- 3 Useful GUI and Terminal Based Linux Disk Scanning Tools
- 1. fsck – Filesystem Consistency Check
- 2. badblock
- 3. S.M.A.R.T System Utilities
- i. Smartctl
- ii. Gnome Disk Utility( or Disks)
- 6 лучших менеджеров разделов (CLI + GUI) для Linux
- 1. Диск
- 2. Разделение GNU
- 3. Разделено
- 4. Диски GNOME, также известные как (Утилита GNOME Disks)
- 5. Диспетчер разделов KDE
- 6. Qtparted
- Управление дисками
- KDE Partition Manager
- Duc
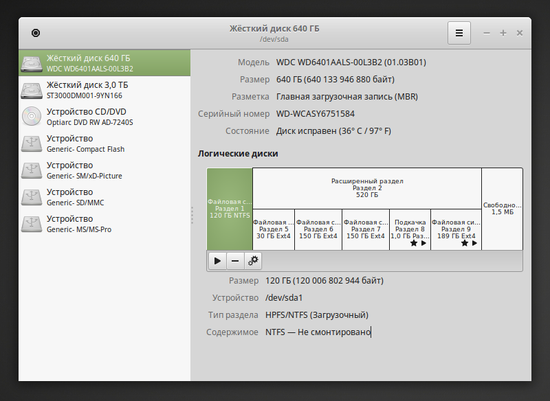
- Gnome Disk Utility
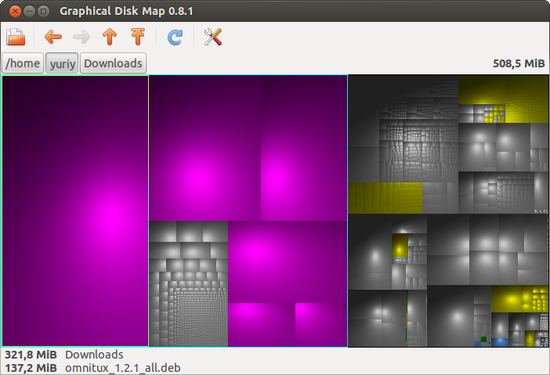
- GdMap
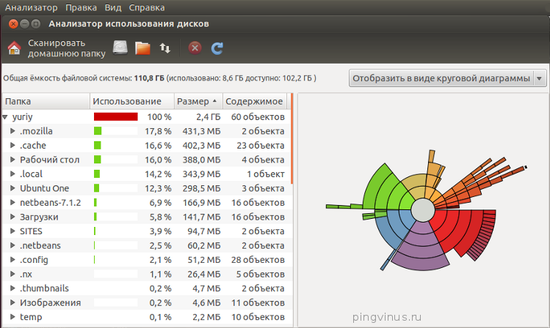
- Disk Usage Analyzer (Baobab)
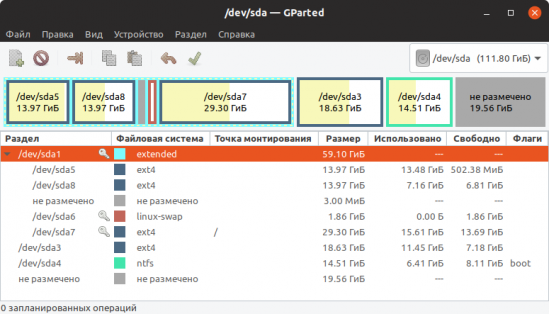
- GParted
- Top 6 Partition Managers (CLI + GUI) for Linux
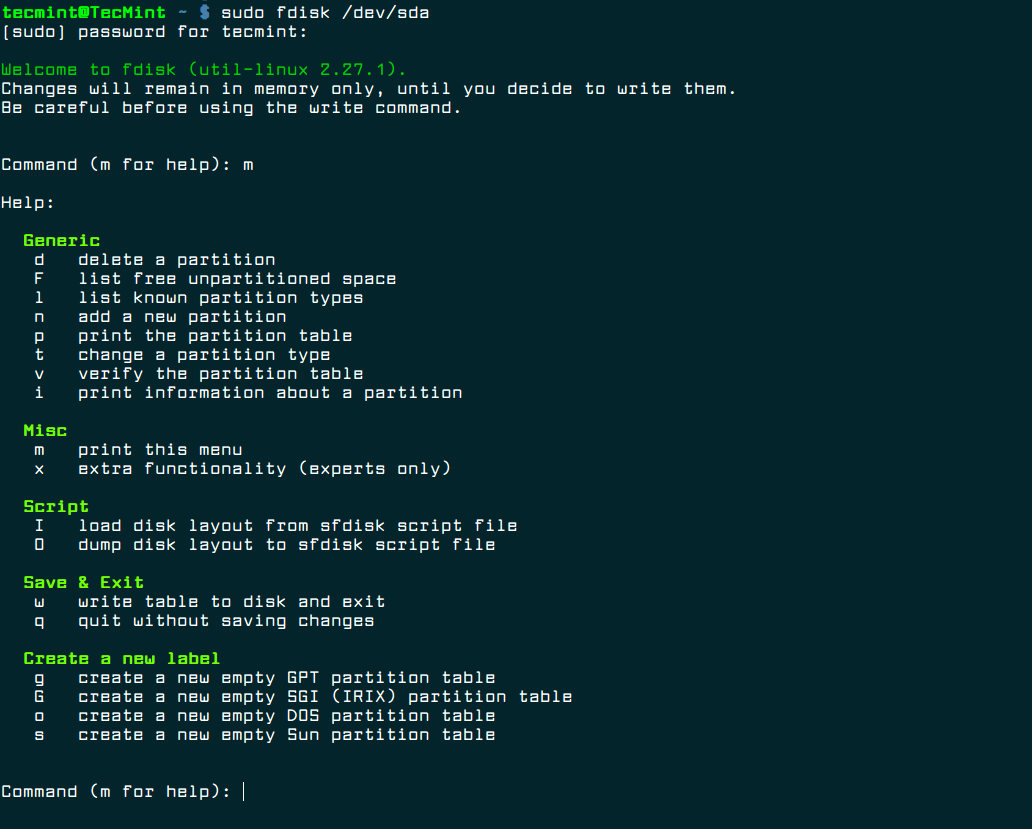
- 1. Fdisk
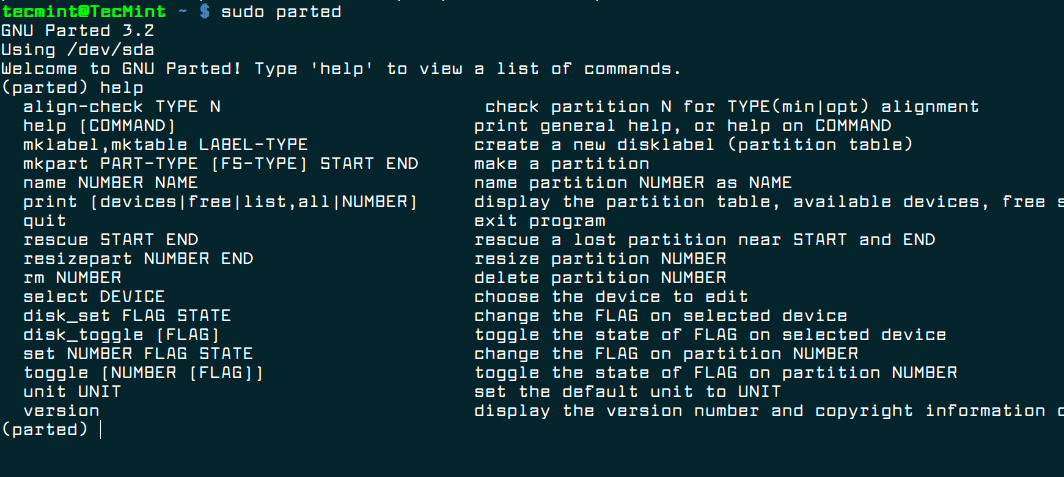
- 2. GNU Parted
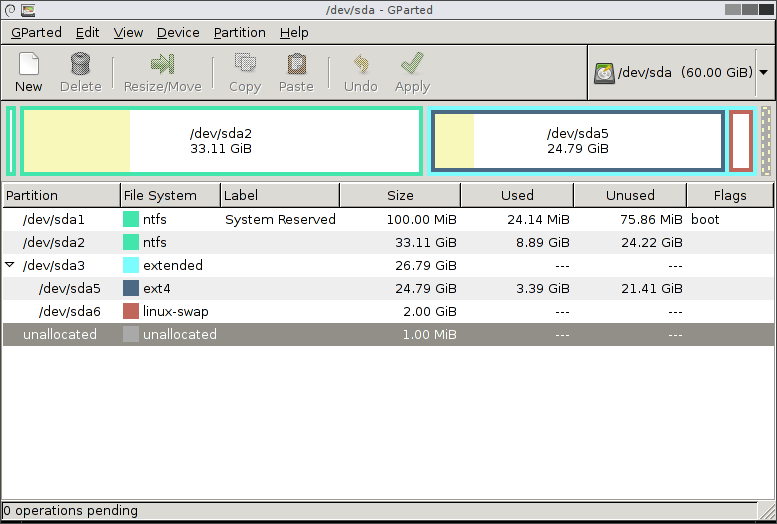
- 3. Gparted
- 4. GNOME Disks a.k.a ( GNOME Disks Utility)
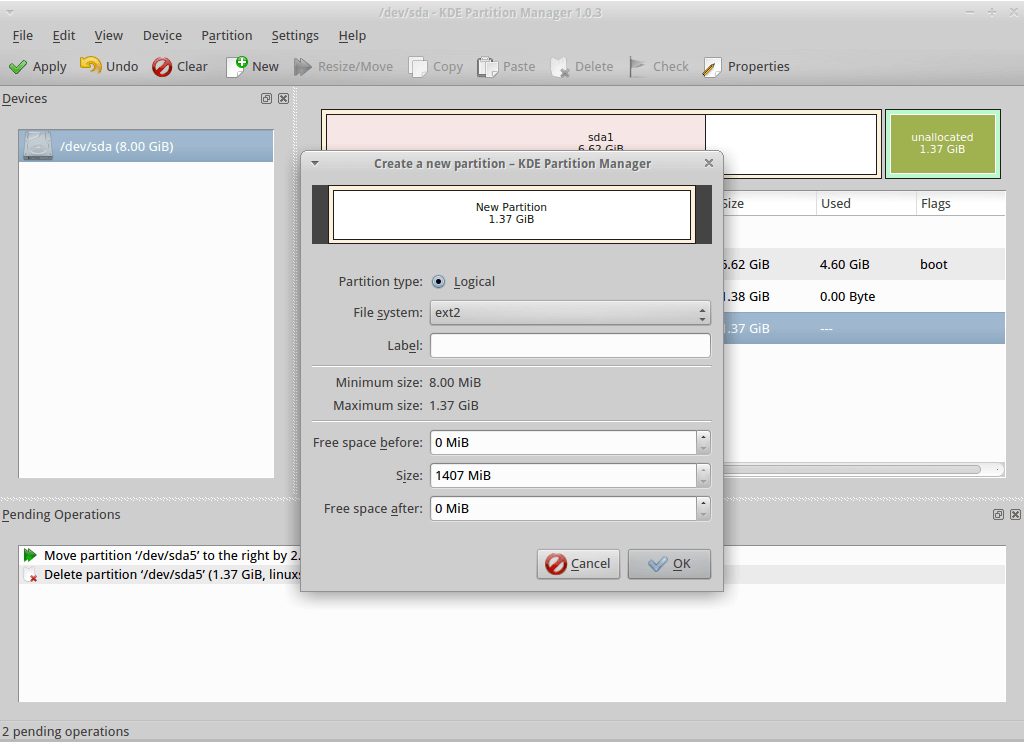
- 5. KDE Partition Manager
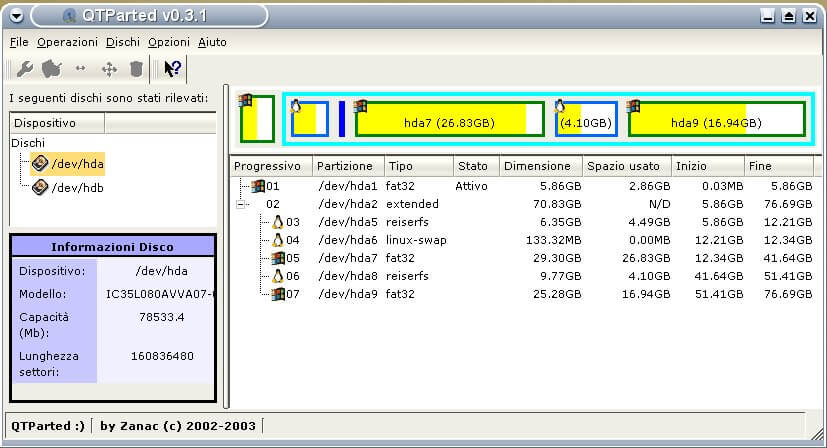
- 6. Qtparted
3 Useful GUI and Terminal Based Linux Disk Scanning Tools
There mainly two reasons for scanning a computer hard disk: one is to examine it for filesystem inconsistencies or errors that can result from persistent system crashes, improper closure of critical system software and more significantly by destructive programs (such as malware, viruses etc).
And another is to analyze its physical condition, where we can check a hard disk for bad sectors resulting from physical damage on the disk surface or failed memory transistor.
In this article, we will review a mix of GUI and terminal based disk scanning utilities for Linux.
In case you notice any unusual behavior from a computer hard disk or a particular partition, one of the first things you can always investigate is filesystem inconsistency or errors and there is no other better utility for performing this other than fsck.
1. fsck – Filesystem Consistency Check
fsck is a system utility used to check and optionally repair a Linux filesystem. It is a front-end for several filesystem checkers.
Warning: Try out fsck commands on test Linux servers only, unless you know what you’re doing..
Always unmount a partition first before you can run fsck on it.
$ sudo unmount /dev/sdc1 $ sudo fsck -Vt vfat /dev/sdc1
In the command below, the switch:
You can find detailed usage instructions in the fsck man page:
Once you have performed filesystem inconsistency tests, you proceed to carry out physical condition assessments.
2. badblock
badblocks is a utility for scanning bad blocks or bad sectors in hard disks. Assuming you detect any bad blocks on your hard disk, you can use it together with fsck or e2fsck to instruct the kernel not to use the bad blocks.
For more information on how to check bad blocks using badblock utility, read: How to Check Bad Sectors or Bad Blocks on Hard Disk in Linux.
3. S.M.A.R.T System Utilities
S.M.A.R.T (Self-Monitoring, Analysis and Reporting Technology) is a system built into nearly all modern ATA/SATA and SCSI/SAS hard disks as well as solid-state disks.
It collects in-depth information about a supported hard disk and you can get that data using the utilities below.
i. Smartctl
smartctl is one of the two utilities under the smartmontools package. It is a command line utility which controls and monitors the S.M.A.R.T system.
To install smartmontools package, run the applicable command below for your distro:
$ sudo apt-get install smartmontools #Debian/Ubuntu systems $ sudo yum install smartmontools #RHEL/CentOS systems
The following is an example of a smartctl command for reporting hard disk partition health where the option -H helps to show the general partition health condition after a self-test:
Look through the smartctl man page for more usage guidelines:
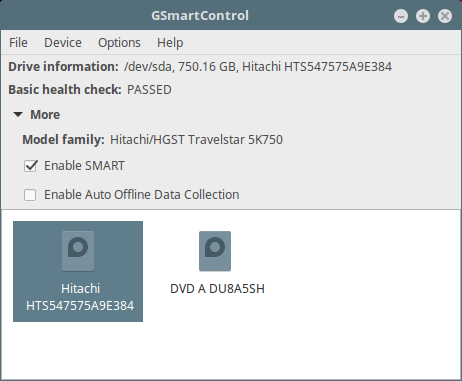
There is a GUI front-end for smartctl called gsmartcontrol which can be installed as follows:
$ sudo apt-get install gsmartcontrol #Debian/Ubuntu systems $ sudo yum install gsmartcontrol #RHEL/CentOS systems
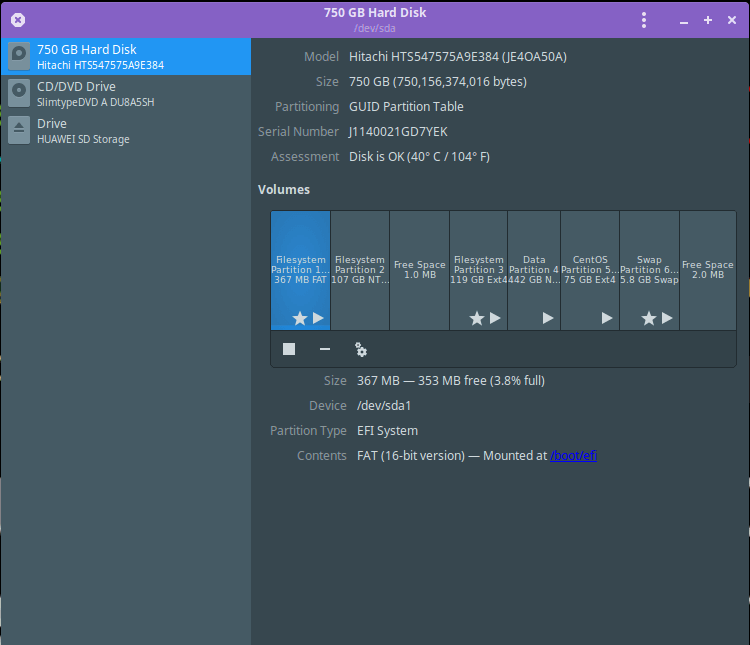
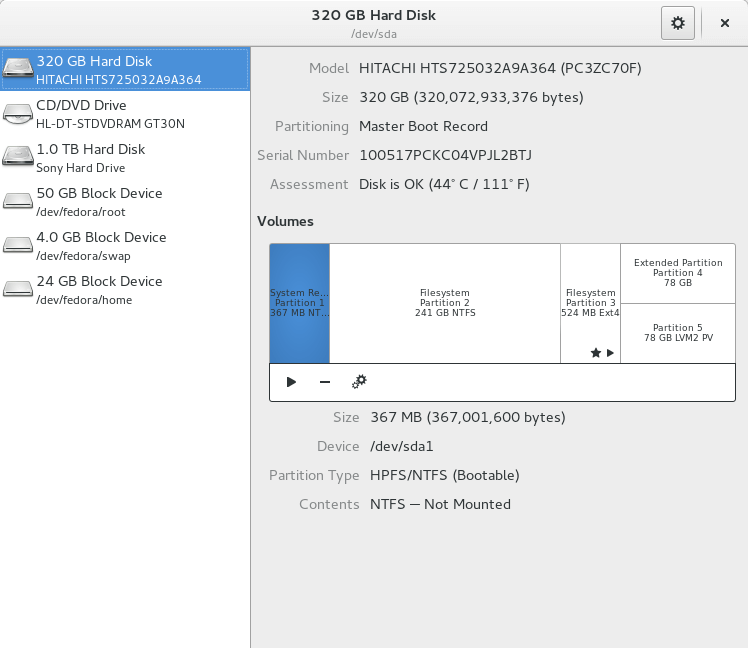
ii. Gnome Disk Utility( or Disks)
Gnome disk utility offers a GUI for doing all the partition management related tasks such as creating, deleting, mounting partitions and beyond. It comes pre-installed in majority of mainstream Linux systems such as Ubuntu, Fedora, Linux Mint and others.
To use it on Ubuntu, open the Dash and search for Disks, on Linux Mint, open Menu and search for Disks and on Fedora, click on Activities type Disks.
More importantly, it can as well provide S.M.A.R.T data and effect self-tests as in the following interface.
That’s it! In this article, we reviewed hard disk scanning utilities for Linux operating system. You can share with us any utilities/tools for the same purpose, that are not mentioned in the list above or ask any related questions all in the comments.
6 лучших менеджеров разделов (CLI + GUI) для Linux
Вы хотите настроить или управлять разделами дисков в Linux? В этой статье мы рассмотрим некоторые из лучших инструментов, которые помогают пользователям Linux создавать разделы и управлять своими дисками. Мы увидим как утилиты командной строки, так и приложения с графическим интерфейсом для управления разделами диска в Linux.
Я предпочитаю командную строку графическому интерфейсу (графическому пользовательскому интерфейсу). Я начну с описания текстовых утилит, а затем приложений с графическим интерфейсом, как показано ниже.
1. Диск
fdisk — мощный и популярный инструмент командной строки, используемый для создания и управления таблицами разделов диска. Он поддерживает несколько форматов таблиц разделов, включая MS-DOS и GPT. Он предоставляет удобный текстовый интерфейс с меню для отображения, создания, изменения размера, удаления, изменения, копирования и перемещения разделов на дисках.
2. Разделение GNU
Parted — популярный инструмент командной строки для управления разделами жесткого диска. Он поддерживает несколько форматов таблиц разделов, включая MS-DOS, GPT, BSD и многие другие. С его помощью вы можете добавлять, удалять, сжимать и расширять разделы диска вместе с расположенными на них файловыми системами.
Это может помочь вам освободить место для установки новых операционных систем, реорганизации использования диска и перемещения данных на новые жесткие диски.
3. Разделено
GParted — это бесплатный, кроссплатформенный и продвинутый графический менеджер разделов диска, который работает в операционных системах Linux, Mac OS X и Windows.
Он используется для изменения размера, копирования, перемещения, маркировки, проверки или удаления разделов без потери данных, позволяя вам увеличивать или уменьшать корневой раздел, освобождать место для новых операционных систем и пытаться восстановить данные из потерянных разделов. Его можно использовать для управления файловыми системами, включая EXT2/3/4.
4. Диски GNOME, также известные как (Утилита GNOME Disks)
GNOME Disks — это основная системная утилита, используемая для управления разделами диска и мониторинга S.M.A.R.T. Он используется для форматирования и создания разделов на дисках, монтирования и размонтирования разделов. Он поставляется с хорошо известной средой рабочего стола GNOME.
В последнее время он приобретает функции для расширенного использования. Последняя версия (на момент написания этой статьи) имеет новую функцию для добавления, изменения размера разделов, проверки файловых систем на наличие повреждений и их восстановления.
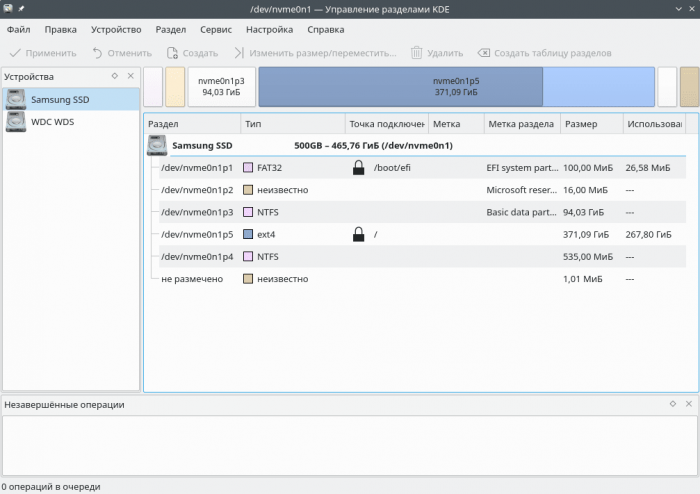
5. Диспетчер разделов KDE
Менеджер разделов KDE — полезная графическая утилита для управления дисковыми устройствами, разделами и файловыми системами на вашем компьютере. Он поставляется с окружением рабочего стола KDE.
Большая часть его основной работы выполняется программами. Его можно использовать для простого создания, копирования, перемещения, удаления, изменения размера без потери данных, резервного копирования и восстановления разделов. Он поддерживает различные форматы, включая EXT2/3/4, BTRFS NTFS, FAT16/32, XFS и другие.
6. Qtparted
Кроме того, вы также можете использовать Qtparted, клон Partition Magic (проприетарное программное обеспечение для Windows) и внешний интерфейс Qt для GNU Parted. Обратите внимание, что он все еще находится в разработке, и у вас могут возникнуть проблемы с последней версией. В этом случае попробуйте использовать версию CVS или предыдущую стабильную версию.
Возможно, сейчас это не лучший вариант, но вы можете попробовать. Дополнительные функции еще добавляются к нему.
Вы также можете прочитать следующие статьи по теме.
- 4 инструмента для управления работоспособностью EXT2, EXT3 и EXT4 в Linux
- 3 полезных инструмента для сканирования дисков Linux с графическим интерфейсом и терминалом
- Восстановление удаленных или потерянных файлов в Linux
Это лучшие менеджеры разделов и редакторы, доступные для операционных систем Linux. Какой инструмент вы используете? Дайте нам знать через раздел комментариев ниже. Также сообщите нам о любых других менеджерах разделов для Linux, отсутствующих в приведенном выше списке.
Управление дисками
Программы для управления дисками в Linux. Создание, изменение разделов дисков в Linux. Программы для форматирования, разметки дисков.
KDE Partition Manager
KDE Partition Manager — программа для работы с дисковыми разделами (создание, форматирование разделов и так далее).
Duc
Duc — утилита для вывода информации об использовании дисков в Linux. Выводит информацию о размерах директорий и файлов.
Gnome Disk Utility
GdMap
GdMap — Graphical Disk Map (Графическая карта диска) — программа для наглядного отображения занятого на диске пространства. Позволяет быстро определить директории и файлы, которые занимают больше всего места.
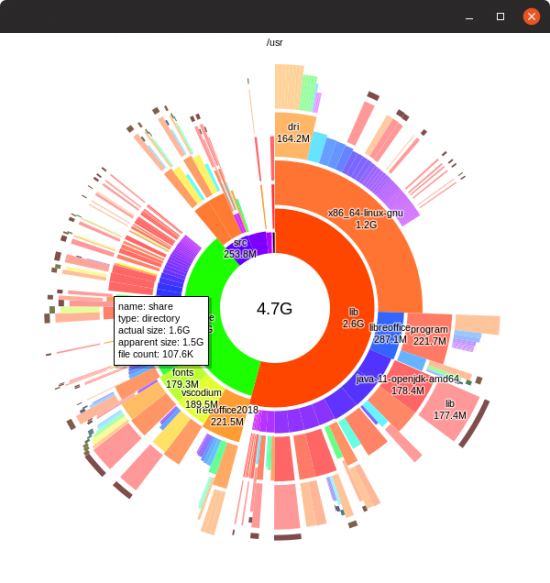
Disk Usage Analyzer (Baobab)
Disk Usage Analyzer (Baobab) — программа под Linux для анализа использования дисков. Выводит наглядную графическую диаграмму использования диска (директории), отображает объем директорий и количество файлов в них.
GParted
GParted — программа для управления дисками в Linux. Позволяет выполнять все необходимые операции над разделами дисков.
Top 6 Partition Managers (CLI + GUI) for Linux
Are you looking to tweak or manage your disks partitions in Linux? In this article, we will review some of the best tools that help Linux users partition and manage their disks. We will see both command line utilities as well as GUI applications for managing disk partitions in Linux.
I favor the command line over GUI (graphical user interface), I will start by describing the text based utilities and then GUI applications as follows.
1. Fdisk
fdisk is a powerful and popular command line tool used for creating and manipulating disk partition tables. It supports multiple partition tables formats, including MS-DOS and GPT. It provides a user-friendly, text based and menu driven interface to display, create, resize, delete, modify, copy and move partitions on disks.
2. GNU Parted
Parted is a popular command line tool for managing hard disk partitions. It supports multiple partition table formats, including MS-DOS, GPT, BSD and many more. With it, you can add, delete, shrink and extend disk partitions along with the file systems located on them.
It can help you create space for installing new operating systems, reorganizing disk usage, and move data to new hard disks.
3. Gparted
GParted is a free, cross platform and advanced graphical disk partition manager that works on Linux operating systems, Mac OS X and Windows.
It is used to resize, copy, move, label, check or delete partitions without data loss, enabling you to grow or shrink root partition, create space for new operating systems and attempt data rescue from lost partitions. It can be used to manipulate file systems including EXT2/3/4.
4. GNOME Disks a.k.a ( GNOME Disks Utility)
GNOME Disks is a core system utility used for disk partition management and S.M.A.R.T monitoring. It is used to format and create partition on drives, mount and unmount partitions. It ships in with the well known GNOME desktop environment.
Lately, it’s been gaining features for advanced usage. The latest version (at the time of this writing) has a new feature for adding, resizing partitions, checking filesystems for any damages and repairing them.
5. KDE Partition Manager
KDE partition manager is a useful graphical utility for managing disk devices, partitions and file systems on your computer. It comes with the KDE desktop environment.
Most of its underlying work is performed by programs. It can be used to easily create, copy, move, delete, resize without losing data, backup and restore partitions. It supports various including EXT2/3/4, BTRFS NTFS, FAT16/32, XFS, and more.
6. Qtparted
In addition, you can also use Qtparted, is a Partition Magic (proprietary software for Windows) clone and Qt front-end to GNU Parted. Note that it still in development and you may likely experience any kind of problem with latest release. In that case try to use the CVS version or a previous stable version.
It may not be one of the best options now but you can give it a try. More features are yet being added to it.
You might also like to read these following related articles.
These are the best partition managers and editors available for Linux operating systems. Which tool do you use? Let us know via the comment section below. Also let us know of any other partition managers for Linux, missing in the list above.