedatectl commands to get the current timezone of system and synchronize with a remote NTP server to enable an automatic and more accurate system time handling.
Well, let us dive into the different ways of finding out our Linux system timezone.
1. We will start by using the traditional date command to find out present timezone as follows:
Alternatively, type the command below, where %Z format prints the alphabetic timezone and %z prints the numeric timezone:
Note: There are many formats in the date man page that you can make use of, to alter the output of the date command:
2. Next, you can likewise use timedatectl, when you run it without any options, the command displays an overview of the system including the timezone like so:
More so, try to employ a pipeline and grep command to only filter the timezone as below:
$ timedatectl | grep “Time zone”
3. In addition, users of Debian and its derivatives can display the content of the file /etc/timezone using cat utility to check your timezone:
Important: For REHL/CentOS 7 and Fedora 25-22 users, the file /etc/localtime is a symbolic link to the timezone file under the directory /usr/share/zoneinfo/.
However, you can use date or timedatectl command to display the current time and timezone as well.
To change the timezone, create the symbolic link /etc/localtime to the appropriate timezone under /usr/share/zoneinfo/:
$ sudo ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/zoneinfo /etc/localtime
The flag -s enables creation of a symbolic link, otherwise a hard link is created by default and -f removes an existing destination file, which in this case is /etc/localtime.
For example, to change the timezone to Africa/Nairobi, issue the command below:
$ sudo ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/Africa/Nairobi /etc/localtime
That’s all! Do not forget to share you thoughts about the article by means of the feedback form below. Importantly, you should look through this time management guide for Linux to get more insight into handling time on your system, it has simple and easy-to-follow examples.
Lastly, always remember to stay tunned to Tecmint for the latest and interesting Linux stuff.
Aaron Kili is a Linux and F.O.S.S enthusiast, an upcoming Linux SysAdmin, web developer, and currently a content creator for TecMint who loves working with computers and strongly believes in sharing knowledge.
Each tutorial at TecMint is created by a team of experienced Linux system administrators so that it meets our high-quality standards.
Related Posts
15 thoughts on “How to Check Timezone in Linux”
Any suggestion where should I check further? All settings seem correct? It looks like there is an extra character at the end of America/Chicago. ERROR:
tzone_read_system: no match found for America/Chicago^? Here are my current settings
[[email protected] etc]# timedatectl Local time: Thu 2020-04-23 11:28:51 CDT Universal time: Thu 2020-04-23 16:28:51 UTC RTC time: Thu 2020-04-23 16:28:51 Time zone: America/Chicago (CDT, -0500) NTP enabled: no NTP synchronized: yes RTC in local TZ: no DST active: yes Last DST change: DST began at Sun 2020-03-08 01:59:59 CST Sun 2020-03-08 03:00:00 CDT Next DST change: DST ends (the clock jumps one hour backwards) at Sun 2020-11-01 01:59:59 CDT Sun 2020-11-01 01:00:00 CST [[email protected] etc]# [[email protected] etc]# ls -ltr /etc/localtime lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 37 Mar 26 12:20 /etc/localtime -> ../usr/share/zoneinfo/America/Chicago [[email protected] etc]# [[email protected] etc]# timedatectl | grep local RTC in local TZ: no [[email protected] etc]# [[email protected] etc]# timedatectl list-timezones | grep Chicago America/Chicago [[email protected] etc]# [[email protected] etc]# date Thu Apr 23 11:34:36 CDT 2020 [[email protected] etc]#
CentOS Linux release 7.7.1908 (Core). We just fixed the issue by “rerunning” the timezone. The log showed bad characters at the end, America/Chicago^? (^?) . We ran tzselect and then chose options 2, 49, 11 for Chicago. Gracefully rebooted the server “shutdown -r now” Thank you, Aaron, for your reply. Reply
@Ketan Great! Many thanks for sharing the solution. This will be of benefit to readers in the future. Reply
The formatting on your «%Z %z» example is a bit off. When your text is displayed, the usual, plain double quotes («) are replaced with “pretty” ones (”) . When I pasted your example into my terminal, I only received errors. You should format your example as:
(Here’s hoping that when I post this comment, the website doesn’t replace my simple quotes with pretty ones!) Reply
Yes, my simple quotes were replaced with pretty ones. That’s not good for displaying things on a technical website. You should see about disabling that feature. Reply
On Centos 7 there’s no “clock” under /etc/sysconfig. And neither is there a /etc/timezone, which, from what you’re saying, should exist on most or all linux distributions. Reply
@lethargo Yap, you can use /etc/localtime instead of /etc/timezone. Thanks for mentioning that. Reply
Indeed, but /etc/localtime is not plain text, it is a binary file. To be more specific, it is a symbolic link to a binary file found in /usr/share/zoneinfo. So you couldn’t simply grep it in Centos 🙂 You simply create a symbolic link to whatever timezone you want and then you can use date or timedatectl to see the current clock. Reply
@lethargos Once again, many thanks for the vital insight into checking and managing timezone on RHEL/CentOS 7, this will be very helpful to users out there. Reply
You’re welcome, but shouldn’t you update the article accordingly, so that other users actually know? There’s a higher chance that they’ll read the article than the comments.
@lethargos As you usefully suggested, we have updated the article to include the correct way of setting and checking timezone in REHL 7/CentOS 7/Fedora 25-22 systems. Many thanks for always following us and offering constructive thoughts.
Hello, How can I change the timezone and how can i set the time period of 12 hrs instead of 24hrs? Reply
How to Check and Set Timezone in Ubuntu 20.04
In this tutorial, you will learn how to check and set the timezone in Ubuntu 20.04 using the timedatectl command.
There are a variety of ways of checking your timezone, from using the date command to the timedatactl command. However, setting your timezone has been greatly simplified and improved with the timedatactl command.
The timedatectl command allows you to output detailed information about your system’s date in time, from NTP info to comparisons between your date with the UTC date.
While we’ve limited the scope of this tutorial to strictly being about setting your timezone, the timedatectl has additional functionality that is very useful for configurations around time and date.
Checking Your Current Timezone
The currently configured timezone is set in the /etc/timezone file. To view your current timezone you can cat the file’s contents.
Another method is to use the date command. By giving it the argument +%Z , you can output your system’s current time zone name.
To get the timezone name and offset, you can use the data command with the +»%Z %z» argument. The uppercase Z prints the timezone name, while the lowercase z outputs the time offset.
The timedatectl command be used to get more details about your system’s current time and date configurations.
Local time: Sat 2020-09-05 03:09:26 UTC Universal time: Sat 2020-09-05 03:09:26 UTC RTC time: Sat 2020-09-05 03:09:26 Time zone: Etc/UTC (UTC, +0000) System clock synchronized: yes NTP service: active RTC in local TZ: no Setting Your Timezone
To set your timezone the timedatectl command will be used. Before you set your new timezone you may want to know what timezones are available. You can list all available timezones using the timedatectl list-timezones command.
timedatectl list-timezonesAfrica/Abidjan Africa/Accra Africa/Algiers Africa/Bissau Africa/Cairo Africa/Casablanca Africa/Ceuta Africa/El_Aaiun Africa/Johannesburg Africa/Juba Africa/Khartoum Africa/Lagos Africa/Maputo Africa/Monrovia Africa/Nairobi Africa/Ndjamena Africa/Sao_Tome . The timezone list is very extensive. To narrow the list down to only your region you can pipe the results to the grep command. For example, to narrow our results to only the Americas, we would run the following command.
timedatectl list-timezones | grep America. America/Santiago America/Santo_Domingo America/Sao_Paulo America/Scoresbysund America/Sitka America/St_Johns America/Swift_Current America/Tegucigalpa America/Thule America/Thunder_Bay America/Tijuana America/Toronto America/Vancouver America/Whitehorse America/Winnipeg America/Yakutat America/YellowknifeOnce you know the time zone you want to set your Ubuntu server to, you use the timedatactl set-timezone command to set it.
sudo timedatectl set-timezone America/Torontoand then confirm your changes were applied by running the timedatactl command.
Local time: Fri 2020-09-04 23:30:58 EDT Universal time: Sat 2020-09-05 03:30:58 UTC RTC time: Sat 2020-09-05 03:30:59 Time zone: America/Toronto (EDT, -0400) System clock synchronized: yes NTP service: active RTC in local TZ: no